Types of spiders in the Voronezh region
Experts say that Voronezh spiders do not pose a danger to humans. They themselves are shy. They prefer to quickly hide out of sight rather than attack. They bite only when there is a threat to their own life. This happens when a person purposefully or accidentally presses on the body of an animal.
The size of spiders does not exceed 1.5 cm. In central Russia there are no poisonous spiders dangerous to humans. There are no representatives of the karakurt family or tarantulas. Therefore, residents of Voronezh can safely relax in nature without fear of spider bites, but caution will not hurt.
All spiders have venom glands that inject poison into the body of the victim. Paralysis occurs almost instantly. The main diet is insects and their larvae. The arachnid family plays an important role in nature - it regulates the number of garden, forest, vegetable, and agricultural pests.
Safe types
Safe species of spiders in Russia hunt insects, waiting for a long time for prey to fall into the net. Their bites are not dangerous for humans. These species live not only in nature; many live in courtyards and settle next to people in their homes.
Safe types of spiders in Russia include the following varieties:
- brownies;
- orb weavers;
- argiope;
- knitters.
People do not like spiders because in their homes they weave webs into hidden and visible areas of walls and ceilings. But in nature, creatures are beneficial and maintain the natural balance, so there is no need to fight them.
House spiders
This species prefers outbuildings and human habitation for its habitat. Preys on moths, bedbugs, cockroaches and other small insects. In nature, dense grass or a crack in tree bark serves as housing. The variety spreads evenly throughout Russia.
External signs of a house spider:
- the body is colored yellow with a brown tint; there is a brown pattern on the surface of the back;
- spider size is from 0.7 to 1.2 cm, females are always larger;
- The legs are colored darker than the body, their length is approximately 2 times the size of the body.
The web in dark areas of an apartment or house has the shape of a funnel. The owner waits for prey in the center of the net; when an insect hits, the spider deals with it with lightning speed.
Orb weaver in nature
The species lives in tree crowns, nets are placed between the branches, and the leaves are used to make shelters. Wheel-shaped traps immediately attract attention in a forest or garden. Sometimes round nets are placed under the eaves, in the window frames of abandoned houses.
The poison is toxic to invertebrates and small vertebrates; it affects rats, rabbits, mice, but horses, dogs, guinea pigs and sheep do not react to the bite. The locust's muscles lock up after 35 minutes, and the frog stops moving within 15 minutes. When bitten, a person experiences mild pain, but the volume of injected poison remains safe.
Orb weavers have an increased appetite and eat up to 8 insects at one time. If there is prey that is unacceptable to it in the trap, then the owner breaks off the web around it and the insect falls. It does network cleaning in the same way.
Argiope arthropods
Arachnids of this species are not dangerous to large mammals and humans. Males are modest in size and rarely exceed 0.5 cm, while females grow up to 2.5−3 cm. The color of the back resembles a wasp due to its bright black and yellow stripes. Short hair grows on the chest and partly on the head. The long legs consist of several jointed sections and are black with pale yellow spots.
Argiopes are spiders of central Russia, because they prefer areas with a temperate climate. They are also found in the southern part of the Stavropol Territory. The bite of an arthropod is compared to that of a bee; spiders do not attack first and do not show aggression. A slight pain is felt at the site of the lesion, swelling appears, but everything returns to normal after 2-3 days.
Trudoviks knitters
The species is distributed throughout the Russian territory and is found more often than in other countries. They almost always prefer nature and do not live in buildings. For hunting, round nets with large rectangular cells are made. The observer sees that such a product is not suitable for fishing due to the rare threads, but it’s all about the specific victim that must fall into the net. Knitters hunt for long-legged mosquitoes, which are a favorite delicacy.
Knitter Description:
- the body has an oblong shape;
- long legs consist of segmented segments;
- many outgrowths are observed on the chelicerae;
- females are large, reaching 3 cm, but males are inferior in height.
The long body saves the knitter in case of danger. At a moment of anxiety, he stretches his legs along his body and in this position resembles a dry twig. If it is disturbed in this state, the spider quickly falls and quickly runs away.
Photos and descriptions of the most prominent representatives
Spiders in Voronezh live in places where there is vegetation and food. You can meet them in nature - forest, river, field, meadow, park, garden, as well as in your own home. House spiders live in the corners of rooms, behind furniture. They are active at night, eating flies, moths, and mosquitoes. They are safe for humans, the main inconvenience is that spiders spin cobwebs almost every night. The most striking representatives of the fauna are found in the wild.
Crosses
Spiders are medium-sized and belong to the orb weavers. At night they weave a large openwork web, during the day they sit in the center of their creation, waiting for the victim. The colors can be different - beige, gray, black, brown, white tones.
Cross spiders
A distinctive feature of this family is the pattern on the upper side of the abdomen in the form of a cross.
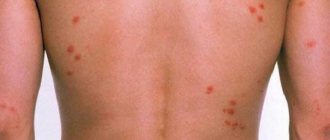
Crosses are classified as poisonous creatures, but their bites do not cause significant harm to humans. Edema, swelling, redness, and pain appear. The skin recovers in 7-14 days. However, individual intolerance to poison occurs. People prone to allergies experience dizziness, weakness, headache, abdominal discomfort, arrhythmia, etc. In this case, medical attention is required.
Spider wasp or Argiope bruennicha
Belongs to the orb weaver family. It has an unusual appearance and bright color. Outwardly it resembles a wasp. The body is elongated, painted with black and yellow stripes. The legs are long and equally striped. Thanks to this camouflage, the paca wasp has practically no natural enemies. Females reach sizes of 15 mm, males are half that size.
They are nocturnal and actively weave fishing nets. They eat insects, their larvae, and small relatives. Argiope brunnich prefers sunny meadows, weaves openwork nets, which then shine under the rays of the sun and attract victims. The hostess herself sits in the center of the web in the “X” position, with her limbs spread apart in pairs.
When it sees a person, the spider continues to sit motionless on the web or tries to quickly hide in a secluded place. It bites only when a person is excessively curious or due to carelessness on his part. The consequences of a bite are similar to those of wasps and bees. Allergy to poison is more severe in young children.
Residents of the region raised the alarm because of one incident that occurred in the Talovsky district. A seven-year-old boy was bitten by an unusual spider. The child's hand was swollen and his health worsened. Spent 7 days in the hospital. Information spread throughout the region that poisonous spiders in the Voronezh region began to attack people. The answer was provided by experts, assuring that there is no reason to panic.
The sak spider became a poisonous creature. Other names: yellow, heyracantium. A predator with a bright color and unusual appearance more closely resembles a scorpion. The legs and abdomen are amber-yellow, the cephalothorax is red. The chelicerae are bent into the shape of fangs or claws. Before rushing to attack, it takes a fighting position - it rises on its hind limbs. Females reach sizes of 1 cm, males are slightly smaller. Together with the leg span it reaches 2.5 cm.
In Europe it is one of the most poisonous. Lives among dense vegetation in dry areas, under stones, in bushes. Spider venom is not fatal to humans, but causes an allergic reaction of varying degrees of intensity. The bite is more difficult for children, people prone to allergies, and people with weak immune systems. The reaction depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
Possible consequences of a bite:
- burning pain;
- edema;
- redness;
- swelling;
- tumor;
- increased body temperature;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- headache;
- dizziness.
The most poisonous spiders in Russia: photos and names
No matter how much I would like to admit it, dangerous arachnids are far from uncommon in our country, although of them only the female karakurt is really worth fearing.
It is the representatives of this species that fall under the category of the most poisonous spider in Russia: the real black widow, the false and the white karakurt (Figure 2). You can deal with the consequences of bites from other arthropods on your own, although the best thing to do is to seek help from a doctor.
The top poisonous spiders in Russia include:
- Phalanx or solfuga - despite the fact that it does not have its own poison, its mandibles contain a large number of microorganisms that can lead to infectious infection.
- The bag spider or bagworm does not pose any serious harm to life, but severe pain at the site of its attack may not go away within a couple of days.
- The mesh also does not have dangerous toxins in its saliva, but the likelihood of infection is extremely high.
- Mizgir is not capable of killing a person, but its poison causes an allergic reaction, painful sensations remain for a long time, and severe swelling is characteristic at the site of the wound.
- The female karakurt is the only one listed whose bite can be fatal if the victim is not provided with timely assistance.
Figure 2. The most poisonous spiders in Russia: 1 - phalanx, 2 - bagworm, 3 - net spider, 4 - mizgir, 5 - karakurt
Let's take a closer look at the poisonous spiders in Russia - photos and names:
- Solpuga, solfuga or phalanx - are active at night, bite quite deeply and only for the purpose of self-defense; if the saliva infected with the infection is not removed from the wound and treated with an antiseptic, it will begin to fester severely.
- Crossworts can also carry infection through their saliva; their distinctive feature is a cross-shaped pattern on the upper side of the abdomen; their females are twice as large as males.
- Chiracantids are wandering hunters and lead an active nocturnal lifestyle, the color of different individuals varies from yellowish to greenish and brown, their bite causes a sharp burning pain, inflammation of the nearest lymph nodes to the lesion;
This is the most dangerous representative of arachnids in the Russian Federation. When talking about what poisonous spiders are found in Russia, one of the first to be named is the true and false black widow (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Common and false karakurt (black widow)
In both cases, only females, which reach a size of 15-20 mm, pose a serious threat. The first bite causes severe pain that spreads throughout the body and can lead to death if you do not use a special serum developed against the toxins it contains.
We suggest you read: Helminths in humans, symptoms, treatment
The consequences of a false widow attack are characterized by prolonged pain, increased general body temperature and weakness, which can be observed for two days.
It is difficult to confuse a female common karakurt with anyone else - the black color with characteristic red spots or dots on the belly itself serves as a signal of danger.
The false individual has a uniform black color, sometimes with a brown tint, a pronounced large abdomen and long legs that are lighter in relation to the body; it is often found in Dagestan and often ends up in the homes of local residents.
The white poisonous spider in Russia, which is also a representative of this species, deserves special attention. It is not aggressive in itself, but its venom is very toxic and causes serious complications.
There are 4 indentations on its white or milky round abdomen. Long legs and head with chest yellow or light brown. The specimen weaves a cone-shaped web connected to a trapping net. The habitat of the species is Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan.
Despite its large size, this individual does not pose a threat to life. It belongs to the family of wolf spiders and is active at night. The arachnid prefers warm, arid regions and lives in burrows lined with cobwebs (Figure 4).
Representatives of the species can be found in the Belgorod, Astrakhan and Tambov regions. Although these are burrowing animals, some of them can easily climb into living quarters in small settlements.
Due to the low concentration of protein toxins, the poison does not cause a paralytic effect and is not capable of causing serious harm to humans or large animals. The glands containing it are located in the cephalothorax, and their ducts open at the top of the chelicera, with which this hunter bites his prey.
Figure 4. Mizgir – appearance
The strength of the bite is comparable to a hornet attack; its consequences are local swelling, severe pain and yellowing of the affected area of the skin, which can last up to two months.
This is the most poisonous representative of the middle zone, which camouflages itself under the foliage of small trees and shrubs (Figure 5).
The yellow poisonous spider in Russia attacks in self-defense, due to the negligence of the person himself, which is accompanied by:
- burning pain in the affected area;
- redness or blueness of the skin;
- over time - the appearance of blisters;
- nausea and vomiting, weakness and body aches;
- sudden increase in temperature and headache.
We suggest you read: Gray spider in the apartment
Figure 5. The most poisonous spider in central Russia
Unpleasant symptoms disappear after 2-3 days, but the mark on the skin remains much longer. If your health worsens, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Web spider
Steatoda is one of the least poisonous, although the most widely represented arachnids in our country (Figure 6).
Figure 6. Appearance of the mesh
These types of poisonous spiders in Russia belong to the subspecies of cross spiders, there are about 70 species in the Russian Federation. They are small in size and vary in color - from whitish to grayish-brown, and weave quite strong and chaotic webs and live in grass. Their mandibles are dangerous not because of the poison, but because of the infection they contain.
A rather aggressive individual that can be found in the steppes of the Volgograd and Rostov regions (Figure 7).
Figure 7. External features of the bagworm
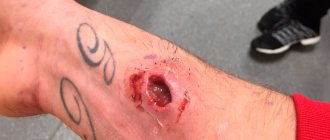
The bite of this brown recluse spider is characterized by a number of symptoms known as loxoscelism: severe pain spreading throughout the body, nausea and fever, malaise with the further appearance of an ulcer up to 25 cm in size and its long healing of several months, even to a gangrenous scab. or necrotic ulcers occurs in extremely rare cases.
Eresus black looks quite cute, but this does not mean that it is worth picking up, since it is this behavior that provokes its attack. It lives in the central part of the country, in the Crimea and the Caucasus, in the south of the Urals (Figure 8).
Figure 8. Black fathead - a beautiful but poisonous spider
The spider moves very quickly, and its attack is characterized by painful sensations, numbness, and swelling in the affected area.
Argiope spider
The color of this representative speaks for itself - the insect is dangerous. Its second name, the wasp spider, is associated with its specific body structure and black and yellow coloring (Figure 9).
The arachnid is not uncommon in our country - it can be found in the Crimea and Kazakhstan, in the Caucasus. This is a forest dweller who weaves a wheel-shaped web and settles between tree branches in gardens and forests, in tall grass in clearings and lawns.
We suggest you read: How to apply stronghold for cats
For humans, an argiope bite does not pose a serious danger - it causes slight redness, pain and swelling for a short time. But an allergic reaction to the toxins contained in its saliva can cause severe abscesses and lead to necrosis of soft tissues.
South Russian tarantula: description
The spider shown in the photo belongs to the family of wolf spiders, which are characterized by a solitary, unpaired existence and a well-developed camouflage system.
Reference! Individuals are relatively small: females reach 30 mm, males - 25 mm.
The structure of both is similar, the color is brownish-red. The expressed glands contain poison. It is dangerous for insects and small animals, but a single bite in itself is not fatal to humans . Death can only occur due to a severe allergic reaction.
Birds
The most beautiful bird, the pink pelican , is under threat of complete extinction. Body size 1.5-1.6 m. Very delicate plumage, the color of early dawn - white with a pink tint. It is found on Lake Manych and on the Chongray Reservoir (KR).
Savka . A waterfowl belonging to the duck family. The size is small, up to 45 cm, painted in fawn tones on the back, brown belly. The head is light gray or white. Males have a black stripe on the neck and a blue beak (BK).
Peregrine Falcon . A bird of prey from the falcon family. It is up to half a meter tall, with a wingspan of up to 1.5 m. Its most important quality is its high flight speed. It accelerates to 300 km per hour. Therefore, our famous high-speed train Moscow - St. Petersburg was named "Sapsan" (KK).
Meadow tirkushka , a bird from the order Plovers. The body is from 25 to 28 cm in size, brown on top, the breast is yellowish, and on the throat there is a beautiful lemon-colored collar with a black border. A bit like a large swallow, especially in flight (KK).
Eagle owl . One of the largest representatives of owls. Registered in the CC of the Stavropol Territory. Size up to 65 cm, black-brown color with variegated stripes and specks of white and black tones (CK).
The black stork , a wary heron bird, is black in color. It lives in tall trees; its numbers are declining due to deforestation and the construction of power transmission lines (PTL).
The steppe eagle is a proud, large-sized bird of prey with a sharp beak (KK Stavropol region).
Short-eared owl , a bird with short tufts of sparse feathers near its ears. The top is painted in rust color, with longitudinal dark and light spots. Selects open wetlands, omnivorous (KK Stavropol).
The bustard is a large bird of the crane-like family, weighing up to 16 kg. It lives in the vast expanses of the steppe, runs quickly and is able to camouflage well, which is facilitated by its variegated coloring (black-white-gray-red color of feathers) (KK Stavropol).
The little bustard is closer in size to the domestic chicken, but looks like a partridge. The back and head are sandy in color. The breast is white, there are several transverse black stripes on the neck
The demoiselle crane is the smallest representative of the cranes, height 90 cm, weighs from 2.8 to 3 kg. Mostly white in color, there are beautiful patches of black feathers on the head, neck and wings. Around the eyes it is painted in a light gray tone, and the beak also has areas of this color. The beak is short and yellow (KK Stavropol).
The Imperial Eagle is a large feathered predator. Size from 80 cm, sometimes up to 90-95 cm. Wings in flight swing up to 2 m 15 cm. Weighs about 5 kg, and females are larger than males. The color of the feathers is dark brown, closer to black; there are snow-white islands on the chest and wings. The tail is gray-brown (KK Stavropol).
The Buzzard eagle has reddish plumage and adheres to the steppe, desert and forest-steppe (KK Stavropol region).
mountain birds
Caucasian snowcock , another name for mountain turkey , a relative of the pheasant, resembles partridge and domestic chicken (KK Stavropol region).
Caucasian grouse , a jet black bird with some blue in the form of individual islands. The tail and wings are decorated with white spots. A distinctive feature is red feather eyebrows. Rare, listed in KK.
Bearded eagle , also known as a scavenger vulture, wings and tail with sharp ends, the plumage on them and on parts of the back are black, the chest and head are light beige. There are black stripes near the eyes (KK Stavropol region).
The griffon vulture is a bird of prey from the hawk family. It is also a scavenger. It is all dark gray, closer to black in places, the chest, neck and head are white. The beak is wide and strong (KK).
South Russian tarantula in natural conditions
Lives in steppe, desert and semi-desert regions . It is less common in forest belts. Habitat in Russia: Siberia, Saratov, Kursk, Lipetsk and Astrakhan regions, Stavropol and Transbaikal Territories . It usually settles near ponds or other sources of moisture. It builds vertical burrows for itself in a loose, moist environment.
Loner . Does not tolerate other spiders near him. Exception: end of summer. In August it is mating season for the South Russian tarantula . It proceeds quickly and is initiated by the male. But if the female does not support his proposal with a reciprocal swaying dance, then the spider will have to urgently retreat.
The Siberian and Russian tarantula is nocturnal, but is active even during the day. For example, when an insect gets caught in his trap. Even a fly just flying into a hole can become a signal for awakening and an immediate aggressive attack. Moreover, the spider does not stop pursuing the victim who survived the attack. He runs after her and bites her until the bitter end.
Important! South Russian tarantulas feed on insects, but are quite capable of attacking a very tiny animal. For example, on another spider, frog or small mouse.
Under natural conditions, an individual lives for about 2 years, and in captivity - a year or a little more than a year . The given values take into account the normal course of existence. If the tarantula is not fatally attacked, begins to molt frequently, does not sleep in winter, systematically overeats, or does not receive a minimum set of nutrients, it will die much earlier than expected.
Important! Females are much stronger, live longer and hibernate when cold weather sets in.
The most poisonous spider in Russia
Here, neither specialists nor ordinary people have any disagreements and there cannot be any. Karakurt is the only one of all the representatives of arthropods living in the vast expanses of our country whose bite can be fatal.
Appearance
Only females reaching a size of 15-20 mm are dangerous to humans. They have two distinctive signs that prevent karakurts from being confused with other representatives of arthropods. There are exactly 13 bright spots or dots on the upper side of the black abdomen. Naturally, there is no time to count them, but the very combination of black with bright spots should serve as a signal of danger. On the underside of the abdomen there is one equally bright spot in the shape of an hourglass.
Karakurt is the only spider in Russia whose bite can be fatal
Habitats
Karakurts are thermophilic. They live in the Southern Urals, the Caucasus and the Black Sea regions. However, recently the habitat of this spider has expanded to more northern regions of Russia, right up to the Moscow region. This is explained by global warming, but more optimistic scientists are confident that this only happens in very hot years, and not always.
Consequences of a bite
Karakurt, which has a very strong poison, unlike other spiders, is very aggressive and bites not only for the purpose of self-defense. He can attack purposefully, so you should not only tease him, but also approach him with great caution. The bite itself is very painful, and after 10-15 minutes the pain spreads throughout the person’s body and becomes almost unbearable.
If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, which consists of administering a special serum, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, rapid heartbeat, fever, headache and dizziness, tremor, profuse sweating, and a feeling of heaviness in the chest may develop.
Even after administration of the serum, symptoms may persist for another day.
First aid
The only thing that can be done for the victim is to take him to the nearest hospital as soon as possible.
Danger to humans
It is not aggressive towards creatures that are significantly larger than itself. Prefers camouflage to attack. If the concealment fails, as well as in the event of severe provocations, it attacks the person .
The bite is not fatal, does not cause tissue necrosis, and does not affect the central nervous system, but swelling appears around the openings from the glands. Inflammation is active. Often accompanied by an allergic reaction.
Important! After an attack by a South Russian tarantula, be sure to take antihistamines.
South Russian tarantula at home
The law does not prohibit keeping such spiders at home. At the same time, you need to be realistic and understand that a dangerous arthropod should not be in the same room as a child. In addition, before buying a tarantula, you should seriously prepare. If you put a spider in a regular aquarium, it will not live long.
Aquarium for tarantula
When choosing an arachnarium, you need to take into account the habits of the arthropod. It jumps up to 20 cm in height (abnormally large individuals jump higher), builds burrows 40 cm high
.
And in natural conditions it is able to move relatively far from its home for the sake of hunting. Therefore, the aquarium should be tall and long. Otherwise, the pet will get hurt, run away, or be unable to exhibit its typical activity.
Due to the fact that the spider instantly switches from a sleeping and inhibited state to running , and also jumps far, the arachnarium will have to be kept closed all the time, with the exception of cleaning days. In this case, the tarantula’s home must be provided with a well-thought-out and functional ventilation system. It is required not only by the pet itself, but also by the plants. An arthropod cannot live without real vegetation for long.
Important! In addition to a small amount of grass, driftwood should be placed in the arachnarium. The ideal option would be to place the branch under a lamp. The pet will climb a tree and bask in the rays of artificial light.
The bottom of the aquarium is sprinkled with the following types of soil:
Insects of the Voronezh region
There are over 10,000 species of insects in the Voronezh region. In addition to species with a wide geographical distribution, both northern and southern insects are represented. The pine forests of the north of the region are inhabited by taiga-forest species. This is the southern border of their distribution. Southern species are steppe, characteristic of broad-leaved forests and Mediterranean species.
The following beetles are typical for broad-leaved forests: beauty beetle, four-spotted carrion beetle, inquisitor, deer beetle, relic woodcutter. Steppe species: independent racer, steppe beauty, humpbacked peon. Mediterranean species: Germanic racer, golden-fringed beauty, blue-headed lebia.
Green and gray grasshoppers are numerous. Dragonflies are found on the banks of reservoirs. Graceful and small - a beautiful arrow and a fierce bride. Heavy and large - red and common dragonflies.
Numerous species of ground beetles, dung beetles, bronze beetles, various types of longhorned beetles, rhinoceros beetles and stag beetles are common in the Voronezh region. Butterflies decorate a summer day: lemongrass, urticaria, mourning butterfly, peacock's eye, admiral, agrimony, Apollo, polyxena, blueberry, white butterfly, moth, and bear.
Hymenoptera insects include numerous bumblebees, hornets, cymbex and others.
Diptera insects: hoverflies (about 200 species). These flies, often similar to wasps, feed on the nectar of flowers. Birds do not touch them, mistaking them for stinging insects.
Anthropogenic impact affected not only large animals, but also insects. But there are still places in the region that are inconvenient for agriculture. There, on lands little changed by man, unique insects have been preserved.
A striking example is valley-shaped beams. They have symmetrical slopes and worn-out bottoms, along which water flows into rivers during spring snowmelt and heavy rains. One of these beams is in the Liskinsky district, on the right bank of the Don, opposite the settlement of Vyazniki. This ravine is called Shatrishchegorsky Yar, as it is located next to the famous chalk hill Shatrishche. It extends from northeast to southeast for 4.7 km and has a convex shape. At the mouth, the bottom of the beam is about 110 m wide. Chalk is exposed in the lower third of the slopes. On the slopes the soil cover and plant associations are very variegated. Such diversity apparently caused the formation of a rare entomofauna. Researchers noted here a huge number of nesting sites of ground bees, galicts (22 species), andren (more than 18 species), euceras (4 species) and others. Eight species of bumblebees nesting on slopes are listed in the Red Book of Russia. These are, among others, Armenian, clayey, lesus and lamellar. The need for a thorough study of such natural complexes and timely and adequate protective measures is obvious.
Khripunskaya steppe - located in the south of the Voronezh region. This is a small (about 80 hectares) area of untouched steppe among fields and forest belts. Various types of fescue and feather grass vegetation grow here. The Khripunskaya steppe is located 5 km south of the village of Novonikolskoye, Bogucharsky district. In the Khripunskaya steppe, not only the vegetation is unique, but also there are numerous insects, many of which are rare and listed in the Red Book of Russia. The following butterflies are noted here: swallowtail, galatea, aurania checkerwort, marigold marigold, sappho moth, meleager blueberry, and ocellated hawk moth. From the order Orthoptera: steppe and big-fronted crickets, blue-winged and red-winged fillies. From the order Homoptera - the mountain cicada. From the order of beetles: the majestic cape, the inconspicuous ladybird, the sandy and steppe slowworms, the globular pimelia. From the order Netoptera – the European antlion. From the order Hymenoptera - Scolia giant and Scolia steppe. Among the bees, the following genera deserve attention: Andrena, Anthophora, Halictas, as well as earthen and clay bumblebees.
Not far from the Khripunskaya steppe, in the Bogucharsky district, south of the village of Krinitsy, there is the virgin steppe of the Shlepchino tract. The following Red Book species of insects have been recorded here: swallowtail, marigold, camilla ribbon grass, meleager blueberry, steppe thicket. Bumblebees are widely represented: ground bees, Armenian bees, clay bees, lesus bees, and field bees. Solitary bees from the genera Galicta, Andrena, Coleta.
Somewhat west of the village of Krinitsy there is an outlier called Makkarte. A typical steppe complex of insects lives here. Among them are rare butterflies: bluebird meleager, ribbon butterfly camilla. Orthoptera: song and gray grasshoppers, blue-winged and red-winged grasshoppers, steppe cricket. Among the Hymenoptera, the Armenian bumblebee is listed in the Red Book of Russia.
South Russian Tarantula: photo, video, description
Belongs to the family of wolf spiders (Lycosidae). Place in classification (Wikipedia):
- Class: Arachnida (Arachnida)
- Order: Spiders (Aranei)
- Suborder: Araneomorphae spiders (Araneomorphae)
- Family: Wolf spiders (Lycosidae)
- Genus: Tarantulas (Lycosa)
- Species: South Russian tarantula (Lycosa singoriensis)
Spider, 25-30 mm in size. Females are larger than males. Covered with thick hairs. The color is brown-red above, dark, almost black below.
South Russian tarantula (Lycosa singoriensis)
The eyes are located on the “crown” of the cephalothorax in three rows. The bottom one has four small eyes, the second one has two large eyes directed forward, the third one has two large eyes on the sides. In total, this optical system gives the tarantula a very good view, perhaps even a full 360 degrees.
Vision is very well developed, because it is one of the spider’s main hunting tools.
South Russian tarantula (Lycosa singoriensis)
The senses of smell, touch, hearing and taste are provided by the sensitive hairs on the spider's legs.
And these sense organs make the tarantula a terrible predator, as I was convinced of during the observation process.
The lifespan of a female South Russian tarantula is more than two years, a male is slightly less.
You can get some idea about the pet from this video:
Distribution area of the South Russian tarantula
Wikipedia tells us that the spider is distributed in Central Asia, Siberia and Ukraine, and is also found in Belarus. That is, here in Tambov, in theory, it cannot exist. But our spider obviously didn't read Wikipedia. One might assume that the tarantula escaped from the terrarium, but several other people reported encounters with tarantulas, so this is not an isolated phenomenon. In addition, few people keep tarantulas in captivity, because... There are more interesting and less biting species of exotic spiders.
Gentlemen, alarmists, take note. Tarantulas are coming to our area along with praying mantises, argiopes and encephalitis ticks.
South Russian tarantula (Lycosa singoriensis): female with baby
Tarantula lifestyle
The South Russian tarantula lives in burrows up to 40 cm deep. The walls of the burrow are intertwined with cobwebs, by the vibration of which the spider senses what is happening on the surface. It also reacts to the shadow of an insect blocking the entrance to the hole. In this regard, there is a well-known method of luring a tarantula out of a hole using a plasticine ball on a string.
Friends! This is not just an advertisement, but my, the author of this site, personal request. Please join the ZooBot group on VK. This is pleasant for me and useful for you: there will be a lot there that will not end up on the site in the form of articles.
Dangerous classes
There are varieties of spiders that secrete a toxic substance. Medical intervention after a bite is required to neutralize the consequences. You need to know the names of the most dangerous spiders in Russia, which live in different regions, in order to protect yourself from bites.
Common crosses
The diet of this arthropod species consists of insects. The cross eats flies, bees, hornets, mosquitoes, butterflies and other flying insects, which it catches with the help of a web. The cross immobilizes prey with poison, then entangles it with threads. He injects liquid digestive enzymes into the victim's body, from which the body softens and turns into a semi-liquid state. After a while, the executioner eats the half-digested contents. The crossfish makes provisions for the future; if it is full, it hangs the prey from the edge of the fishing net.
This species is not one of the largest spiders in Russia; females grow up to 20−25 mm, but males are smaller in size (10−11 mm), as with all arachnids. The white cross lives in all regions of the country and prefers the atmosphere of beech, spruce or pine forests. Individual representatives are found in arable lands, swamps, meadows and orchards with fruit trees.
Characteristic features of the appearance of the cross:
Body color depends on external lighting. On the back there is a pattern in the shape of a cross, for which the spider got its name.
Representatives breed in August; for males, mating games often end with eating. The male attracts the female by twitching the signal thread on the web. To lay eggs in the fall, the female makes cocoons from specially spun webs and dies after laying. The eggs overwinter in this cocoon, and the spiders are born in mid-spring. Sexual maturity occurs only after the next wintering.
Harmful chiracantids
Dangerous arthropods are found in grass and shrub thickets. This species belongs to the poisonous spiders of the middle zone. Chiracantids are vagrant individuals and do not weave any web traps. The highest activity occurs at night, hunting from tactile contact with the spider. Usually the victim touches the legs of a hidden hunter, who attacks her in a jump. The diet consists of caterpillars, grasshoppers, moths, aphids, and mites. Spiders of this species avoid contact with wasps and ants.
Characteristic appearance features:
After a bite, severe pain appears at the site of the lesion, a burning sensation is felt, and the symptoms gradually spread to nearby areas. There is no itching or numbness in the muscles, but the lymph nodes located in the path of the poison begin to swell and ache. Stiffness and swelling develop a little later, sometimes the person cannot breathe freely.
If help arrives in time, the pain subsides within a day, and other symptoms disappear within 2 days.
Poisonous karakurt
This species is recognized as the most poisonous and belongs to the so-called black widows. Representatives live in the southern regions of the Urals, in the Caucasus, in the Astrakhan and Volgograd regions. In recent years, the range has shifted to the northern regions, reaching the Moscow region, which scientists explain by climate warming.
The species does not settle in residential buildings and will never live in a multi-story building. Prefers a hot climate and lives in steppe regions. The spider's enemies are hedgehogs and wasps. Near housing, the spider builds burrows in landfills, in piles of firewood, and in cluttered areas of dachas.
Appearance of karakurt:
- the body is black or gray-black, with red spots with white edging;
- The size of the female reaches 1.5−2.0 cm, and the males grow up to 0.7 cm.
The older the spider, the darker its body, and the bright spots become less noticeable over the years. The female's venom is dangerous to humans only after 5-6 molts; before that, the venom is not so poisonous.
The female builds a den in soil depressions, often uses ready-made rodent burrows, drainage pipes, and places nets at the entrance for protection. The eggs spend the winter in a cocoon, and in the spring the young spiders scatter in the wind with their webs.
The karakurt attacks animals and humans if it is disturbed. After a bite, a burning pain quickly spreads throughout the body. Severe pain occurs in the abdomen, chest, lower back, shortness of breath appears, the pulse and heartbeat increase. In later periods, excitement gives way to depression, delirium appears, and consciousness becomes confused. For relief, anti-karakurt serum, novocaine, sodium hydrogen sulfate, and calcium chloride are used. The patient needs urgent medical attention.
South Russian tarantula
A light gray spider with a body length of up to 3 cm lives mainly in dry climates, settling in forest-steppe, semi-desert, steppe. To live, it digs a hole up to 40 cm deep and covers the walls with cobwebs. Looks out for the victim in the shadows as it passes by the entrance. After this, it instantly bites the prey, immobilizing it.
South Russian tarantula: keeping in captivity, personal experience
The spider was brought from the village and planted in a small (35*20*25 cm) aquarium. I poured a 3-5 cm layer of soil at the bottom and placed a lid from a jar as a pool.
According to recommendations on the Internet, the tarantula needs to be filled with more soil so that it can dig holes, but for now I limited myself to this layer, because... an aquarium half covered with soil will be too heavy, and in this case this is important.
At first, the tarantula sat motionless, and with all its appearance made it clear that nothing in this world could excite it. Even three bread ground beetles released into the aquarium did not make any impression on him... as long as the light was on.
South Russian tarantula (Lycosa singoriensis) eating
Without waiting for anything interesting, I went to bed. A few minutes later there were sounds of some kind of fuss and even knocks on the glass. I jumped up, shined a flashlight... The spider was sitting in the same place, however, in its chelicerae a ground beetle was now helplessly moving its legs.
By morning, the position of the spider had not changed, but part of the soil in the aquarium was now covered with a layer of cobwebs, and only sucked shells remained of two more ground beetles.
But the tarantula's hunt for flying food is especially impressive. Actually, I think that in keeping such a spider, feeding is the most interesting and exciting spectacle. The speed with which the tarantula grabs its prey never ceases to amaze me.
Spiders in the Stavropol region. A creepy tarantula of enormous size frightened the residents of Stavropol
Yes, we think about it first of all when we talk about poisonous creatures. In fact, it very rarely bites, and one person in a hundred dies from its bite. And only if you don’t get help in time or if he has allergies. The viper itself does not rush out just like that. But she will defend herself if she is stepped on or poked with a stick.
If you are relaxing in Besputskie glades or just in nature, it is best to wear high boots, thick pants and walk with someone who can provide first aid. Also, make noise, move the grass with a stick, knock it on the ground so that the snake itself moves away from danger.
The viper is often confused with snakes because of their similar color. The main thing to remember is that the viper grows no more than a meter in length, the snake is usually twice as long.
It is also called the yellow-bellied snake. It lives in the steppes, grows up to two meters in length and has a girth like a human wrist. You can recognize him by his solid dark color and light belly. The snake has no poison, which is compensated by unhealthy aggression. If it seems to him that you are dangerous, he may attack and bite you, but not kill you.
There is one funny myth associated with the snake, according to which it can break a horse’s leg with one blow of its tail. Don’t be afraid, this is not a Basilisk or Godzilla, he is not capable of this, just like the yellow belly. This is an even more harmless creature. The only thing he can break is the stereotype about snakes, because the yellowbell is not a snake at all, but a lizard without legs.
Another name is “phalanx”, because this spider is the size of the phalanx of a finger. Recently, he began to be noticed in the Trunovsky and Krasnogvardeysky districts. It does not pose a mortal danger, but its bite does not bring anything pleasant. Residues of food on the nodules are dangerous; through them it can infect a person. When talking about spiders, people often think of karakurts. They are listed in the Red Book and are extremely rare.
What happened to the little tarantula?
South Russian tarantula (Lycosa singoriensis): female with baby
I took the little spider away from its mother and put it in a soy sauce container. By the way, these containers are extremely convenient for keeping and holding various kinds of small animals.
South Russian tarantula (Lycosa singoriensis): female with baby
The baby is not far from his mother in terms of agility and insatiability. He bravely rushed at mosquitoes noticeably larger than himself, and in a split second crushed them into wet lumps with legs and wings sticking out of them. In addition to mosquitoes, moths were also tested. In general, there was plenty of food, and in two days the little tarantula grew a noticeable abdomen.