The cunning of rodents
The mouse genus, due to its high fertility and ability to adapt to any conditions, is widespread throughout the world. You can meet a gray rodent in the garden, vegetable garden, in outbuildings where the animals go in search of warmth, food, and making a nest. While there are few of them, mice are shy and cautious. But when populating basements and attics, animals become aggressive in the fight for feeding places. The mouse is designed in such a way that it cannot live more than three days without food. Therefore, any bait has a hypnotic effect on them.
Mice are afraid of people. But they may well bite under the following circumstances:
- Threat to home. Mice make burrows underground, settle in abandoned hollows, and inhabit any secluded corners in basements and attics. If you step on a mink, reach into a hollow, or stir up old things with a mouse nest in the attic, then an angry animal will certainly grab your arm or leg.
- Danger to life. Tourists are familiar with situations where mice climbed onto sleeping people in a tent. A careless movement by a person will cause the crushed animal to sink its teeth into the body of the sleeping person.
- Protection of offspring. Naturally curious children sometimes find secluded places in their yards inhabited by rodents. If pups are pulled out of the nest, the female will attack the invaders. Maternal instinct makes the little animal fearless, ready to fight an enemy many times larger in size.
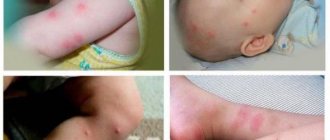
What does a mouse bite look like? The damage is not extensive - usually a couple of bleeding wounds. The pain from the incisors of the gray predator is moderate, but the unpleasant sensations are intensified by the realization that the attacked animal is an inhabitant of landfills and garbage cans.
11
If the mouse is decorative and lives as a pet, then an attack is possible:
- in a moment of fright;
- when several individuals are crowded in a small area;
- in conditions of increased noise indoors.
Owners of decorative pets are also concerned about whether a house mouse bite is dangerous. There is undoubtedly less risk in terms of infections in a tame animal, but pathogenic microflora, the cause of the inflammatory process, can potentially get into the wound.
What to do if bitten by a mouse - consequences and first aid
People often consider a mouse bite to be a harmless injury: the pain is minor, there is almost no blood, the wound will heal on its own in a few days. Such a misconception can lead to disastrous results and even death. There is no need to immediately panic; with proper and timely assistance, doctors will reduce the risk of serious consequences to zero, and soon you will forget about the unpleasant incident.
Consequences of a mouse and other rodent bite
Admit it to yourself honestly, do you always treat every scratch with disinfectants and protect it from dirt? If not, then a hundred wounds may heal without consequences, but the hundred and first will suddenly fester. Perhaps this case will be a mouse bite. Inflammation is not the worst consequence, and if a dangerous infection has not entered the bloodstream, it is not difficult to cure.
Rodents living in the wild can carry infections that are dangerous to humans. The victim decided not to go to the hospital, but simply monitor his well-being.
After a week, there was no deterioration in his health; he forgot about the unpleasant incident.
Each organism is individual, so the incubation period may be much longer than indicated in medical reference books.
Headaches or fever that occur later are attributed to a cold, magnetic storms and other reasons. But the infection does its destructive work, and the later treatment is started, the more unfavorable the prognosis. To minimize the consequences of a mouse bite, show the wound to a doctor immediately.
What diseases can occur after a mouse bite?
The list of diseases carried by rodents is huge.
It is impossible to make a diagnosis yourself without special equipment, so do not rummage through medical reference books, but seek help from a specialist.
You need to take the wound especially seriously if a child, a pregnant woman, or an elderly or weakened person has been injured. Here is just a small part of the possible dangerous diseases transmitted through a mouse bite:
- Rabies;
- Tetanus;
- Plague;
- Tularemia;
- Leptospirosis;
- Hemorrhagic fever;
- Salmonellosis.
Rabies is considered the most dangerous disease transmitted from animals to humans. The virus enters the brain and destroys nerve cells. If medical assistance is delayed, the victim may remain disabled and even die.
When leptospirosis infection enters the bloodstream, the pathogens primarily attack the nervous system, kidneys and liver. The disease is very insidious; without proper and timely treatment, about 20% of those infected die.
No less dangerous are other infections that enter the body through a mouse bite. Even if after the examination you were not diagnosed with infection, be attentive to your well-being. Any discomfort should be a reason to go to the clinic. Contact your doctor immediately if you notice the following symptoms:
- Temperature increase;
- Disorders of the nervous system: seizures, convulsions, insomnia, apathy;
- Headache;
- Vomiting, especially if traces of blood are noticed in the masses;
- Pain in muscles and joints;
- Deterioration of vision or hearing.
There is information that rodent-borne infections are not dangerous for cats and dogs. Their saliva serves as an excellent healing agent.
It’s up to you to decide what to do, but it’s better to show the injured animal to a veterinarian. Rabies from a mouse bite can be transmitted to any animal.
Your four-legged pet suffered while protecting your home from mice, respect his actions and take care of your pet yourself.
First aid for a mouse bite victim
The teeth of small rodents are small and very sharp. The mouse rarely bites until it bleeds; only small droplets may appear. There is no need to rejoice, there is a great danger here.
The skin will close, close the wound, and it will not be possible to treat it well. A rat bite is more serious and painful and is almost always accompanied by bleeding from the wound. Don't rush to apply the bandage.
The blood will wash away most of the pathogenic bacteria that have entered the injured area.
Remember and tell the children what to do if bitten by a rat or mouse. Wash the damaged area thoroughly with water and laundry soap. Disinfect the wound, lubricate it with iodine and apply a bandage. You can apply ichthyol or other ointment to heal wounds.
After this, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. At the clinic, you will be given a vaccine and prescribed the necessary tests or examinations. Sometimes it is recommended to hospitalize the victim to monitor his condition.
Keep disinfectants in the house that will help if a mouse bite occurs, and in other cases:
- Hydrogen peroxide is a very weak remedy, but suitable for first aid;
- Any alcohol disinfectant solution, you can use perfume, cologne or lotion;
- Chlorhexine;
- Furacilin.
A person can be bitten by a decorative rat, white mouse or other pet. The danger of infection here is less than from contact with wild animals, but it won’t hurt to see a specialist.
In school living corners and at youth stations, all inhabitants constantly undergo veterinary examination. Make the same rule for your pet rodents.
You need to pay special attention to your health if the mouse bite occurred after the animal escaped from the cage and spent some time in the wild. No one knows what infections he encountered during this adventure.
If possible, bring a live rodent or a dead rodent to the laboratory. Be careful not to touch the animal with your hands and place it in an airtight container. If specialists have the necessary material in their hands, they will be able to determine whether the animal has been infected and whether a mouse bite is dangerous for infection. It is better to burn all items that came into contact with the animal.
How to Avoid a Mouse Bite
Rodents rarely attack humans; this usually happens when the animal is forced to defend itself or protect its nest. In a hopeless situation, not only rats, but also mice bite.
If you need to go to a place where rodents like to live: basement, attic, garbage dump, take water with you. Only a cold shower can stop an animal's aggression. Read here what to do if bitten by a rat.
Follow these simple rules yourself and explain to your children:
- You should not play with a wild mouse or touch dead animals with your bare hands;
- Avoid contact with rodents: if you encounter them, it is better to step aside than to suffer from an attack by a rat defending its nest;
- Don't bring wild rodents home in hopes of taming them;
- Buy pets only from pet stores; they may sell you an infected animal at the market;
- You cannot torture tame rodents and provoke them into aggression;
- All pets should undergo regular veterinary examinations.
If there are rodents in your home, do not try to remove them on your own; contact the sanitary service. A cat can protect a house from a small family, but it cannot cope with huge hordes. Even if you have never had rodents, everyone should know what to do if they are bitten by a mouse.
If you are careful, a bite from a hamster, mouse or rat is unlikely, but rodents in the house must be exterminated. Infection can enter the human body not only through a wound, but also from feces, hairs, and saliva remaining on chewed foods. Free your home from parasites, and the risk of getting a mouse bite and infection will be minimal.
Source: https://otravilsya.com/ukusy/chto-delat-esli-ukusila-mysh/
Specifics of the bite
A mouse's mouth is filled with all kinds of bacteria. Whatever the bite, microbes will certainly enter the puncture cavity.
There are several types of damage:
- superficial - the easiest, since the infection has not penetrated into the deep layers of the skin;
- partially torn layers of skin - the animal moved during the bite, the incisors cut off the top layer horizontally in a limited area;
- punctures - through holes, usually four. The animal's infected saliva enters the blood and human tissues. After a bite, deep wounds form from the sharp teeth of the rodent, usually bleeding. The edges of the wound quickly close.
The weak immunity of the bitten person provokes the development of the inflammatory process. Getting injured against the background of an ongoing illness is especially fraught with consequences. Children and the elderly are at high risk of infection if they are bitten by a mouse. What are the dangers of skin puncture?
Bitten by a mouse - what to do and is it dangerous?
Of course, a fatal outcome in a situation where a mouse bites a finger or other place is impossible, but a large number of microbes can get into the wound. Because rodents love to explore landfills and garbage cans, and never brush their teeth. The cutting wound will still be quite deep, its edges will close after damage and access to treatment will be complicated.
If a person has a weak immune system, then a dangerous inflammatory process will begin at the site of the bite. This is especially true when there is a current third-party disease. Experts say that rodents transmit infectious diseases to the human body in 10% of cases.
A complex disease called sodoku is often associated with mouse bites. Symptoms of the disease include skin rashes, fever and arthritis. If timely treatment is not started, the disease takes a generalized form and threatens relapses.
At first, the symptoms of sodoku can be easily confused with rheumatoid arthritis, which complicates the correct diagnosis and treatment. In addition to the above symptoms, the victim often develops endocarditis. Mortality from sodoku is possible in 53% of cases. What to do? Treatment consists of injections of a powerful antibiotic.
In addition to it, leptospirosis, tularemia, tick-borne encephalitis, and plague are dangerous to humans. We will tell you more about these dangerous diseases a little later.
How to protect yourself
What to do to avoid becoming a victim of rodents? You should avoid contact with wild and domestic mice, stay away from landfills, trash cans, basements, and sewers. In nature, you need to be careful near fields and ponds. If you cannot avoid contact with the mouse, do not provoke it into aggression.
You should not drive the animal into a corner, wave your arms, or pinch its tail with your foot. What to do? It's better to let the rodent hide. If you buy a rodent as a pet, be sure to show it to your veterinarian. Most likely, he will check the animal for diseases and prescribe vaccination.
When a house mouse shows aggression, it can be calmed down, for example, by spraying water on the rodent. In order to properly raise a pet and show it who is in charge, it is advised to turn it over on its back at the slightest sign of aggression and hold it until the animal calms down.
“How to catch mice - catch the mouse with your hands”
The author of the video made a short video about how to catch an annoying mouse without traps or other rodent repellents, but simply with your own hands.
Possible consequences
Most often, rodents damage human fingers. You can never be sure that a mouse will not infect you with any disease.
Many people believe that when nothing bothers you after a bite, then there is no need to contact a specialist. However, not all diseases manifest themselves immediately.
For example, rabies, when it is not detected in the initial stages, after a while is practically untreatable and leads to the death of the victim.
Its symptoms are weakness and severe headaches, a slight increase in temperature to 37 - 37.3 degrees. Visual and olfactory hallucinations, symptoms of depression, fear and apathy appear. A little later, paralysis and epilepsy join all the symptoms. The infection then attacks the brain cells, resulting in death.
With leptospirosis, the normal functioning of the nervous system, kidneys, and liver is disrupted, and jaundice is possible. It is possible to recognize an infection by chills, high fever, weakness, headache, insomnia and pain in the calf muscles.
With tularemia, danger threatens the lymph nodes, eyes, skin and lungs. Intoxication is often observed. Characterized by an increase in temperature from 38 to 40 degrees, weakness, headaches and muscle pain, chills, low blood pressure, and anorexia.
A viral infection - tick-borne encephalitis - is accompanied by chills and fever, weakness, headache, vomiting, numbness of the neck and facial muscles, and the appearance of convulsions.
With the plague, there is also an increase in normal body temperature, excruciating thirst, sometimes vomiting with blood, pain in the joints and muscles, hallucinations and delirium, arrhythmia and tachycardia are common.
“What happens if you get rabies”
A short educational video about rabies in humans.
Source: https://parazit.guru/zhivotnye/myshi-i-krysy/ukusila-mysh-1129/
Consequences of injury
The wound received after an attack by an animal is not just damage to the skin, like a scratch. The saliva of a mouse, a potential carrier of pathogens of dangerous diseases, inevitably penetrates through the tissues affected by the teeth into the blood of the victim. Blood loss is minimal, but this does not mean that infectious infection has not occurred. Neglecting a mouse bite can result in irreversible health problems.
The insidiousness of injury lies in the fact that the symptoms of the disease do not appear immediately, and after the infection spreads in the body, systemic failures in the functioning of the internal organs begin. It may be impossible to get rid of pathology at a later stage. This is why prevention is so important in the first days after unpleasant contact with rodents.
If you are bitten by a mouse, the consequences may be as follows:
- leptospirosis - causes pathology of the liver, kidneys, nervous system, provokes the development of jaundice. Human susceptibility to bacteria of the genus Leptospira is the cause of the most frequent infections. The development of hemorrhagic syndrome accompanies a severe form of the disease;
- tularemia - leads to damage to the skin, eyes, and lungs. Characterized by a decrease in blood pressure, signs of anorexia, weakness, muscle pain and headaches. Inpatient treatment required;
- encephalitis - affects the nervous system, accompanied by severe muscle pain, cramps, numbness of the neck and face, chills, and high fever. The development of pathology leads to paralysis and death;
- listeriosis - develops in people with weakened immune systems; the infection is especially dangerous for women during pregnancy, as it leads to miscarriage;
- yersiniosis (pseudotuberculosis) - manifests itself in general intoxication, damage to the gastrointestinal tract. Difficult to diagnose due to various clinical manifestations. Lack of adequate treatment leads to paralysis of internal organs and the musculoskeletal system;
- cryptospiridiosis - dehydrates the body by disrupting the digestive system; urgent medical attention is required.
One of the causes of severe sodoku disease is also considered to be a mouse bite. Photos of patients reflect characteristic skin rashes. Manifestations of fever accompany the development of pathology. Without a correct diagnosis, which is difficult to make due to the similarity of symptoms with rheumatoid arthritis, and timely treatment, death occurs in more than half of those affected. It is possible to stop the development of the disease by injections with potent antibiotics.
Mice are carriers of the most terrible diseases - plague, rabies, tetanus, although cases of infection from them are extremely rare. Infected rodents themselves have no protection against dangerous infections and quickly die.
The insidiousness of a mouse attack is that many do not take minor damage from the animal seriously. The absence of severe pain misleads you into thinking that the threat has passed and there is no need to seek medical help.
It is important to remember about a mouse bite and the consequences. The doctor decides what to do to prevent infection, but before visiting doctors, it is equally important to provide first aid.
Bitten by a mouse: what to do?
Mice, like other rodents, are dangerous to humans - they are carriers of infectious diseases.
Pathogens that infect rodents can be transmitted through nutrition and airborne droplets, but the most dangerous is considered to be contact. If a mouse bites until it bleeds, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
The doctor will not only tell you what to do if you are bitten by a mouse, but will also give you a referral for tests, tetanus vaccination, and prescribe treatment.
The main dangers of mouse bites
Mice show aggression only when fighting for their own lives or the lives of their offspring. Sometimes a mouse may bite in agony, so a rodent caught in a mousetrap should not be handled with bare hands.
Diseases that can be contracted from mice pose a mortal danger to humans. It is important not to wait for signs of the disease to appear (symptoms do not appear immediately), but to go to the emergency room as quickly as possible.
Pathogens enter the human body through damaged skin with the saliva of a sick animal. Most often, wild and field mice suffer from the following pathologies:
- Leptospirosis. The incubation period is up to 14 days. This is an infectious disease caused by the spiral-shaped bacterium Leptospira, which belongs to the class of spirochetes of the genus Gram-negative. The disease disrupts the functioning of the nervous system, kidneys, and liver.
- Sodoku. The incubation period is up to 14 days, sometimes up to 2 months. The causative agent of the disease is spirillum minus. Manifested by fever, skin rashes, and attacks of arthritis. A deadly disease.
- Pseudotuberculosis. The incubation period averages about 8 days. There are several forms - some are dangerous to human life.
- Plague. The disease is characterized by extreme contagiousness and high mortality.
- Tularemia. The causative agent of zooanthroponotic infection is the bacterium Francisella tularensis. The incubation period can last 21 days, but on average it is 3–7 days. Fever lasts up to 30 days. Complications of the disease are meningoencephalitis, tularemia pneumonia, peritonitis, pericarditis, abscesses.
Recent studies have revealed that mouse mammary tumor virus, transmitted by rodents, can cause breast cancer in humans. Mice are often infested with blood-sucking arthropods, which are easily transmitted to humans.
What does a mouse bite look like?
The mouse has sharp teeth, which the rodent uses to easily damage human skin. A mouse bite may appear as 1 or 2 punctures - from the upper and/or lower incisors. The punctures are quite deep and therefore dangerous. If a person jerks instinctively, the wound may be larger, with the flesh torn off: the damage is painful, but easier to treat than punctures.
First aid
In any situation, a person who has been bitten by a mouse (even a domestic one) needs to competently provide first aid.
Afterwards, you should immediately go to the doctor, if possible taking the attacked rodent in a container or jar so that a laboratory can study whether the mouse could cause any infection.
If the skin is damaged to the point of bleeding, the algorithm for providing first aid after contact with a mouse should be as follows:
- You need to rinse the damaged area with running water and try to squeeze out as much blood as possible from the deep bite. The procedure should last at least 15–20 minutes. You can use laundry soap.
- Treat the damaged area with hydrogen peroxide. You can use iodine, alcohol, vodka or cologne if peroxide is not on hand.
- Apply a sterile dressing (bandage or bactericidal patch) to the wound.
Further assistance is provided by doctors. After examining the wound and assessing the condition of the victim, the specialist prescribes preventive vaccination against tetanus. To reduce the risk of infection, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Not all diseases transmitted through a bite manifest themselves immediately, so the victim is registered. You will have to be under medical supervision for at least a month - most infections have a long latent period.
Consequences of a mouse bite
People do not consider the bite of a small rodent dangerous, because rabies is transmitted through the bites of large animals, and no cases of infection with this dangerous disease from mice have yet been recorded.
Mice live in basements and garbage dumps. Rodents are omnivores, so their mouths are a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms. If the bite is deep, the bacteria can cause sepsis.
Most often, human hands suffer when handling rodents carelessly. In deep lacerated wounds, suppuration will certainly begin, so disinfection measures should be taken to ensure the release of pus.
Contact with a wild rodent can cause an allergic reaction even in people who have not previously complained of such symptoms. This may include redness, swelling, rash, or more severe symptoms.
How to protect yourself?
People living in private homes are more often attacked by mice. Rodents live in multi-apartment city buildings, but their population is controlled by epidemiological services.
To avoid encounters with wild mice, you must adhere to the rules developed by sanitary doctors:
- Avoid visiting basements, landfills, sewer systems and other places where rats and mice are crowded.
- Homemade mousetraps should be placed in the basement and attic areas of the house to prevent uncontrolled breeding of rodents.
- Removing mice should be entrusted to special services.
When meeting rodents, you should try not to provoke them into aggressive behavior: you should not make sudden movements, seek contact, or drive the mouse into a corner, because a bite is a defensive reaction of the animal.
If mice are kept as pets, adult family members should teach children how to handle rodents. To prevent the risk of infection and to be sure that the animals are healthy, you should regularly show your pets to veterinarians, vaccinate them, and keep their habitat clean.
Pulmonologist, Therapist, Cardiologist, Functional Diagnostics Doctor. Doctor of the highest category. Work experience: 9 years. Graduated from Khabarovsk State Medical Institute, clinical residency in therapy. I am engaged in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases of internal organs, and also conduct medical examinations. I treat diseases of the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, and cardiovascular system. Bespalova Irina Leonidovna published articles: 515
Source: https://ObOtravlenii.ru/ukusy-nasekomyh-i-zhivotnyh/chto-delat-esli-ukusila-mysh.html
Treatment of the wound
For any injury, it is important to thoroughly rinse the wound to remove as many pathogenic microbes as possible with running water. Before the procedure, you should squeeze out a little blood from the wound; along with it, some of the infected rodent saliva will flow out.
Washing the wound is most effective when using laundry soap. The alkali in the product neutralizes the effects of many viruses and bacteria. It is recommended to clean the wound for 15-20 minutes. Deep punctures should be washed with a stream of soapy water using a syringe or syringe.
Superficial scratches and wound edges should be disinfected with 3% hydrogen peroxide or any alcohol solution. After treatment, all that remains is to stick a patch on the damaged area or bandage the wounded area with a sterile bandage with an antiseptic (furacilin).
There is a misconception about the destruction of viruses by cauterizing the bite site. This procedure is painful and does not remove the infection from the wound. The victim receives additional injury in the form of a burn.
When treating a mouse bite, special attention should be paid to people prone to severe allergic manifestations.
A foreign protein that enters the body can cause severe symptoms of irritation:
- swelling of the injury site;
- severe redness of the bite;
- skin rash.
Taking an antihistamine will prevent the body’s protest reaction and improve the victim’s well-being.
Proper first aid reduces the risk of infection and the development of an inflammatory process. But thorough infection prevention is only possible in a medical facility.
Vaccination
In the nearest trauma center or treatment room of the clinic, after a medical examination of the patient, the injury will be thoroughly treated with medications.
When bitten by a decorative mouse, primary measures are enough to prevent complications. Damage from a wild rodent is more dangerous. Antibacterial therapy, vaccination against tetanus and rabies are required. Treatment with folk remedies is inappropriate.
After the procedures are prescribed, the first injection of rabies vaccine is given on the day of treatment, then according to the schedule for the next three months.
Information about the infection of the bitten animal is important. If the rodent was caught after the attack, its delivery alive to the laboratory will allow us to identify all types of infections that the mouse could potentially infect after the bite. Vaccination is stopped when the animal is not a carrier of the rabies virus.
The victim’s refusal to visit a doctor carries a high risk of developing the active phase of the disease. Many symptoms of infectious diseases initially resemble a common cold. It can be difficult for a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis based on a vague clinical picture. When characteristic signs of diseases appear, time for effective measures is lost.
Refusal of vaccination and medical control is dangerous due to severe chronic diseases, relapses, and disability of the victim.
Prevention of bites
How to prevent a mouse bite in the future, what to do if contact with an animal cannot be avoided - such questions often arise from those people who have felt the sharp teeth of a rodent on themselves.
Some tips will help you avoid mouse attacks:
- avoid landfills and garbage cans;
- do not try to catch an animal that happens to be nearby, let the rodent escape;
- Be careful near bodies of water and on forest meadows while relaxing;
- Bring the purchased mouse to the veterinarian for vaccination before actively contacting the pet;
- Sprinkle water on any domestic animal that has shown aggression.
People living in risk zones: near water bodies, warehouses, in old houses with basements are recommended to install an ultrasonic rodent repeller. Such products are safe for people and effective in protecting against mice.
Prevention of bites and precautions are important for both adults and children, who are more at risk of infection due to fragile immunity.
City residents talk about the rodent problem and how to protect themselves