The process of reproduction and development of lice occurs very quickly. Only 14-16 days under suitable conditions will be needed for the emergence of an adult from the moment the egg appears.
If the conditions for the development of the parasite are not so comfortable, it may take a month instead of a couple of weeks to reach the adult phase.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
In general, the life of lice goes through the following stages:
- An adult female lays 2-5 eggs at a time, which she firmly “glues” to the hairs at some distance from the scalp. The reliability of this attachment is ensured by the adhesive shell in which the egg is enclosed. These are nits. Outwardly, they may resemble dandruff, but if you try to remove them from the hair, you will encounter certain difficulties due to their secure attachment. In the nit stage, the louse develops from 5 to 8 days.
- After emerging from the egg, a small individual is born, conventionally called a larva (in the usual sense, the larva of any insect should not be outwardly similar to the imago), in general exactly the same as an adult insect, but much smaller and with a still underdeveloped reproductive system. After the first meal (blood), the larva molts for the first time and becomes a nymph. It takes about 5 days for the first instar nymph to develop.
- Lice nymphs go through three stages, corresponding to the number of moults. The molting of nymphs occurs because the chitinous cover does not grow with the body of the parasites, over time it becomes “out of size”, and the insect has to change it.
- After the third change of chitinous cover, the insect enters the adult stage. The adult female mates almost immediately and lays eggs just a day later (and sometimes only a few hours later). During her life, on average, she is able to lay from 80 to 140 eggs, which indicates the high fertility of the parasite. From 30 to 42 days is how long a louse (adult) lives.
Now it’s easy to calculate how long lice live: it takes on average 2 months from the appearance of the eggs to the end of the parasite’s life.
Can a head louse survive outside of humans?
There is only one answer to the question of where lice (head lice) live: humans are the only creature on which these parasites can live. Sometimes they settle on some species of monkeys, but they feel uncomfortable there.
How long do lice live outside the head? Situations may occur when, for some reason, the parasite is separated from its “carrier” (it is combed out, remains on personal hygiene items, etc.). Thus, if the louse does not have the opportunity to return to the human head as soon as possible, it will be left without food. This is enough to last another 1-3 days, and that’s all how long lice live outside a person, after which they die of starvation.
Interesting! Lice spend their entire life cycle - from egg to death - on humans, and as long as a louse lives, it feeds on human blood. Without food, the parasite will not last long.
Regarding the survival of parasites outside their usual environment or where lice live other than the head, there are a number of frequently asked questions:
- Is it possible for lice to live without a person, for example, on another animal? The head louse is not capable of living anywhere in nature except on the human head (except for rare cases with monkeys, which have already been mentioned). Therefore, it is impossible to infect your pets with these bloodsuckers or become infected from them yourself.
- How long do lice live on clothes? It happens that a combed louse ends up outside the head, for example, on clothing, where its lifespan will also average 2 days. But to a greater extent, this question applies to body lice, which live on clothes (in seams and folds), “visiting” the human body for food.
- Can lice live in pillows? To live is not, but to exist for a few hours is quite possible. Lice can end up on a pillow if they crawl onto it from the head of an infected person. Having remained there, the parasites will hold out for some time, waiting for the person’s head to fall back onto the pillow, after which they will return “to their homeland.” Therefore, to the question of whether lice live in bed linen in general and on pillows in particular, there is only one answer: even body bloodsuckers, not to mention head lice, are incapable of this, due to the periodic long absence of a person in bed.
- Do lice live on colored hair? Modern hair dyes often contain hydrogen peroxide, which is already toxic to lice. Many individuals may die, however, a sufficient number of individuals (especially nits) will remain alive, so hair coloring cannot be called widespread bullying. The surviving parasites will continue to actively reproduce, and the pointlessness of destroying them in this way will be obvious.
Features of the life of the parasite
The life of lice is not long; an individual can lay 100-150 eggs. Bloodsuckers have a good ability to reproduce. Adults mate for two days, then the egg-laying period begins. A louse lays 2-4 eggs per day. Without fertilization, the eggs are empty. An adult feeds 4-6 times a day.
This makes it clear how long a louse lives without food, usually 1-2 days. If the parasite has left the body and moved to the bed linen, then the bloodsucker strives to quickly return to the food source.
Interesting fact: the female bloodsucker lasts longer than the male and can immediately consume three times more blood.
Pediculosis is diagnosed regardless of age, gender and social niche. Parasites feed on blood and do not exist outside the body. Nits are also unable to produce on their own. When laying, they are fixed near the hair root with an adhesive substance.
It is difficult to remove parasites with regular hair washing; treatment with insecticides is required.
Maintaining personal hygiene, avoiding wearing other people's things, and inspecting your hair if characteristic itching occurs after visiting public places will help reduce the risk of infection.
A timely visit to a doctor will relieve the disease within a few days.
Lice lifespan
In order to understand how long lice can live, let’s first remember the life cycle of a lice from the moment the nit forms.
Fact. In science, it is believed that lice do not have a larval stage of development. Therefore, the first stage is the formation of a nit egg, in the shell of which there is a louse embryo.
Under favorable conditions, the nit stage lasts 5 days. Next comes the stage of nymphs - young lice, already very similar to adult individuals, but not yet capable of reproduction. In total, the nymph experiences three molts, which are necessary to form a larger shell. The nymph needs about 3 days before the first molt, then another 5 days pass, after which the parasite molts a second time. Before the third molt you need to wait a little more than a week - 8 days. After the last change of shell, already on the first day the female lays her first nit. Adult ectoparasites live from 30 to 42 days. During this time, the head louse lays up to 140 nits, the pubic louse – only 50, and the body louse – as many as 300 eggs of the new generation. The more sexually mature adults there are in the hair, the faster mating occurs, which means more nits are formed.
Terminology. Imago is the stage of an adult insect of an arthropod species that has a complex stage of development. At the imago stage, insects are capable of reproduction and settlement, but are no longer capable of development and growth.
Realizing the speed of development and reproduction of lice, it becomes clear how important it is to start treatment on time and stop their development. Lice quickly develop and reproduce in the following favorable conditions:
- The source of food, which is a person, is always nearby. An adult feeds once every 3-4 hours. When released into the outside world, outside the human body, the head louse lives no more than 3 days. Pubic louse is less hardy - death from hunger occurs within 10 hours;
- the most favorable temperature for lice to live is human body temperature, fluctuations should not exceed 10 degrees Celsius;
- lice cannot live without air, so its absence leads to their death within a few days. This is used when killing body lice - things are folded into a thick plastic bag and tied securely. The knot is left for a couple of weeks, after which the dead lice bodies are simply shaken off.
When comfortable environmental conditions change, lice slow down in development, reproduce more slowly, or stop doing so altogether.
People often wonder: Where do lice live? Everything is very simple: the head and pubic hairs live exclusively in the hairy area of the human body, and the body parts live in clothes. Head lice are also known to occur in some species of monkeys. It turns out that the ectoparasite cannot live outside the human body. If they lose their host, they die within a few days.
Interesting. Ectoparasites can live on the surface of the water for two days, waiting for a new host to appear. Clothing insects are especially hardy to such conditions - they can swim and can survive in water for more than two days if the temperature is comfortable for them.
How do lice develop and where do they live?
The life cycle of a parasite includes several stages:
- Fertilization, which becomes possible immediately after the transformation of the larva into an adult.
- Laying eggs . The female can lay eggs without contact with the male, but they will all be empty. But 2 days after contact, those nits that will subsequently give birth to offspring will appear on the hair.
- Nits are lice eggs that mature within 4 to 13 days.
- Larvae developing from nits. It goes through 3 stages of development - nymphs, at the end of each of them the larva changes its chitinous cover. The third moult finally transforms it into an adult.
- An imago is a mature louse capable of reproduction.
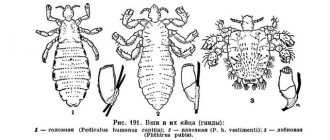
The head louse lives exclusively on human hair. If she finds herself outside her carrier, then in an effort to survive she may be content with a “snack” in the form of the blood of a rabbit or cat. But she only needs a person to live.
There are other varieties of this parasite:
- Body louse lives on clothes or bedding. For her, a person, or rather his blood, is a source of nutrition, but she cannot live on him.
- Pubic louse lives where coarse body hair grows.: pubis, eyelashes, mustache.
Each of these varieties will bring a lot of trouble to a person, and, most importantly, will increase the risk of contracting such serious diseases as typhus and relapsing fever, Volyn or trench fever.
How long do lice live on clothes and linen?
The development cycle of the parasite from the larva to a healthy individual lasts 20 days, and the life expectancy of an adult insect is from 27 to 46 days. Without food, they can maintain their viability for a much shorter period:
- The death of a human louse occurs on the second day. When the temperature drops, the fasting period can increase to 10 days.
- The fish can maintain vital functions outside the host’s body for about 8-9 hours, and in water for no more than 2 days.
Lice development cycle
It does not take too much time for an egg to grow into an adult. On average, this will take approximately 15 days. However, if the conditions for reproduction are not very favorable, then this process can last for a month.
A louse goes through a full development cycle in 15 days.
Insect development is divided into the following stages:
- At one time, an adult female lays up to five eggs, which she firmly attaches to the hair. She chooses a place for this purpose as close to the scalp as possible, gluing the eggs with an adhesive substance present in the outer shell of the egg. It takes five to eight days for a nit to develop into a larva.
- The hatched larva resembles a small louse in appearance, but its reproductive system is still in an underdeveloped state. After the first meal, she sheds. From this moment on, the larva is called a nymph. The first stage of its development lasts about five days. Since the nymph molts three times, it has three stages of development. Molting occurs because its shell consists of chitin, so it cannot grow with it. We have to change it.
- After passing through all stages of development, the hatched larva becomes an adult. This stage is called imago. The female immediately finds a mate and begins laying eggs on the same day. Sometimes this happens literally after a few hours.
It is easy to calculate that from the moment a louse lays an egg until it dies, about two months pass. This is how long an insect lives if it exists on a human body.
Can nits survive without humans?
Lice eggs are called nits. During her life, the female lays up to 120 eggs. They are small, round, white and attached to the base of the hair with an adhesive substance. The larva matures in them within a week. The nit has a fairly strong shell that protects the larva from mechanical and partly from chemical damage.
nit on hair
When unfavorable conditions occur, nits, or more precisely, the larvae in them, are capable of falling into a state of suspended animation. This is a conditional deep sleep with “freezing” of all body functions. The larva stops its development, but remains alive. Some nits spend up to two weeks in a state of suspended animation. If after this they find themselves in normal conditions, they will continue their development and turn into adults, and then into adult lice.
How long do nits live?
After the female louse has laid larvae on human hair, the eggs must go through 3 phases of development. A nit is a cocoon containing a future louse. During maturation, it does not need nutrition, so if for some reason it leaves the host’s body, it will be able to maintain its vital functions for about 8 days before hatching from the egg. If a small louse cannot immediately find food, it dies within 24 hours
For the maturation of nits, the most important is the temperature regime. If the nit is in hot conditions, the louse may hatch after 4-5 days. This is possible when wearing hats in winter, since a kind of greenhouse conditions are created under it. Therefore, after combing your hair, you need to thoroughly disinfect the entire room.
Can lice live on animals?
There are several types of lice in animals:
- Sucking louse - feeds exclusively on blood;
- Biting louse - feeds on skin particles.
Cats can be infested with lice. For many, this reality was astonishing. But it is so. Lice, or they are also called lice-eaters, live on animals in the fur and feed not on its blood, but on the skin. Therefore, one of the symptoms of infection will be bald patches or lack of hair on parts of the body.
Dogs are also susceptible to this disease. Parasites cling to hairs and attach to the skin. They feed on the blood, sebaceous glands and skin of the victim. The pet suffers from itching and loses its fur.
Pediculosis can cause more serious illnesses. Such as wasting or tapeworm. Therefore, animals need urgent treatment.
Can you get lice from contact with animals? No! The lifestyle of these parasites is significantly different. They are adapted to higher body temperatures than humans.
How to deal with lice and nits
There are several ways to combat parasites. These can be specialized drugs or traditional methods. However, the most effective are special means - insecticides. However, their use has a number of contraindications. These are pregnancy, childhood, allergies and asthma. In such cases, milder means can be used. Or resort to natural recipes. It should be remembered how long lice live outside the human head - up to 48 hours.
Natural remedies for parasite control include:
- cranberry juice;
- vegetable oil;
- tansy decoction;
- juice or decoction of wild garlic and wild rosemary;
- cosmetic hairspray.
When these products are applied to the hair, lice and nits die, after which they are usually combed out with a comb. If you managed to comb out the louse, but it is still alive, then you should remember how long lice live outside the head. It depends on how quickly the insect hits the person again. Therefore, all combed individuals should be destroyed immediately.
How to avoid lice infestation
The process of getting rid of lice is quite unpleasant, so you should follow some rules to avoid infection with parasites:
- do not use other people’s personal hygiene products for the head and jewelry (towels, combs, combs, hairpins);
- maintain hygiene;
- systematically check all family members for lice infection;
- do not wear other people's hats.
By following these simple precautions, you can save yourself and your loved ones from such an unpleasant disease as lice. After all, everyone now knows how long lice live outside the human head and body.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Interesting to know: