General information about ticks
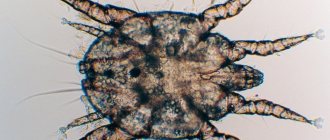
A tick is a blood-sucking insect that is a carrier of various deadly diseases.
The parasite's body produces an anesthetic substance that helps hide the moment of the bite. Through a wound caused by an infected insect, bacteria and viruses enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the human body. Ticks are most active in spring and summer. Habitats: mountains, forests, areas with tall grass. Ticks can also bite pets.
Why are they dangerous?
The main danger of ticks is that they harm human health. Ticks are ectoparasites and causative agents of natural focal diseases. Pests are capable of transmitting various pathogens through the process of sucking blood.
Diseases
The most common diseases carried by ticks are borreliosis, ehrlichiosis and encephalitis. Infections are severe and can cause disability. As a rule, the diseases are chronic in nature and have a long rehabilitation period of up to a year. In addition to the diseases listed above, ticks carry:
- spotted fever;
- tularemia;
- babesiosis;
- tick-borne typhus
The variety of linen mites is not a blood-sucking pest, but these insects are also dangerous to humans. Microscopic excrement of insects along with dust penetrates the lungs and provokes the development of allergic reactions. In combination with a cold, allergies can cause bronchial asthma.
Allergy symptoms
The manifestation of disease symptoms depends on the pathogen that enters the human body after an insect bite. Since pests carry a large number of diseases, each of them is characterized by individual symptoms. In particular:
- Borreliosis is characterized by the appearance of migraines, general fatigue of the body, fever, attacks of nausea and vomiting. The most pronounced sign of the disease is a rash on the skin in the form of a ring-shaped redness.
- Tick-borne encephalitis causes a sharp increase in temperature to 39 degrees. Other symptoms include muscle soreness, vomiting and migraines.
- Ehrlichiosis is characterized by a sudden increase in body temperature and chills, joint pain, and a feeling of malaise. In severe cases, a skin rash appears.
- Symptoms of tick-borne relapsing fever develop gradually over a couple of weeks. Primary signs are insomnia, lack of appetite and feeling weak. Subsequently, the temperature rises, pain in muscles and joints occurs, and a severe rash forms on the skin.
Why is a tick bite dangerous?
When attached, the insect pierces the skin of a person or animal with its proboscis and sucks out blood. In order to attach itself, the parasite selects the most delicate areas of the skin - the head, neck, armpits, lower back, abdomen, groin area. The bite itself is painless and may go unnoticed for some time. The effects begin to appear after about two to three hours. Appears:
- Weakness, lethargy.
- Shiver.
- Photophobia.
- Skin reactions (rashes and itching).
- Sore muscles and joints.
- The temperature rises sharply.
- Lymph nodes enlarge.
- Heart rate increases.
- A headache appears.
In addition to the listed symptoms, you may experience:
- Dizziness.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath.
- Hallucinations.
If you experience even one of these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
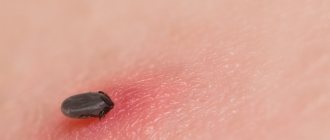
The area around the bite is pink or red, in the center there is a noticeable depression deep into the skin. The bite itself is not dangerous to humans; only the infected insect poses a threat.
How to kill a tick
If the parasite has bitten, but there is no opportunity to go to the hospital to examine it for the presence of pathogens, then the parasite must be destroyed. But not every person knows how to kill a tick found on their body. The surface of the insect consists of a chitinous shell, which is quite difficult to crush with fingers, and during action it can slip out.
It is important to remember that squashing a tick with your fingers or fingernails risks transmitting infection. There may be cuts and cracks on the hands through which the pathogen can enter the body.
Crushing an insect is not as easy as it seems, and such an action is dangerous, so you should familiarize yourself with methods for safely removing it from the body, as well as methods for destroying it.
The tick should not be released into the wild, as it will continue to search for its victim. In order to properly destroy the parasite, you must use the following tips:
- if a parasite is found on the surface of clothing, it must be thoroughly treated with hot water and powder, since ticks die from high temperatures;
- place it in the microwave in a closed jar and heat for 5–10 minutes;
- crush it using a large stone, after sticking adhesive paper or tape on it;
- burn at the stake using a lighter or matches.
It is impossible to kill a tick with water, but if there are no other options, then the parasite can be flushed down the toilet. But you won’t be able to drown it; the parasite does not die in water, so vinegar or bleach should be used as a liquid. You can also kill the parasite using alcohol; to do this, you need to stick tape on the tick and lower it into a container with alcohol, cover with a lid and wait until the insect dies.
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to crush a tick with your fingers? If you find it on your body or clothing, you should not rush to crush it with your hands, as this is fraught with serious consequences. You should not touch the parasite with your bare hands, as there is a high risk of transmitting the infection. There may be cracks or scratches on the fingers into which the pathogen can easily enter.
When crushed, the contents of the parasite get on your hands, and without washing your hands, it can be carried into the eyes, mouth, nose or other mucous membranes. You can remove the tick using a cloth, napkin or container. The clothes where the parasite was sitting must be washed in hot water.
Ways to destroy a tick
If at the time of a tick bite a person is far from medical facilities, and there is no way to transfer the parasite to a laboratory for research, it must be destroyed. But not everyone knows whether it is possible to crush a tick after it has been found on a human body. The parasite is covered with a chitinous shell, and it is almost impossible to crush the tick with your fingers. During manipulation, it will slip between your fingers.
Important!
You can crush a tick with your fingernail, but then there is a high risk of being infected with the infected contents of its stomach and entrails. If there are microcracks in the skin of the hands and secretions from an infected tick get there, the virus can enter the human body.
Ticks
It is also impossible to leave an arthropod alive; it will continue to search for its prey. Therefore, certain methods will help to properly kill a tick without harming others:
- ticks must be burned on fire - to do this, you need to squeeze it with tweezers and set it on fire with a regular lighter or match;
- It is very difficult to drown a tick in water, but if there are no other options, then you need to drown it in the toilet, flushing the parasite down the drain;
- It is unlikely that it will be possible to crush an arthropod with your foot, but it can be crushed with a stone, having previously been wrapped in adhesive tape or tape;
- A regular microwave will help exterminate ticks if you place the parasite inside a closed container and heat it at maximum power for several minutes;
- If mites are found on clothing, it must be washed with powder and placed in a dryer, where the parasites will die at high temperatures.
How to get rid of a parasite on the body
The tick is a dangerous insect that can cause serious harm to human health. It can cause infection with the following diseases:
- ehrlichiosis;
- tick-borne typhus;
- borreliosis (Lyme disease);
- tick-borne encephalitis.
Having found a vulnerable spot, the parasite inserts its proboscis into the skin, then its jaw and dives deep with its head. If removed incorrectly, there is a risk of damaging the insect and leaving the head buried under the skin. During the rupture of the body, its contents enter the human body along with the existing infectious agent. For the same reason, you should not crush the parasite with your hands.
It is not recommended to use kerosene or oil to extract the insect; if there is a lack of oxygen, the parasite can release infected fluid into the wound.
How to remove a tick if it is deep in the skin? There are several safe and easy ways to remove the parasite, these include:
- Pull it out using a curved hook tool. To do this, you need to pick it up with your teeth and carefully pull out the body without pressing on it.
- Make a loop from the thread, drape it over the parasite’s body and pull it out with swaying movements.
- Removal with tweezers is not always successful, since there is a risk of crushing the tick. It is necessary to grab the body with a tool and, without pressing movements, twist the insect out of the skin.
- Removal using a syringe. Take a thin syringe and cut off its tip, place the resulting hole tightly against the skin and pull the plunger towards you, after which the parasite will be removed (the method is quite controversial).
Or do this:
It is worth remembering that after the tick is removed from the skin, you should not touch it with your hands, since discharge containing infection remains on its surface and proboscis.
The parasite must be removed using a napkin or cloth, then it should be inspected for the presence of all parts and the absence of damage, particles of which may be in the wound.
Removing a tick from the skin does not cause pain; many people note the appearance of unpleasant sensations, itching and burning. If the tick is removed soon after it has been bitten, the affected area may be slightly numb under the influence of the anesthetic released by the tick. Therefore, during the removal of the parasite, a person does not feel pain.
How to remove ticks at home. How to properly and safely remove ticks from children and adults: 6 ways
I was bitten by a tick: action plan
A tick attached to the skin is difficult to ignore. In addition to the fact that its bite causes pain and discomfort, it is very dangerous, because ticks carry dangerous diseases: viral encephalitis, Lyme disease, tularemia and others. In this article we will tell you how to properly remove a tick, what to do with it, how to treat the wound, what consequences to expect and what to do to prevent the bite from happening again.
Signs of a bite, what a sucking tick looks like
Most often we do not feel the moment of a tick bite. It is painless, as the tick secretes an anesthetic substance into the wound. Therefore, usually the only signs of a bite that can be seen are the bloodsucker itself (Fig. 1) or the area where it bit. Sometimes those bitten feel pain and difficulty breathing, and some develop rashes or blisters.
Where to look for a tick?
Ticks stick to places where they are difficult to notice and where the skin is thinner. After a walk in nature during tick season, be sure to inspect yourself, paying special attention to:
- areas covered with hair
- area behind the ears,
- armpits,
- abdominal area,
- inner thighs,
- areas under the knees.
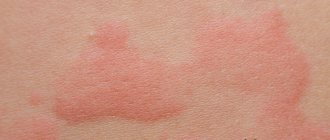
After the tick falls off, the site of its attachment bleeds slightly, gradually turning into a rounded red spot. It increases in size and itches. As it expands, the picture changes. The center of the bite becomes bright red or bluish, and a red spot forms around it due to inflammation.
If a parasite is detected, you need to remove it as quickly as possible and consult a doctor. It is worth going to the clinic if you find a suspicious wound on the skin.
How to get a tick and how to treat the bite site
If a tick has attached itself, it is best to consult a doctor as soon as possible. He will professionally remove the tick and treat the wound. However, a long search for a specialist can increase the likelihood of transmitting various infections from ticks. Therefore, it is often wiser to remove the tick yourself immediately after discovering it.
The first step is to treat the bite site with any antiseptic that you have on hand. Then use tweezers or strong thread to grab the tick as close to the surface of the skin as possible. This is necessary in order to remove the entire tick along with its oral apparatus. The tick must be removed with uniform, moderate force, strictly vertically, without sudden movements or twisting (Fig. 2). After removing the tick, treat the bite mark with an antiseptic again.
Be careful not to damage the tick while removing it from your body. If there are still fragments of it in the wound, do not be alarmed. After some time, the remains of the arthropod will come out of the skin on their own.
If you can't find tweezers, you can try to remove the tick with your fingers, but it is better not to crush the tick with your bare hands. To protect your skin, use a bandage or rubber gloves. You can first wrap the tick in gauze. After the tick is removed, do not forget to wash your hands with soap, or you can wipe your hands with alcohol.
Important! Some people are sure that the tick will crawl out of the wound on its own if you pour vegetable oil or other fat on it. The tick will simply have nothing to breathe. However, doctors do not recommend using this method. Due to blockage of the respiratory tract, the tick may die, having previously released substances into the wound, possibly containing the causative agent of the disease. A lit match is also useless; it will only cause the tick to burrow deeper.
Unfortunately, if you have not been vaccinated, once you have been bitten, it is no longer possible to prevent the disease. As a preventative measure for borreliosis, if the tick has been swollen with blood and there is a suspicion that it has been on the body for at least 24 hours, doctors advise adults and children over 8 years of age to take 4.4 mg/kg, but not more than 200 mg, of doxycycline.
What to do with a tick
Methods for diagnosing infections transmitted by ticks include examining the tick for the presence of pathogens (tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis).
A tick removed at home can be saved in case the doctor asks for it for examination. In this case, place the tick in a glass container with a lid and place a damp cotton wool in it to create increased humidity. Place the container in the refrigerator.
Important! Don't worry if you couldn't save the tick. Post-contact prophylaxis in the event of an infection in a tick is possible only for borreliosis, however, it is indicated for all patients, regardless of the result of the “dispensary examination” of the tick, provided that the tick was on the body for more than 36 hours (this is the time required for transmission of the infection).
Ticks and how to deal with them: folk remedies
It is useless to fight ixodid blood-sucking ticks in the garden, vegetable garden and grass with folk remedies. On the Internet you can find rare mentions of garlic or vinegar solution, birch tar, essential oils, but in any case, trying to destroy ticks with their help throughout the entire area will not work. The maximum that such homemade products are capable of is to scare away pests from any small area in the garden, but even that is not a fact.
Natural ingredients and improvised means are much more often used to prepare repellents that are applied to clothing, the body or equipment. All of them are water-based, poured into a spray bottle and applied as a spray to clothing and garden furniture.
- Water (2 cups) + 9% apple cider vinegar (2 tablespoons) + neem oil (2 tablespoons).
- Eucalyptus oil (20 drops) + water (2 cups).
- Citronella oil (9 drops) + tea tree oil (6 drops) + mint oil (6 drops) + water (2 cups).
- Orange/grapefruit oil (10-12 drops) + 2 glasses of water.
How to remove a tick correctly and what to do with it?
If you see a tick on your skin or in the fur of a cat or dog, it should be removed using tweezers or thread. Use the sharp edges of tweezers to grab the insect's head and pull without making sudden movements. While pulling, you need to rotate the tweezers around its axis. Do not use a tool with wide edges. It can destroy the insect's body and squeeze out liquid from it. Also, watch the pressure, you don’t need to be too zealous.
You should not crush ticks with your hands, fingers and nails, or apply nail polish; this can cause the parasite, under stress, to release much more saliva into the wound, and this will increase the risk of infection.
If you don't have tweezers at hand, use a regular thread tied like a lasso. The ixodid tick is grabbed with a loop and turned counterclockwise.
There are also special hooks that are sold in pharmacies. They grab the tick closer to the skin and pull it up. At this time, it is advisable not to press too hard on his abdomen.
Do not drop oil or kerosene . Firstly, the parasite, sensing a lack of oxygen, will weaken its proboscis, which will cause the contents of its stomach to enter the wound, and with it the infection. Secondly, then it will be difficult to remove it, since the tweezers will begin to slide over the body. On top of that, kerosene can cause an allergic reaction.
You can also wrap the tick in duct tape. It is wrapped on all sides with tape and left for a while. The insect dies from lack of oxygen. It is then removed with tweezers or thread. This method is not very correct, just like processing with sunflower oil, so we do not recommend using it.
There is a way to remove the parasite using a regular syringe. It is purchased at a pharmacy and the end where the needle is inserted is cut off. The resulting hole is placed at the site of the bite, and the piston is pulled several times. After the manipulations, the insect crawls out of the wound on its own.
This method is not suitable for removing ticks from the hairy part of the body, for example from the head and from a pet. A hair or six will not allow you to create a vacuum in the syringe.
After the procedure, the bite site must be disinfected and examined. If its head remains in the wound, it must be removed with a disinfected needle, like a splinter. If you lack confidence in your abilities, it is better to consult a doctor.
When the parasite is completely removed, hands and the bite site should be thoroughly washed. Afterwards, wipe the wound with medical alcohol or iodine solution. If you don’t have these remedies on hand, use vinegar or vodka, this will reduce the likelihood of infection.
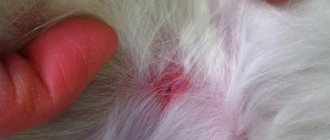
Removing ticks from pets
If a cat or dog has been bitten by a tick, tweezers or thread will also work in this case. Be sure to remove the entire parasite from the skin of the animal, otherwise its remains may lead to suppuration or cause inflammation.
When removing a tick from an animal's skin, be sure to wear gloves. The bite site will need to be lubricated with brilliant green or iodine. If the tick has been in the animal’s body for a long time, it becomes easier to pull it out; it will happily fall off on its own. After removing the tick from the cat, wash it with zoo shampoo, check the wound for the presence of particles of the proboscis or head of the tick, remove it and treat it with an antiseptic. There is no need to use any bandages.
How to remove a tick correctly
(Video
: “How to properly remove a tick”)
If removed carelessly, the tick's head may remain under the skin.
In this case, a sharp needle, previously heated over a fire, is often used. However, if you have never done this, this option is unlikely to work. Quite often, remains of the head remain under the skin and begin to rot. If part of the head is on the surface of the skin, you can try to grab it with a loop of thread and then twist it out. You can also use small tweezers that can grab the head and twist it. There is an opinion that the tick should be twisted in a certain direction. But that's not true. The insect's trunk does not have a thread, so the thread can be twisted in any direction. This is done in order to carefully pull out the trunk, which clings to the skin with the help of small antennae. If you simply pull the thread, the insect's body will come off, but the head will remain inside.
This method may seem effective, given the structural features of the tick's respiratory organs. They are located at the back. By lowering its head into the wound, the respiratory organs remain on the surface of the skin, so the insect breathes without problems. When using oil, breathing is blocked, which forces the tick to crawl out. Everything seems to be correct here, but this option has negative consequences.
Precautionary measures
When going on a hike, you need to pay attention to your clothes. For example, pants should be tucked into shoes
You can use trousers and a jacket that have thick cuffs on the legs and sleeves; wear socks and shoes, scarves or high-necked clothing. It is advisable to wear gloves on your hands. Of course, in the summer heat this will look stupid, but it’s worth remembering that ticks are attracted to all exposed areas of the body. To avoid being hot, you can wear thin cotton clothes; Be sure to wear a cap or panama hat. It is advisable that the headdress have wide brims, which will provide more reliable protection; do not forget to use various ointments and sprays designed to repel dangerous bloodsuckers;
Consequences of crushing a tick
After extraction, the tick will naturally go in search of food to find a new victim. You can destroy it by crushing the tick with your fingers (nail), but you should take into account the danger of splashing the contents of the gastrointestinal tract. If it gets on unhealed wounds, scratches or microcracks, there is a risk of infection.
The insect's chitinous cover is highly durable, comparable in density to human nails, so crushing a tick can be quite difficult. To do this, use solid objects.
What is prohibited to do
There are very popular methods that are often used during removal. But it is worth saying that the actions listed below can significantly aggravate the situation and increase the likelihood of contracting dangerous diseases.
These include:
- Use of oils and kerosene. These methods are the most common in which the situation becomes most dangerous. The fact is that if you water a tick with such products, air will stop flowing to it, which will lead to its death. It would seem that this is a great solution, but no, it is a completely erroneous opinion. When it suffocates, such a stressful situation for the insect will lead to the release of a large amount of saliva, and as we know, such a process is extremely dangerous.
- A method such as gluing the insect with tape or adhesive tape is also used. The principle of operation is similar to the previous option, when the parasite suffocates, and accordingly, the result of such manipulations is extremely dangerous.
In addition, it is very important to avoid mistakes during the withdrawal procedure. It is forbidden to crush the insect, pull it out, pull it out with your nails or a needle. You cannot make sudden movements. All these actions damage the parasite and increase the chances of infection.
How to properly remove an attached tick from a person
As soon as the sun warms up and the grass begins to turn green, people flock to nature en masse. And here a person faces the danger of becoming a victim of an ixodid tick attack.
If such a situation occurs, and there is no medical facility nearby, then the rules for how to remove a tick from a person should help in field conditions.
Features of removing attached ticks
In order to understand how to properly remove a tick from a person, you need to have an idea of the structure of the parasite and the way it penetrates the skin to become saturated with blood.
The ixodid tick has a freely rotating head with a mouthpart attached to the body. Once on the victim’s body, it can crawl over the body or clothing for a long time, up to an hour, choosing a place suitable for a calm and safe “meal.”
Such “favorite” places on the human body are places with the thinnest skin and closely located blood vessels.
- Groin;
- Popliteal cavities;
- Elbow cavities;
- Armpits;
- Areas behind the ear;
- Temporal and occipital region;
- The scalp.
Having chosen a secluded place, the parasite attaches itself to it with suction cups on its legs and uses its proboscis to carefully and painlessly pierce the victim’s skin. Then it begins to twist the proboscis, plunging it into the thickness of the skin to reach the bloodstream.
As the body of the small spider becomes saturated with blood, it swells, increasing in size up to 10 times. By this sign, you can determine how long the bloodsucker has been under the skin - for a long time or has just penetrated. In any case, it should be removed.
How to properly remove a tick
As soon as the bloodsucker is detected, the best solution is to contact any medical institution, where a specialist who knows how to remove a tick will do it professionally and without consequences.
There they can take the extracted parasite for analysis to determine whether it has “rewarded” the victim with an infection. But if there is no such opportunity for a person bitten by a tick, then the insect will have to be removed independently.
Hand extraction
The riskiest method is to pull the parasite out with your hands, because there is a great danger of crushing or tearing the bloodsucker’s body, and then infecting a person, if this tick is a carrier of the infection, becomes much more likely. But nevertheless, they most often resort to it forcedly, when they do not have suitable tools with them.
- It is necessary to wrap your fingers not around the body itself, but at the place of articulation with the head, which is already in the subcutaneous layer;
- You need to grab it carefully, as close to the skin as possible;
- With several rotational movements, as if unscrewing a screw, you need to gradually remove the bloodsucker along with the head and proboscis so that there are no remnants of the spider under the skin;
- If there is a natural disgust towards the insect, you can wrap your fingers with a handkerchief, gauze or bandage;
- After removing the attached parasite, the affected area must be immediately treated with any available antiseptic.
If possible, it is better to place the extracted bloodsucker in some container with a lid and deliver it to the hospital within 2 days for analysis in order to examine the presence or absence of pathogens of serious diseases in it.
Extraction with tweezers
This method is suitable in case of quick detection of the parasite, when its size is too small to be removed with your fingers. This also has its own deletion rules.
- In the same way, you need to grab tweezers not by the body, but near the skin itself, and with careful rotational movements, unscrew the entire tick.
- It is better to place the tweezers parallel to the skin, and not at an angle or perpendicular.
- There is no need to pull or make sudden movements, and it is also unacceptable to squeeze the bloodsucker’s body itself. The probable rupture of the parasite promises serious troubles in the future - infection and suppuration of the bite site.
Removal by thread
This method is rightly considered dubious in terms of flawless results, since it requires skill and patience. Otherwise, there is a risk of the body being torn off from the head embedded in the skin.
- Take a strong thread or thin cord;
- A thread grip is made around the bloodsucker, at the very site of the bite;
- Then a loop is made;
- Using loosening, vibrating or twisting movements, the sucked bloodsucker is gradually removed.
If the parasite has just entered the body and its size is too small, this method is most likely not suitable, because most likely it will not be possible to tie a thread around a tiny spider and make a catching loop.
But if you have a magnifying glass, you can try, if you don’t have tweezers and the hospital is far away.
Extraction with oil
A simple, but at the same time, a risky method, questionable from a medical point of view. It consists in the principle of blocking the tick’s access to air and depriving it of the ability to breathe, which supposedly forces it to leave the victim.
- The ingrained parasite is poured with sunflower oil or any other oil that has a liquid fraction;
- To prevent the oily liquid from spreading, it is better to place a ring on the bite area and pour oil into its circle;
- After a few minutes, the bloodsucker should come out on its own, after which it must either be saved for analysis or destroyed.
Not always, as doctors state, the bloodsucker leaves the victim on its own. There are often cases when the parasite, deprived of the ability to breathe, dies, but before that it injects back the pumped blood along with saliva infected with infections.
How not to remove a tick
The above methods of extracting a tick that has ingrained itself into the skin have exhausted the correct ones.
Contrary to common recipes for getting out a bloodsucker using soap suds, gasoline, alcohol and other exotic means, doctors do not recommend resorting to them. And that's why.
- The bloodsucker dies from aggressive influences, remaining embedded in the human skin;
- But before death, it often relaxes its proboscis, and the blood it managed to suck on, along with saliva contaminated with possible infections, enters the victim’s bloodstream.
And then the risk of getting encephalitis or borreliosis increases many times over.
If it was not possible to completely remove the tick
Often, due to inexperience or because of panic, people pull out the tick, tearing its body protruding from the outside from the head buried in the thickness of the skin. What to do in such cases?
- The main thing is not to panic and calm down;
- Find a sewing or injection needle from a syringe, a pin, or any piercing sharp object;
- Heat it on a flame;
- Treat the place where the bloodsucker was just pulled out with any available antiseptic;
- Proceed as when removing an ordinary splinter;
- After removing the remains of the pest, thoroughly treat the wound with an antiseptic again.
If suppuration could not be avoided and the wound became inflamed, then do not worry! The remaining parts of the parasite will come out along with the pus, the skin will cleanse, and the bite site will heal.
Prevention of bites
To avoid attacks by dangerous arthropods on humans, measures should be taken to protect against them. Before you go for a walk in a park or forest, you need to dress properly. Cover your neck, arms and legs with thick clothing. When hiking in the forest, try not to shake tree branches and avoid tall grass.
To repel arthropods, you can use special products based on the chemical permethrin. It is toxic to blood-sucking insects and parasites. Taking measures to protect yourself from ticks will help you avoid direct contact with them.
How to kill ticks on pets and clothes
Today, a wide variety of herbal and chemical products are available on the market to help remove these insects from pets. But some of them can be dangerous for young animals or children playing with them, so it is recommended to consult a veterinarian first, if possible.
You need to choose a product that is intended for specific animals (for example, dogs or cats).
It is not recommended to use preparations containing organic phosphates. Before purchasing, you need to check whether the composition contains amitraz, permethrin, fenoxycarb, tetrachlorvinphos, propoxur.
How to kill ticks on clothes?
- First you should put it in the dryer. Dry hot air will kill almost all insects. After this, the clothes must be washed and dried again.
- Spray things with Permethrin. This chemical can kill ticks faster than other insecticides. In addition, it is relatively safe for humans.
Tick bite prevention
- When going for a walk in shelterbelts, forests or bodies of water, you need to know one rule: to attack, parasites choose those places on the body from which it is easiest to reach the human circulatory system. It is important to take care of clothing that covers the neck, groin, and armpits. It would be good if it was made of thick fabric. It is recommended to choose closed shoes.
- To repel ticks, it is advisable to treat clothing and body with special products.
- When walking through the forest, do not tear off branches or deliberately pull them away. With these actions you can shake off a lot of ticks.
- It must be remembered that you should not remove or crush discovered insects with unprotected hands. To do this, you need to use gloves (rubber or leather).
- If a tick has stuck, to remove it, you can try dropping iodine or any oil on it - the insect should fall off on its own in a few minutes.
- When you come back from a walk, you should definitely examine yourself, as you may not feel the tick bite.
If you follow the precautionary rules, your vacation will be completely safe and will only give you a good mood!
Removing a tick from a person at home
The main task on your part will be to prevent infection and avoid damage to the insect itself. It is quite possible to remove an already attached tick at home from a person:
- In any case, you will need a disinfectant. This is worth taking care of first;
- Next, decide what to use to capture the small parasite. After all, you can grab it with your thumb and index finger, or use tweezers. If you are squeamish or afraid of infection, or are not performing the procedure on yourself, it is better to get gloves or lightly wrap gauze bandages around your fingers;
- The capture should be made as close to the proboscis or skin surface as possible. In order to avoid reverse blood flow from the body of the parasite, the clamp should be made starting from the head of the insect.
Cautions
There are a number of precautionary measures that, when followed, can help prevent negative consequences:
- During trips to nature, you can use special preparations and products designed to combat ticks. However, before using them, you must carefully read the instructions, since some of them are intended for external application to the skin, while others are strictly prohibited from being used in this way.
- For long-term stops or outdoor recreation, it is better to choose forests consisting mostly of dry pine trees, as well as places with sandy soil or simply no grass.
- Donate blood for analysis after a bite only after a few weeks , since at an earlier period the diseases carried by these parasites cannot be diagnosed.
- Under no circumstances should you crush ticks or touch them with your bare hands.
How to remove a tick:
It is best to remove the tick with special devices that resemble a small copy of a nail puller, allowing you to grab it at the very base of the head and twist it, no matter which way. But you most likely don’t have this, because they are bought mainly by those who have already encountered tick bites and know what to do best.
Don't worry, a strong thread is perfect for removing a tick. Tie a loop around the head of the parasite and make several turns so as not to tear the tick in half with the thread. Holding the thread at an angle of 45 degrees to the bite site, begin to twist the reptile.
You can use small tweezers - grab as close to the skin as possible, on the head of the tick, under the abdomen.
Place the tick in a jar or other container suitable for transportation. Take your passport with you. If you have a medical insurance policy with you, take that too, just in case.
You need to get your tick tested right away: you have about a 4-day incubation period for tick-borne encephalitis to begin. Lyme disease (tick-borne borreliosis) is not so terrible, but in no case should you delay diagnosis and treatment.
In Moscow, tick testing for encephalitis, borreliosis and piroplasmosis can be carried out in two government organizations. Ticks are accepted for analysis on weekdays, from 9 a.m. to 4 p.m., and the results are ready the next day. There are rumors that there are parking problems at Grafskie Ponds.
How to fight mites on plants
In addition to ixodid ticks, other ticks – spider mites – can live on the site. Unlike their blood-sucking counterparts, they feed exclusively on plant sap. You can find them at:
- strawberries
- Tomatoes
- cucumbers
- Currant
- Gooseberry
- Malina
Sometimes spider mites can settle on coniferous plants and fruit trees. The main characteristic sign of their presence is a white web that envelops only the underside of leaves and shoots, or the entire sprouts. You need to fight spider mites in other ways, not the same as with ixodid mites, and folk remedies here can be very effective, unlike their use against blood-sucking mites.
- Neem oil.
Add 10–15 drops of neem oil to 1 liter of warm water and shake. The first time, apply the mixture liberally to the shoots with a brush. After 3 days, start spraying the infected plant with the solution weekly. Each time you need to prepare a new solution. You need to repeat the procedure throughout the summer season. - Soap.
Take a bowl of warm water, a soft sponge and soap. Both a bar and liquid soap are suitable, preferably with a minimum of ingredients and without fragrances. You need to wash the infested plant by hand in the same way you wash your body. Apply soap generously, latheringly and evenly. Then leave for 3-4 hours, then rinse thoroughly with a hose. Repeat as necessary. - Garlic.
Plants can be wiped and sprayed with a 5-day infusion of 1 liter of water and 2 heads of garlic. Garlic must be crushed to a mushy state before being placed in water. - Yarrow.
Pour a pack of yarrow herb (about 50 grams) into a saucepan, add water, boil and stir for 10–15 minutes. Leave the resulting infusion for a day. Wipe the affected shoots with the resulting infusion and periodically spray the entire plants. - Rosemary.
Mix 5-10 drops of rosemary essential oil with 1 liter of warm water. For the first time, wipe the infected plant, and subsequently spray it every 2 weeks.
To destroy spider mites, you can use special means, for example, such as:
- Aktara
- Green soap
- Inta-vir
- Iskra Golden
- Fitoverm
In the same way as with ixodid blood-sucking ticks, garden pests can be controlled with the help of professional SES treatments.
How to protect yourself from ticks and remove a tick after a bite
How to protect yourself from ticks while walking
When going to the forest or out of town, choose suitable clothes. If your stay in nature will be long and associated with work, it is best to use special anti-encephalitis suits. For short walks, light-colored clothing with long sleeves and cuffs is suitable - uninvited guests will be more visible on it. A hood that fits tightly to the skin will also not be amiss; it will protect the neck. It is best to wear high boots or high boots; trousers should be tucked into shoes. You should avoid staying in tall grass.
Stock up on anti-tick aerosols in advance. When purchasing, carefully read the instructions for use: some anti-tick products are intended for use on the skin, while others are intended exclusively for spraying on clothing.
Remember that, unlike mosquitoes, a tick bite is not accompanied by pain and therefore may not be detected immediately. The mite can remain on human skin for a long time undetected. Ideally, inspect clothing from bottom to top once an hour, and once every two hours it is better to inspect open areas of the body in case a tick has already bitten.
The most likely places to find ticks on the human body:
- earlobes and open neck area;
- chest and armpits;
- abdomen and lumbar region;
- arms, legs, groin.
An inflammatory process begins at the site of the bite, and a local allergic reaction in the form of rounded redness may appear on the skin.
What should I do if bitten by a tick
If you cannot avoid a tick bite, it is best to immediately go to the nearest emergency room or clinic. Doctors know well how to act in case of tick bites and will quickly provide help. Moreover, modern Moscow clinics today are comfortable medical centers, and medical care itself has become much better and more accessible.
If you are far away and cannot get medical help right away, you will have to remove the tick yourself. It is very important to remove it from the skin carefully and without sudden movements, so as not to crush it under any circumstances. The insect itself will need to be stored in a tightly closed box or jar in order to be sent to the laboratory for analysis.
The easiest way to remove a tick yourself is with tweezers. You can use a regular one or a special one, with a clamp, purchased at a pharmacy. If none of this is available, you will have to remove the tick with your fingers wrapped in gauze.
Grab the insect with tweezers or your fingers as close to the bite site as possible, rotate it approximately 180 degrees and carefully remove it from the skin. Disinfect the bite site with iodine, alcohol solution or hydrogen peroxide. Be sure to wash your hands with soap.
Don't worry if a black dot remains under the skin after removing the tick. Most likely, this is the proboscis of a tick; it is no more dangerous than a small splinter. It should not be removed by breaking the skin; it is enough to spot treat the wound with iodine solution.
Even if the tick was removed on its own, you should still see a doctor. He will check whether you removed the tick correctly and will issue a referral for a blood test, which will show whether you have been infected with dangerous diseases. Within 10 days after a tick bite, it is necessary to check your body temperature: even a slight increase in temperature may indicate infection.
Symptoms after a tick bite: how to recognize an infection
As a rule, signs of infection appear on average 2-3 hours after a tick bite in the form of chills, drowsiness, aching joints, and sometimes photophobia. Depending on the infection, symptoms of infection may include the following:
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- headache, nausea, vomiting;
- itching and rashes on the skin;
- severe tachycardia;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- hallucinations.
It is important to understand that inflammation from a tick bite may go away after a few days, but this does not guarantee a complete recovery. Some diseases become chronic and may appear several days after the bite. Here are the two main tick-borne infections .
disease (borreliosis) is characterized by a chronic course with relapses. This infection primarily affects the skin, nervous system, musculoskeletal system and heart. It manifests itself as an increase in body temperature in combination with migraines, chills, muscle and joint pain.
With Lyme disease (with the erythema form), the bite site appears as a specific erythema, which increases to 10-20 cm in diameter (sometimes up to 60 cm). The shape of the spot can be round or oval, sometimes irregular. After some time, a rim of characteristic red color forms along the contour. Subsequently, a crust and scar are formed. All these external manifestations disappear after a few weeks, and the disease becomes chronic.
It is important to remember that Lyme disease can occur without the appearance of erythema on the skin.
Tick-borne encephalitis is an infectious disease caused by damage to the brain and spinal cord by a flavivirus, transmitted to humans through the bites of ixodid ticks. Depending on the form of the disease, its manifestations are fever, headache, convulsions, vomiting, impaired coordination of movements, pain along the nerves, flaccid paresis and paralysis.
You can find out whether your dacha is located in an area where there are encephalitis ticks from a clinic physician or general practitioner. You can also get a referral for free vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis.
Link to publication: https://www.7ya.ru/article/Kak-zawititsya-ot-klewej-i-vytawit-klewa-posle-ukusa/
How to prevent bed mites?
Obviously, it is much easier to prevent dust mites from appearing in the house than to fight them.
You can minimize the likelihood of dust mites settling in your home if:
- regularly wash and clean bed linen and other things (outerwear, children's toys, etc.);
- iron bed linen or treat it with a steam cleaner;
- take mattresses, blankets and pillows outside and leave them in the sun;
- put a special cover on the mattress;
- vacuum upholstered furniture and carpets;
- periodically carry out wet cleaning to clean the house of dust (it is recommended to add a little salt to the water);
- During general cleaning, use special cleaning products.
When cleaning, you need not to be lazy and thoroughly rinse not only visible areas, but also hard-to-reach corners and cracks. It is necessary to try to remove all dust: the less there is, the lower the likelihood of pests appearing in the house.
If, however, it was not possible to prevent bed mites from settling in the house, then when parasites are detected, it is necessary to begin the fight against them.
Ixodid ticks on the balcony, in the apartment
In the warm season, another dangerous tick becomes active - the ixodid tick. It is dangerous due to the spread of deadly diseases - tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis. Lives in tall grass, on the lower branches of bushes. Found in the wild, among urban civilization.
If you find a tick at home or notice it on the balcony, it must be mercilessly destroyed. In the future, take care of protecting the premises. Treat the balcony with insecticidal repellents or a spray with essential oils. For 1 liter of water, 5 drops of geranium, lemongrass, eucalyptus, lavender or orange oil. Spraying with a home remedy should be repeated every 3 days during the parasite activity season.
If a tick has escaped at home, you need to vacuum the carpets, wash the floor, and carefully inspect the room using a magnifying glass. The arachnid can go without food for several months; the possibility of a bite if the parasite is not detected remains. It is recommended to treat the room with an insecticidal spray, leave it closed for 2 hours, ventilate, wash the floors and furniture with a soap-soda solution.
Why is it dangerous to have a parasite on the human body?
Ticks are potential carriers of dangerous infections. The bite itself is not dangerous to humans, but pathogens can penetrate the damaged tissue along with the insect’s saliva.
Moreover, the longer a tick feeds, the greater the likelihood of infection.
An insect can be a carrier of one or several infections at once, the most common of which are:
- encephalitis;
- borreliosis;
- ehrlichiosis;
- anaplasmosis
An increase in temperature is the body’s protective reaction to the tick’s saliva. If hyperthermia appears a few days after the bite, then this is the first sign of an infectious disease. In this case, failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner can lead to irreversible changes in the nervous system and even death.
Every year, 400 thousand Russians come to hospitals with complaints of tick bites, including 25% children under 14 years of age.
Sometimes the female mite lays eggs under the skin. But you should not be afraid of the appearance of offspring - the eggs will die after a while and form suppuration in the wound area.
What to do if the tick ruptures and the head of the parasite remains in the human body? In this case, you can resort to the following methods:
- Using thread. If a small part of the parasite remains on the surface, then you can use the method described above with a loop.
- Removal with a needle. You will need a regular sewing needle. It is pre-disinfected or heated over a fire. Then the remaining head of the parasite is carefully pryed with the tip (based on the principle of removing a splinter) and pulled out of the wound.
Ticks live in forests, parks and wooded areas. They search for their “prey” by smell, thus determining the approach of a person. The main danger is that ticks are very small insects; it is almost impossible to notice them in nature. Therefore, after each walk in the forest you need to carefully examine your skin and hair.
If you jerk sharply with tweezers or thread while pulling out a tick, its body will come off, and the head will remain inside the person. From the outside it will look like a small black dot, which is not always noticeable. The tick's head, of course, must be removed from the wound, and then treated with a disinfectant - hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green or iodine.
Some advise treating it like a splinter, that is, sterilizing an ordinary needle in alcohol and using it to pull out the tick’s proboscis, but it is better to seek qualified surgical help. If you have contracted a disease, it has already happened. And removing the tick head yourself can be fraught with the wound becoming suppurated. You can go straight to the emergency room, where the surgeon will make a small incision and remove the head.
Another advice that can often be found on forums is to leave the head of the tick in the body so that it later comes out on its own. In this case, the wound will fester and the proboscis will come out along with the pus, but this option is dangerous, especially if the tick is the causative agent of encephalitis or borreliosis.
After a tick bite and its removal, a small wound remains, which gradually heals. If an incision was made, healing will take longer. Treat the bite area periodically and try not to scratch it.
When trying to remove a tick completely, it is important to know what to do if the tick comes off and the head remains under the person’s skin, because it is with the help of the head, or rather the proboscis and jaws in it, that the tick is attached to the skin, “cements” the wound, thereby sticking tightly , and injects saliva into the blood - a carrier of dangerous infections. Many people believe that because the tick's salivary ducts remain under the skin, the infection continues.
Others believe that if a tick bites and the head remains, then there is nothing to worry about - that such a small foreign body can be compared to a splinter. And everyone agrees that leaving half the tick under the skin is unwise, because... if the proboscis or antennae of the tick remains under the skin, this can, at a minimum, cause suppuration or irritation of the skin
Many people believe that because the tick's salivary ducts remain under the skin, the infection continues. Others believe that if a tick bites and the head remains, then there is nothing to worry about - that such a small foreign body can be compared to a splinter. And everyone agrees that leaving half the tick under the skin is unwise, because... if the proboscis or antennae of the tick remains under the skin, this can, at a minimum, cause suppuration or irritation of the skin.
In any case, and especially if your region is considered dangerous for tick-borne encephalitis, you should consult a doctor after a tick bite!
Chemicals for home control
Effective extermination of pests in residential areas is possible with the help of highly active chemicals. A powerful effect on ticks repels or kills them, preventing re-invasion.
Bedlam Plus
Bedlam Plus is produced in aerosol form and is intended to combat ticks and their eggs, fleas, beetles, bedbugs and other harmful insects in residential areas. The substance can be used to treat bedding, carpets, upholstery and toys. The required surface is sprayed with an aerosol and then left for a couple of hours. After using Bedlam Plus, you should wash the treated product.
Acaril
Acaril is a component added during washing of textile materials. The product contains a mixture of alcohols, surfactants and tea tree oil in a suspension of methyl salicylate. The purpose of Acaril is to eliminate dust mites and combat allergens. The substance is safe for colored fabrics and produces results when washed in water of any temperature.
All-Rug
Highly concentrated All-Rug shampoo is suitable for treating carpets, upholstered furniture, mattresses and bedding. The product can be added to a washing vacuum cleaner. The main advantages of All-Rug include the following:
- slight foaming;
- anti-mite purpose;
- the ability to clean pile, eliminate insect allergens and prevent the proliferation of pests.
X-mite
X-mite powder is used to kill allergens caused by dust mites, pets and various pests. The optimal frequency of processing bedding, carpets and upholstery is once every 3-4 months.
Allergoff
Allergoff is available in a form designed to spray a surface up to 20 square meters in size. The aerosol ensures the destruction of dust mites at all stages of their spread. After treatment, the effect lasts for six months. Spraying with Allergoff spray must be combined with treatment with an anti-allergenic drug.
Tips and tricks
To summarize, we can give a few final recommendations that can help in some cases:
- You should not delay the tick removal procedure; this must be done as quickly as possible after detection. Even if an infected individual was caught, poisoning might not yet have occurred.
- Even in the absence of any side effects, seeking medical help and consulting a specialist are mandatory measures.
- If the tests were negative, but 2-2.5 weeks after the bite a sharp and severe increase in body temperature and severe headaches were recorded, then the person needs urgent professional medical help. In particularly advanced cases, such symptoms can lead to paralysis of some muscle groups or entering a coma.
- During family vacations in nature, it is necessary to teach children about ticks and the threat they pose, as well as inform them about basic safety measures. Accordingly, you yourself also need to avoid visiting potentially dangerous places.
Sources
- https://www.syl.ru/article/338648/kak-ubivat-kleschey-mojno-li-razdavit-klescha-paltsami
- https://hozzi.ru/uborka/kak-izbavitsya-ot-kleshhej
- https://kleshun.ru/kak-ubit-kleshha/
- https://Dezoff.ru/kleshhej/kak-borotsya-s-kleshchami/
- https://TaraKlop.ru/kleshchi/kak-ubit-kleshha/
- https://GdeKlop.ru/kleshchi/kak-ubit-v-domashnih-usloviyah/
- https://KlopVred.ru/kleshhi/kak-ubit-kleshha/
- https://apest.ru/kleshhi/kak-izbavitsya-ot-kleshhej/kak-ubit-kleshcha/
- https://obnaruzhil.ru/kleshh/kak-vytashhit.html
- https://domvred.ru/kak-izbavitsya-ot-postelnyx-kleshhej/
- https://apest.ru/kleshhi/kak-izbavitsya-ot-kleshhej/kak-izbavitsya-ot-kleshcha/
[collapse]
The sequence of actions after detecting a parasite at the site of the bite
If the tick has already attached itself and it turns out to be a carrier of the disease, it is most likely too late to panic. It is recommended to place the parasite in a sealed container and deliver it to the laboratory for analysis as quickly as possible. In practice, this is rarely used, since 1–2% of ticks carry the infection, and people have immunity.
The tick can be removed, and it is best to use special tweezers with sharp curved legs, or any other device that does not put pressure on the abdomen. After removing the parasite, you should check the wound to see if there are any parts of the tick's body or foreign fragments left. If there are any, squeeze them out. Then treat the wound.
For some time, you should strengthen control over the well-being of the bitten person. Signs of the disease may be:
- fever, chills;
- pain, pulling sensations in the muscles, twisting in the joints;
- dizziness and headaches;
- vomiting, nausea, diarrhea;
- enlarged lymph nodes, their pain;
- rash on the body, decay of the bite site.
If even one of the described symptoms occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor. Sometimes it takes up to 20 days for your health to deteriorate - the incubation period of some microbes is long.
When removing a tick, you should not experiment with Vaseline, alcohol, oil and other organic liquids. Parasites can remain in a comfortable state for a long time even with minimal access to oxygen - immersed in the skin. Oil will not kill or suffocate them, just like pressure. But flammable liquids, such as kerosene, can cause irritation and allergies.