Causes of scabies
Scabies can be contracted for only one reason: contact with the parasite.
When interacting with infected individuals, the pet is in serious danger. Therefore, if an animal behaves restlessly, constantly itches, or is nervous, it is better to isolate it until the exact cause of this behavior is established. The presence of scabies mites cannot be detected without special equipment - they are not visible to the naked eye. Only a scraping can confirm or refute the diagnosis. So you can’t do without a visit to the doctor. The veterinarian will be able to accurately determine not only the presence, but also the type of tick
And this is very important for the correct choice of treatment tactics
The causative agent of scabies can be a mite belonging to the family:
- sarcoptoids (Sarcoptes scabiei);
- notoedrosis (Notoedres cati);
- demodex (Demodex);
- otodex (Otodectes cynotis);
- Cheyletiella.
Parasites most often choose the most favorable conditions for their habitat. Therefore, infection is more likely if the cat’s body provides an environment comfortable for ticks. Thus, the provoking factors of the disease include:
- genetic predisposition (some breeds are very susceptible to the disease);
- decreased protective functions of the epidermis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- painful heredity;
- postoperative period;
- age (kittens are at risk).
The severity of the disease increases in proportion to the number of aggravating factors.
Features of the manifestation of the disease
Different types of ticks can live under a cat’s skin:
- Notoedres sati
- Otodectes cynotis
- Sarcoptes scabiei
- Demodex cati.
The first type causes the development of a disease called notoedrosis, the second provokes otodectosis. The third type of mite (pruritus) usually causes sarcoptic mange (pruritic scabies). The last type of mite is a source of demodicosis. In animals, these parasites live in certain areas where they find more suitable living conditions.
Description of demodicosis
It is generally accepted that the type of tick that is the source of this disease is not dangerous for cats, since it is always present in the body anyway. However, this is not entirely true, because parasites are able to multiply intensively under certain conditions. This leads to a sharp onset of scabies symptoms due to an increase in the number of mites. The cause of the development of the disease in this case is weakened immunity.
The disease is characterized by: pinpoint pustular rashes covered with a crust consisting of dried pus and blood cells.
There are many factors that contribute to a decrease in the body’s protective functions and the proliferation of this type of tick:
- Stress
- Recent illness
- Injuries
- Pregnancy, lactation
- Old age.
In an animal, the tick is most often localized on the face, but the disease may well appear in other parts of the body. Demodex cati is not transmitted from cats to humans.
Sarcoptic mange
The disease is quite rare. Parasites are localized in the muzzle, behind the ears, on the stomach, and elbows. The first symptom is baldness of the affected areas. As parasitism occurs, bleeding wounds form, which causes blood poisoning. Sarcoptic mange develops in pets of different ages, however, the disease is much more often diagnosed in young animals.
It is very difficult to remove the symptoms, and especially the itching. The animal does not respond to treatment and continues to itch. When a tick appears, a severe allergy develops, which provokes quite serious symptoms.
Notoedrosis
Main manifestations: redness of the affected area, baldness, skin begins to peel off. The disease is contagious and can be transmitted from pet to person. However, a tick of this species will not be able to parasitize humans for a long time, since it needs certain conditions for reproduction. He will die in a month, but during this time he will cause a lot of problems.
Consequences of nodoedrosis mite
Diagnosis of the disease
When the first alarming and warning signs appear, the animal should be immediately shown to a veterinarian . Since the symptoms of notoedrosis are similar to the clinical manifestations of damage to other mites (otodectosis, demodicosis), as well as bacterial and fungal infections, a deep skin scraping is necessary to make a diagnosis. Pieces of skin are taken at the border between healthy and affected areas, since ticks can only be found there (they gradually move to new places, leaving those where they no longer have anything to eat).
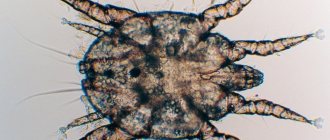
The tick is clearly visible under a microscope; high magnification is not required
As a result of a thorough examination of the collected material under a microscope and detection of the parasite, a final diagnosis is made.
Video: Notoedres cati mite under a microscope
The first signs of scabies in a cat
Before the main signs appear in the animal, indirect symptoms of the disorder can be noticed. Mite reproduction begins from the scalp. Typically, the manifestation of the parasite can be seen at the bottom of the ears, above the eyes and on the bridge of the nose. The epidermis in these areas begins to thicken, becomes unpleasant to look and feel, and may become covered with purulent crusts. Wounds take a long time to heal and cause discomfort to the pet.
Periodic examination of your pet's ears will be a reliable prevention of ear parasites.
The cat's behavior is marked by anxiety and irritability. The pet constantly tries to scratch the sore spot, stops eating and playing normally. Because of this, the cat’s appearance begins to suffer and its body weight decreases. Taking into account the deterioration of the sick animal's condition, other signs of scabies appear.
In later stages, the disease is easily recognized by the characteristic behavior of the cat.
Treatment at home
To effectively combat ticks, it is necessary to understand that treatment must be comprehensive and take at least three weeks. At the same time, every pet that is in the apartment must undergo examination and appropriate prevention. It is necessary to reduce the likelihood of re-infection and re-infection. As for treatment methods, they include the following techniques:
- Bathe your pet daily using antiparasitic drugs, usually lime sulfur.
- Alternative treatment. It involves the use of Ivermermectin once every 14 days for three procedures. Certain types of cats, usually Siamese, react negatively to the active substances in Ivermectin, so this treatment often does not give good results.
- Revolution. The medication comes in the form of drops or ointments and is an effective monthly treatment for your pet to prevent heartworms, fleas and other parasites. In addition, the drug can fight scabies mites, eliminating the consequences of chronic sarcoptic mange.
- Treatment with antibiotics. Such drugs are effective in the development of secondary bacterial infection and aggravation of symptoms.
- Regular cleaning, which includes vacuuming and washing clothes. This action is considered preventive, as it helps prevent the appearance of scabies mites in the house, protecting residents and pets from these annoying parasites.
As for external preparations, including drops on the withers, they are practically useless, since they do not give visible results. Therefore, when choosing treatment methods, it is better to give preference to more effective options.
However, self-medication without first consulting a trained veterinary professional is not recommended. This approach can only worsen the pet’s condition and lead to fatal consequences.
As for sulfur-containing products, they are completely harmless, although they pose a threat to household items and can damage acrylic surfaces and porcelain. Such objects quickly become yellowed and begin to deform. In addition, sulfur is a mineral element with a specific odor that resembles the smell of “rotten eggs.” Therefore, when performing processing operations it is necessary to wear gloves.
It is better to carry out bathing procedures outdoors, not allowing the animal to return indoors until it is completely dry. This measure will protect furniture and carpet surfaces from being stained yellow. And to avoid damage to the conjunctival mucosa, you may have to use eye drops.
It is known that ticks are not able to live long in the environment. Therefore, regular cleaning of textiles and soft surfaces, vacuuming and washing clothes is the best prevention of such a dangerous problem. At the same time, we must not forget that the scabies mite poses a threat to people, so when caring for an infected cat, you need to remember about personal safety.
As for the prevention of sarcoptic mange, it involves preventing the interaction of healthy pets with infected ones. And although the life expectancy of a parasite in the environment is very short, upon contact with another favorable creature it will certainly lead to the development of the disease. When faced with sarcoptic mange, it is necessary to carefully examine all pets at a veterinary clinic.
How to treat demodicosis in cats
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the pathogen. For this purpose, injections, ointments, solutions for internal use, sprays, and bathing are prescribed. Be sure to use products to strengthen the immune system, restore the condition of the skin, and adjust the diet for vitamins and proteins. Treatment of demodicosis in cats is complex.
There is no one universal remedy that can remove the parasite. Having discovered a tick in cats, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment, combining medications.
Therapy for local form
The disease caused by D. cati and characterized by local damage can go away on its own, but not if the immune system is weakened.
The main treatment for cats with demodicosis:
- Use of Amitrazine solution once a day with an interval of 3 days. In this case, it is important to treat not only the affected area, but also the area a centimeter nearby. On average, 6-8 treatments are required for the signs of demodicosis to disappear. The drug is well tolerated by animals. However, if there is scratching, the pet experiences a burning sensation. To prevent the cat from licking the product, the jaw is closed using a loop. Amitrazine is not only destructive to parasites, but also has an anti-inflammatory and softening effect.
- An effective method of treating subcutaneous mites is considered to be feeding the animal with a 1% Ivermek solution at a rate of 0.3-0.5 mg/kg.
- To get rid of the cat mite D. gatoi, use the medicinal solution Lime Sulfur (lime sulfur). The wool is wetted every 3 days or a week. Duration of treatment is 1-2 months. The first signs of improvement are observed after 3-4 weeks of therapy.
Generalized form
In case of extensive demodicosis caused by D. cati, the following treatment regimen is considered effective:
- Treatment of the entire body with Lime Sulfur solution. The interval is a week.
- Subcutaneous administration of the drug Doramectin. The dosage is calculated strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
- Lubricate the body completely with Amitrazine every 1-2 weeks. The drug should be used with caution in the generalized form, and should not be used at all in animals with diabetes.
In severely advanced cases, treatment of the generalized form is often ineffective.
For any type of disease, treatment of subcutaneous mites in cats requires up to two negative scrapings with an interval of 1 month and elimination of lesions. Therefore, it is possible to cure subcutaneous mites in a cat no earlier than 2 months. Some veterinarians perform 3 control scrapings 2-3 weeks apart
Recommended drugs
To treat subcutaneous mites in cats, it is recommended to use the following drugs.
- Sulfur ointment helps cats against subcutaneous demodex mites only in the initial phase of the localized process. The ointment is applied to previously washed and dried skin once a day in those places where the cat’s tongue cannot reach. Do not allow water to enter until the next treatment. In case of a generalized form, the pet is bathed in a solution of lime sulfur (Lime Sulfur). Process weekly until the desired result is obtained. The first signs of improvement are observed in the fourth week of use. The course of treatment is at least six baths.
- Shampoos for demodicosis for cats and dogs based on benzoyl peroxide are used in treatment. The active substance destroys mites, as well as fungi and bacteria. The animal is bathed daily. Apply shampoo for 5-10 minutes, then rinse. The duration of treatment is indicated in the instructions for use for each drug.
- The following remedies for subcutaneous mites are used to treat cats: “Aversectin ointment”, “Ivermec gel”, “Amidel-gel Neo” and others.
- Drops “Stronghold”, as well as “Inspector” for demodicosis for cats are applied to the withers. The drugs have an acaricidal effect for four weeks in case of local damage.
- As a preventive measure, Bravecto spot-on drops for demodicosis in cats can protect against infection for 12 weeks. The drug is also effective for the local form of the disease.
- “Ivermec spray” against subcutaneous ticks is sprayed on a cat in the open air or in a well-ventilated area. Ivermectin (the active ingredient of the drug) is poisonous to cold-blooded animals, therefore, if there are aquariums in the apartment, they are carefully covered. Pre-clean the affected surface from scabs. The drug is applied, covering 1-1.5 cm of healthy skin around the affected area. The treatment is repeated after 3-5 days. If clinical recovery has occurred, scrapings are performed. Treatment is considered complete if no mites are found in two consecutive scrapings. In case of large-scale lesions, one side of the body is treated, and the second the next day. To prevent your pet from licking the medicine, wear a cervical collar for half an hour. When there are several animals in the house, the treated cat is isolated from the rest until dry.
- For injections of cats against subcutaneous ticks, Ivermec and similar preparations based on ivermectin or doramectin are used. For demodicosis in a cat, a single subcutaneous injection of 0.1 ml/5 kg is given with an insulin syringe. At the discretion of the veterinarian, the injection is repeated after 8-10 days.
To suppress pathogenic microflora (bacteria and fungi) with subcutaneous ticks in cats, antibiotics or antimycotics in tablets are used.
Medicinal feed
A speedy recovery of your pet after an illness caused by a subcutaneous tick is ensured by a special veterinary diet. During treatment and for some time after recovery, the veterinarian may recommend keeping your pet on medicated food. After restoring the beauty of the coat and the health of the skin, the pet, in agreement with a specialist, is transferred to either a balanced natural diet or to food of at least premium class.
Symptoms of scabies
Cats often scratch themselves behind the ear with their paw. This should not be a cause for concern. This animal behavior is natural and is not a sign of illness. Symptoms of scabies in cats are more severe. A loving owner will definitely notice them. Depending on the type of scabies mite, the well-being of a sick animal may vary. However, infection should be suspected if the following signs are present:
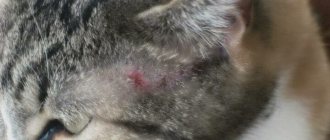
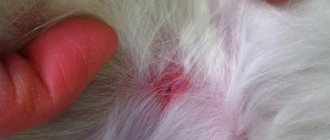
• Unbearable itching. Ticks bite into the upper layer of the skin, making passages there, which causes a strong desire to scratch. • Redness of the skin. • Clear localization of lesions. The habitat of the parasite depends on its species. For example, ear mites can be recognized by the presence of scratches behind the ears. Hair loss in the area of the face, paws and shoulders most likely indicates demodex. • Anxiety. The animal suffers from unbearable itching and scratching, becomes irritable, sometimes even aggressive. • Enlargement and consolidation of lesions - in the absence of timely treatment. • Formation of compactions, gradually filling with purulent contents. • The appearance of crusts or scales in the lesions.
If the cat owner does not respond to the manifestations of his pet's illness, then the symptoms begin to intensify. The disease itself will not go away. Therefore, when the first suspicions arise, measures should be taken immediately. Advanced scabies is dangerous due to the addition of a bacterial infection, since any pathogens can easily penetrate under the skin through wounds.
Diagnostics
Treatment of the animal begins after a correct diagnosis, which must be carried out by a veterinarian. Depending on the type of scabies mite and additional complications, treatment regimens will be different.
In addition, the symptoms of the onset of the disease at the initial stage can easily be confused with allergies , vitamin deficiency, dermatitis or lichen, so the cat should be shown to a specialist as soon as possible.
The doctor will take a scraping from the skin with a small incision, conduct a microscopic examination, determine the type of scabies pathogen and determine whether the cat has additional complications.
It is not always possible to identify the parasite even in laboratory conditions, so the veterinarian must pay attention to all symptoms of the disease.
Possible reasons
Localized ear scabies in cats, or generalized scabies, occur as a result of the activity of certain types of microscopic mites. The period from the penetration of parasites into the layers of the epidermis until the onset of characteristic signs is quite extensive and does not have clear boundaries. Microscopic mites penetrate the layers of the epidermis, making their way to the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, feeding on blood, particles of the dermis and lymph.
A pet can become infected with scabies through close contact with other pets - cats or dogs, as well as humans. Microscopic mites also infect wild birds, so the disease can be transmitted from pigeons caught by a cat on the street. Cats often become infected through animal care items.
More often, animals that are severely malnourished, have a history of chronic diseases, and also those with weak immune defenses become infected with scabies. Scabies poses the greatest danger to small kittens. Due to the fact that their body’s resistance is much weaker due to an underdeveloped immune system, their degenerative processes go much faster.
The particular danger of the disease lies in the ability of scabies to be transmitted from cats to humans.
The main factors that can cause scabies mite infection are:
- genetic predisposition;
- skin diseases that provoke a weakening of the body's defenses;
- the age of the animal (statistically, small kittens and cats under the age of 2 years are affected by subcutaneous mites);
- decrease in the general resistance of the body;
- disruption of internal metabolic processes in the body;
- violation of the rules of keeping and hygiene of a pet;
- stressful conditions in an animal.
There are several types of microscopic parasites that can cause the development of scabies. Among them are:
- Ear mites - otodectosis, a disease provoked by specific microorganisms, causes severe itching in the area of the external auditory canal. Provokes scratching and infection with secondary pathogenic microflora. A characteristic feature of ear scabies is the appearance of a specific plaque from the inner surface of the ear with an unpleasant, repulsive odor. Lack of therapy leads to generalization of the pathological process and the penetration of a secondary infection along the ascending path to the membranes of the brain.
- Sarcoptic mange is a pruritic scabies caused by the Sarcoptoses mite. The parasitic microorganism can affect any part of the animal’s body – ears, head, knee joints, and abdominal area. At the site of damage, specific papules form, darkening and coarsening over time. If left untreated, tumors appear on the body.
- Notoedrosis - caused by the Notoedric mite, provokes the appearance on the skin in the muzzle area (nose, brow ridges, back of the head). Causes severe itching, provokes inflammation and easily spreads throughout the body. Notoedrosis is also dangerous for humans.
- Demodicosis is caused by mites of the genus Demodex. Present on the skin of healthy animals, without showing its pathogenicity for a long time. With a decrease in the body's defenses and a sharp increase in the population, a pathological process occurs. Ticks begin to actively gnaw their own passages, affecting the skin in the area of the muzzle, neck and eyes. Lack of therapy leads to damage to the entire body, severe itching and alopecia.
- Cheylithiosis is a rarely diagnosed disease in cats, caused by the development of mites of the genus Cheyletiella. This disease is characterized by the appearance of flaking on the skin; sometimes in medical sources you can see the name - wandering dandruff. The disease, provoked by microscopic mites, provokes thickening of the affected area of the skin, leading to severe itching and a general discomfort in the animal. A person can also get the disease. Cheyletiosis causes peeling skin and itching.
Types of ticks
Scabies in cats is caused by the following types of parasites:
- Ear mite. It becomes the cause of a disease called otodectosis. Insects are usually localized on the inner surface of the ear, gradually occupying the entire ear canal. As a result of severe itching, the cat constantly shakes its head, scratches its ears, and meows pitifully. A dark brown coating forms on the auricle, and a putrid odor is felt. If untreated, the pathological process affects the inner ear, and the possibility of damage to the meninges cannot be ruled out. This type of parasite is not dangerous to humans.
- Mite S provokes the development of sarcoptic mange (pruritic scabies). The parasite can be found on any part of the body - on the ears, stomach, knee, elbow joints. The skin at the site of the lesion becomes covered with papules, turns black, becomes thick, rough, gradually leading to the appearance of a neoplasm.
- Notoedric Mange is a mite that causes notoedric mange. The disease, which often occurs in young cats, is also dangerous for humans. Rashes in the form of papules form first near the brow ridges, on the nose and back of the animal’s head. Gradually, when scratching the affected areas, the parasites are spread throughout the body. The disease is easily transmitted to other animals and humans.
- Mites D Their presence in the sebaceous glands, hair follicles of cats and cats does not always lead to the development of the disease. Pathology occurs when there is a significant increase in the number of parasites, when the immune system is unable to cope with the control of them. By intensively gnawing passages in the epidermis layer, mites cause the disease demodicosis. Infection is added to skin lesions that occur on the face, neck, and areas near the eyes. The disease is contagious to humans who come into contact with a sick animal.
- Cheyletiella mites are a rare species of parasites that live on the surface of the skin. They provoke a disease called cheyletiellosis (wandering dandruff). Numerous scales resembling dandruff form on the animal's skin. The disease is accompanied by hair loss and thickening of the skin in the affected area. Capable of being transmitted to humans.
Treatment of scabies in a cat depends on the type of pathogen and the degree of damage. To establish an accurate diagnosis, your pet must be shown to a specialist.
Treatment of scabies
Treatment for mange in cats is almost always possible at home. Only in the most severe stages does the doctor recommend hospitalization. For treatment, both injections and ointments, various drops are used. Only a qualified doctor should prescribe drugs, because injections and ointments are extremely toxic not only to parasites, but also to the animal itself.
An affordable and easy-to-use method of treating your pet for scabies. For this purpose, sulfur-based preparations or aversectin ointment are used.
Before application, it is necessary to clean the skin of hair and secretions, put a cone collar on the animal in order to prevent the licking of toxic drugs and to calm the animal. Dermatological shampoos are perfect for preparing the skin for treatment; when washed, keratinized scales, discharge and hair adhering to them will come off from the skin. After washing, the animal should be dried, then apply the drug to the affected areas of the skin. Repeat the treatment 2-3 times a day, depending on the stage and doctor’s orders.
Drops on the withers
Most often they are used in conjunction with any other drugs, because do not relieve inflammation.
Any drops aimed at combating ticks are suitable for treatment. The drug should be applied to the cat's withers. After spreading the fur, place the required number of drops on the skin and wait for it to spread. It is best to use a cone collar when treating in this way; the drops are toxic to the animal. Do not allow the drug to be licked from the fur.
Drops in the ears
Drops in the ears are used if the cat has otodectosis and the ear canal is affected. The tick leaves a brown discharge on the pet's ear, and you can often smell a foul odor from this discharge. For effective treatment, first of all, the owner must clean the ears of his pet with a cotton swab from crusts and wet discharge. Then, drops are instilled into the ear canal in accordance with the instructions and recommendation of the doctor.
The most dangerous treatment method for the animal, since due to its low weight it is easy to miscalculate the dosage. All veterinarian recommendations must be strictly followed!
For injections, drugs based on ivermectin are used. The drug disrupts the nervous activity of the parasite, causing its death. The course usually lasts no more than a week.
Antibiotics
A number of antibiotics are used in the treatment of secondary infections developed against the background of scabies. They are prescribed exclusively by a doctor, since in most cases there is no need to use them. The choice of drug and dosage depends on the weight of the animal and the type of infection.
Drugs to stimulate the immune system
They are used to maintain the general health of the animal while fighting ticks. They are used in the form of injections, the dosage is calculated based on the size of the animal.
Aids and devices
To treat scabies in cats and other animals, the main assistant for the owner will be a cone collar, which can be purchased at pet stores or veterinary pharmacies. A collar is really necessary for treatment due to the fact that most drugs can cause serious poisoning in a pet if he licks them from his fur.
Animal shampoo will be another helper. Washing once or twice a week will help clear your pet's skin of scabs, discharge, and dried hair before applying ointments or drops.
Treatment of notoedrosis in a cat
Since notoedrosis is contagious, after confirming the diagnosis, it is necessary to immediately isolate the sick animal to prevent the spread of the disease . Then the hair in the lesions is trimmed to facilitate access and better effect of the medications. A sick cat is bathed using neutral soap or pet shampoo (preferably with acaricidal properties), and the soaked scabs are carefully removed with tweezers.
Before starting treatment procedures, the cat should be bathed
Only after this do they begin treatment directly, using the following drugs:
- Gels and ointments for external use, which are applied to the affected areas using a spatula or stick, capturing a little (no more than 8–10 mm) of healthy skin: Amitrazine (liniment and solution);
- Ivermek-gel;
- Demos (liniment);
- Amidel-gel;
- Neostomazan (oil emulsion);
- Neocidol (emulsion);
- novertine ointment;
- Sulfuric ointment;
- aversectin ointment.
Aversectin ointment for cats is used in the treatment of dermatological diseases caused by ectoparasites
It must be remembered that when treating notohedrosis, all treatments are used repeatedly. This is due to the fact that medications have a detrimental effect only on adult ticks; they do not destroy their eggs.
Liniments are a dosage form intended for external use only; It is a liquid ointment or a mixture of various irritating substances with oils, oils with alkali solutions, soap-water or soap-alcohol solutions.
If the degree of damage to the skin is large, then systemic drugs are used:
- drops on the withers (Stronghold, Lawyer);
- injections (Ivermectin, Aversect).
In severe cases of the disease, cats are given injections
It is also possible to use additional measures:
- If there is an associated infection, a course of antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin) and immunomodulators (Gamapren, Anandin) is prescribed.
- To relieve itching, the use of synthetic glucocorticoid drugs (Prednisolone) is indicated.
- As measures to strengthen the body's resistance, it is recommended to add vitamin and mineral complexes to the feed.
The exact dosage and frequency of use of all drugs is prescribed by a veterinarian, guided by the condition of the sick cat, since most of them are toxic, and an overdose (if self-medicated) is extremely dangerous.
In some cases, in the initial stages of the disease and very minor skin lesions, homemade ointments are used from:
- Vaseline and tar (9:1);
- green soap and tar (1:1);
- Vaseline and sedimentary sulfur (10:1).
The ointments are rubbed in three times, taking breaks of 5–6 days. But folk remedies for combating ectoparasites are ineffective, so one cannot place much hope on them.
Video: subcutaneous mites in cats
Treatment of sarcoptic mange in cats
A severe form of the disease, which quickly provokes a deterioration in the pet’s condition. After contact with the skin, the mite gnaws small passages in the epidermis, where it can place up to five dozen eggs.
Sarcoptic mange poses the greatest threat to pet health due to the extreme activity of the mite
Within a few days they reach the larval stage, and after two weeks they can lay new offspring. The animal constantly suffers from itching, due to which it can die within a few weeks. Treatment uses one of the medications described below or a combination of them.
Stronghold
To eliminate sarcoptic mange, you should take a 6% concentrate. It is used on kittens and adult cats over 2.5 months of age. If the cat weighs less than 2.5 kg, the dose of the solution is 0.25 ml; for larger weights, dosages of 0.75 ml of concentrate are used.
Drops of Stronghold
The active substance must be applied strictly to healthy skin, choosing an area closer to the base of the neck. Taking into account the pet’s condition, the treatment is repeated after 2-4 weeks.
Levomekol
An antibacterial ointment that protects your pet from secondary infection and allows the skin to heal and remove inflamed and purulent areas. Levomekol should be applied to the affected areas in a small layer.
Levomekol effectively fights microbes and heals complex wounds
If large areas of skin are affected, you need to spread the ointment over a bandage and fix it on the animal. Shoot daily. Antibacterial ointment against scabies should be used for 5-10 days.
Butox
Available in small capsules for preparing a bathing solution. To eliminate scabies, you need to use a type of drug Butox 50. The dosage of the medication, regardless of the age and condition of the animal, is 1 ml per liter of warm water.
Butox in ampoules
The resulting emulsion should be used to thoroughly bathe the sick animal. Repeated treatment is carried out after a week. If it is difficult to bathe your pet or there are no conditions for this, you can spray the solution over the fur and skin. The dose of the active substance and the number of repeated applications do not change with this treatment.
Demos
It is also prescribed for the treatment of demodicosis and notohedrosis, and is available in the form of liniment. It is necessary to apply the drug using a cotton swab at the rate of 0.1-0.3 cm3 per 1 kg. For severe lesions, the treatment is repeated every other day.
Demos copes well with various types of parasites, but it is not recommended to apply it to extensive wounds
If the pet's condition is relatively normal, repeated treatments are done at intervals of five days 2-3 times. Do not use on very young kittens or nursing cats.
Attention! Butox 50 shows a good effect against scabies mites of any type. But it is strictly not recommended for use on large open wounds.
Treatment of ear scabies in cats
The disease is quite easy to treat if you choose the right drugs and combine them correctly in the presence of associated problems in the form of suppuration. For treatment, you first need to thoroughly clean your pet’s ears from accumulated crusts and dirt.
Remember that cats' eardrums are very delicate.
To do this, you can use ordinary sunflower oil, which is used to treat the outer and inner parts with a cotton swab or disk. It is important to do everything as carefully as possible so as not to damage the animal’s hearing. After treatment of the ear canal, medications are used to suppress ear mite activity.
Video - What ear mites look like on a cat
Barrier
Used for the treatment and prevention of ear mites. Treatment is carried out in three stages every 8-10 days. The dose of the active substance is selected taking into account the weight of the cat. The drug has a strong effect, so it is used with caution on kittens up to 12 weeks.
Example of packaging for flea and tick drops
The therapy involves applying 0.5-1 ml of the active substance for animals weighing up to 10 kg per ear. Drops are applied to the inner skin of the ear and gently rubbed.
Amitrazine
The drug is available in the form of drops and can cure even advanced cases of otodecosis. The medication must be instilled using a special pipette included in the kit. Treatment involves a dose of 0.5-1 ml of the active ingredient in each ear.
Amitrazine drops
At the same time, for better results, it is recommended that after using Amitrazine, lightly massage the sore spot, folding the auricle in half. Treatments are carried out 1-3 times every 5-7 days, taking into account the severity of the violation.
Deltamethrin
Antiparasitic powder, belongs to the second generation. When treating ear mites, it is necessary to prepare a solution for instillation. To do this, take 0.3 g of powder for every kilogram of the cat’s body.
The required dose of deltamethrin is calculated depending on the pet’s parameters
After preparing the concentrate, 1 ml is instilled into each passage and massaged well. The treatment must be repeated after two weeks. If necessary, Deltamethrin is used 2-3 times at the recommended time interval.
Ordermil
A powerful anti-mite medication that additionally has an antibacterial effect and accelerates wound healing. For treatment, you need to put Oridermil gel into each ear and evenly distribute the active substance over the diseased areas. Apply the ointment 1-2 times a day, every other day. The recommended course of therapy is 10 days. For less severe scabies – no more than six days.
An example of Oridermil ointment packaging
Hydrogen peroxide is used to eliminate purulent lesions on and near the ears. It requires treating sore spots up to five times a day using a sterile stick or disk. In severe cases and infection, the doctor decides to prescribe an antibacterial ointment. The usual Erythromycin and Levomycin are suitable for this. They should be applied in a thin layer every day for no more than five days.
If there are animals in the house other than the infected pet, treatment is prescribed to all
Attention! With odecosis, it is necessary to treat both ears of a sick cat, regardless of whether there are signs of damage on it. If there are other animals in the house, they also require drug treatment as a single application of the selected medication.
Basic principles of treatment
When a diagnosis of scabies caused by microscopic subcutaneous mites is confirmed, the veterinarian prescribes a treatment regimen individually selected for each pet.
Being an infectious disease, treatment of scabies in cats includes a whole range of therapeutic measures.
The main thing is to eliminate the cause of the disease, that is, to destroy the parasite.
For this purpose, antiparasitic drugs are widely used, which have a detrimental effect on the vital activity of ticks:
- Albendazole;
- Benzyl benzonate;
- Permethrin;
- Esdepaletrin;
- Lindan;
- Amitrazine.
Medicines for scabies for cats are selected individually, depending on the type of microorganism and the degree of damage. An important role is played by the dosage of the active substance, calculated according to the weight and age of the pet.
Treatment of ear scabies in cats includes the use of special drops that are instilled into the external auditory canal after preliminary hygienic cleaning.
The course of therapy is prescribed by the attending veterinarian. In addition to the main treatment, there is also symptomatic therapy to eliminate the manifestations of the pathological condition. So, to strengthen the body's defenses, immunostimulating drugs are used.
Elimination of itching and inflammation is done through the use of systemic antihistamines or ointments for external use with glucocorticosteroids.
The presence of secondary bacterial microflora implies the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics prescribed for a course of at least 5 days. Complex therapy also includes the use of vitamin and mineral complexes to ensure a complete and balanced diet.
Treatment of scabies in cats at home is possible, but it is still recommended to consult a veterinarian and combine traditional methods with pharmaceutical drugs. To eliminate itching in a cat, you can make a special decoction of buckthorn bark. They wipe the skin with it several times a day. A mixture of crushed bay leaves mixed with butter has the same effect. The paste is applied to the skin of the animal 3-4 times a day.
You can treat scabies with home methods only to improve the condition of the skin and eliminate itching. It is not possible to identify the root cause - the scabies mite - using these methods.
Treatment of scabies mites in cats
Therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating symptoms, destroying the parasite, and strengthening the immune system. Professional preparations for scabies mites are produced in the form of drops, tablets, ointments, creams, lotions, and sprays. Means to enhance the body’s protective functions – Gamavit, Tetravit. The dosage is selected individually. The choice of specific antiparasitic agents depends on the type of scabies mite.
- Lime sulfur (LymDip). The solution is applied once a week. The course consists of 6 procedures. To increase the effectiveness of the drug, the hair is cut off in areas of greatest infection. Before treating your cat with gray, it is recommended to wash it with keratolytic shampoo. The cost of sulfur is from 10 rubles.
- Ivermectin (Ivomec). The drug is used daily for 5 days. The cat makes a full recovery within a month. Price from 400 rub.
- Amitraz (Mitaban). Treatment lasts 2 weeks, the product is applied 8 times during this time. It causes a number of side effects, so it should not be used by sick, weakened animals or kittens. The cost is within 40 rubles.
- Selamectin (REVOLUTION). An avermectin-based drug that is completely safe for cats. It is quickly absorbed and relieves symptoms almost instantly. To get rid of scabies and destroy the scabies mite, 1 treatment is enough. Price about 300 rubles.
- Benzyl benzoate emulsion. Rub into the affected areas of the skin every 3 days for 2 weeks. Elimination of unpleasant symptoms occurs after the first procedure. On average 100 rubles.
Treatment of scabies mites in cats
On a note!
Stop Itching is prescribed as an additional therapy. Produced in the form of a suspension. Normalizes sebum production. Inject with a syringe without a needle into the cat's oral cavity. For ear scabies, drops for cats Ivermectin, Acaromectin are dripped into both ears, and Otoferolone and Stronghold are applied.
More about mange in cats
Scabies can cause a lot of inconvenience for both the pet and the owner.
The insect chooses a habitat in the inner layer of the cat’s skin, where it actively adapts. Migrating in the inner layers, it makes its way, thereby injuring the inner layer of the epidermis - the subcutis. It feeds directly on subcutis particles and lymph.
The most common localization is observed in the neck and head. Making passages in the stratum corneum, female insects lay eggs there, with a total of up to eight eggs per day. Over the entire life cycle, the female is capable of producing about twenty pieces. The insect's lifespan is approximately twenty days.
Can you get scabies from a cat?
Scabies is transmitted from animal to person.
Animals that have not undergone sanitary treatment against external parasites are most susceptible to infection. The parasite can live on a person's arms, legs, thighs, chest and stomach. The disease can be easily cured by contacting a dermatologist, but it can still cause a lot of unpleasant moments.
Main symptoms of mange in cats
Scabies can be recognized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- severe hair loss in areas where scabies mites are concentrated, most often the paws, stomach, eyebrows, eyes, nose, area around the mouth and nose;
- Gradually, the foci of tick-borne infestation become larger and begin to merge with each other, forming bald spots and bald spots;
- Vinegars cause the formation of papules filled with a thick, colorless or white substance;
- around the papules the skin is red, sensitive, and serious purulent lesions appear;
- After their rupture, painful and purulent crusts appear on the papules, the epidermis becomes covered with scales;
- the itching is constant, which causes severe aggression in the cat;
- lymph nodes are additionally enlarged.
Scratching irritated areas of the cat in the worst case leads to blood poisoning
Attention! Due to the appearance of purulent foci after constant scratching of scabies wounds, the infection that enters the body in some cases becomes the cause of blood poisoning, which leads to death through the painful death of the pet