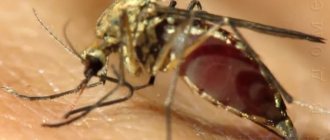
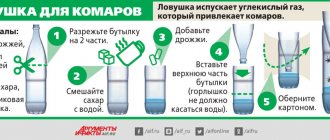
The malaria mosquito is one of the insects dangerous to humans. Horror stories are told about malaria mosquitoes and it is not surprising that they cause the death of more than half a million people every year. In Russia, little is known about them, and sometimes the centipede is mistaken for a malaria mosquito. Are malaria mosquitoes found in Russia, where and how are they dangerous?
Malaria mosquito - how dangerous it is for humans
Malaria is one of the medical problems that attracts the attention of doctors and scientists from all over the world. The disease appeared supposedly 12,000 years ago. Research has shown that malaria appeared later in India and the Mediterranean, about 6,000 years ago.
For the most part, this disease is common in the subtropics and tropics. Symptoms of malaria are nausea, fever, chills, clouding of consciousness, fever, hallucinations. As a result, the death of the carrier of malarial plasmodium occurs.
How dangerous is the malaria mosquito? The insect itself is not dangerous, but if it is infected with malarial plasmodium, it transmits it to a person when it bites. Malaria was also known in ancient Rus'.
Five types of parasites are transmitted to people, some cause severe disease, others mild. Parasites multiply in the liver, then they destroy red blood cells. If malaria is detected early, it can be cured. There is one malaria vaccine registered in Europe that will prevent infection.
The disease is treated with artemisinin in combination with other drugs.
Do malaria mosquitoes bite? Of course, the disease is transmitted by females through a bite. But remember that not all of them are carriers of diseases.
How to save yourself: choosing ointments
When deciding what to apply to mosquito bites, it is recommended to involve a doctor in the discussion. There are also folk remedies for mosquito bites. They are effective, but do not act as quickly as pharmaceutical formulations. Several products that can be found in pharmacies are effective. They cope with itching, relieve swelling, and allergic manifestations. You can find out what to apply on mosquito bites from your doctor. Most often, experts prescribe:
- "Fenistil".
- "Sinaflan".
- "Advantan".
- Balm “Star”.
- "Rescuer".
- "Psilo-Balm".
Each proposed ointment for mosquito bites makes it possible to quickly forget about the consequences of an encounter with blood-sucking mosquitoes. You can use them regardless of who the mosquitoes bite. However, it is still better to use formulations (ointments, creams) after preliminary testing.
Attention! Apply cream or ointment against mosquito bites to clean skin. To do this, the cover is pre-treated with a disinfectant composition, after which a pharmaceutical or folk remedy for mosquito bites is applied in a thin layer. As the latter, we can recommend calendula tincture, mint or aloe juice, vinegar diluted in water.
Malaria mosquito - where it lives in Russia
Malaria affects 106 countries, but this is not a reason to panic. The main foci of the disease are Africa, Colombia, India, Brazil, Cambodia.
Where do malaria mosquitoes live in Russia, do we have them? Anopheleses adapt to any conditions and do not live only in areas with harsh climates.
There are 10 species of malaria mosquitoes in Russia, most of which live in the central part. Malaria mosquitoes have been discovered in Moscow and the Moscow region. Three species are potential carriers of a dangerous disease.
In Russia there are anopheles plants that are resistant to negative factors; their habitat is the taiga. Plasmodium falciparum does not survive in such conditions, but not mosquitoes.
Pests live in the Far East, western Siberia, the European part of the country, and the south. Every year, several cases of malaria infection are diagnosed in Crimea.
The malaria mosquito is not found in the north of Russia and in the east of Siberia; the climate here is unsuitable for their life.
How long do mosquitoes live after they bite?
It is a mistake to believe that female mosquitoes die like bees after biting a person or animal. In fact, the female can feed on blood 6-8 times within a few hours. This explains the fact that if there are 4-6 mosquitoes in a room, it seems that there are 10 times more of them.
Life expectancy has nothing to do with the number of bites committed. The only danger for mosquitoes is the possibility of being destroyed while sucking on the victim's skin. Therefore, the lifespan of a blood-sucking insect rather depends on the accuracy and speed of reaction of a person or animal.
Are malaria mosquitoes dangerous in Russia?
Anopheles is most abundant in regions where malaria is common. But they also live in areas where there is no disease. In Siberia and the western part of the country, the risk of infection is minimal, but the danger still exists. In the North Caucasus and southern Russia the situation is more complicated. Imported cases have been reported in recent years. But, for example, in the period from 1996 to 2005, 30% of cases were local transmission of malarial plasmodia.
According to scientists, now the risk of getting malaria in Moscow is much higher than 50 years ago.
Malaria in Russia was defeated in the 19th century, when the swamps in the south of the country were drained. But point outbreaks occur, mostly imported cases. In general, there is no need to worry about a malaria outbreak, but there is no need to relax either. After all, the common malaria mosquito can be dangerous not only as a carrier of malaria, but also of other infections and pathogens.
Proper treatment: what to use for bites?
If there is even a hint of an allergic reaction, you need to quickly get rid of the flying bloodsuckers. If the bite has already occurred, the use of cream and treatment will be required. The pharmacy offers more than one effective remedy for mosquito bites. Creams can be used as an antihistamine, and tablets can also be taken orally:
- "Claritin."
- "Suprastin".
- Telfast.
- "Tavegil".
- Zyrtec.
Each product effectively helps prevent swelling and relieve itching. Some of them can be given to children. Manifestations of attacks need to be treated promptly. If the bite is in the eye, you can use an inexpensive remedy for mosquito bites - this is Albucid. To decide how to get rid of itching after a mosquito bite if you have a severe allergic reaction, you should consult a doctor.
Healthy Family clinic of evidence-based pediatrics
Summer time makes us happy with sunny weather, vacations and trips to nature. But the joy of summer is overshadowed by the invasion of mosquitoes, because of which it is impossible to go out for a walk in the evening, and to sleep at night with the windows open, because the annoying bloodsuckers are able to fly even to the upper floors of high-rise buildings. Mosquitoes can irritate us not only with their bites and squeaks. The main trouble is that they are carriers of various infections, so it is important to know how to effectively protect your family from mosquito bites.
Why do mosquitoes bite?
Male mosquitoes feed on the juices and nectars of plants, but the mouthparts of female mosquitoes are capable of piercing the skin of mammals in order to feed on blood. Blood for females is a source of useful substances and energy, which mosquitoes obtain from proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the blood of the victim. In addition to providing life support to the insect, the nutrients in the blood provide female mosquitoes with everything they need to produce and lay more eggs.
The life cycle of a mosquito consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa and adult. Only an adult female mosquito is capable of feeding on the blood of humans, animals and even fish.
Damp wetlands are a comfortable habitat for mosquitoes. In urban environments, insects live in dark, warm and humid places, such as basements. In sunny weather, mosquitoes are in an inactive state, but in shaded places or in the evening they fly out to hunt. The optimal temperature for them is considered to be 15-25ºС, and at temperatures closer to 0ºС they fall into a state of torpor.
Female mosquitoes find their prey using the following characteristics:
— Movement of a person or animal, as well as thermal radiation at a distance of several meters;
— Carbon dioxide emitted by humans is felt by insects at a distance of hundreds of meters;
— Lactic acid released in sweat can be felt by mosquitoes at a distance of several kilometers.
Before the female mosquito begins to drink blood, along with its bite, it injects a substance secreted with saliva - an anticoagulant, which prevents blood clotting. This substance causes itching and redness at the site of the bite, as well as allergic reactions of varying severity.
How to protect your child
To protect children from mosquito bites, you can use special anti-mosquito protection products - repellents. Such products are produced in the form of sprays, creams, lotions, wet wipes, etc. It is necessary to use only those products that are appropriate for the baby’s age. Children's repellents have the least toxicity compared to products for adults. Children's repellents are intended for children from three years old, but protection products for younger ages are also available on sale. Such products must be used with extreme caution, as they contain chemicals.
When using repellents, you need to remember that you should avoid getting the product on damaged areas of the skin - wounds and scratches and on mucous membranes. If the product does get into your eyes, mouth or wound, rinse the area with water. Also, you should not treat the child’s face and hands, as active children can get the product into their eyes or mucous membranes. In order to protect the child as much as possible from the toxic effects of the anti-mosquito agent, if possible, the child’s clothes and hats should be treated as much as possible. Babies in strollers can be protected from mosquitoes by treating the stroller itself.
Repellents should be applied no more than three times a day. There is no need to apply additional product, even if mosquitoes hover around the child. The effect of any such protective agent is designed for at least 2 hours. If the protection does not work, then perhaps some personal smell, such as perfume, attracts insects, or the product turned out to be a fake. Upon returning from the street, it is necessary to wash off the product from the child’s skin.
Repellent bracelets are one of the latest inventions to protect against annoying mosquitoes. This product is considered safe because it does not contain toxic substances, and is recommended for use even in newborns. The bracelet is made of soft hypoallergenic material and impregnated with lemon and citronella extract. For protection during night sleep, such a bracelet can be worn on the wrist or leg or hung from the crib. However, since the bracelets have a pronounced aroma, you should monitor the child’s reaction to avoid allergy attacks.
You should be very careful when purchasing repellents. Today it is known that mosquito repellents are one of the most frequently counterfeited products. Therefore, it is better to purchase such products in trusted stores or pharmacies.
What do the words on the packaging mean?
On the packaging of mosquito repellent you will find the word “DEET”, which means poison. The concentration of such a substance should not exceed 40%. A product where the concentration of DEET is less than 7% can protect children. Also, on the packaging of the children's repellent it should be indicated that the product contains a “prolongator”. A product with a prolongator will allow you to significantly reduce the amount of the active substance, but the action of the product will be as effective as a standard product designed to protect from 2 to 5 hours. Thus, children's mosquito repellents should contain a minimum amount of poison, prolongators and essential oils. You should also note that the maximum protection time for the product is no more than 4 hours. If the packaging indicates a mosquito protection time of 8-10 hours, then such a product is not approved by the Ministry of Health, which means it can be dangerous.
Mosquito repellents intended for indoor protection
Fumigants, fumigators, are pesticides (chemicals) that are strong insecticides, but have no effect on people and domestic animals. Fumigants evaporate and destroy pests indoors. To protect children, products are produced that have a special composition and odorless products. Such drugs include Mosquitall plates and liquid, Fumitox “Nezhenka”, Raptor “Nekusayka”. In the children's room, before the child goes to bed, the electric fumigator is turned on for 1-2 hours in the absence of the baby and at a distance of no closer than one meter from the crib. If a child has an allergic reaction in the form of sneezing, coughing, or watery eyes, it is necessary to turn off the device and ventilate the room.
Ultrasonic insect repellers are electronic devices that produce ultrasound that is not harmful to people or pets, but is not tolerated by mosquitoes. The device imitates the sound of a dragonfly or a male mosquito flying, from which female mosquitoes try to stay away. Also in the mosquito protection line there are ultrasonic children's key fobs that operate on batteries. Such devices are convenient to use outdoors, but their protection extends over a short distance (up to 1 meter).
How to choose the right repellent for your child
The choice of repellent for a child should be taken seriously, because such a product contains chemical additives, which means it must be safe, of high quality and not harm the baby. In Russia, children's mosquito repellents undergo mandatory certification, so before purchasing, to ensure the quality of the product, you can ask to see a quality certificate.
Don’t be tempted by the inexpensive price and buy the product at the first street stall you come across. Such products require special conditions of transportation and proper storage. Jars that are overheated in the heat can lose their effectiveness or change their composition, thereby harming the baby. When purchasing a product, you should pay attention to the expiration dates and integrity of the packaging.
Before purchasing, you need to pay attention to the age limit indicated on the packaging. Under no circumstances should you use products not intended for children. The concentration of poisons included in the product can have a toxic effect on the child.
Age restrictions are calculated by the manufacturer based on the average weight and height of the child. Therefore, if the child’s anthropometric indicators are slightly below average, then it is better to purchase a product for a younger age group.
Before using a repellent, you should carefully read the instructions, since similar products can be used differently. For example, some sprays can be applied to the skin, while others can be applied exclusively to clothing. Despite their safety, sprays should be used with extreme caution, since the sprayed substance can easily enter the child’s respiratory tract and eyes. Therefore, use repellent sprays outdoors or in well-ventilated areas.
First rub repellents with a creamy texture in your hands and then apply them to your baby’s skin. Such products should not be applied under clothing, as the effectiveness of the drug will decrease under a layer of fabric.
To safely use repellent sprays, try to apply the products to clothing, not the child's skin. When spending time outdoors, choose light-colored clothing with long sleeves and long legs - insects are more noticeable on light-colored items. To protect your head, you can use a mosquito net, having previously treated it with a protective agent. This way the product will be applied to clothing, which will avoid unnecessary toxic effects than if it were applied to the skin.
If you'll be traveling to another country, check in advance for mosquito forecasts and insect-borne disease warnings. It is worth purchasing repellents at home in advance, since it may be difficult to purchase such a product abroad, for example, there is a risk of purchasing a fake. You also need to remember that you need to carry repellents in your luggage, as such products are subject to confiscation at the airport.
DIY products to protect children from insects
Attention! Before using essential oils, make sure your child is not allergic. Dilute essential oils with cream or vegetable oil to avoid sunburn where the oil is applied.
Since insects are repelled by strong odors, you can use natural essential oils to repel mosquitoes:
— you can prepare a natural remedy that is safe to apply even to sensitive skin: mix 5 drops of clove oil, 30 drops of tea tree oil and 50 ml of vegetable oil. Pour the resulting product into a dark container.
- apply a little eucalyptus or clove oil to clothes or bedding if the child is sleeping.
- a mixture of baby cream with vanillin powder can be applied to the baby’s skin and clothes.
To relieve itching and soothe irritated skin, you can apply Fenistil-gel or Tsindol suspension, zinc ointment, or make a soda lotion to the bite site (1 glass of water - 1 teaspoon of soda.)
Diseases carried by mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are dangerous because they can carry various infectious diseases. For the most part, these are various fevers and encephalitis, some of which are fatal. Human infection occurs through transmissible transmission of the virus in contaminated blood from a sick person to a healthy person.
Nowadays, scientific research and work is being conducted to prevent and eliminate infections that are spread by mosquitoes. But since it is impossible to defeat mosquitoes, diseases, despite efforts, are not decreasing.
Below is a description of just some of the types of diseases transmitted by mosquitoes.
Malaria
Malaria is a life-threatening disease transmitted by Anopheles mosquitoes. The infection occurs with fever and chills, an increase in the size of the liver (hepatomegaly), spleen (splenomegaly), and severe anemia.
Previously, this disease was called swamp fever. The incidence of malaria is growing, isolated cases of imported malaria are recorded even in areas where there are no living conditions for malaria mosquitoes. Nowadays, when drainage of swamps has stopped and reclamation work is not carried out, there are ideal conditions for the breeding of mosquitoes, and therefore the spread of malaria will increase.
Every year, up to 300 million cases of malaria are detected in the world, of which up to 0.5 million are fatal. The majority of malaria cases occur in Central African countries, where the majority of those infected are children under 5 years of age. Malaria is also common in Afghanistan and India. On the territory of Russia, malaria is recorded in the lower reaches of the Volga, and it is also suffered from in countries that are former Soviet republics.
Lymphatic filariasis, also known as elephantiasis
Lymphatic filariasis is a group of tropical helminthiasis that affects humans and animals. Infection occurs when the helminth is ingested by a mosquito bite. When infected with filariasis, the subcutaneous retina, serous membranes, eyes, and lymphatic system are affected. In the lymphatic and circulatory systems, parasites clog blood vessels, creating blood clots and accumulation of lymph in the limbs, causing the limbs to enlarge to enormous sizes. Filariasis can lead to disability, and deaths are recorded as a result of purulent-septic complications. This parasitic infection is widespread in Asia, Africa and South America. Tourists traveling to these regions have the opportunity to become infected with filariasis through mosquito bites.
Tularemia
Tularemia is a natural focal disease caused by rodents (muskrats, rats, mice, gophers, hares). Blood-sucking insects (ticks, mosquitoes, horseflies) carry the infection from pathogens to a healthy person. Farmers, hunters, and agricultural workers often become infected with tularemia through direct contact with infected animals, as well as through contaminated products and through inhalation of dust during grain threshing.
Tularemia is a particularly dangerous infectious disease characterized by severe intoxication, fever, and damage to the lymph nodes. In endemic areas, mass vaccination of the population against tularemia is carried out to prevent infection. On the territory of Russia, in different years, outbreaks of tularemia were registered in the Orenburg, Rostov, Smolensk regions, Moscow, Bashkortostan, etc.
West Nile fever
Fever or West Nile Virus is a dangerous infection that can cause severe illness and death. The infection is transmitted to people most often through the bites of infected mosquitoes. Mosquitoes become infected by feeding on the blood of sick birds and rodents. Mosquitoes can infect people, horses and other animals with the virus. The viability of West Nile Virus is ensured by the transmission of the virus between mosquitoes and birds. West Nile virus is typically found in North America, Western Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Europe.
Yellow fever or amaryllosis
Yellow fever is an acute hemorrhagic disease transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes. As a result of infection, some patients develop jaundice, which is why the disease is called “yellow”. The infection is common in Africa and Central and South America.
Yellow fever occurs with high fever, headache and muscle pain, vomiting and is accompanied by bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, damage to the kidneys and liver. Fever affects 200,000 people each year, of whom about a seventh of those infected die from severe symptoms.
Yellow fever epidemics occur when infected people bring the virus to areas where mosquito populations are high and most of the population lacks immunity to the fever. This is how the virus is transmitted among humans by infected mosquitoes.
There are currently no antiviral drugs against yellow fever, but infection can be prevented through vaccination. The yellow fever vaccine is very effective and safe. One dose of yellow fever vaccine provides lifelong immunity against infection.
Features of an infected insect bite
Externally, an infected insect is difficult to distinguish from a simple mosquito. Pay attention to the photo of the malaria mosquito and familiarize yourself with all its distinctive features:
- black spots on the wings;
- elongated legs;
- infected females raise their abdomen upward.
The malaria mosquito bites, and at the site of its bite itching, swelling occurs, and the skin around it turns red. After a bite, convulsions, chills and fever, headache, bloody urine, as well as nausea and vomiting may occur. A person bitten by an insect begins to feel feverish.
An infected mosquito can pose a great danger to pregnant women and children. 30 minutes after the bite, parasites entering the bloodstream enter the liver and begin to develop there. The liver enlarges and its cells are destroyed. Microbes that enter the blood destroy red blood cells, causing fever and anemia. Due to blockage of the cerebral blood vessels, death can occur.
After a bite, it is necessary to treat the skin with an alcohol-containing solution as quickly as possible and apply something cold. If there is no improvement, you should consult an infectious disease specialist.
When walking in the forest area, use repellents that repel blood-sucking insects. Wear tight clothing that covers your body well. If you have to go camping overnight in the forest, make fires; mosquitoes don’t like them. This way, you will protect yourself from bites from infected parasites.