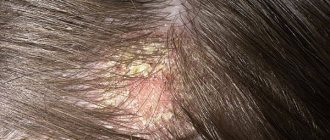
A parasite is an organism adapted to unfavorable conditions that can live in any part of the human body. A special treatment has been drawn up for parasites in the hair, in case the parasites live in the head. In addition, these creatures live in all internal organs, on the scalp and under the skin. This article will discuss the types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of parasites on the human head.
Types of parasites in hair and symptoms
There are entire classes of organisms that parasitize human hair. A component of their nutrition is human tissue, that is, skin, sebum, blood. By feeding on tissues, parasites make themselves felt by itching, scalp pain, hair loss and creating significant discomfort. It is difficult not to detect such parasites; they are extremely dangerous to human health.
Head lice
Pediculosis or, in other words, lice is known to every parent and every child. The main risk group is school-age children. The main danger of lice is that they are invisible to the naked eye. They look like tiny bugs that can masquerade as the light skin of a person’s scalp, thanks to the pale color of their body. Nits are lice eggs that stick tightly to the hair roots, making them often difficult to get rid of. The nits contain larvae. Lice are able to run quickly and are transmitted through direct contact between people, that is, when their heads touch, with hats or clothing. They leave bites behind, and feel most comfortable at the temples and on the back of a person’s head.
The flea is an omnivorous parasite
The flea in the past was a carrier of plague and typhoid. Most often found in animal fur, but also found in humans. These are bugs of different shades - from yellowish to dark brown. The classification of fleas corresponds to the type of carrier. They are divided into the following types:
- Household: linen;
- sexual
- canine;
Human fleas are universal. They are able to feed on the blood of humans, dogs or cats. In addition, there are species that choose habitats in the form of rugs and upholstered furniture. Such fleas are called house fleas. Earth fleas live in the yard, which do not pose a danger to humans because they do not feed on blood. The main danger of fleas is that they carry infectious diseases.
Parasites under the scalp
Scheme of human infection with dirophyllaria.
Subcutaneous parasites are often found in hot, tropical countries. Getting rid of them requires much more time and effort than those that live on the surface of the skin. Under the skin of the head, wrists, armpits, and between the fingers, microscopic scabies mites parasitize, causing the disease scabies. It feeds on human skin tissue, gnawing paths under the skin and causing unbearable itching. Another dangerous subcutaneous pest is dirophyllaria. This parasite develops under the mucous membrane of the eye, which can impair vision or even make a person blind. It can only be removed surgically.
Hair mites
The hair mite or demodex lives in human hair and eyelashes. Having a detrimental effect on the scalp and hair structure, it causes excessive hair loss. At first they feed on dry scales - pieces of dead skin, then they get into the follicles and cause serious damage, resulting in hair loss. Mites on eyelashes provoke the formation of white or yellowish scales between the hairs, as well as their loss. This parasite often causes bright red acne on the face. For a long time, it may not remind you of itself in any way, but when the immune system weakens, it makes itself felt by the reactions described above.
What do lice eggs - nits - look like on hair?
With active head lice, from a distance or in poor lighting, the hair may appear strewn with dandruff. However, it is easy to shake off, while nits on the head are attached very firmly.
Photo No. 2. Nits on hair
Females place their clutches closer to the base of the hair, where the temperature is higher. Each hair can contain from one to several eggs. What do lice eggs look like? They look like small elongated capsules of grayish or beige color. If the capsule contains an egg inside, the presence of a dark inclusion can be determined by looking at the light. If the larva has already emerged, the capsule looks dry and transparent in the light
Nits are attached to the hair with a very strong compound. This is what makes it difficult to remove them from hair. Parasite eggs can be crushed with a quiet click, but they can only be scratched off with some effort. They can be located not only at the base of the hair, but also in the middle if the hair is often collected in a bun or ponytail. It’s easier to notice them on dark strands, while on light brown ones the surest way is to use a comb and a clean napkin.
Causes of parasites on the human head
Each type of parasite comes into the human body from the external environment. Lice are transmitted directly from person to person or through the belongings of an infested person. Fleas are brought into the house by pets, transmitted from animal to animal, and also from animal to person and vice versa. Subcutaneous parasites enter the human body along with raw water, as a result of swimming in contaminated bodies of water, from animals, as well as through direct contact between people. Demodex lives in the human body without causing any discomfort or harm, but if the quality of skin and hair care deteriorates, or the use of aggressive cosmetics, it becomes active and provokes the extremely unpleasant symptoms described above.
Insect species
Depending on the structural features and place of residence, lice are divided into three groups.
Living on the head (head)
The most common variety, the appearance of which depends little on human living conditions.
Reference. Parasitizes the scalp. In men, larvae can be deposited on sideburns or stubble.
Clothes (linen)
Outwardly it resembles a head parasite, but settles exclusively on dirty clothes or bedding used on a regular basis. This species is not able to live on the human body or hair, so it is the easiest to fight.
The body louse is a variation of the other two and has a similar genome. It appeared as a result of evolution and spread due to human fault.
Pubic
It parasitizes the intimate area, but with severe infection it can spread to the eyebrows or eyelashes.
Important! This variety is most often transmitted through sexual intercourse, less often through water in the pool or the use of other people's things.
Equated to sexually transmitted diseases.
Treatment of uninvited guests
Treatment of pediculosis
Each type of parasite that lives in the human head requires a specific approach to treatment. Pediculosis is usually treated at home. They use medications intended for this purpose, which can be in the form of a spray, shampoo, cream, or emulsion. To choose the right product from the variety available in stores and pharmacies, you should pay attention to the composition of the drug.
Getting rid of fleas
The flea is a non-permanent inhabitant of the human body. She is constantly moving. The parasite, having drunk blood, leaves the body until it gets hungry again and begins to look for a new victim. Therefore, the premises or fur of an animal are considered a more or less permanent habitat for this parasite. There are many medications available for treating pets that are sold in pet stores. And to get rid of fleas indoors, different disinfection methods are used. They do the cleaning themselves by purchasing a special product, or order this service from the appropriate service. In addition, it is worth remembering that if fleas are found on an animal, you should be sure that they have already managed to lay larvae in different parts of the home. Therefore, treating the animal alone is not enough. Usually disinfection of the premises is combined with the treatment of animal hair.
Expulsion of subcutaneous parasites
Compared to cutaneous parasites, parasites under the skin are a much greater nuisance, and even a danger to human health. Treating hair for parasites that live under the skin requires a lot of time and effort. This type is difficult to diagnose because the symptoms are often falsely perceived as diseases of the internal organs. Most often they are removed surgically, but some of them, for example the scabies mite, are expelled with the help of ointments, solutions and other medications.
Demodex therapy
Demodex lives harmlessly in the human body until external conditions provoke its active feeding and rapid development. Treatment requires a lot of time, effort and systematicity. To cope with this problem, your own efforts are not enough: you cannot do without an experienced dermatologist. Once you are sure that the symptoms indicate demodex, you should stock up on:
- medications prescribed by a doctor (such as medications with added sulfur, tar, zinc and mercury ointments);
- antifungal ointments;
- anti-inflammatory ointments;
- vitamins.
Be careful with anti-demodex medications! As a rule, these agents are quite toxic. Therefore, they are contraindicated during pregnancy, breastfeeding, kidney and liver diseases.
How to get rid of lice in 5 steps?
Knowing the mechanisms of the appearance and reproduction of lice, it becomes clear: it is dangerous to get rid of them “somehow” or not completely. Even a couple of eggs left in the head can again create a colony of blood-sucking lice. But you don't need to shave your head, especially if your hair is long. This is too radical a solution to the problem, and it is only suitable for brutal men or very young children. There is no need to sacrifice your hair - in the process of eliminating lice, it is quite important to be consistent and patient and use the right products. We present you our step-by-step guide.
Step 1: Head Exam
Infestation in this case is the presence of living adult lice, young larvae and/or white (brown) eggs. Look for any possible signs of head lice by examining all areas of the scalp. Pay special attention to the back of the head and the area behind the ears. Not only the sick person, but also those who are in close contact with him are subject to examination. Therefore, keeping silent about lice is a very bad option! If you or your child has lice, it is not your fault, so it is better to inform those closest to you.
Step 2: Prepare your tools: What will you need to get rid of lice?
To get rid of head lice, you will need a pediculicidal shampoo, a special comb for combing out eggs and adult lice, and oil (tea tree, olive) to make combing out easier. Simply washing your hair with regular shampoo will not solve the problem - you will just waste time! Lice are too tight in your hair! It is better to use these products in combination with each other to ensure that you get rid of all stages of lice - adults, larvae and eggs.
In addition to the main products, you may also need auxiliary tools: nail scissors, cloth, a bowl of water, a magnifying glass and a regular comb.
Step 3: Shampoo
Pediculicidal shampoo is the first stage of head lice treatment. Getting rid of adult lice (eggs, to a lesser extent) largely depends on the effectiveness of the shampoo. In this regard, the question arises about active substances with a proven pediculicidal effect. What to look for in a shampoo? Pyrmethrin and pyrethrin are the most active and effective pediculicides.
Step 4: Combing out nits with a comb
As we said above, shampoo will not get rid of all the eggs - some of them will still survive and become larvae. Therefore, in addition to repeated treatment with shampoo, you need to use a mechanical method - comb out all the hair, strand by strand, with a special metal comb with frequent fine teeth - simple or electronic. But after the procedure, do not relax: to achieve the effect, you need to repeat the procedure every day for all sick people for at least a week to make sure that not a single egg is missed.
Step 5: Cleaning and washing
The two most important measures in the fight against head lice are shampooing and combing. Since lice do not live long after being removed from the head, cleaning the house will not have any effect on the development of head lice. It is needed more to maintain hygiene (removal of lice feces and dead nits) and your own peace of mind. This includes washing and vacuuming:
- Wash the infected person's bedding, towels and clothing in hot water (at least 60°C). Also pay special attention to hats and outerwear. Even better - after washing, dry all items in a hot dryer, and then iron them with a hot iron. If items cannot be washed at home, take them to the dry cleaner.
- Use a vacuum cleaner to clean the sleeping area, upholstery and carpets that may contain hair with glued nits. Don't forget about any objects that may have come into contact with your head, such as car seats.
Do without fanaticism: the cleaning measures given are quite enough to live peacefully in your home after recovery. There is no need to douse furniture and household items with insecticides; it is better to spend more time brushing your hair daily.
Prevention
Like treatment, every disease has its own preventive measures. To prevent your child from getting lice, you should teach him to use only his own comb, hats, and not allow other children to take personal hygiene products. In public places (cafes, schools, clubs), we recommend hanging outerwear on a common hanger, first turning them inside out.
To prevent fleas in animals, special flea collars for cats and dogs are used. Bathe pets using preventive shampoos. As for preventing fleas indoors, it is enough to keep the house clean. To avoid the problem of parasites under the skin, you should not drink unboiled water, swim in stagnant bodies of water (especially in countries with hot climates), or eat raw meat. And demodex, as already mentioned, will not create a problem if you follow the rules of hair and skin hygiene and use suitable cosmetics.
Head lice
Head lice are blood-sucking parasites that live and feed on the scalp. These are species-specific parasites, meaning human head lice live only on the human head. The appearance of lice and nits is possible in any person. This does not depend on age, gender, social status or lifestyle.
How does lice infestation occur?
Head lice infestation occurs from person to person. These parasites do not have wings and cannot fly or jump long distances. For a louse to move from one person to another, you need fairly close contact - less than 50 cm. You can also become infected with lice if you use the things of an infected person - a comb, a towel, a hat, bedding.
Lice can live off the human head for a limited time - up to 2 days. That is, you can catch lice, for example, on long-distance trains, on the headrests of seats in transport, and in other public places. You can even become infected in a swimming pool or bathhouse - lice can live in water and at elevated air temperatures for some time.
The main ways of becoming infected with lice:
- in very close contact with an infected person;
- when using his personal belongings;
- in common areas.
It is believed that lice appear in people who do not maintain personal hygiene. This is wrong. Lice are attracted to blood, and not other human secretions, so they live on both clean and dirty hair and skin.
People with an antisocial lifestyle do not have the opportunity to fight parasites, so they are more likely to become infected from them. You don't need to wear their hats or use their combs (if they exist) to do this.
It's enough just to walk or stand nearby.
Lice are the causative agent of pediculosis
There are several varieties of human lice. They differ in their habitat. Headworms live only on the scalp and in the human hair growing on the head. This is how they differ from pubic and wardrobe hair.
A louse is an insect up to 4 mm in size. Females are larger than males. They have a chitinous, translucent, elongated body, gray-brown, which darkens when saturated with blood. The insect has three pairs of legs. Their shape is such that they can easily move along hairs with a circular cross-section.
Parasites have a well-developed oral apparatus, with which they pierce the skin and suck out blood. When they bite, they inject saliva, which prevents the blood from clotting and causes severe itching. The louse feeds every 3 to 4 hours.
Lice infestation is called pediculosis. Signs of lice:
- severe itching;
- if there are a lot of bites, they constantly itch, scratches appear on the scalp that do not heal well;
- wounds become infected, skin lesions can be significant;
- with severe infection and a large number of parasites, many traces of their vital activity remain on the hair and skin, the hair becomes sticky, tangled, and tangles form;
- a person with lice becomes irritable and nervous due to constant itching.
Lice can be detected visually. They are clearly visible on light hair. Dark ones require more attention. Nits can be seen at the roots of the hair - these are lice eggs.
Life cycle of lice
The life cycle of this parasite averages 35 days. First, the female lays eggs. Translucent oval nits are attached to the hair at the very base. They are very small and can be difficult to see. After 7 days, nymphs emerge from the eggs.
They survive several moults and after 7 days they turn into an adult capable of reproduction. The female lays 4–5 eggs every day; in total, she lays about 120 eggs in her life. If you don't fight lice, they multiply very quickly.
Lice eggs are laid at temperatures above 32 degrees, that is, the temperature of the human body is optimal for their reproduction. When the temperature drops, lice do not reproduce, but their life cycle also takes longer.
When the temperature drops to +10 degrees, the louse can live up to 10 days, hibernating. A nit can also survive difficult times even outside the human body, and then - when optimal conditions occur - hatch and continue to parasitize.
Can head lice live on people other than humans?
Yes, head louse can exist outside of human skin and hair. For example, they can live for some time in a pillow, blanket, bedding, clothing and hats, upholstered furniture, combs and hair accessories. They can live and move on any surface - even in water. You can catch lice, for example, on the beach - they can move on sand or pebbles.
The louse crawls quite quickly and can run about 50 cm in a minute.
The head louse is a human parasite. That is, it does not feed on the blood of dogs, cats, other animals and birds. They have their own parasites. But the louse can live temporarily on animals. For example, a dog can bring back a louse that has fallen on it from a walk, and an insect can pass from a dog to a person.
Adults can live outside humans for no more than two days. Usually they die earlier - within 24 hours, since they are left without food, and they need food every 3 - 4 hours. Nits can remain outside the human body longer - up to 4 days.
Lice live in a wide range of temperatures. When the temperature drops below 10 degrees, they hibernate. At temperatures below 8 degrees they die. At high temperatures they can survive if the heating is short-lived. If cooked for a long time, they die.
How dangerous are lice?
Head lice cause lice. This disease is unpleasant in itself. The bite sites itch, the person scratches the wounds. They can become infected and take a long time to heal. Crusts appear on the head. Bites can also cause allergic reactions.
Without treatment, lice will multiply endlessly. With severe damage, many traces of lice remain on the scalp and hair - their bodies, empty nit shells, excrement, saliva.
All this covers the hair, tangles it, tangles form, and an unpleasant odor appears.
Unlike body lice, which carry typhus, for example, or pubic lice, which carry sexually transmitted diseases, head lice are less dangerous. But you can’t help but fight them.
How to deal with head lice
First you need to examine the head and assess the extent of the damage. A fine-tooth comb will help you find lice. It is necessary to comb wet hair with it. Insects will remain between the teeth or on the comb. You can also comb dry hair, but it is easier to do it on wet hair. You need to comb your hair from the very roots.
Lice can be seen in good lighting and without additional equipment. Detecting nits is more difficult. They may look like hair product residue or dandruff. Nits are usually located behind the ears, along the hairline on the neck.
Combing hair is not only a way to detect parasites, but also one of the ways to combat them - mechanically.
It only works in one case - if there are very few insects and their eggs in the hair, that is, immediately after infection. Careful brushing can remove all adults and individual eggs.
But if even one nit remains, in a few days everything will repeat itself, the insects will multiply.
Important: if the disease is detected in one family member, it is necessary to check all other household members for the presence of head lice and nits.
It is impossible to wash off lice with regular water. They are not afraid of water and can live in it for up to two days. Regular shampoos don't help either.
If the hair is short, the treatment will be faster and more effective. With a short hair length, there is little space left for laying eggs, so the rate of parasite reproduction decreases. And it's much easier to process short hair. Shaving your head has always been the most effective way to control lice. But this is not always possible for aesthetic reasons.
Traditional methods
There are many folk remedies to combat lice. They are preferred for use in cases of head lice infestation in children. It is believed that folk remedies are less harmful and cannot harm health.
To combat lice use:
- washing hair with kerosene;
- vinegar wrap;
- rinsing with tansy infusion or wormwood decoction;
- masks made from crushed cranberries;
- masks made from onion pulp.
Kerosene and vinegar are good because they not only kill insects, but also clean the hair roots and dissolve the substance that attaches nits to the hairs. After this treatment, it is easier to remove them from the hair.
The danger of these methods is that, firstly, you need to know the exact concentration and time of exposure, otherwise you can burn your scalp or get an allergic reaction.
Secondly, kerosene and vinegar damage hair; it will take a long time to restore it after such treatment. Traditional methods require repeated use.
The fight against lice can take a long time, and during this time new individuals will appear from the nits remaining on the hair.
Dust soap is effective against lice and nits. They wash their hair with it several times for several days in a row. It is necessary to rinse your hair well and comb out dead insects and eggs from your hair each time.
Effective treatment
An effective way to get rid of lice is to use special lotions or sprays. These drugs - pediculicides - can get rid of lice in one application. If the infection is severe, it will take longer.
We offer medications for treatment: Medilis-BIO, Medilis-Malathion, Medilis-Permifen, Medilis-Super. Lotions are rubbed into the scalp, left on the hair for a certain time required for effect, after which the head is thoroughly washed. To remove nits and dead insects remaining in the hair, the hair must be combed thoroughly.
A spray differs from a lotion only in the form of application. Spraying the head is a more dangerous method, since with such application you can inhale a dangerous substance.
It is not dangerous to humans in itself, but in high concentrations it can cause allergic reactions.
Spray products are not recommended for use in the treatment of children, pregnant women, people suffering from asthma and respiratory diseases.
When using any means, you must follow safety precautions, in particular, protect your eyes from contact with toxic substances. Leave the product on your head for no more than the permitted time to prevent skin irritation and chemical burns. When processing, it is necessary to provide access to fresh air into the room; after processing, the room must be ventilated.
Each drug has instructions for use, which must be strictly followed.
These products are not suitable for treating pregnant and lactating women and children under 5 years of age. For them, it is better to use less dangerous folk remedies.
When using any products - professional or folk - in addition to the head, you need to treat combs, towels - everything that can come into contact with the hair and where lice can move.
Preventing lice infestation
As mentioned above, no one is immune from head lice. Most often, children are susceptible to it after being in a group. It is easy to pick up parasites at a health camp and even at school.
One person can spread pests many times over. Children bring lice home from children's institutions and infect all family members with them.
It is impossible to guarantee yourself protection from this, but some measures should be taken to get rid of pests immediately and prevent a severe infestation.
What you need to do to avoid getting lice:
- Do not under any circumstances wear other people’s hats;
- do not use other people’s combs and hair accessories;
- avoid direct contact with people who do not maintain personal hygiene and lead an antisocial lifestyle;
- regularly inspect children’s heads for nits and lice;
- If you suspect an infection, comb your hair, you can use weakly concentrated anti-parasitic shampoos.
You can use parasite repellents. It is believed that they do not like strong odors, for example, tea tree, geranium, caraway, mint, etc. You can use herbal decoctions to rinse and flavor your hair. This will not protect against infection 100 percent, but it may repel insects.
The main thing when detecting pests in your hair is not to turn a blind eye to the problem and start fighting immediately. This way you can get rid of them faster and without harm to your health.
Source: https://medilis.ru/articles/vshi/golovnye-vshi.html
What causes lice
Pediculosis is an infectious disease, the prevalence of which increases during disasters and in unsanitary conditions. But the question of where lice come from gives rise to many myths.
Causes of lice on the human body.
Signs and causes of lice and nits
Symptoms of a disease called pediculosis do not appear immediately. It may take 2-3 weeks from the moment of infection until characteristic symptoms appear.
Signs of lice include:
- large dandruff in the hair;
- itchy skin (in the area where lice have bitten);
- small red spots.
Scratching may occur, and when it becomes infected, rashes with pustules develop.
You can become infected with parasites, even while leading a healthy lifestyle, through contact with an infected person. We need to consider where they come from in the first place. This occurs under the following conditions:
- use of infected hygiene and household items;
- unsanitary conditions;
- intimate contact or even friendly hugs;
- swimming in the pool or taking a bath;
- Beds and lockers are located close to each other in the kindergarten.
Infection also occurs if the patient shakes his head: with a wave, he spreads lice onto the hair of a healthy person.
Places where lice are found and where you can catch them:
- public transport;
- large crowds of people (for example, during a crush in extreme situations);
- places of detention;
- shops (while trying on a headdress);
- establishments that involve close contact between people.
Appearance
The appearance of insects is signaled by severe itching. This means that the parasites are there and are already starting to drink
Appearance of lice.
blood. When examining red areas, you can find the following types of insects:
- oval body;
- no wings;
- 3 pairs of legs;
- voluminous abdomen;
- claw-shaped claws;
- oblong head;
- flat back.
The size of large individuals reaches up to 6 mm, and small ones - up to 0.5 mm. The first ones can be seen visually during inspection.
Parasites secrete waste products, which causes the patient to develop dermatitis. Nits or insect eggs are white or gray in color. Visually they resemble dandruff.
How are they transmitted?
Even with frequent washing and good personal hygiene, you will not be able to protect yourself from lice. Parasites like dirty and clean hair equally. It is also a myth that head lice can only be contracted through clothing or personal items. This is possible, but the risk of infection is greater if you come into contact with a carrier.
There are different types of lice, and depending on this, the modes of transmission are distinguished:
- head - direct contact with an infected person or through things;
- pubic (plates) – sexually or through bed or underwear;
- clothing parasites live on clothing and are transmitted through it.
Parasites of the first type can cause typhus, as well as acute febrile conditions provoked by rickettsia.
How are lice transmitted?
From person to person
Communication is the most likely reason that ectoparasites are acquired in humans. Prolonged contact with an infected person or his belongings, frequent business trips and associated hotel stays on dirty linen increase the risk of infection.
The situation worsens with low immunity, even among clean people. Lice live on the head, and the body needs strength to suppress insect activity.
Body or bed lice can get on the body:
- from items of clothing;
- with a sheet;
- from pillowcases;
- from duvet covers.
The pads are placed on the pubis. They are characterized by reduced activity and feed on blood from one place. The risk of infection increases when using shared things.
Lice in children
Children are at greater risk of contracting head lice than adults. Preschool educational institutions and kindergartens become habitats for parasites. In them, the child often and closely spends time with peers. Not all parents ensure that their children follow the rules of personal hygiene.
Symptoms of lice in children.
Using other people's things
The use of other people's household and personal items, linen and clothing is a way of becoming infected with ectoparasites. You must use only your own towel and comb.
Nits are spread by wearing other people's hats.
Hair salons and swimming pools
In public places and in swimming pools you can become infected with lice. This is explained by the fact that they can swim. The same applies to reservoirs with standing water. To prevent infection, you should use a swimming cap.
If a hairdresser does not properly process the tool or there are larvae on his clothes, then the visitor is at risk.
Can lice pass from animals to humans?
Lice live on the body not only of humans, but also of animals, in fur. Upon contact, they can transfer to human skin, but do not linger for long. Their permanent habitat is dogs or cats. Therefore, apartment owners cannot become infected with parasites from their pets.
Do lice jump?
The ectoparasites in question do not jump like fleas. Their body is not adapted to overcome distances and flights.
Favorable conditions for the spread of lice
Parasites are characterized by slow movement, so it takes time for them to move to another area. Most often, the disease occurs in winter, cold spring or autumn, when people spend a long time indoors with an infected person.
Other favorable conditions for the spread of ectoparasites:
- low standard of living;
- frequent contacts;
- promiscuous intimate relationships.
How lice lay their larvae on the head.
Methods of disposal
To get rid of nits and parasites, you need to use all the methods simultaneously:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- folk
The first is to comb the hair with your fingers or a specially purchased comb. In parallel with this, you need to use chemicals - pediculicides with effective insecticides:
- benzyl benzoate;
- malathion;
- permethrin;
- phenothrin.
Folk methods of fighting parasites include:
- washing the hair and affected areas of the body with tar soap;
- shaving your head;
- use of Dichlorvos;
- applying hellebore water or vinegar solution;
- using a mixture of kerosene and vegetable oil.
Ways to get rid of lice.
Myths about lice
There are many myths about these ectoparasites, one of which concerns the cause of their occurrence. It is believed that they can only live on a dirty head. Dirt on the body or hair does not lead to insects unless there is an infestation. On the contrary, lice will try to occupy clean skin faster, because it is easier to bite through it.
In addition, lice have the following characteristics:
- they cannot come out of nowhere, jump over, fly;
- do not arise from emotional experiences;
- are not transmitted from animals (in humans, human lice).
You cannot become infected with nits (the eggs of ectoparasites are immobile). If one infected hair comes into contact with the body, infection will not occur. Infection takes from several days to 2 weeks, and during this time the foreign hair will leave the human body. If this does not happen, then the surviving individual will still not produce offspring: a pair is needed for reproduction.
Can the appearance of lice be associated with stress?
Emotional shocks and prolonged stressful situations in themselves are not the causes of the appearance of nits. But against the background of these factors, there is a decrease in the immune system, which increases the risk of infection.
For ectoparasites to appear, close contact is required. This is confirmed by the low statistics of lice in developed cities, where stress levels are high.
Reasons for relapse
You can become infected with lice again at any time, even while undergoing treatment. Reasons for relapse include:
- contact with a person who has picked up parasites;
- weak immune system;
- wrong treatment.
During therapy, you need to ensure that not only adult lice are destroyed, but also their eggs (nits). It only takes 14 days for parasites to reappear from the nits.
Where do lice come from initially, 12 reasons how you can get infected with them
Both children and adults can experience head lice. Why lice appear even in clean people puzzles many. There are many misconceptions regarding this issue and not everyone knows where human lice come from initially. Therefore, it would be useful to consider the mechanism of infection and possible causes.
The main reasons for the appearance
The main reason for the appearance of lice is transmission from an infected person.
When thinking about where lice come from, you should remember that they are ectoparasites (external), and only humans can act as their carrier. It is impossible to catch lice through food or animals.
The main causes of head lice:
- the person does not observe basic rules of personal hygiene and has a low cultural level;
- a healthy person comes into close contact with those who are already infected with head lice;
- home conditions are completely unsanitary, which contributes to the rapid spread of such parasites;
- a person has a large number of sexual partners, which increases the likelihood of contracting lice pubis;
- close contact of children with carriers of the disease in children's educational institutions, educational institutions, recreation centers or playgrounds;
- general use of hats and other individual items of clothing or household items that may contain nits from a person infected with head lice;
- an adult can become infected when visiting public baths, saunas or using sun loungers, towels and other items that have not been properly disinfected;
- visiting hairdressers or beauty salons where basic hygiene rules are not followed;
- frequent business trips that require long stays on trains, as well as accommodation in hostels or hotels;
- regularly moving around the city in crowded public transport;
- crowded queues or public cloakrooms in large public places;
- swimming in pools or still natural bodies of water.
If lice are transmitted from person to person, then the explanation of where the nits come from is somewhat different. Nits are lice eggs. An adult lays about 4 eggs every day.
Nits are attached to the hair using a special excretory secretion. It hardens when exposed to air, allowing it to adhere firmly to the hair.
After the bite and the appearance of nits on the hair, the period of time may vary.
Based on the location of nits on the hair, the approximate time of infection can be assumed. The louse lays its eggs as close as possible to the roots of the hair (1 cm). As hair grows, it spreads over the scalp.
The duration of larval development is 1-2 weeks. Hatched individuals are similar to adults, but differ in small size - up to 1 mm. Over the course of a week, they experience 3 molts and become sexually mature lice.
Mechanism of infection by head lice
Many people would like to know where lice on a person’s head come from and what is the mechanism of infection. Lice do not jump or fly, they only run. Therefore, lice infection most often occurs through direct contact between people. Head lice can travel between people's heads through their hair. Those with long and thick hair are at particular risk.
It may take 1-3 weeks from the moment the first specimens enter the head of a healthy person until the first signs of head lice appear. Once on a new owner, the louse, with the help of its paws, firmly attaches itself to the hair and begins to establish life in new conditions. The parasite feeds on human blood. It obtains food for itself by piercing the host's skin with its proboscis.
The salivary glands of louse produce a special enzyme that digests blood, but does not allow it to clot. Small bruises remain at the bite sites, which cause severe itching for the lice owner. The female lays eggs and attaches them to the hair so that they are not washed off by water. After some time, new lice are born from the nits.
Transfer methods
How lice are transmitted from person to person:
- Public places. They are the most potential risk areas. A striking example of how you can become infected with lice is in child care institutions. Schools and kindergartens often become hotbeds of outbreaks of head lice in children.
- Water. A liquid medium can also be a source of infection, since lice are able to maintain their vital activity in it for some time. It is quite possible to pick up blood-sucking parasites in swimming pools or a rural lake where the water is stagnant.
- Close contacts. The appearance of lice on the head is possible through close contact between people. Kissing, sex, children's group games in educational institutions - all this can provoke infection with parasites.
- Insufficient level of personal hygiene. Lice can definitely appear in those who do not adhere to basic rules of personal hygiene and live in unsanitary conditions.
- Personal belongings of infected people. Personal items belonging to those who suffer from head lice may contain lice or nits and therefore pose a great danger to healthy people. If you use the patient’s personal belongings, the risk of infection increases significantly.
Some also wonder whether lice are transmitted from animals. No, the transmission routes for head lice do not include this method. Ectoparasites do not have wings and, unlike fleas, are not able to jump. They can only crawl from the hair or clothing of an infected person onto a healthy person through direct physical contact.
Can they appear on their own?
There is a common misconception among people that lice appear due to stress.
Given this theory, some wonder whether lice can appear on their own. In fact, lice are transmitted exclusively from infected people, but are not inherited and do not lie latent on human skin, waiting for the right opportunity to become active.
What causes head lice
Optimal conditions for distribution
The sources of spread of pediculosis are varied. Places where you can become infected with lice most often: kindergarten, school, recreation centers, educational clubs, children's clinics. Schools and kindergartens suffer the most from this problem. In what conditions are adults most often infected: prisons, barracks, barracks, communal apartments.
Lice are highly contagious and the following individuals are at particular risk:
- children of preschool and school age;
- people who are promiscuous (pediculosis pubis);
- homeless people, drug addicts, alcoholics, prisoners;
- conscripts living in barracks;
- persons living in hostels, hotels;
- people with poor personal hygiene.
Experts note that lice most often become infected in the autumn or winter, since at this time of year people spend more time indoors, in close contact with each other.
Thus, the optimal conditions for the spread of lice for both children and adults are: unsanitary conditions, overcrowding or cramped conditions.
The period of egg maturation is not affected by the frequency of hair washing. This period may increase or decrease depending on the ambient temperature. On average, a new individual emerges from a nit in 5-8 days.
Primary insect bites are not yet manifestations of pediculosis. In addition, the infected person may not even feel the activity of 2-3 individuals.
But after 3-4 weeks, the larvae manage to develop and join their adult relatives in a parasitic lifestyle.
And if all this time you do not influence them in any way, then several generations can be bred. At this stage, the patient begins to experience unbearable itching.
The causes of outbreaks of pediculosis include a milder climate, as well as frequent re-infection, which occurs due to the lack of simultaneous treatment in the school community or in the family. This is often due to the lack of awareness among parents about head lice, as well as the incorrect use of anti-pediculosis drugs.
To prevent head lice from spreading to a large number of people, it is necessary to promptly identify and isolate carriers of the disease.
, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma
(2 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Source: https://parazitdoma.ru/vshi/otkuda-berutsya