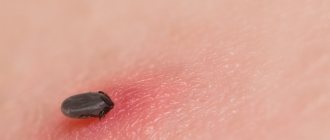
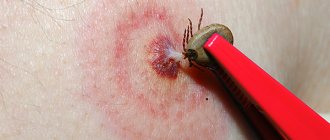
Tick habitats
Nowadays, you don’t have to go into the forest to find a tick on your clothes or skin. It is enough to walk through a city square or on the grass near your house to pick up this parasite. Not all people know what these blood-sucking arthropods look like.
Ticks belong to the order Arachnids. Currently, 650 of their species are known, most of which are harmless to humans. Among them there are also carriers of serious health diseases:
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- borreliosis.
It must be remembered that a tick bite may not be felt, because when the skin is damaged, it releases saliva containing pain-relieving components. It is not surprising that a person can notice a parasite on his body only some time after the bite. It is advisable to detect it when the tick has not yet penetrated deep into the skin. Then it's easier to pull it out.
Is it possible to submit your head for analysis?
Study of mites and their particles
Ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases - borreliosis, tick-borne encephalitis. The first virus enters the human body with saliva during a bite, the second infection enters along with the blood of the infected parasite. This happens when the pest is removed incorrectly, the head is torn off, and the body may burst.
To be completely sure that there is no infection, the body of the extracted tick must be placed in a jar, with damp cotton wool placed at the bottom, and taken to the laboratory. In a few days, experts will render a verdict - whether the tick is infectious or not. Otherwise, you can find out about the presence of the disease within 14-30 days. This is how long the incubation period lasts. There is no point in taking tests before this time, they will not correspond to reality. For prevention after a bite, experts recommend vaccination or administration of immunoglobulin.
A live or dead tick should be brought to the laboratory. The main requirement is that it must be whole. The parasite must be placed in a humid environment, after moistening the cotton wool. There is no point in taking the body or the extracted head for analysis.
Features of behavior
Evolution has helped ticks acquire qualities that have helped them exist successfully for many hundreds of years. They can sit quietly for a long time on tall grass or bushes. When the opportunity arises, they jump on animals or humans. This is basically how ixodid ticks behave - they are carriers of dangerous diseases. They don't bite right away. First, the parasite crawls along clothing from bottom to top, trying to find a suitable place.
If the tick has burrowed under the skin, it means it has been found. Typically, it bites where blood vessels are close to the surface of the body. It can take him up to 3 hours to find such a place. During this time you can easily get rid of it. After the location is found, the tick bites and gradually immerses its head into the skin to get to the blood. His abdomen remains outside.
It is easy to detect a tick under the skin, although this is a rather rare occurrence. It looks like a small tumor, but when you touch it you can feel a hard lump. The behavior of bloodsuckers depends on their species. Some, having drunk blood, fall off on their own after about 3 hours. These are mostly males. Females penetrate deeper into the subcutaneous tissue.
How to pull it out
It will be more difficult to remove a tick under the skin of a person, but it is possible at home
It is worth remembering that it is necessary to get rid of the “tenant” immediately after detection, no matter whether he has only bitten through the skin or is located deep under it
The parasite is removed in several ways:
- It is easier to seek help from specialists immediately after detection. There is no need to call an ambulance; after a bite, a person can move independently and calmly get to the nearest emergency room, where he will receive the necessary assistance.
- What to do if a tick has crawled under the skin, but there is no way to contact a specialist: you can deal with the arachnid yourself, just arm yourself with tweezers and means of disinfecting the affected area. It is advisable to wipe the instrument with alcohol or hydrogen peroxide. Then move one of the blades so as to catch the jaws of the tick. They press down on the second one and try to remove it from the skin using circular movements. It is strictly forbidden to tug or pull sharply, as this can tear the tick and the infection from it will quickly enter the human body. The remaining particles will soon cause an inflammatory process, which can only be neutralized in a hospital.
- Within the locality you can go to a pharmacy. There is a special hook that is used to remove a tick that is completely buried under the skin. The tip of the product is inserted into the hole made by the pest. It falls between the teeth, which allows you to remove it completely without tearing or injury.
- The tick breathes under the skin through the bitten hole. The observation allowed us to come up with another extraction method. The bite site is generously smeared with vegetable oil, a couple of drops of paraffin are dripped, blocking the access of oxygen. The parasite begins to look for air, climbs out, and here it can be captured. This method is not recognized as the safest; with a lack of oxygen, the tick releases more toxic substances and releases them into the selected organism.
Don't neglect your health and let everything take its course. In case of a tick bite, you must promptly seek help from specialists. Getting rid of it on your own is encouraged, but it is necessary to investigate the parasite in order to avoid other health problems.
Bite symptoms
Many people wonder whether a tick can completely crawl under a person’s skin. There are species that are not able to penetrate the subcutaneous layer, live there and reproduce. They bury only the head with the proboscis into the skin, and the abdomen remains outside and swells as the parasite is saturated with the blood of its victim. How to recognize a tick under the skin? Signs that indicate that a person has been bitten by a tick include:
- the appearance of a small wound on the skin for no apparent reason;
- redness around the wound;
- a small round and smooth compaction appears in the center of the spot;
- rapid and unexpected appearance of a dark mole.
The occurrence of these signs indicates that a person has a tick under the skin. You shouldn't panic, but you shouldn't be careless about it either. If you have never pulled out ticks, there is one rule to remember. There is no need to pull out the parasite or make sudden movements trying to throw it off the body. In this case, its head may come off and remain under the skin.
How to remove a tick
If you see a bloodsucker attached to your body, then you need to get rid of it quickly. If you have the opportunity to go to a clinic, then visit a doctor who will quickly remove the tick and treat the wound with antiseptics. You should also consult a doctor if the tick's head remains under the skin, as suppuration may occur. An inept attempt to remove the parasite will lead to the fact that the tick may go deeper under the skin.
This phenomenon is extremely rare and dangerous. If you can’t visit a doctor, you should try to get the bloodsucker out yourself. Here are some recommendations on how to do this correctly:
1. If a person has a tick under his skin, how do you pull it out without tearing the body off the head? The surest way is to use a special device that is sold in pharmacies. Outwardly, it looks like a fork with two teeth. The tick body is passed between them. Next, you need to start turning the device counterclockwise, gradually removing the tick. The advantage of this device is that the body of the parasite remains intact. There is no danger that some part of it will remain in the human skin.
2.If there is no such device, then you can use simple cosmetic tweezers. It should be placed as close to the surface of the skin as possible. The body of the parasite is grasped with tweezers. Next, they begin to turn the tool counterclockwise and gradually remove the tick from the human body.
3.If you don’t have a hook or tweezers, you can use a strong thread.
A loop is made from it, which is placed over the tick. The thread should be placed as close to the victim's skin as possible. Next, you need to start gently rocking the parasite. In this way, it is gradually removed from the human body.
4.If the tick is deep under the skin, then it is better to visit a doctor who will remove the parasite and treat the wound.
After the tick is removed, you need to disinfect the bite site and take an anti-inflammatory medicine. To be sure that the bloodsucker is not a carrier of a dangerous disease, you need to place it in a clean jar with a tight-fitting lid and submit it for analysis.
What should you not do if you are bitten by a blood-sucking parasite? There is no need to drip oil, gasoline or other harmful substances onto it. It is believed that this forces the tick to get out of the victim’s body on its own. However, this does not always happen. You will only waste time and complicate the process of removing the parasite from the body.
Can a tick fall off on its own after a bite?
The tick can fall off the person itself after saturation. A mark remains at the site of the bite, by which the parasite can be identified. A person also develops characteristic symptoms that indicate the need to consult a specialist.
Can a tick come out on its own after a bite?
When a tick lands on a person’s body, it looks for a convenient place to bite.
Most often, parasites choose:
- groin area;
- armpits;
- stomach;
- lower back;
- area behind the ears;
- scalp;
- breast;
- popliteal fossa;
- neck.
In these places the skin is thinnest with closely adjacent vessels. It takes from a few minutes to half an hour to find a place for an insect bite. The greatest activity of parasites is observed from mid-spring to late autumn.
When bitten, the tick releases an anesthetic substance, which makes the insect invasion painless. The parasite completely immerses the head under the skin, leaving only the abdomen on the surface.
A hungry pest does not exceed 3 mm in size. As it fills with blood, it increases in diameter many times over. A well-fed individual can reach 1.5 cm. Once satiated, the tick itself crawls out of the skin.
If a tick falls off within the walls of a house, the chance of a repeated attack by the parasite is minimal. A well-fed insect leaves in search of a good place to breed; enclosed spaces are not suitable for this.
The length of time the parasite stays on the body depends on its gender. The male can bite and, having had enough, detach himself after a few minutes. The time a male spends on a person increases if there is a female ready for reproduction.
Females require more blood to drink, so they can spend up to 10 days on a person, after which they detach and look for a place for successful reproduction.
Penetration of the insect's mouthparts under the skin and its removal may remain unnoticeable. A person discovers only a bite mark, which itches and swells after the pest leaves.
A tick cannot fall off a person on its own if he is hungry. But it can come unstuck and stick to another place. This is what individuals do if they did not find a convenient area for food the first time. In this case, several marks from one parasite remain on the body.
Despite the fact that in the process of eating blood, the tick swells to enormous sizes, it cannot burst. The integrity of the insect can only be damaged by physical force.
When removing the parasite yourself, you should be careful not to damage it. It is extremely difficult to pull out an insect piece by piece. If part of the pest remains in the body, suppuration will begin in this place.
Experts' opinion
Experts do not deny that a tick can bite and leave a person on its own, but they argue that you should not wait for this to happen. Parasites are carriers of various diseases that can lead to disability and death. The most dangerous are tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis.
When infected with these infections, a person experiences symptoms similar to acute respiratory diseases:
- increased body temperature;
- muscle discomfort;
- weakness;
- headache;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting.
Negative manifestations disappear after 1-2 weeks, but after a while they return in parallel with damage to internal organs and the central nervous system.
Also, the invasion of the parasite can provoke the development of an extensive allergic reaction.
Allergies manifest themselves as:
- swelling;
- vague redness in the bite area;
- weaknesses;
- headache;
- rash.
If an insect bite is detected, you need to take an antihistamine in a dosage appropriate to the person’s age and weight.
If you find a pest on your skin, you should remove it yourself or contact a specialist. You can remove the insect:
- With tweezers. The insect is grabbed at the base by the tool and pulled outward with rotational movements.
- Thread. A thin thread or fishing line is tied where the parasite comes into contact with the skin, and then twisted until the insect is removed.
- With your hands. Fingers are wrapped in gauze for better grip. The tick is grabbed at the base and pulled out of the skin using rotational movements.
Do not apply oil or other substances to the pest to block the access of oxygen. This won't make him come out any faster. The parasite obtains oxygen from the blood.
You should not remove the insect from the skin with sharp jerks. Its oral apparatus has special teeth that do not allow it to be easily removed. A strong tug will tear the abdomen away from the head, and part of the pest will remain under the skin.
After removing the insect, a visit to a specialist is made as soon as possible. Let's call an ambulance to your home. It is recommended to place the extracted parasite in a jar and send it to the laboratory to determine the pathogen it carries. It is not possible to identify an infected individual by appearance.
You should also contact a specialist if the tick crawled out unnoticed and only the bite site was found. Its signs are as follows:
- swelling and redness, reaching up to 60 mm in diameter;
- dark spot at the site of the bite;
- local or general increase in body temperature;
- itching;
- burning.
After the tick itself crawls out of the skin after the bite, unpleasant symptoms of infection or complications may appear in the interval from 1 to 30 days. During this time, the person must be in touch with the attending physician.
If the body has a strong immune system, the incubation period for some tick-borne diseases can last up to 2 months.
An insect bite is dangerous to human health. Even if the parasite was not a carrier of the disease, its penetration under the skin can provoke an allergic reaction and other unpleasant manifestations.
Source: https://GdeKlop.ru/kleshchi/posle-ukusa-otvalitsya-sam/
Preventive measures
To protect yourself from ixodid tick bites, you must take precautions while walking in nature. Particularly dangerous periods are spring and early summer. At this time, ticks are especially aggressive, as they experience severe hunger after hibernation.
When going for a walk, you need to take all precautions to protect yourself from getting ticks on your body. To do this you need to follow simple rules:
- Choose clothes that cover almost the entire surface of the body. Ticks live in tall grass, so they first fall on their feet. Gradually they rise up, trying to find a bare area of skin. When walking you need to wear long trousers and closed shoes.
- Clothing should be worn in such a way as to prevent the entry of parasites. The bottom of your shirt or T-shirt must be tucked into your trousers. Pants legs should be tucked into socks. The shirt must have long sleeves. If it is cool, you should wear a light jacket with a hood. If it is hot, then the head should be protected with a cap or hat.
- During a walk, clothes should be periodically inspected in order to notice parasites in time. If you are going to spend the night in the forest, you need to inspect your sleeping bags and tents.
- It is advisable that clothes for hiking be light in color, since it is harder to notice ticks on dark ones.
- Currently, there are a large number of protective drugs that can repel parasites. These are special gels, sprays, aerosols, ointments. You can buy them in a store or pharmacy. The most popular: “Biban”, “Taiga”, “Picnic-Antiklesch”, “Tornado”, “Deta-Vokko”.
Types of ticks. Classification of ticks.
There are more than 40,000 species of ticks, which scientists have divided into 2 main superorders:
Description of the main types of ticks:
.
It is absolutely harmless to birds, animals and humans, since it is a complete “vegetarian” and feeds on plant juices, settling on the bottom of the leaf and sucking the juices out of it. It is a carrier of gray rot, which is destructive for plants.
It feeds on its relatives, so sometimes it is specially introduced by humans into greenhouses and hothouse farms to combat spider mites.
Granary (flour, bread)
mite
.
For humans, in principle, it is safe, but for grain or flour stocks it is a serious pest: the products become clogged with waste from the flour mite, which leads to its rotting and mold formation.
lives in the southern part of Russia, Kazakhstan, Transcaucasia, the mountains of Central Asia, and the south of Western Siberia. Mainly settles in forest-steppes or forests. Dangerous for animals and humans, it can be a carrier of encephalitis, plague, brucellosis, and fever.
harmless to humans, but dangerous to dogs. Lives everywhere. Particularly active in coastal areas and on the Black Sea coast.
Mites under the skin
A large number of parasitic creatures live on humans. The subcutaneous layer is the habitat of some types of mites. Many of them are pathogenic. These include scabies mites and demodexes.
The latter are opportunistic. This suggests that the human body is able to cope with these mites on its own if there is a strong immune system. Demodexes live on the human body, but do not cause harm. If the immune system is weakened, ticks begin to actively reproduce. In this case, the disease demodicosis occurs.
Depending on the area of the skin in which mites parasitize, they are divided into types:
- Demodex folliculorum. They live in hair follicles.
- Demodex brevis. This species lives and reproduces in sebaceous ducts and glands.
What does a tick look like under the skin of a person? This can be seen with multiple magnifications. the parasite is 0.4 mm in size and is not visible to the naked eye.
How ticks bite: ways to identify a bite
The target of a tick attack is the blood of a person or animal. The tick burrows into the body and feeds on the blood of the chosen victim for several days. In addition to the bite, a big problem is the likelihood of infection with dangerous diseases.
How to understand that a tick has bitten and how dangerous it is
In the forest or in the countryside, various insects can bite, one of them may be an infectious tick. How to understand that it was a tick that bit you? This can be determined by the appearance of the bite site. Quite often it starts to itch. In addition, the abdomen of the insect that absorbs blood increases in size. It can be detected by feeling the bite site.
It is important after each visit to an area potentially dangerous for insect attacks to inspect and feel your body from head to toe. Otherwise, how can you find out that a tick has bitten, because its bite is completely painless due to the release of a substance with analgesic properties by the insect at the time of the bite.
First of all, you need to identify the insect found on the body. How can you tell if it’s a tick or not? Perhaps its species has nothing to do with blood-sucking insects.
How do you know if you have a tick that can infect you with encephalitis? You need to be able to identify encephalitic or otherwise ixodid ticks. Their body does not exceed 4 mm in size.
It looks like an oval pouch to which the proboscis and paws are attached. The insect's brain is located in the central part of the body. A hungry tick has a flat shape. The protective chitinous skeleton can be of different shades.
There are light yellow mites and dark brown ones.
There are suckers on 4 pairs of legs. Their presence allows you to move not only along horizontal and inclined, but also along vertical surfaces. The paws contain tools for attaching to the victim's body. They are in the form of microscopic sized spines and denticles.
The chitinous dorsal shield in females covers a small part, only 1/3 of the back. Males have everything. This structure allows you to increase the elasticity of the female’s body and contributes to its increase in size by 15 times.
A female that has drunk blood turns a dark gray color. Dangerous carriers of encephalitis are mainly the taiga and dog ticks, which are similar in size and shape. The taiga has a characteristic bright color of the abdomen.
The ventral part of the dog is gray in different shades.
Knowing the appearance of the encephalitis tick allows you to promptly avoid contracting a serious illness. It is possible to know for sure whether someone is a carrier or not only after a laboratory test. Not only the ixodid mite, but also scabies, bed bugs, ear mites, spider mites and other types of parasites can cause harm to humans.
For those who have been bitten by a tick, the type of insect is not very important, what is important is whether or not it is a carrier of encephalitis. This can only be determined by testing the blood in a laboratory setting. However, sometimes the symptoms of the disease are manifested by the following signs:
- the appearance of blistering at the site of the bite, accompanied by redness;
- constant chills and an increase in the temperature of the bitten person up to 40 degrees;
- skin rash;
- the presence of general weakness, aching joints and headaches;
- photophobia;
- loss of consciousness for a short time;
- gastrointestinal upset accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- an increase in the size of the liver and (or) spleen;
- yellowing of the skin, etc.
If any of the listed symptoms are present, the person bitten should immediately contact a physician or infectious disease specialist!
The question of how to understand what kind of mite is under the skin is asked by many people on the Internet. Non-standard problem. If the insect ends up completely under the skin, this is considered the worst case scenario.
The insect under the skin looks like a new mole or a small ball different in color from the skin. If a tick has embedded itself, you feel discomfort in the area of contact.
Can a tick fall off on its own?
After receiving the dose of blood it needs, the insect falls off on its own. This can happen either after a couple of hours or after a few days.
If the parasite, despite the symptoms of burning and itching accompanying the bite, was not detected while on the body after it left the body, how can you tell whether the tick has bitten or not? This is quite difficult, because the bite site in appearance will resemble the bite of a fly, gadfly or mosquito. In this case, the indicators are symptoms of fever, in some cases dizziness.
In these cases, you should immediately consult a doctor. The complexity of the situation with a tick that has fallen off the body is the impossibility of presenting the insect to the laboratory for analysis.
It is important to record the date of the probable bite and exactly 10 days later go to the clinic and be tested for tick-borne encephalitis. In some cases, it may be appropriate to get checked again in a couple of weeks.
It is especially important to undergo all control procedures if burning, itching and redness of the skin suddenly reappear at the healed bite site. The moment of the bite may not be noticed due to the anesthesia introduced by the insect, but unpleasant consequences will certainly appear.
How does demodicosis infection occur?
Many readers are interested in whether a tick can crawl completely under the skin. The answer is yes. Demodexes live, feed and reproduce under the skin. This species has two routes of infection - direct contact with an infected person or through common household items: clothing, bedding, towels, and so on.
Demodexes can remain on the surface of the skin for up to three hours. Next, they penetrate the hair follicle or sebaceous gland, where they begin to actively feed on the epithelium and adipose tissue.
Most often, they choose to live on the face, back or cervical region of a person. On the face, the area of the nose, eyes, eyelashes and eyebrows are mainly affected. However, Demodex can live on any part of the body.
What does the site of infection look like?
The bite site is mostly not inflamed, no hematoma occurs, but severe itching may be felt - this is how the skin reacts to substances introduced into it that prevent blood clotting (this is the only way the tick can suck it out). A slight swelling appears only after 12-24 hours. Even then, the bite mark swells a little, often becomes purple (a certain part of the blood becomes blood clots), and already in that place you can see the tick itself, more precisely, its back part. After all, the insect itself is quite small in size, about the size of an ant. However, it can drink a volume of blood that is 20 times its own body weight.
If after a tick bite the wound does not decrease within 3-4 days, then you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The most important thing is that the bite site does not increase in size. If this happens, then with a 90% probability an infection has occurred with some kind of virus or infection (ticks are carriers of more than 120 types of pathogenic bacteria and bacilli).
If after a tick bite a person’s wound begins to fester, this indicates an intensification of the process of foreign body rejection. This is even good, because the body is actively trying to get rid of the insect remaining in the scalp and, thanks to white blood cells, destroys the entire infection.
By the way, if a bite is found in a child, he may develop a total allergic reaction. In such cases, the place where the tick was attached becomes very swollen. Swelling occurs in an area of approximately 20 cm². If liquid begins to accumulate there, it must be removed immediately. But under no circumstances should you do this yourself.
Is the tick's head itself visible? In most cases no. It also depends on the depth to which the insect has penetrated in search of a blood capillary. For example, on the head they are located at a depth of only 1-2 mm. On the back – up to 4 mm. The deepest capillaries are located on the leg, as well as on the palms. But most often the tick attaches itself to thin skin. These are the following areas:
- armpits;
- at the temples;
- behind the ears;
- in the area of the feet.
Causes of demodicosis
An opportunistic tick begins to activate in the presence of the following reasons:
- Unhealthy eating. Excessive content of glucose and easily digestible carbohydrates in tissue and blood cells causes activation of the tick, since this substance is an excellent nutrient medium.
- Sharing common household items or clothing.
- Passive lifestyle. This leads to a decrease in the body's resistance.
- Treatment with antibiotics and hormonal agents.
- Presence of chronic diseases.
- Stress and nervous tension.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Use of low-quality cosmetics, leading to clogging of sebaceous ducts, glands and follicles.
Signs of demodicosis
Infection occurs when a tick gets under the skin. What to do in this case? How to determine the onset of the disease? The first sign of the presence of this parasite is a general persistent redness of the facial skin. Further symptoms:
- The appearance of acne with ulcers on the face.
- Inflammation, irritation and hardening of the skin around the eyes, increased tearing, dryness, the appearance of stye that does not respond to conventional treatment. As the disease progresses, the cornea becomes damaged and vision decreases.
- Dilated blood vessels.
- Purulent rashes on other areas of the skin.
Direct sunlight helps reduce the area of inflammation.
How to recognize tick bites
- Why IGeneX? IGeneX Advantage
- Licenses and certificates
- our history
- Leadership
- Patient success stories
- All COVID-19 tests
COVID-19 Testing Program Student Testing Program
- Order a kit How it works
- View all sets
- Blood collection kit
- Urine collection kit
- Miscellaneous collection kit
- Check the tick
- Babesia
- Forms
- Why IGeneX? Benefits of IGeneX
.
Therapy for demodicosis
The main method of control is complex treatment, which consists of the external use of special ointments, creams, solutions, as well as strengthening the immune system.
It should be borne in mind that only by eliminating the causes of the disease can good results be achieved and relapses avoided.
Doctors recommend regularly cleansing your facial skin with special cosmetics and doing mild peeling. Patients may be prescribed Permethrin and Metronidazole ointments. The full course of treatment for mites under the skin usually lasts just over a month.
Scabies mites
The sizes of these parasites are approximately the same as Demodex. Therefore, you can only see what a scabies mite looks like using a microscope. It digs passages under human skin. This causes unbearable itching. Therefore, the second name for the scabies mite is itching. It causes scabies, a highly contagious disease.
Itching can infect any part of the body, but prefers the area between the fingers, perineum and armpits. A man scratches the affected areas. In these places, wounds appear, into which infection penetrates.
Infection occurs mainly through contact with a sick person. Sexual transmission is also possible. Sometimes children who sleep in the same bed with sick parents become infected.
The itching only becomes active at night. A sign of the disease is not only itching, but also a rash.
If scabies is diagnosed, quarantine is declared. Therapy is carried out using special ointments. In this case, all people in contact with the patient should receive treatment.
For scabies, medications containing peritrins or benzyl benzoate are used. Doctors can prescribe Spregal, Lindane, Crotamiton, Ivermectin, and sulfur ointment.
After the destruction of ticks, medications based on antibiotics “Neomycin” and “Baneocin” can be prescribed.
Treatment of rosacea
Local therapy:
- Symptomatic: to treat redness, lotions with herbal tinctures (chamomile, sage, St. John's wort, etc.) and 1 - 2% solution of resorcinol or boric acid are used. If you apply the lotions to the skin cold, they have a soothing effect, eliminating the feeling of burning and heat due to the constriction of blood vessels in the area of application.
- Pathogenetic: sulfur preparations for topical use, Spregal, antibiotic-based ointments (metronidazole, tetracyclines). Papules and pustules can be treated with azelaic acid preparations, which reduces the production of sebaceous glands and normalizes keratinization processes.
The most effective means for systemic treatment of rosacea are tetracycline antibiotics, which penetrate the sebaceous glands and accumulate in them, which inhibits the proliferation of pathogenic flora, which aggravates the course of rosacea. Metronidazole, which has anti-edematous and bacteriostatic effects, has been successfully used.
Resorcion and spregal are suitable for local therapy
The reduction in edema occurs due to inhibition of the synthesis of inflammatory mediators by neutrophils. Retinoids are used for severe forms of rosacea; their therapeutic effect is due to their immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and sebostatic effects. The sebostatic effect is carried out due to the regulation of the processes of keratinization and differentiation of skin cells and sebaceous glands. In particularly severe cases, glucocorticoid therapy is performed.
The method is based on a number of effects:
- Electrodynamic - destruction of tissues and cells (including foreign and pathogenic) under the influence of high temperatures and steam.
- Biological - strengthening of regeneration processes.
- Physico-chemical - destruction of complex molecular bonds of cells.
Cryotherapy - massage or application of liquid nitrogen. Promotes deep exfoliation, has anti-inflammatory and vasospastic effects. Skin mites usually die when exposed to low temperatures of liquid nitrogen.
Laser therapy is used to treat telangiectasias by destroying small blood vessels, the breakdown products of which are absorbed by surrounding tissues within a few days.
Prevention
It is well known that disease is easier to prevent than to treat. As already mentioned, one of the main causes of demodicosis is a weakened immune system. Therefore, proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are one of the main conditions that help to avoid the disease.
To prevent ticks from parasitizing under the skin of a person, you should follow the rules of personal hygiene, constantly wash your hands, and do not use common household items.
It is also necessary to take a shower and visit the bathhouse at least once a week. During this procedure, the pores and sebaceous ducts are cleaned.
It's hard to believe, but scabies mite infection is not related to hygiene. This parasite feels great on both clean and dirty bodies. It can remain on the surface for no more than 30 minutes. During this time, the tick gnaws through the passage and hides under the skin. A preventative measure that will help avoid infection with this parasite is to minimize physical contact with strangers.
Compliance with all these measures will protect you not only from diseases caused by subcutaneous mites, but also other dangerous ailments.
Treatment of demodicosis
With timely treatment and proper treatment, the diagnosis can be cured fairly quickly. But this is only possible under the supervision of a dermatologist and after conducting the necessary laboratory tests.
Important! Clinics that promise a miracle in the form of quick treatment are scammers. Demodicosis has a characteristic feature - the microorganism that caused it is not eradicated from the human body for the reason that it is a natural part of the body
Treatment depends on timely treatment and proper treatment and can last at least several weeks, and in rare cases – for years.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is as follows:
- The use of antiparasitic agents based on sulfur, ichthyol tar and other things.
- Products that normalize and improve metabolism in the skin.
- To normalize the skin microflora, drugs based on metronidazole are used.
- Preparations based on azelaic acid as powerful antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agents.
- An antihistamine may be prescribed to prevent allergic reactions.
- An increase in vitamin intake is prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
- Sorbents are prescribed to cleanse the body and skin.
- Drugs to improve the condition of blood vessels.
- Antibiotics are used if the disease progresses extensively.
Physiotherapy
Typically, treatment for demodicosis takes an integrated approach, and the hospital offers a course of physiotherapy for advanced stages:
- Cryomassage. The procedure involves treating the skin with liquid nitrogen.
- Oxygen or ozone therapy. The action is to accelerate the metabolic processes occurring in the skin tissues.
- Phototherapy. This therapy is aimed at improving adjacent vessels by treating the surface with light rays.
- Mesotherapy. The procedure is to relieve inflammation due to its anti-inflammatory effect.
- Electrophoresis. In some cases, electrophoresis therapy may be prescribed.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can be used as additional treatment with permission and in consultation with your doctor.
The methods are as follows:
- Using washes with tar soap. This soap has antimicrobial, antiseptic and antifungal effects. You can also use decoctions of chamomile, wormwood, celandine or hemlock for washing.
- Rubbing the affected areas of the skin with lotions based on eucalyptus alcohol, solutions of wormwood or dimexide - these products have an excellent disinfectant effect.
- To facilitate and speed up treatment, you can use eucalyptus essential oil - an oil that has an antiseptic effect, diluted with water and rubbed on problem areas.
- Kerosene is also suitable for rubbing.
- Laundry soap is acceptable for use - the soap is brought to the state of shavings, diluted with warm water. After whipping until foamy, the mask is applied to the affected areas. Closes after complete drying.
- A clay mask is acceptable for use - pharmaceutical powder is diluted to a cross-shaped state in warm water and applied in a thick layer overnight. The place is bandaged in any way. It is usually washed off in the morning.
Diet during treatment
Following a diet is strictly recommended for the reason that subcutaneous mites without the following products begin to experience starvation.
You should avoid the following products:
- Various semi-finished products and fast food.
- Canned food, pasta and sausages.
- Various crackers and chips.
- Various spicy, smoked or salty dishes.
- Various sweet fruits, berries and dried fruits. This also applies to confectionery products.
- Various citrus products.
- Abstinence also applies to products with a sauce or marinade base.
- Carbonated, alcoholic or caffeinated drinks.
Personal hygiene
Maintaining personal hygiene allows treatment to proceed at a normal pace. When prescribing treatment, the dermatologist discusses this point with the patient separately, depending on the stage of the disease.
The following points can be highlighted:
- Using moisturizing and antibacterial ointments.
- Elimination of various abrasive products - scrubs, sponges and others.
- Use only warm water to wash your face – not too hot and not too cold.
- Men with decomecosis are recommended to use electric razors and avoid all kinds of irritating shaving products.
- Before applying the daubs, after washing, allow to dry completely for 30-60 minutes.