In the warm season, your pet faces danger outside in the form of ticks, which skillfully hide in fallen leaves, dry tree branches and even in ordinary grass, not to mention bushes.
Parasites choose the most inaccessible places for the animal to bite. Where you can't scratch or bite, the skin is the most tender. Ticks quietly climb onto the animal, and when bitten, the dog may not even experience any discomfort. If immediately after a walk you find a lightly attached or simply crawling insect, then there will be no consequences. It is not necessary to accompany every bite with a trip to the veterinarian. Be attentive to your pet, learn what types of ticks there are in dogs and what symptoms can be used to determine the presence of an infection or serious disease.
Types of ticks on dogs
Whatever the species of the parasite, it, one way or another, feeds on the blood or particles of your pet’s skin. It is necessary to remember the danger such a “neighborhood” poses, because in addition to unpleasant sensations, there is the possibility of picking up some kind of infection, which in turn can lead to dire consequences, including the death of the dog. Ticks in dogs are an age-old problem, because it is practically impossible to keep track of our active and inquisitive brother, so the owner must know what types of parasites are dangerous for the animal. The following types of ticks are mainly dangerous:
- Subcutaneous;
- Ixodidae;
- Sarcoptoid mites.
You can buy unpleasant insects anywhere, so vigilance, hygiene and prevention are necessary. It is necessary to use acaricides on an ongoing basis; they can be in the form of drops, in special collars and aerosols.
Actions to take if bitten by a tick
What to do if a tick has attached itself:
- remove the parasite in a medical facility. If this is not possible, remove the tick yourself using a special tool or thread;
- 25% of the tick population are carriers of viruses and infections. Therefore, the extracted arthropod must be submitted to a laboratory for analysis;
- If the tick is infected or you feel unwell, contact an infectious disease specialist. Borreliosis responds well to antibiotic therapy, and tick-borne encephalitis in the initial stage is treated with immunoglobulin.
Symptoms of subcutaneous mites in dogs
The skin of dogs is quite sensitive and delicate. In this regard, the sensations from parasite bites can cause significant discomfort. Subcutaneous mites in dogs are the cause of many skin diseases, and the symptoms are quite varied:
- Itching, in which the pet can scratch itself until it bleeds;
- Hair loss - especially noticeable in short-haired dogs or in places where the hair is somewhat shorter (ear areas, muzzle, paws, belly and genital area);
- Aggressive or agitated state due to pain and itching;
- If the situation is neglected, then the development of anemia or other pathological conditions is possible.
Do not treat yourself; you need to find out what is causing the symptoms.
If you suspect any disease in your pet, to be on the safe side, you can have a skin scraping done at the veterinary clinic. Subcutaneous mites cause demodicosis - it is with this disease that hair loss and itching occur.
Ixodid ticks in dogs
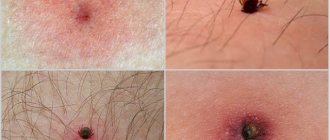
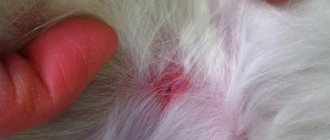
As a rule, it is ixodid ticks that are found in parks, courtyards and summer cottages, and they are dangerous not only for pets, but also for people. Therefore, with the onset of spring, owners of private dacha areas carry out preventive disinfestation. The treatment of the area is carried out by professionals and one day is enough to destroy all parasitic individuals. It’s worth being safe, because the consequences may be irreversible. Ixodid ticks are carriers of piroplasmosis - this is a blood disease, and it, in turn, is dangerous in dogs because it leads to kidney failure, destroys the liver and the central nervous system. Convulsions may occur, which progress to coma, and then lead to death. You need to know what ixodid ticks look like in dogs; the photo shows the places where these bloodsuckers mainly accumulate.
Which ticks are white?
More than 50 thousand arachnid insects are known to science, of which a good third are mites, but none of them, under natural conditions, are white in color. Visually, mites may appear white due to the coating or the state they are in at the moment. So, which ticks are white?
Turn white when they drink blood:
- Forest.
- Poselkovy.
- Taiga.
- Canine.
Important! All four species listed above are relatives belonging to the species of grassland or ixodid ticks.
Scabies, dust and spider mites have a white coating, but they are microscopic. Flour mites have a white edge but are not parasitic on dogs. Ear mites are almost white in color. However, in fact, these parasites have an almost transparent shell.
Sarcoptic mites in dogs
In addition to the fact that they are dangerous for pets, there is a possibility of tick transmission to humans. This species is popularly called the scabies mite. It is able to live both on the skin and in the upper layers of the skin, and as it moves around the body it leaves characteristic “white burrows”. Sarcoptic mites in dogs manifest themselves in the fact that the pet constantly itches, as it feels itchy, and the fur can thin out and dense crusts form on the skin. Your pet will be restless and possibly aggressive, and in some cases sleep may be disrupted. However, this type of tick can be treated, but you should consult a veterinarian before treatment.
What argas mites look like: appearance (with photo)
Argasid mites (argasids) are external parasites, as well as carriers of some pathogens of infectious and protozoal diseases. They are most often found in the southern regions. Some species of argasids can live in poultry houses and livestock buildings, where they briefly parasitize animals, feeding on their blood at night.
When describing this variety of ticks, it is worth noting that, unlike ixodids, argasid parasites lack dorsal and ventral scutes. The proboscis of imagoes and nymphs is on the ventral surface, so it is not visible from above. The general characteristics of argasid mites are their particularly large size and the presence of a flattened soft body. The proboscis of these parasites is similar in appearance to the proboscis of ixodid ticks.
Nymphs, like adults, have four pairs of limbs, but they lack a genital opening. The round larva has three pairs of limbs. Her proboscis is located in the front of her body.
The body structure of the Persian tick is similar in appearance to a bug. It has a flat, grayish-yellow, ovoid body with a visible edging around it. The length of the tick is 10 mm and the width is 6 mm. The insect has two pairs of legs pointing forward and two pairs pointing back. Ticks go through all stages of development: eggs, larvae, three nymphs and adults. The female parasite is capable of laying from 30 to 100 eggs, from which larvae appear after 2-3 weeks, parasitizing mainly poultry. Each tick in the nymph stage before molting feeds once on the blood of an animal for 1-2 hours, and in the adult stage - several times. It takes 3 to 8 months for the development of one generation of the Persian tick. All stages of the parasite can overwinter. The Persian tick is mainly a carrier of the causative agent of spirochetosis.
The cat tick is distinguished by a thickened body of a grayish color, which is narrowed at the anterior end. Body length can reach 15 mm. The parasite has claws on its feet. The sheep tick parasitizes sheep and other domestic animals.
This parasite goes through all stages of development: eggs, larvae, three nymphs and adults. Female ticks lay eggs in cracks in the walls of barnyards. The entire process can take from 7 to 30 days. During this time, one female is capable of laying from 50 to 500 eggs. After about 30-45 days, larvae emerge from the eggs, which attack animals in the fall. Larvae and nymphs of the cat tick can parasitize animals for up to 45 days. Having had their fill of blood, the nymphs go into hiding, where they turn into adults. Adult ticks repeatedly suck the animal's blood for 10-40 minutes. The main characteristic of cat ticks is winter blood sucking.
In summer, females lay eggs in crevices and cracks in rooms where animals are kept.
Infection with the sheep tick can lead to paralysis (sometimes death) of sheep. In addition, these ticks can be carriers of some sheep hemosporidia. Ticks are carriers and carriers of the pathogens of equine infectious encephalomyelitis, brucellosis and tularemia.
Look what argas mites look like in these photos:
Ticks in dogs symptoms and treatment
Let's talk in more detail about ixodid ticks, since this species can cause irreparable harm to the animal. Symptoms after a tick bite may vary from person to person, but there are a number of behavioral reactions of your pet that you should pay attention to:
- The animal is lethargic, eats poorly or refuses to eat;
- Itching occurs at the bite sites, the pet may try to scratch or rub them against objects, corners or roughness;
- If the parasite is not detected immediately, then after a while it is easier to do so, since it swells with blood to a noticeable size.
Due to the fact that ticks can be infectious agents, it is worth taking prevention seriously.
There are a lot of special collars, sprays and drops for dogs, but no one has ruled out fighting ticks in other ways. If you often travel outside the city or live in a private house, then with the onset of spring, make sure that your area is free of dangerous insects. By ordering pest control services, you will contribute to the healthy future of your four-legged friend. What to do if the bite could not be prevented? The best course of action would be a trip to the veterinarian. However, if you have successfully completed the tick removal procedure, then you do not need to go to the doctor. Disinfect the bite site and just watch your pet for the next couple of days. You can also take the parasite to the laboratory.
Ticks in dogs are quite common, but if you know what symptoms should alert you and what treatment to apply, they will not lead to tragedy. Ticks in dogs, or rather the consequences after them and treatment, can be eliminated and carried out at home. Depending on which tick your pet has picked up, treatment will be selected. Immunomodulators and antibiotics are often prescribed in advanced cases, and in the early stages or immediately after a bite, it may be enough to treat the wound and protect it from bacterial penetration. It happens that ticks in dogs grow in the ears, since there is very delicate skin and a fairly secluded place; after looking at the photo, you can understand how to carry out an inspection after walks, especially in the warm season. You should know that when dealing with ear mites, treatment without medication will not give results, so visiting a veterinary clinic is a mandatory procedure.
And remember, it is easier to prevent than to treat later. Prevention is and remains the basis of protection. There are many drugs available on the market (collars, drops, sprays), but only through your own experience can you determine which drug is more convenient and effective. Therefore, you can buy several drugs and either use them in combination or sequentially, and monitor the dog’s reaction.
Dog tick: life cycle of development and danger to humans
Ixodid ticks are external blood-sucking parasites. The dog tick is one of them. It is dangerous for both humans and animals. From its name one can conclude that its main victims are dogs, but this is not so.
Parasites pose a threat because they are carriers of rare diseases. These are Marseilles fever, Lyme disease, inflammation of the brain, tularemia. The tick is similar to its Siberian counterpart, but they have differences. If a tick attacks a dog, the consequences can be different - from intoxication to death.
Distinctive features of the dog tick
The dog tick does not have the vision we are accustomed to; it has no eyes. To navigate, the arthropod uses Haller's organ.
This is how he orients himself in space, feeling the temperature, the percentage of carbon dioxide in the air, and vibration. With the help of vibrations, he senses when a victim is approaching him.
Appearance
The dog tick has an oval-shaped body with a shield located on the back. Males differ from females in the size of this shield. In females it is small. When the parasite drinks blood, it can increase in size several times.
Dog tick
The length of the tick varies between 2-5mm. Larvae have 6 legs, and nymphs and adult ticks have 8. The plate, which is located on the back of the tick, not only determines the sex of the individual. It protects it from damage.
Taiga and dog ticks are difficult to distinguish from each other. Because there are many similarities between them.
The difference is in the color of the tick:
- The dog tick has a black front part of the body, and its back is red;
- taiga tick – brown.
Diet
Questing is a phenomenon during which a tick waits for its victim. The arthropod’s algorithm of actions is similar to maneuvers during an “ambush.” He climbs to the very top of the plant and waits for his prey there. During such a passive hunt, the tick actively loses fluid; it seems to “dry out.”
To maintain water balance, it needs to descend closer to the soil from time to time to become saturated with moisture. Therefore, there is a direct relationship between humidity and the duration of questing.
Haller's organ helps the tick find the optimal place for hunting, and also, through vibration, reports the proximity of the victim.
In order to maintain its condition, the tick needs to drink the host's blood throughout the day. The development of an individual occurs cyclically, each cycle requires nutrition. After the tick has drunk blood, it detaches itself from the victim. This is followed by molting or laying of eggs.
The larva is unable to move, so it waits for a potential host. After it is saturated with blood, molting occurs.
Tick saliva has different properties:
- stops bleeding;
- relieves inflammation;
- has antiviral substances.
Rodents, animals, mammals, and birds are attacked by the dog tick. Each stage of tick development requires a new host. For example, larvae choose small individuals - mice. Adult ticks attach themselves to large animals.
The larger the victim, the easier it is to attack. Thus, while moving on an animal, ticks migrate.
Reproduction and life cycle
The stages of tick development include four stages:
- at first it is in the form of an egg;
- then the larvae;
- next is the nymph;
- imago (sexually mature individual).
During these periods, the arthropod changes its hosts. Its life cycle is just over a year. Female and male individuals are rarely found and end up on the same host. They have a better chance of getting along in natural conditions.
The male must find the female and fertilize her. The process of fertilization in them is not associated with intercourse. Seed material is transmitted in its own way. It is located in a pouch, which is a protective factor from external influences. It is called a spermatophore. The female has valves near the genital opening, with which she picks up sperm. Thus, fertilizing itself.
After this, the female begins to feel the need for additional nutrition. She urgently needs a donor body. The development of eggs depends on how much she eats. Since all the nutrients go only to them. Their maturation is closely linked to the mother's food. This process is called “gonotrophic harmony”
Therefore, before laying eggs, the female must receive nutrients from the blood. This explains their increased appetite. Because the better the nutrition, the better the reproduction. The male needs much less to maintain life, and not so often. There are species of mites in which the males die after the sperm is transferred.
It takes up to 10 days for the female to become saturated. The structure of the body allows it to accommodate a large amount of food. But males are less demanding; their satiation process takes about 20 minutes.
Oviposition begins 7-30 days after the female is saturated with blood. Moreover, she does not give away all the eggs at once, but as they mature. That is, in small batches.
Tick eggs
The fertility of ixoid ticks is quite high. One clutch can contain up to 2000 eggs. The quantity is influenced by many factors. But, first of all, this is the degree of saturation of the female, as well as her condition. She can additionally find food for herself during the period of laying future offspring. This, of course, slows down the overall process.
As a rule, eggs are found in the substrate. But there are situations when laying occurs on the host’s body. After 30 days, larvae emerge from the eggs. Outwardly, they resemble adults. But they have three pairs of legs and no genital opening.
After their body is covered with hard shields, they begin to look for prey. Before this, they wait on the clutch.
There are larvae that remain in the clutch, even though their covers are already ready, and they are tormented by hunger. They wait on the ground in search of a suitable victim. And they attach themselves to it in batches. This reduces the immunity of the donor organism and also provides more nutrients for the tick.
Habitat
The dog tick cannot be found in the Arctic and Antarctica. It is common on other continents. Its range is from Europe to the Sea of Japan. A large number of ticks live in northern Africa, as well as in a number of Scandinavian countries. Since individuals are found everywhere, this suggests that the species is adapted to different temperature conditions.
Climatic conditions are important for ticks. This includes humidity and temperatures up to 30°C. Therefore, he chooses either a temperate climate zone or one with a lot of rainfall and plants.
The greatest concentration of arthropods is observed in European countries, as well as in Russia. Especially in the forests. But it is worth noting that they are absent in the taiga.
What danger does the dog tick pose?
The dog tick finds victims not only among large animals. It can also attack humans. Especially in conditions of long absence of food. The main danger that comes from it is the transmission of diseases through a bite. The diseases are all quite serious, they were discussed above.
Sometimes a person can become infected with several diseases at once:
- Encephalitis.
- Borreliosis.
In this case, you should immediately go to the hospital, because the possible consequences are very serious.
The following signs appear as a result of a tick bite:
- pain;
- allergy;
- skin puncture.
Diseases transmitted by ticks are very difficult to diagnose. Despite all their seriousness, this delay is very dangerous. You need to be vigilant in the summer, as well as in May, when ticks are especially active.
How to protect yourself from dog ticks
Pets
There are several ways to protect your cat or dog from ticks:
- A special solution that is applied dropwise to the animal’s withers. It becomes active within a few days. You need to treat the animal's skin, simultaneously moving away the fur. Move along the spine. Water procedures are excluded a few days before and after application of the drug. The secreted substance repels ticks from the victim.
- If you use an anti-tick spray, the effect will also be good. It does not allow the bloodsucker to gain a foothold on the animal’s body. All fur should be treated, avoiding contact with eyes or nose. The effect of the product is immediate, it lasts for three days.
- You can buy a collar. It will cope with ticks for six months. It cannot be removed.
Human protection
In order to protect yourself and your children, you should use the following measures:
- A variety of protection against ticks in different release forms (gel, aerosol, ointment).
- It is important to wear light-colored clothing that covers your legs and arms.
- If a person is in an area where there are outbreaks of infections, it is better to get vaccinated.
See the topic - How to protect yourself from encephalitis ticks using chemicals and vaccinations
Conclusion
The dog tick is a dangerous representative of Ixodid ticks. Its habitats can be found all over the world, with the exception of cold continents. During its development, a tick goes through 4 stages, from egg to adult. He chooses representatives of small and large fauna as his victims. Sometimes it is found on humans.
Ticks, by attaching themselves to a sick animal, can easily spread the infection. Therefore, you should not neglect safety measures. A person must protect both himself and his pet. People are advised to use repellents that repel ticks when walking in the forest. It is also worth wearing as closed clothing as possible.
Special products in the form of drops have been developed for dogs. You can also purchase a tick collar or use a coat spray.
You need to be vigilant during tick activity. These are the months from May to September. Carefully examine yourself and your pet after a walk in nature.