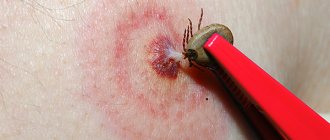
Scabies mite
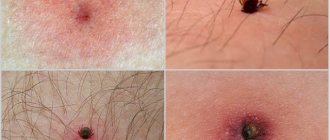
Traces of scabies mite activity
Life cycle of a tick
Treatment of scabies
Subcutaneous lice are small insects that build numerous tunnels in the skin. Their presence causes severe itching and damage to the epidermis. The disease begins in the hands. The most interesting question is whether it is true that lice live under the scalp.
Myths and reality
In past centuries, when science had not yet advanced so far, reality was not entirely plausible. Experts claimed that during surgery they discovered tubercles filled with insect eggs on the human body. The parasites are called subcutaneous lice.
There was some truth in such statements, but these were completely different parasites. Similar symptoms - unbearable itching, wounds on the body, led to the conclusion that lice are parasitic.
Interesting!
A detailed examination of the tiny insects under a microscope revealed that the appearance was different from the familiar head lice that live on the head. They looked more like small crabs, and there were 1 pair more limbs. Subcutaneous lice are nothing more than scabies mites.
Scabies mite
Symptoms
After penetrating the body, the parasite attaches to the skin and begins to feed on blood. In parallel with this, a special component is released that provokes unbearable itching. When feeding is completed, a secretion is injected into the wound of the insects, preventing blood from clotting. Because of this, a blood-sucking bite does not heal for a long time.
You can get rid of the disease quickly if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. To do this, you need to pay attention to early symptoms, which manifest themselves:
- unbearable itching, which intensifies at night. This is due to the activity of lice during this period of time;
- swollen eyelids. It is difficult for a person to open his eyes in the morning;
- glued eyelashes. Since lice eggs are attached to the hairs with an adhesive component;
- pimples. Their cavity contains a liquid similar to purulent discharge of a white-yellow hue;
- darkened eyelids as a result of nit deposits;
- During palpation, small nodules are detected. These are lice larvae;
- If the patient has a tendency to allergies, then the eye increases to enormous size.
An important sign of the presence of phthiriasis are dark spots, as if from unwashed cosmetics. If they are not washed off with warm water, then this is a reason to assume a disease. Doctors say that a similar clinical picture occurs in other eye diseases. Simultaneously with the listed symptoms, small blood spots may appear on the underwear in the groin area.
Attention! It is impossible to independently determine the presence of phthiriasis. To do this, you should consult a doctor and undergo the necessary diagnostics.
Symptoms of subcutaneous lice or scabies
Subcutaneous lice in humans appear upon contact with contaminated objects or the skin of a sick person. The incubation period lasts about 2 weeks. But from the first days you can notice the symptoms of subcutaneous lice.
- Scabies begins with skin lesions between the fingers. An unbearable itching appears, which intensifies in the evening and progresses at night. At this time, the scabies mite is especially active.
- Bubbles filled with liquid appear on the affected area. After scratching, wounds remain and passages can be seen.
- As the disease progresses, the extent of damage to the body spreads. The pathological process involves the arms, legs, neck, abdomen, back, genitals, and face. Lice do not live under the scalp.
- The body is covered with a small rash, and large red blisters appear in some places. The manifestations on the buttocks are clearly visible.
- The skin in the affected areas becomes thicker, and swelling of the hands is observed.
Lack of measures leads to the addition of a secondary infection, complicating the situation.
Diseases caused by lice and mites
There are a number of symptoms that allow you to recognize different types of “subcutaneous lice”. It is important not to confuse these parasites, since the methods of combating them differ.
Pediculosis
Lice come in head lice, body lice and pubic lice. The first live on the scalp, the second on clothing, and the third on the genitals. The first option is most common. Symptoms of head lice infestation are as follows:
- severe itching, causing you to constantly scratch your head and neck, resulting in characteristic abrasions;
- Red bite marks can be seen behind the ears, on the neck and scalp;
- There are nits on the hair - small white dots, grains that can be confused with dandruff. But, unlike her, they are well fixed, and you won’t be able to simply shake them off your head.
Thanks to special devices on the paws, lice can move very quickly along the surface of the hair.
Lice are transmitted by contact when an infected person is nearby, and the louse can crawl over. It is also possible for the parasite to come from the personal belongings of a person with pediculosis.
Scabies
Scabies mites, also known as scabies, cause a disease known as scabies.
Sometimes this is the name for any disease accompanied by severe itching, but true scabies is also accompanied by other symptoms:
- itching intensifies after a hot shower, as well as at night;
- a characteristic rash appears in the form of plaques, small pimples, or thin winding stripes with a vesicle at the end;
- you can notice a rash arranged in stripes - these are the passages that the female scabies mite gnaws under the top layer of skin. New itches are also born there.
Typically, the scabies mite affects areas with the thinnest skin: the bends of the joints, various folds, the surface between the fingers, the sides of the body.
Scabies is recognized by the presence of a rash and scabies, but in some cases the latter may not be present
In children, scabies most often appears in other places: on the face, scalp, palms and soles, and buttocks.
The tick that causes the disease is transmitted from person to person through close contact. Infection rarely occurs through personal belongings or bedding, but it still happens.
Read more about the scabies mite and treatment after its bite in our article: Scabies - from symptoms to prevention.
Based on data from skin and venereal disease clinics, statistics on the most typical places with scabies rash were collected.
Table: places most often affected by itching
| Percentage of infected people from the total number | Location of the rash |
| 50% | Wrists, area between fingers |
| 25% | Feet |
| 25% | Torso |
| 25% | Arms and legs (except hands and feet) |
| 50% men | Genitals |
| 10% women | Mammary gland |
Demodicosis
The disease is caused by an arthropod called demodex. Depending on the affected area, gland mites, or, as they are also called, acne gland mites, manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- itching of the skin of the face, scalp;
- hair loss, fragility;
- the appearance of dandruff;
- pimples, pustules on affected areas;
- peeling of the skin, pink and red spots, increased fat secretion;
- when the eyes are infected with Demodex - discharge from them, lacrimation.
Unlike scabies, demodex lives deep in the skin. In this case, a person may experience pain and a feeling that something is crawling inside. Rarely, only with severe infection can glandular insects settle on the chest and upper back. Usually they affect the corners of the lips, nose, areas above the upper lip or on the chin, forehead, eyelids, cheeks, and less often the scalp.
The appearance of acne is a characteristic feature of destruction by the demodex mite.
Children, as a rule, do not get demodectic mange because their skin produces less of the mite-loved oil. Demodectic mange can only be contracted through close contact with a person who has quite a lot of iron mites.
Demodex often affects women who excessively use cosmetics, hair dyes and chemical personal care products, as all this disrupts the balance of the skin.
How to distinguish pediculosis from scabies and demodicosis
Lice and scabies infestations are quite easy to distinguish:
- with scabies there are no nits on the hair;
- when infested with lice, there is no rash;
- itching from lice does not intensify after taking a warm bath or shower, while this phenomenon is observed when infected with scabies mites.
It is also easy to distinguish between pediculosis and demodicosis:
- when affected by Demodex, there are also no nits;
- pimples appear, which do not occur from lice;
- like itching, glands affect the scalp less often than the face;
- Lice do not cause dandruff and hair loss.
One of the most common medicines for scabies and demodicosis is ordinary sulfur ointment.
Life cycle of a tick
The female goes deep under the skin and lays eggs. During its life, it makes numerous passages, and its excrement provokes a severe allergic reaction in the form of itching. Insects can only live under the skin; they come to the surface to mate.
Life cycle of a tick An adult female lives about 1.5 months. The larvae develop in the egg for about 2 weeks. The young generation crawls out at night to mate. The males die, the females again burrow under the skin and build burrows.
Important!
A clear clinical picture of scabies appears within 1 month after infection. Every day the itching intensifies, the appearance of scabies throughout the body causes insomnia, irritability, fever, and a general deterioration in well-being. A child or an adult can get sick.
How to distinguish pediculosis from mite infestation?
- The first sign that a person has lice is severe itching of the scalp. It is the hair that lice need to lay eggs. The louse cannot penetrate the skin, and is not able to live there.
- Hair, on the contrary, interferes with mites. Therefore, the defeat begins primarily from the “bare” areas of the human body: the abdomen, arms, face. Itching is also present, but it spreads throughout the body as the female mite moves under the skin.
And if lice can sometimes be removed just by washing your hair with a special shampoo, then to destroy the subcutaneous mite, the use of antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory drugs is required.
Therapy
How to cure subcutaneous lice, there is a certain algorithm of actions. At the first signs of infection, you should seek help from a dermatologist. The specialist prescribes qualified treatment and prescribes medications.
The most common and most affordable product is benzyl benzoate emulsion or cream. The product is intended for external use, has a specific odor, and is quickly absorbed:
- Apply a thin layer to the affected areas twice a day for 5 days.
- Hands should be sanitized every time after contact with water.
- After the specified time, the patient takes a shower or bath.
- Applies the medicine to the body again.
Treatment can be considered complete if unpleasant symptoms do not reappear within a week. Otherwise, the entire skin is treated again after preliminary water procedures.
Treatment of scabies Other effective drugs that can treat the disease:
- Spregal;
- Sulfuric ointment;
- Permethrin.
Therapy and remedies for scabies
Treatment of scabies should only take place in an infectious diseases hospital and under the strict supervision of doctors. Any tactile contact with the patient is prohibited. The treatment period is about 2 weeks.
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations during and after treatment, there will be no relapse of the disease.
For human treatment, antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory drugs are needed.
Attention! Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, turn to alternative medicine or take dietary supplements!
Most often, the following drugs are used in the treatment of scabies:
Sulfuric ointment
The cheapest and one of the most effective drugs. Should be used daily for about a week. In advanced cases – longer. The main disadvantage of the ointment is its pungent odor. Therefore, this ointment is not recommended for children or people with a high allergic threshold.
Spregal
This aerosol kills scabies mites, as well as lice, fleas and bed bugs. Often the required effect is achieved within a day, but experts usually recommend repeating the use of Spregal against ticks after three days.
Benzyl benzoate
Another name is benzoic acid. This is also an inexpensive but very effective remedy. In pharmacology it is available in two forms: emulsion or ointment. Its advantage is that after use it does not leave stains on clothes, and the smell is not as strong as, for example, sulfur ointment.
Before applying the product to your skin, you should take a warm shower. The ointment is usually applied at night, that is, during the period when the mite is most active. In the morning, you should take a shower again to eliminate the unpleasant odor and dead parasites on the skin.
Permethrin
The cream is used strictly according to the instructions. Usually 1-2 applications are enough. Apply at night and wash off in the morning with warm water and soap.
Ivermectin
Also an effective drug. Available in the form of injections. It is toxic and therefore contraindicated for children and pregnant women. Use strictly as prescribed by a doctor. Exceeding the dosage is not allowed.
If necessary, the doctor can also add antibiotics.
Are there subcutaneous lice?
Subcutaneous lice do not exist as such. They can only live on the surface of the body. These external parasitic insects are very small in size.
Even from a physiological point of view, they cannot penetrate the skin. They need air to exist , so if a louse gets into a wound, it will not burrow deeper, but will quickly begin to get out of it. The subcutaneous louse is the name given to the scabies mite , which causes the disease scabies .
This special type of mite lives under the epidermis , the outer layer of the dermis. It feels great on the human body . Another myth about subcutaneous lice is that they appear on their own due to stress. But this is not true, since lice are parasites that are carried by animals or humans . It is impossible to become infected with them if these adult insects or their eggs do not fall on a person.
Main symptoms
It is worth noting that it is possible to get rid of lice of any type, and the earlier treatment is started, the easier it is. Treatment for lice pubis is local. This type affects the adult population and mainly through sexual contact, so it would be a good idea to undergo screening for sexually transmitted diseases.
We invite you to read: What causes nits and how are they transmitted? Ways to combat parasites
To treat parasites in humans, special antiparasitic agents are used:
- Gels.
- Sprays.
- Solutions.
These products are purchased at the pharmacy. Treatment also includes removal of pubic hair. To prevent re-infection of a person, it is necessary to wash bed linen at high temperatures and then carefully iron it. Furniture, clothing, and mattresses are also treated. If the treatment is carried out according to all the rules, you will be able to get rid of parasitic insects.
Treating clothing is also necessary to get rid of body lice, but this will require boiling or steaming. They will be followed by a long, at least a week, airing of the clothes. Head lice mainly affects children, so a particularly careful approach is required. Treatment will not work if the source of the infection is not identified.
Treatment can be carried out without the use of drugs. This is especially important if the child suffers from allergic reactions to medications. This will require good eyesight, a fine comb and a lot of patience. The hair on the head is divided into strands and methodically combed. In the process, detected insects and their eggs - nits - are destroyed by crushing. This is much easier to do on short hair.
For treatment to be effective, several treatments will be required over several days. Drug treatment can also be used. The pharmacy sells many products for eliminating head lice to help get rid of the symptoms of head lice. When choosing, it is worth clarifying their effect, since there are drugs that kill only adult individuals. In this case, the removal of lice eggs should be done manually.
Are there subcutaneous lice? This question interests many people who suffer from itching and scabies. Experts say that such pests do not exist, and patients confuse them with scabies mites. Moreover, it is impossible to examine parasites without a microscope. But lately, lice under the skin have become increasingly common.
When people become infected with subcutaneous lice, they experience the same symptoms as with regular head lice. But such pests appear on the stomach, sides, buttock and elbow areas, as well as in other places where there is hair. Such lice on the head cannot exist. After parasite bites there are no characteristic marks, but only passages left by pests. They are quite easy to feel with your fingers. A rash appears on the body in the form of ulcers, which occurs if a person begins to scratch the bite sites.
The parasitic effect of ticks can be determined by a number of symptoms:
- unbearable itching, which is more active at night;
- rashes on the skin caused by the presence of subcutaneous tunnels;
- slight but steady increase in body temperature.
Up to 15 sexually mature individuals can carry out their life activities on the human body at the same time. The maximum possible number of parasitic mites at one time quite often becomes the cause of severe itching and discomfort, which causes general weakness of the body and excessive fatigue. In particularly advanced cases, hospitalization is required. Typically, inpatient treatment lasts approximately 7 days.
In addition, unbearable itching and the desire to scratch are not beneficial. It is worth understanding that scabies is a disease that needs to be treated carefully. The slightest omission during therapy can lead to relapse.
To date, the scabies mite has been well studied. Scabies responds well to treatment, especially in the initial stages. Thus, there is no need to practice self-medication; at the slightest suspicion, you need to consult a doctor.
What is a louse? This is a very small, but noticeable and visually distinguishable parasite that lives in the hair of a person or animal. These parasites can be compared to fleas in dogs and cats, as they are very similar.
The disease caused by the parasites described above is called pediculosis. The provocateurs of lice, even if they get into the wound, immediately get out of it, since they are not able to function inside.
And they do not lay their eggs (nits in common parlance) inside the dermis, they attach them to the hair at a distance of 1 cm (approximately) from the epidermis.
Larvae also cannot live in the epidermis, despite their minimal size. Therefore, the answer to the question whether subcutaneous lice exist in nature can be answered with a 100% guarantee - no!
Pediculosis often affects the hair on the head, since it is the thickest and most convenient for parasites.
Therefore, the symptoms of this disease can only be felt on the head. And if itching and irritation are felt throughout the body, then most likely it is scabies.
Scabies is a highly contagious disease of the epidermis caused by the scabies mite. This parasite can infect any area of the body and prefers to live inside the epidermis. Therefore, only this mite can be called a subcutaneous louse.
We suggest you read: Lice remedy for kittens
Living in the epidermis, it digs passages, which causes itching, lays its eggs there, then larvae hatch from them, which independently dig passages, which is why the symptoms intensify. These parasites, like the previous ones, also feed on blood.
Typically, an infected person may have between 1 and 20 ticks living on their body. In this case, the symptoms will be as follows:
- itching that gets worse at night (the period of parasite activity);
- irritation, often allergic (the waste products of mites are very toxic and provoke allergies in everyone);
- scabies - thin stripes, like scratches, with a pimple-ulcer at the end (at this place the mite comes to the surface).
You can easily distinguish the causative agent of scabies from the causative agent of pediculosis, knowing its features:
- scabies mites rarely live on the head (most often they are located on the arms, stomach, and also in the genital area, where the softest dermis is);
- it does not leave characteristic bite marks;
- it leaves passages that can be seen visually, and sometimes also palpated.
You can become infected with lice only through direct contact with a sick person, his bedding, comb or hat. This parasite does not have the ability to jump. Therefore, without close communication with an infected person, he does not have the opportunity to move. This requires extremely close contact, for example, a hug. Or lie on the bed where a person infected with lice is sleeping.
Due to certain circumstances, children are more susceptible to infection than adults. They rarely adhere to safety measures and do not behave carefully, since they do not know all the features. And their games often involve close contact. Teenagers are much less likely to become infected. Among adults, failed individuals, such as homeless people and drunkards, are at risk.