What does a tarantula look like?
The tarantula belongs to the phylum Arthropods, the class Arachnids, the order Spiders, the family Wolf Spiders and the genus Tarantulas proper.
Like many arthropods, the body of the tarantula is covered with small hairs. In general, the tarantula’s body structure has two main parts: the cephalothorax and abdomen. At the top of the tarantula's head there are as many as eight eyes, with 4 of them located in a straight line, and the remaining larger eyes located in a trapezoid. Thanks to this arrangement of the eyes, tarantulas have a viewing angle of 360 degrees. Also, in addition to well-developed vision, these spiders also have an excellent sense of smell, with which they can sense potential prey at a considerable distance (for these insects).
The size of the tarantula varies from 2.5 to 10 cm. The span of the legs of this spider can reach 30 cm. Like many insects in the world, female tarantulas are usually several times larger than males.
Throughout their lives, tarantulas change the peculiar chitinous “armor” that covers their body several times. The tarantula also has four pairs of long, hairy legs, allowing the spider to move comfortably across loose or even water surfaces.
The mandibles of the tarantula are covered with poisonous canals, they are very strong and serve the spider as a means of defense and attack.
The color of the tarantula is usually brown, gray or black. Although sometimes there are representatives of these spiders that have lighter colors.
In the photo, the tarantula strongly resembles a tarantula spider, but the latter is a mygalomorphic spider and is particularly large in size.
Tarantula.
Tarantulas are quite large spiders, growing up to 10 cm in length with a body weight of about 90 g. The size of the legendary Apulian tarantulas usually does not exceed 7 cm, southern Russian relatives are much smaller and grow up to 2.5 - 3.5 cm. Females of any species are larger than males .
Tarantula.
The fluffy body of the tarantula is formed by two sections: the cephalothorax and abdomen, connected by a thin hollow bridge - a stalk. The upper part of the body is covered with a dense chitinous shell, the stomach remains defenseless. There are 4 pairs of eyes on the head, allowing one to see the blurry outlines of prey at a distance of 20–30 cm.
The long legs of predators are densely studded with sensitive hairs, which play an important tactile role in searching for prey and protect the spider from natural enemies. When in contact with human skin, the hairs can cause an allergic reaction.
South Russian tarantula or Mizgir: close-up view of the muzzle.
The protective coloration allows tarantulas to successfully camouflage themselves against the background of the surrounding landscape. Apulian tarantulas are painted in dark colors with a light edging; the abdomen of females is red, decorated with one longitudinal and several transverse black and white stripes. You can recognize the South Russian tarantula in the photo by its black belly and brown-red top.
What is the difference between a tarantula and a tarantula?
Very often the name "tarantula" is applied to tarantula spiders, although this is a mistake.
Tarantulas differ from tarantula spiders (lat. Theraphosidae), with which they are often confused, in the structure of their chelicerae. In representatives of the tarantula family, these organs move in a parallel direction, in contrast to wolf spiders, in which the chelicerae move in a medial direction towards each other.
Additionally, tarantulas belong to the family wolf spiders, and tarantula spiders belong to a family called tarantula spiders.
Lifestyle
The South Russian tarantula is the most impressive spider that lives in the vast territory of the former Soviet Union. Lycosa singoriensis lives in the Caucasus, Central Asia, Ukraine and Belarus (where it was spotted in the floodplains of the Sozh, Dnieper and Pripyat rivers in 2008).
In our country, it is distributed almost everywhere: residents of the Tambov, Oryol, Nizhny Novgorod, Saratov, Belgorod, Kursk and Lipetsk regions find it in their garden beds.
The spider is found in large quantities in the Astrakhan and Volgograd regions (especially near the Volga), as well as in the Stavropol Territory. The tarantula has long been “registered” in Crimea, after which it managed to crawl to Bashkiria, Siberia and even to the Trans-Baikal Territory.
The South Russian tarantula loves arid climates, often settling in steppe, semi-desert and desert zones (with access to natural bodies of water). Villagers encounter the spider in fields, garden plots, orchards (during potato harvest) and on hillsides.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zv87kc5rZyM
The tarantula digs burrows mainly on mountain slopes. Burrows are up to 50-60 centimeters deep. The entrance to them is bordered by a small ridge consisting of dry leaves. During the day, the tarantula usually sits in a hole, and at night it goes for prey, which consists of various insects. In winter, the tarantula clogs its home with dry plants intertwined with cobwebs. Young spiders (up to 300 pieces) emerge from the facial cocoon and stay on the mother’s body for some time.
In Russia, the most common type of tarantula is the Mizgir (Latin name Lycosa singoriensis). Its color is very variable and can be black-brown, light brown, or reddish with various spots. It has been noticed that the color is largely adapted to the surrounding environment, mainly the color of the soil.
In the warm season, adults are busy searching for a mate. In males, the instinct of self-preservation is dulled, so they can be seen even during the day. When it finds a female, it taps its legs on the ground, vibrates its abdomen and quickly moves its limbs, announcing its presence.
If she accepts advances, she repeats his movements. Everything else happens at lightning speed. After transferring the sperm, the male runs away so as not to be eaten by the female, since during this period she needs protein. Then the female falls asleep in her burrow until spring.
In the spring, it will come to the surface to expose its abdomen to the sun's rays, then lay eggs (300-400 pieces) in a woven web. Then he puts it into a cocoon and carries it on himself. As soon as the babies show signs of life, the mother will gnaw through the cocoon and help the spiderlings come out. The babies will be placed on their mother's body in multiple layers until they become independent. Then the mother will resettle the young people, gradually throwing them off of her.
Tarantulas are typical inhabitants of deserts, semi-deserts and arid steppe regions of Eurasia, Central and South America, North Africa, and Australia.
Apulian tarantula (Lycosa tarantula).
These nocturnal predators during the day prefer to hole up in burrows up to 60 cm deep, camouflaged by fallen leaves. Tarantulas do not build trapping nets, but use cobwebs to frame the walls of the burrow, and females weave a cocoon from threads to bear offspring.
Tarantula hole, steppe of Kherson region.
With the onset of darkness, tarantulas go out hunting, lying in wait for prey right in their hiding place or wandering around the surrounding area. The tarantula's hunting method is characteristic of most wolf spiders: the predator attacks its prey, paralyzing or killing it with its poison, and then sucks out the contents.
Tarantula hunting without leaving its hole.
Uzbekistan – 04/05/2008. The basis of the diet of tarantulas consists mainly of insects and their larvae: flies, cockroaches, crickets, beetles, as well as smaller representatives of their own order. Enlarged photos of tarantulas eating their prey are quite impressive.
Meadow moth in the arms of the South Russian tarantula.
The tarantula digs burrows mainly on mountain slopes. Burrows are up to 50-60 centimeters deep. The entrance to them is bordered by a small ridge consisting of dry leaves. During the day, the tarantula usually sits in a hole, and at night it goes for prey, which consists of various insects. In winter, the tarantula clogs its home with dry plants intertwined with cobwebs. Young spiders (up to 300 pieces) emerge from the facial cocoon and stay on the mother’s body for some time.
We suggest you read: Yorkshire Terrier: diseases, symptoms and treatment
If she accepts advances, she repeats his movements. Everything else happens at lightning speed. After transferring the sperm, the male runs away so as not to be eaten by the female, since during this period she needs protein. Then the female falls asleep in her burrow until spring.
The tarantula is a member of the wolf spider. These are nocturnal inhabitants, so during the day they sleep in their burrows, but at night they go in search of prey. Tarantulas use the web they weave not for trapping, but as decoration for the walls of their home, or to decorate a cocoon during oviposition.
An interesting fact is the length of the tarantula's hole; it can have a depth of 0.6 m, and in the cold season, tarantulas are able to burrow to a distance of a whole meter. The most similar to a tarantula in appearance is. If you do not pay attention to the differences in size, they have an external similarity, so most people confuse these two species with each other.
However, they have different classifications: tarantulas are wolf spiders, and tarantulas are descended from tarantulas. The biggest difference between these two species is the work of the spider's jaws. Their movements are made in different directions. Tarantulas work with their jaws towards each other, but tarantulas work with their chylicerae in a parallel direction.
Many people are interested in where the tarantula lives in order to avoid meeting it. For example, residents of central, eastern, and northern Russia are unlikely to encounter this arthropod in natural areas, since it is not typical for them to live in such a climatic zone, unless it is possible to meet a tarantula at home as a pet.
But in the southern part of the Russian Federation, Europe, as well as in the African, American and Asian expanses of tarantulas, there are plenty of tarantulas.
Interesting fact: to date, scientists have discovered more than two hundred species of tarantula.
In the spring, it will come to the surface to expose its abdomen to the sun's rays, then lay eggs (300-400 pieces) in a woven web. Then he puts it into a cocoon and carries it on himself.
As soon as the babies show signs of life, the mother will gnaw through the cocoon and help the spiderlings come out. The babies will be placed on their mother's body in multiple layers until they become independent. Then the mother will resettle the young people, gradually throwing them off of her.
Where do tarantulas live?
Poisonous tarantula spiders live in steppe, forest-steppe, desert and semi-desert climatic zones of Southern Europe, America, North Africa, Central and Asia Minor. Representatives of the genus are found in Russia, Austria, Italy, Mongolia, Egypt, Hungary, China, Portugal, Algeria, Belarus, Spain, Ukraine, Libya, Romania, Morocco, Greece, Sudan, Argentina, Uruguay, Brazil, Paraguay.
During the day, spiders hide in deep (up to 60 cm) vertical burrows, often lined with cobwebs, and at night they emerge from their hiding places in search of food.
Tarantula - description of a spider
As we mentioned above, there are over two hundred species of tarantulas; even a simple listing of their Latin names will take up quite a lot of space, so in our review only those that are most popular among lovers of these animals will be mentioned.
South Russian
The South Russian tarantula, also called Mizgir, as the name suggests, is found in the south of our country. Depending on external conditions, the color of this individual of this species varies from gray to brown. Females reach three centimeters in size, males are a centimeter to one and a half smaller.
With climate warming, the habitat of southern Russian tarantulas is gradually expanding, soon we will meet them in the middle zone, then the prefix “southern” can be discarded.
Apulian
The Apulian tarantula, also called the real one, is twice as large as the domestic species. Females of the Puglian reach a size of seven centimeters.
This type of spider is widespread throughout the Mediterranean countries, both in southern Europe and northern Africa. The burrows of this spider are located in rocky shores and rocky beaches.
Brazilian
The Brazilian tarantula has a beautiful coloration. It is small, three centimeters long, its body is colored in various shades of brown, and there is an elongated light stripe on the head and back.
The distribution area of the handsome man is the countries of South America: Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay, Argentina.
Spanish
The Spanish tarantula was previously considered one of the subspecies of the Apulian spider, which shares the same habitat with it. More recently, the Spanish spider began to be considered an independent species; this happened only in 2013.
Polyastomy
This species is adjacent to the Brazilian spider, but differs from the latter in the gray color of the hairs covering the body, but in size it is similar to its neighbor and has a three-centimeter body, excluding the length of the legs.
Leocarti
This tarantula is from the Australian continent. a small gray-brown spider, the body length of the female is only 1.2 centimeters, and the males are nine millimeters long.
Black-bellied
This species of tarantula lives in the Pacific Islands, Japan and Taiwan. The brown body of females barely reaches two centimeters in length, the male is half a centimeter shorter. The spider's abdomen is black, which determined its name, and there are two dark stripes on the back.
At the end of our story about unusual spiders, we invite you to watch a fascinating video about a tarantula spider hunting a mouse.
- The spider has a body covered with a large number of hairs.
- The body of the arthropod is divided into the abdomen and the head, which smoothly transitions into the chest and is one part.
- There are 8 eyes on the spider's head, the largest eyes are located in the shape of a trapezoid, the remaining four smaller eyes are located in one line.
- This arrangement of the eyes allows arthropods to observe 360 degrees.
- The size of the spider can reach up to 10 cm; most often the arthropods have a brown body color with minor impurities of a gray tint.
- The spider has 8 legs covered with hairs and special bristles, with the help of which the arthropod can move on various surfaces.
- On the front of the head there are mandibles that secrete poisonous substances, with the help of which the spider paralyzes its prey and also defends itself during an attack. In winter, spiders sleep; males and females contact only during the fertilization period.
The autumn spider rarely attacks a person on its own. Most often, bites occur as a result of defense or accidental contact with a person.
The Guinness Book of Records tells us that this is one of the most dangerous spiders. But besides this, the Brazilian wandering spider is quite large.
The body of the pack reaches 5–7 centimeters, and the span of its legs is 17 centimeters. The diet is very varied. It eats other spiders, birds, small lizards, insects and even bananas. Therefore, they can often be found in boxes where these southern fruits are packaged.
Possessing a terrifying size and dangerous poison, this type of spider will never attack a person first. Therefore, when meeting, it is better to avoid him.
The large representative of the arachnids received its name due to the similarity of its long legs with the fingers of a baboon. And the spider’s legs are really impressive, growing up to 30 centimeters, with a body size of 5–6 centimeters.
We suggest you read: The cat yells at night the reasons for this phenomenon and what owners should do
The spider, whose body size reaches 8–10 centimeters, lives in the tropical rainforests of Latin America. It belongs to a group of rare spiders.
Due to their original color and peculiar hairiness, they are often kept at home as a pet, but their habits are quite aggressive, and one must be careful, since contact with the hairs can cause an allegorical reaction.
It feeds on mice, frogs, and insects, hunting its victims from cover.
Another member of the large family of tarantulas, and one of the few that people keep as pets.
They have a truly gigantic furry abdomen that grows 10 centimeters and a paw span of up to 30 centimeters. This tarantula also has an original color, black in the center gradually turning into gray at the ends of the legs.
The spider defends itself with stinging hairs, so you need to be careful to avoid allergic reactions.
A paw span of 25 centimeters allows the crab spider to easily climb trees and crawl into the most secluded crevices. The legs of the hunting spider are curved, which is why it received such an unusual name.
The habitat of this giant among arachnids is the forests of Australia, where it likes to hide under stones or the bark of mighty trees. Due to the peculiar structure of its legs, it can move not only forward, but also quite quickly - to the side.
An interesting fact about the habits of the crab spider is that the female selflessly, like a fighter, protects the clutch and offspring.
In nature, tarantulas form a separate family. Animals live in warm, humid and dry climates. Large variety of arthropods in South America. Individuals are distinguished by their bright colors and large sizes.
In Africa and Asia, tarantulas have discreet hair colors, but are distinguished by highly toxic venom. India is home to a unique blue spider, which is listed in the International Red Book. There are many tarantula spiders in Australia and the northern American continent.
- Individuals are distinguished by their large body size and limb span. The body length of many spiders is 7-10 cm. The limbs are 14-28 cm. The dimensions of the tarantula are smaller.
- There are 4 pairs of eyes on the head, but the animals do not differ in visual acuity. They can only determine the outline of objects that are nearby. They receive basic information, size, color, smell, taste, with the help of the organs of touch and hairs that cover the entire body of animals.
- Tarantulas have 6 pairs of limbs. They move on 8 legs. When the left limbs move forward, the right ones point backward.
- The pair of forelimbs are called pedipalps. The hairs on them are especially sensitive.
- Another pair of limbs are transformed into chelicerae. They are located in the oral cavity. The chelicerae have exits from the glands, which produce a poisonous secretion.
- The lifespan of females is up to 15-30 years. Males in the wild live up to 3-5 years. Puberty occurs faster in males than in females. Females develop more slowly.
- After fertilization, females weave a cocoon in which they lay eggs. The number of eggs in some species can be more than a thousand. The incubation period is 4-8 weeks.
- Tarantulas, like tarantulas, feed on large insects, rodents, and lizards.
Based on their habitat, they distinguish between arboreal, terrestrial and burrow spiders. To arrange their shelter, individuals use cobwebs. Burrowing arthropods strengthen the soil with threads.
Goliath tarantula
Tree spiders build tunnels from webs on the branches of trees and shrubs. Terrestrial individuals hide under snags, in hollow, fallen trees, under stones. They reliably cover their shelters with fabric.
The largest spider in the world
Like most arthropods, the body structure of the tarantula, covered with the finest small hairs, has two main parts: the cephalothorax and abdomen.
In the upper part of the tarantula's cephalothorax there are 8 eyes, four of which form a straight line, the rest, larger, are placed in the form of a trapezoid. Thanks to this structure of the visual organs, poisonous tarantula spiders have the ability to inspect their surroundings at 360°. In search of food or a female during the breeding season, these arthropods, in addition to excellent vision, use a well-developed sense of smell. The internal organs of the spider are located in its abdominal region.
The size of the tarantula ranges from 2.5 to 10 cm, and the paw span can reach 30 centimeters. It is noteworthy that female tarantulas are much larger than males, and the weight of a female can reach 90 grams.
Throughout their life, tarantula spiders change the chitinous “armor” covering their body several times. Four pairs of long, powerful paws of the tarantula are covered with thin bristle hairs, increasing the area of support when moving along loose or water surfaces.
Powerful mandibles (chelicerae), thanks to the poisonous ducts that open on their jagged tips, are not only an oral appendage for spiders from this family, but also a means of attack and defense.
Usually the color of tarantulas is brown, gray or black, but light-colored individuals are also found. Sexual dimorphism is well developed. Males differ from females in being smaller in size and having more developed forelimbs.
Tarantulas are typical representatives of arachnids leading a solitary lifestyle. They meet with members of the opposite sex only during the breeding season. Male tarantulas quarrel with each other at any time of the year, with the exception of hibernation.
The genus Tarantula includes more than 200 species of spiders. Among them, the most famous are the following types:
- The Apulian tarantula (true tarantula) (lat. Lycosa tarantula) has a size of 7 cm. Females of this species are characterized by a combined coloration, consisting of a dark cephalothorax outlined by a light thin stripe, and a red abdomen, decorated with several transverse stripes framed by a red and white border. The male tarantula has a more modest, monochromatic appearance. Apulian tarantulas live mainly on mountain slopes in vertical burrows up to 0.6 m deep, which can be detected by a characteristic roll of dried leaves framing the entrance. Unlike many of their fellow spiders, true tarantulas do not spin webs. During the day they prefer to hide in a hole, and at twilight and night hours they leave their shelter to hunt insects. On the eve of winter cold, poisonous spiders seal the entrance to their home using dry grass intertwined with cobwebs and hibernate. The life expectancy of a tarantula in natural conditions after the onset of puberty does not exceed 2-3 years for males and 4-5 years for females. Apulian tarantulas live in countries such as Italy and Algeria, Spain and Libya, Portugal and Morocco, Egypt and Sudan.
- The South Russian tarantula or Mizgir (lat. Lycosa singoriensis) is an inhabitant of fields, gardens and vegetable gardens, slopes of ravines and river banks. The habitat of the tarantula is the steppe, semi-desert and desert zones of Russia, Belarus, Ukraine and the countries of Central Asia. The size of the Mizgir tarantula rarely exceeds 35 mm in females and 25 mm in males. The color of the spider depends on the color of the soil in the area where it lives, so there are light brown, black-brown or reddish specimens with spots of various shapes and sizes. A characteristic feature of this type of spider is the presence of a dark “cap” on its head. The depth of the burrows in which poisonous tarantulas live often reaches 0.5 m. The entrance to the burrow is protected by a low wall consisting of excavated soil and reinforced with grass and plant remains. During the rain or molting process, the entrance to the shelter is sealed with earth and cobwebs. Like all members of the wolf spider family, Mizgiri do not weave webs to catch prey, but hunt insects while sitting in or near a burrow. In anticipation of the onset of cold weather, South Russian tarantulas descend to the very bottom of the hole, having previously sealed the entrance to it with a thick earthen plug. South Russian tarantulas live no more than 3-5 years. The life expectancy of females is longer than that of males.
- The Lycosanarbonensis tarantula reaches a size of 5-6 cm. The body of the poisonous spider is brown-black, the legs are long, covered with hairs. Tarantulas are found in Italy, France, Macedonia, Malta, Spain, the countries of the former Yugoslavia and northern Africa.
- The Spanish tarantula (lat. Lycosa hispanica, Tarantula iberica) lives in southern Europe and northern Africa. Tarantulas eat small invertebrates and also practice cannibalism. Previously, the spider was considered a subspecies of the Apulian tarantula, but since 2013 it has been considered as a separate species.
- The Brazilian tarantula (lat. Lycosa erythrognatha, formerly Lycosaraptoria) lives in the countries of South America: Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay, in the northern, northeastern and central parts of Argentina. Like other members of the genus, the Brazilian tarantula has 8 eyes arranged in 3 rows. In the bottom row there are 4 small eyes, a little higher there are 2 large eyes, and 2 more are on the sides of the head. The size of the tarantula is approximately 3 cm excluding the legs. The color of the spider is dark brown. There is a light longitudinal stripe on the head, which acquires a yellowish tint in the upper part of the back. In the center of the upper part of the abdomen, the stripe takes the shape of an arrow that points forward. The lower part of the abdomen of a poisonous spider is black. The chelicerae are reddish-brown in color. Tarantulas feed on crickets, cockroaches and other spiders.
- Tarantula Lycosapoliostoma lives in the countries of South America: Brazil, Uruguay, Argentina, Paraguay. It lives in gardens, steppes, meadows, during the day it hides among the grass or in trees, in stones or holes, and is nocturnal. Like other species, these tarantulas eat crickets, cockroaches, small insects and other spiders. The length of the spider, excluding the legs, is 3 cm. The color of the tarantula is gray-brown or dark brown. There is a light longitudinal stripe on the head. In the upper part of the abdomen, the strip takes the shape of an arrow that points forward. The lower part of the tarantula's abdomen is black. The color of the chelicerae is light, which distinguishes this type of spider from the Brazilian tarantula. Females are larger than males, but females have shorter legs.
- Tarantula Lycosaleuckarti is a gray-brown spider. The length of males reaches 0.9 cm, females - 1.2 cm (excluding paws). This species of tarantula lives in Australia.
- The Lycosacoelestis tarantula lives in Japan and Taiwan. The length of females reaches 13-18 mm. The male tarantula measures 11-13 mm. The body color is brown, there are 2 longitudinal dark stripes on the back. The inner side of the tarantula's abdomen is black, for which the spider received the name "black-bellied tarantula."
Directories list about 200 species of tarantulas. The largest and most widespread is the Apulian tarantula. It has a rather inconspicuous monochromatic brown color. The female is slightly different: she has a brighter brown cephalothorax, framed by thick beige stripes. The female's abdomen is red, with red and white stripes.
Another name for representatives of this species is True tarantula. Individuals live in vertical burrows on mountain slopes. They are nocturnal and hibernate in winter.
We suggest you read: Types of bugs in the apartment
This type of spider weaves a web only to line its burrow. They hunt the prey at night and attack it, piercing the chelicerae and injecting poison, which immobilizes and kills the victim.
The web also serves to connect the tarantula with its burrow. Usually he does not hunt far from his habitat, and the web follows him from the burrow itself, along which he then returns home. If the web breaks, the spider will be forced to look for a new home.
The largest tarantula lives in dry and hot countries: Libya, Sudan, Spain, Morocco, Algeria, Italy, Portugal, Egypt.
The largest tarantula in the world is Goliath. It is mistakenly called a giant tarantula. Tarantulas actually look like tarantulas and are often confused. However, this is a misconception.
Tarantulas can lay claim to the role of those very heroes from horror films. They really have an impressive size and thick, furry paws.
The simplest sign by which a tarantula can be distinguished from a tarantula is size. The former are capable of reaching 30 cm in paw span, while the latter are only 10 cm. The second feature by which they are classified into different families is the structure of the chelicerae. In tarantulas they are located parallel to each other, in tarantulas - medially.
The Goliath tarantula has an impressive size. The span of its paws is 28 cm.
It is worth noting that researchers disagree on who should take precedence. The largest Goliath spider was discovered back in 1985, its paw span was 28 cm. Later, in 2001, another species of huge spider was discovered. The paw span of Heteropoda maxima was 30 cm.
However, the new species is not in a hurry to be considered the largest, since the size of its body and the width of its paws are significantly inferior to the tarantula, and accordingly, it looks smaller. Let's compare the sizes of the two largest spiders in the world.
- The body of Heteropoda maxima is 30 mm in males and 46 mm in females, the paw span is from 25 to 30 cm.
- The body of Theraphosa blondi (Goliath) reaches 85 mm in males and 100.4 mm in females, the paw span is up to 28 cm.
We suggest you read: What is the difference between a wasp and a bee and a bumblebee?
The giant spider lives in the tropical forests of the South American continent: Venezuela, Guyana, Northern Brazil, Suriname. It lives in deep burrows, which, like the tarantula, are lined with cobwebs. It also does not use webs to catch prey.
It feeds on insects, amphibians, certain types of snakes, and mice. In captivity, the spider practically does not reproduce (exceptions are extremely rare), since it requires a change in certain climatic conditions.
Reproduction and lifespan of a tarantula
The mating season for tarantulas usually begins in late summer. A sexually mature male finds a smooth, flat surface and spins a web on it. Having completed the preparations, he begins to rub his belly against her. As a result of such stimulation, seminal fluid is erupted, after which the male tarantula plunges his pedipalps into it, which absorb it until the fertilization process occurs.
Having found a female, the male begins a courtship ritual, consisting of a kind of mating dance. If the female tarantula reciprocates the partner's feelings, he plunges his pedipalps with a portion of seed into her cloaca and fertilizes her. After this, the male needs to leave his partner as soon as possible so as not to become another portion of food for her.
The female tarantula, having descended into the hole, weaves a cocoon from the web, into which she lays fertilized eggs, the number of which ranges from 50 to 2000 pieces.
For 40-50 days, the female carries the maturing offspring on her arachnoid warts (special paired outgrowths located on the abdomen). The hatched spiderlings climb onto their mother's back and stay there until they learn to feed without her help.
After this, the tarantula cubs leave their mother and begin to live independently. Small tarantulas reach sexual maturity in the second or third year of life.
The method of reproduction of tarantulas is practically no different from other species of its relatives. It all starts with a specific mating dance, thanks to which males capture the attention of females. It is by this action that the female determines the male she needs. Tarantulas perform the following steps for the breeding process:
- The male sets out to look for the female at the end of summer, as the instincts of procreation take possession of him.
- Having chosen a suitable female that he likes, he performs a mating dance.
- If the female is satisfied with the partner, she repeats exactly the same movements with which her partner has just lured her.
- Next, the mating of the tarantulas itself occurs, after which the male quickly leaves so as not to become food for his female. In this regard, males are much faster than their spider relatives.
After the entire process is completed, the female finds a warm hole for wintering, where she remains until spring.
With the arrival of warmer weather, the female develops eggs; depending on the type of spider, their number can reach 700 pieces. Next, she forms a cocoon from her web on her stomach to accommodate eggs, which she will carry throughout the entire time until the moment of hatching of the young comes.
Before small individuals appear, the female gnaws through the cocoon and releases them into the wild. But they do not leave her, but simply climb onto the mother’s back, where they remain until the period of independent feeding begins.
Females live about 4 years, males - up to 2. In spring, females emerge from their burrows and bask in the sun. They can travel long distances in search of a mate. They court the female they like for a short time. They mate at the end of summer once in their entire lives; the males die immediately, as the female bites her lover after fertilization.
Lays eggs in a hole. Females carry them on themselves in a web cocoon, carefully caring for future offspring. After maturation, young spiders crawl out of the cocoon and live on the female’s belly for some time. As they grow up, the spiders become independent and move away from her. Sometimes the mother provokes the younger generation to enter adulthood earlier.
The mating season of these spiders occurs at the end of summer - beginning of autumn. The male, having noticed the female, begins a kind of dance, invitingly shaking and tapping his especially developed forelimbs. The female responds something similar and folds her front legs, which becomes a signal for the male to mate. Upon completion of the process, the male hurries to retreat, and the fertilized female hibernates in a tightly sealed burrow.
Female South Russian tarantula with offspring.
In spring, females crawl out of their shelters and expose their bellies to the sun. Then they lay eggs (about 50 pieces) and weave the future offspring into a strong cocoon, which they carry under their abdomen, attached to the arachnoid warts.
We suggest you read: What you need to know about the karakurt spider?
A female South Russian tarantula drags her cocoon with eggs. Kinburn Spit in the Black Sea.
Feeling movement inside the cocoon, the mother helps the offspring get out and at first carries the spiders on herself, gradually scattering them around the surrounding area. The lifespan of a tarantula in nature is about 2 years.
Homemade tarantula - care and maintenance. What to feed a tarantula at home?
The tarantula is an unusual pet, but today there are quite a few lovers of exotic animals, which include tarantula spiders. These are quite unpretentious arthropods, which can be kept in special terrariums or even in aquariums that have a lid with ventilation holes.
A substrate consisting of a mixture of earth, sand and clay is poured onto the bottom of the container. The thickness of the layer should be within 20-30 cm. In addition, it is necessary to equip the tarantula terrarium with an automatic drinking bowl with fresh water and a shallow pool so that the pet can take water treatments. To create conditions similar to natural ones, it is recommended to place small driftwood and unpretentious grass in the container.
The optimal temperature for keeping tarantulas at home ranges from 25° to 27°C, and since such pets do not need ultraviolet radiation, ordinary incandescent lamps are sufficient to maintain it. To maintain humidity inside the terrarium, you need to periodically irrigate the soil using a spray bottle.
Tarantula spiders are unpretentious in their diet. You can feed your pet tarantula small pieces of fresh beef. As mineral supplements, you can add calcium gluconate to the meatball once every two weeks and multivitamin preparations once every 30 days. The portion should be fed on the tip of a stick directly into the spider's chelicerae.
However, the best food for a domestic tarantula will be insect larvae, small cockroaches and grasshoppers, worms and small frogs, in general, any insect that is not larger than the pet. The frequency of feeding of the tarantula depends on the age of the spider. If young individuals need to be fed two to three times a week, then an adult tarantula needs one meal every 8 days. After finishing feeding, all leftovers from the feast must be removed.
It should be remembered that only 1 domestic tarantula can be kept in a terrarium. Otherwise, fights will constantly arise between neighbors, which will lead to the death of one of the pets.
Cerbal Arabian
The inhabitant of the desert expanses of Jordan and Israel was discovered by zoologists relatively recently; until 2003, the world did not know about its existence.
A spider with a color adapted for life among sands has a paw size of 14 centimeters. But some experts claim that the length of the paws can reach 20 centimeters.
The habitat also determined the lifestyle of the majestic inhabitant of Arabia. During the day, the spider hides from the scorching rays of the sun, and at night it goes out hunting.
Nephiles-orb-weavers and their description
Nephila is a large spider that weaves the largest and strongest webs in the world. In some of them, scientists even discovered entangled birds. And fishermen of the Pacific and Indian Oceans use their web to catch fish.
Nephilic orb weavers weave the strongest webs
This type of arthropod has quite a few names, the most popular of which are tree spider and banana spider . Nephiles are poisonous, but their poison is not dangerous to humans. After a bite, slight redness or rashes may appear on the body, which completely disappear after a day.
The body length does not exceed 4 cm, but the paws can reach a length of 12 cm. The body color is bright, warning of its danger to small animals and insects. Most often, nephiles are orange or red in color. These arthropods are found in Australia, Madagascar, Asia and Africa.
The largest spiders are described in the video:
Tarantula: description, structure, characteristics
The tarantula belongs to the phylum Arthropods, the class Arachnids, the order Spiders, the family Wolf Spiders and the genus Tarantulas proper. Like many arthropods, the body of the tarantula is covered with small hairs. In general, the tarantula’s body structure has two main parts: the cephalothorax and abdomen.
Throughout their lives, tarantulas change the peculiar chitinous “armor” that covers their body several times. The tarantula also has four pairs of long, hairy legs, allowing the spider to move comfortably across loose or even water surfaces. The mandibles of the tarantula are covered with poisonous channels, they are very strong and serve the spider as a means of defense and attack.
Tarantulas have a double, hairy body and two pairs of four legs. It consists of two parts - the cephalothorax and abdomen. The spider's head has eight eyes that allow it to look around 360 degrees. Almost all subspecies are black or brown in color (there are bright exceptions).
Many people confuse the species of tarantulas with other large spiders, for example, tarantulas (most consider them to be tarantulas). This opinion is fundamentally incorrect, since the tarantula belongs to mygalomorphic spiders. Over time, the error became entrenched in society and culture.
The appearance of these beauties can be appreciated in the photo.
Phylum - arthropods, class - arachnids. The furry body consists of two parts: 1-head-chest, 2-stomach, which are connected by a tube - a stalk. The head and chest are covered with chitin; the belly, on the contrary, is soft and tender. 8 eyes located at the top, reminiscent of a periscope, help you see the area from all sides at once.
The tarantula's feet are equipped with claws for extra traction when climbing, just like a cat's. In the wild, tarantulas usually move along earthen surfaces, but sometimes they have to climb a tree or other object.
In case of a threat to life, the tarantula uses its hind legs to rip off hairs from its abdomen and throw them at the enemy (if this happens, irritation and itching are felt - an allergic reaction).
Of course, the tarantula itself suffers from such actions, since a bald spot will remain on its abdomen. In moments of danger, they make sounds reminiscent of the vibration of the teeth of a comb. They have excellent hearing. Recognize the sounds of human steps at a distance of up to 15 km.
Tarantulas are brown or black in color with red spots and stripes. In nature there are small, medium, and large tarantulas. American spiders reach sizes of up to 10 cm. Ours are much smaller than their overseas relatives: females -4.5 cm, males -2.5 cm.
A tarantula bite is not fatal to humans, but is very painful.
Minks dig to a depth of up to half a meter near water bodies. The stones are removed. The interior of the dwelling, closer to the entrance, is woven with cobwebs, the threads stretch deeper, their vibration tells the tarantula about the events taking place above. During the cold season, the hole is deepened and the entrance is covered with foliage intertwined with cobwebs.
The Apulian tarantula (photo below) grows up to 7 cm in length. The body is brown-gray, covered with white fluffy hairs.
The whole body is lined, as it were, with transverse and longitudinal stripes of light and dark shades. The paw span reaches 30 cm. The tarantula has the ability to regenerate limbs. During molting, a new paw grows in place of the severed paw, which increases in size with each molt and acquires the desired size.
The spider has very interesting and unusual three rows of shiny eyes on its head. Four small balls are located in the lowest row, on top of which there are two large eyes and another pair located on the sides. Thanks to its developed visual organs, the tarantula closely monitors what is happening around it. Distinguishes the silhouettes of insects, as well as shadow and light. Spiders have excellent hearing. Female tarantulas are larger than males, their weight can reach 90 g.
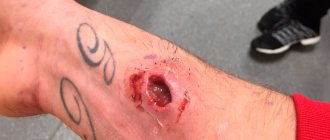
Tarantula bite and the effect of poison on humans. Is the tarantula dangerous?
Usually the tarantula does not attack people on its own. An attack can be forced by the actions of the person himself, who comes close to the mink or accidentally touches the spider. Fortunately, a venomous tarantula bite is not dangerous to a healthy adult. The exceptions are children and people with a predisposition to allergic reactions.
Symptoms and consequences of a tarantula bite can be expressed as follows:
- local pain and redness of the skin, as well as swelling;
- drowsiness and general malaise;
- a sharp short-term increase in general body temperature;
- in exceptional cases, nausea, vomiting and difficulty breathing may occur.
What to do if you are bitten by a tarantula to minimize the consequences?
First aid for a tarantula bite:
- wash the wound with antibacterial soap;
- treat it with an antiseptic;
- call for medical help;
- Cool the tarantula bite area with an ice pack;
- take antihistamines;
- Give the bitten person a large amount of fluid to help remove toxins quickly.
Phalanx
The habitat of this amazing spider stretches from the Iberian Peninsula to the Gobi Desert. It is correct to call these arachnids, which number about 1 thousand species, salpuga, which literally translates as “running away from the sun.”
The size of the phalanges, reaching a length of 5–8 centimeters, placed them among the largest arachnids on our planet. Large individuals are capable of biting through human skin, and chelicerae, which do not have poison, can lead to blood poisoning when bitten.
What do tarantulas eat?
The food of tarantulas is quite varied and consists of small insects and amphibians. Tarantulas eat caterpillars, mole crickets, cockroaches, and hunt beetles and small frogs.
These predators wait for their prey, hiding in a hole, or choose another shelter for this. Having attacked the victim, tarantulas paralyze it with their poison, which dissolves all the insides of the prey, turning them into a nutritious liquid. After waiting the time, the spiders simply suck out the resulting “energy cocktail.”
It is noted that the size of tarantula prey does not exceed the size of the hunter himself, and the process of absorbing it can last several days. Despite their gluttony, poisonous spiders are able to go without food for a long time, as long as they have access to water. There was a recorded case where a female Apulian tarantula was able to live without food for more than 2 years.
Interesting facts about the tarantula:
- The best antidote for tarantula venom is its blood, so often to neutralize the effect of the toxin, it is enough to smear the bite site with the blood of a crushed spider.
- The web is the connecting link between the spider and its home. If the web breaks during the tarantula's escape from the hole, the spider will be forced to dig a new shelter for itself.
- Tarantulas are capable of regenerating lost limbs. After the next molt, a new leg grows in place of the severed paw, slightly smaller in size. With each subsequent change of protective cover, the length of the limb increases until it reaches the original length.
- To stay firmly on tree branches or other surfaces, these spiders are able to extend their claws on all their legs.
- The skin on the abdomen of tarantulas is very delicate and can tear if it falls even from a small height.
- During the mating season, males in search of a female are able to move quite long distances.