Of course, no one wants to think about ticks. They are nasty creatures that spread disease. But that’s precisely why we need to think about them! Ultimately, ticks can spread diseases that lead to death. Another terrible disease is Lyme disease. This is the most common illness that parasites bring to humans. In short, facts about ticks are good for everyone - you can't ignore this topic! Study all the necessary information, because it can save your life in the future.
How the attack occurs
It’s worth immediately dispelling the main myth: ticks cannot fly. They simply do not have the adaptations for flight, as well as for jumping. But the main danger is different: they have very tenacious limbs. As soon as you touch the grass or bush where the tick lives, the parasite will immediately cling to your clothing and crawl.
An insect can fall on a person, but again, the height of its habitat is limited. Maximum - if you carelessly touch the bush. There are people who claim to have seen ticks flying. They are mistaken - there is an insect that is similar in appearance and properties to this parasite, but is not it.
Why are ticks and their bites dangerous?
Among the ixodid species living in the Russian Federation, 2 species pose a danger to humans:
- European forest, distributed throughout Europe, except for the northernmost regions, in North Africa and the European part of Russia;
- taiga tick, whose habitat is in the middle and southern taiga.
These parasites are carriers of dangerous infectious diseases: viral encephalitis, Lyme disease or borreliosis, ehrlichiosis, and some types of fevers. However, this does not mean that every tick that bites can infect a person.
Regions where there are the most ticks with a high risk of disease:
- borreliosis - Moscow and Moscow region, Krasnodar region;
- dangerous areas regarding encephalitis - the North-West of the Russian Federation, the Volga region, Karelia, the regions of the Central District, the Far East, the most cases are registered in Vladivostok and the region;
- hemorrhagic fever – Volgograd, Rostov regions, Caucasus.
According to Rospotrebnadzor, this year you can find regions where there are no encephalitis ticks in Russia. These are the central regions of the European part, including Moscow, Tula, Kursk, Oryol, Ryazan, Smolensk, Lipetsk, Tambov, Murmansk regions, Southern and North Caucasus federal districts, Magadan region, Kamchatka Territory, Yakutia and Chukotka.
Diseases from ticks
Mite with wings - description of the pest
The elk tick lives on artiodactyl animals, such as deer, elk and others. They often attack:
- bears;
- badgers;
- fox;
- wild boars;
- sheep;
- goats;
- cattle.
During an attack, the insect's wings break off and its legs are attached by hairs. That is why it is confused with a tick.
To avoid such a mistake, you need to remember exactly what the parasite looks like:
- Outwardly, it looks like a small light brown fly. The body size is no more than 3.5 mm. Moreover, males are smaller than females.
- It has an elastic soft belly. When eating or bearing offspring, it can easily stretch.
- He has 6 strong legs that grow from his chest. At the ends you can see small asymmetrical claws.
- The eyes have a faceted structure, and the antennae are located on the head. The insect's vision is quite poor, so it has to navigate the terrain and contours of its prey.
- Transparent wings are arranged according to the gods of the body. They are quite developed, but the insect is not capable of flying over long distances.
- It easily manages to pierce human or animal skin, as it has a piercing-sucking type of mouthparts.
Does the moose bloodsucker attack humans?
As practice has shown, people also become victims of insects. Most often, attacks occur in a forest or field during the day, when there is no wind. Therefore, shepherds, hunters and foresters are primarily at risk. Rapid activity of parasites occurs in mid-August and September.
A statistical study was carried out, during which it was revealed that the deer bloodsucker is attracted to large dynamic objects.
Let's celebrate! That's why they attack adults and are not interested in children. There are several cases when a person was attacked by just under 100 individuals in one minute.
How does suction occur?
As soon as the parasite has climbed onto a person, it begins to make its way under clothes and suck out blood. This does not happen immediately, but after half an hour. Basically, bloodsuckers try to get on the head, as there is an opportunity to catch on the hair.
Note! The parasite is quite difficult to shake off or remove. They can hold up even while running or in strong winds. The moose tick will remain on the human body until it accidentally falls off or is removed.
Danger to humans
Reactions to deer bloodsucker bites can vary. It all depends on the individuality of the human body.
The following consequences are observed:
- Mild discomfort that usually goes away after a couple of days.
- Severe pain syndrome, which is accompanied by itching, redness, burning and swelling. This may take several weeks.
- Dermatitis of various types appears. The mild form of manifestation is redness, and the severe form is rash, crusts and blisters.
Let's celebrate! Unlike an ordinary tick, this parasite does not cause serious harm to the human body, since it is not a carrier of encephalitis and other diseases.
Do ticks fly or not?
Forests and fields are inhabited by many insects. Among them there are particularly dangerous species that are carriers of various diseases.
In spring, their activity increases rapidly and nature lovers should be careful when going into the forest. Insects lie in wait for them near every blade of grass and twig. Ticks are considered the most dangerous because they can infect humans with tick-borne encephalitis or borreliosis.
Do ticks have wings?
Some people believe that flying ticks exist. But these insects cannot fly because they do not have wings. They are often confused with moose ticks.
It sheds its wings when it attacks a prey, clings to the hair with its paws and becomes like a simple tick. It is also known as moose fly, deer louse, and bloodsucker. The parasite prefers to live on elk and deer. Often its victims are:
- forest boars, bears;
- smaller animals: foxes, badgers;
- domestic animals: sheep, goats.
To protect yourself from a bloodsucker, you need to know what it looks like and where it prefers to live.
Description of the moose fly
Moose ticks are blood-sucking insects. These parasites belong to the family of bloodsuckers, from the order Diptera. External description:
- The size of the insect is 5 mm, with males smaller than females. The color is pale brown. Most of the body is occupied by the head, with antennae located on it. Externally, the tick resembles a small fly.
- The parasite got its name “fly” for its transparent wings located on the sides of its body. Their length is 6 mm. The wings are poorly developed, so the insect cannot fly long distances.
- The abdomen is soft and elastic. When the parasite absorbs a large volume of blood or bears offspring, the size of the abdomen doubles.
- The bloodsucker differs from the ixodid tick in the number of legs. The tick has 8 of them, and the bloodsuckers grow asymmetrically from the chest. There are small claws at the tips of the paws.
- The parasite has 5 compound eyes: 2 large lateral eyes, 3 simple small ones. He has poor vision, he sees only the general contours of an object. The larger the victim, the better for him.
- The type of mouthparts is piercing-sucking, similar to a proboscis. Thanks to the proboscis, the parasite easily pierces the skin of the victim.
If a deer bloodsucker begins to feed on human blood, it will not be able to give birth to offspring, since such nutrition is not suitable for it. Therefore, they do not stay on the human body for more than 2 days.
Stages of development and habitat
The habitat of moose flies is quite large. They are found in Scandinavian countries, North America, and China. On the territory of Russia they inhabit the European part, north-west Asia, and the Primorsky Territory. The number of insects is directly related to the number of animals living in forests. Stages of development:
- The moose flea does not lay eggs or larvae. They develop directly in the female's womb.
- By September, pupae or puparia measuring 4 mm appear. They are born one at a time, every 2 days. One female can reproduce 30 pupae in her life.
- Gradually the puparia darkens, the body hardens, and its growth stops. She spends the entire winter on the surface of the earth. In spring, development continues until the end of August.
- Then an adult with wings appears. Sometimes their appearance is delayed until October.
- An adult tick goes through an adaptation stage. He sits on a bush or grass, waiting there for his prey. Having found it, it bites in and actively sucks out the blood.
- After 20 days, the body of the insects acquires a dark color, the abdomen increases, the head decreases, and the muscles of the wings atrophy. The mating phase begins.
- Insects are looking for pairs to mate with. The male clings to the female, they begin to live together.
- In order for a female to have offspring, she needs to eat 20 times a day. At one time, the insect sucks up to 1.5 ml of blood. Males eat 2 times less.
- The birth of new puparia and pupae resumes 30 days after the appearance of the winged fly.
- Flightless individuals do not leave artiodactyl animals for 6 months. Because of this life cycle, they will only be able to get rid of elk bloodsuckers in late spring.
Up to 1 thousand moose flies can live on 1 animal. Regular loss of blood leads to the fact that the animal becomes nervous, stops eating and sleeping. If the creature affected by ticks is weak, it dies.
Danger to humans
In addition to animals, the insect is capable of attacking people. Whether a person should be afraid of an elk bloodsucker, and what consequences arise after a bite, worries many.
The main locations of attacks were recorded in forest areas and fields. Therefore, their victims are often shepherds, foresters, and hunters. The attacks occurred when the weather was calm and windless. Once on the victim, the parasite sneaks under clothing for 30 minutes, attaches itself with its proboscis, and then drinks blood.
It is more convenient for him to cling to the hair, so he tries to jump on his head. The reaction from bites can be unpredictable, since the human body reacts to them differently:
- victims feel severe pain and malaise;
- sometimes hyperemia occurs at the site of the bite;
- the affected area of skin is very itchy.
Some people do not feel pain from the bite. They develop a red spot, which goes away after 2-3 days. If you are susceptible to insect saliva, serious complications are possible:
- In addition to redness, the bite site swells, hardens, and itches.
- Various dermatitis appears, accompanied by a severe rash with blisters or crusts.
- In people predisposed to urticaria, red, swollen dermographism occurs.
This condition lasts 14-21 days. When an acute inflammatory process occurs, medications are used. If the bite was primary, the human immune system will quickly cope with the toxins that have entered the body. Important! Symptoms worsen and consequences become more severe with subsequent bites. According to studies, it was revealed that 20-25% of elk bloodsuckers were carriers of spirochetes, the causative agents of Lyme disease. The moose bloodsucker does not touch children under 8 years of age; it attacks only adults. This is due to the fact that she is attracted to tall, dynamic objects.
Cases have been recorded when up to 100 individuals simultaneously attacked a person in 1 minute. And such cases are not isolated.
How high can ticks climb?
When hunting, the optimal height for climbing a plant or shrub is from 20 to 50 centimeters above ground level. Depending on the bends of the plant and the terrain, the tick can rise to a height of up to one meter. Such low positions allow the parasite to remain invisible and easily latch onto the host’s legs.
Having attached itself to a person, the bloodsucker can reach the head in about an hour. Therefore, after returning from the forest, it is important to inspect clothing and exposed parts of the body for ticks. In most cases, due to the slow movement, it is possible to remove the parasite that is still crawling towards the head.
How do ticks move?
Ticks from the ixodid family are not always passive hunters, waiting for their future host on the grass and bushes. They are able to find their prey by thermal radiation and crawl in its direction.
Even if you stop for a picnic in a place where arthropods are completely absent, they will sooner or later crawl to the vacationers. Because of this, the question of how fast and how ticks move is very relevant. When going out into nature for long periods of time, a visit from Ixodes cannot be avoided.
Do ticks run fast?
In the absence of nearby thermal radiation, ticks in nature move very slowly and preferably vertically. Ticks have no eyes, they “don’t know” where to crawl. Attention! Infrared vision organs, which replace ordinary eyes in arachnids, are activated only when a warm-blooded object appears nearby. Experiments were conducted on one of the species of ixodids - Pavlovsky's mites. The average speed of movement of arachnids was 3 cm. The purpose of the experiment: to establish whether bloodsuckers can crawl towards the path purposefully or whether it is an accidental hit.
We found out that ixodids move purposefully. It has been established that if the path is well-trodden, then the speed of movement of arachnids increases significantly. It takes ixodes from 2 days to 3 months to overcome 120 m. Tip: The speed depends on the number of people walking along the trail. In the absence of victims nearby, the arthropod hardly moves or crawls only upward to wait for the owner in a more convenient place. A well-fed arachnid is not capable of movement. If a hungry arthropod is disturbed and senses danger, it moves its paws very quickly. Fleeing from danger, ixodids are able to cover a distance of about 1 m in 10 seconds.
Can ticks jump?
There is a belief that ticks jump from trees onto their prey. There is some truth in this, but no more. Ixodids cannot jump. At most, they can fall on a small animal from a bush branch. But dermacentors are capable of climbing to a height of up to 1.5 m, which can already be equated to an ambush on a tree.
In an ambush, the bloodsucker waits motionless, with its front paws spread, until some warm-blooded object passes nearby. The parasite falls on a small animal and clings to a large animal with its paws.
Sometimes this large organism is a person. This is where the belief that ticks jump from trees came from. In early spring, when there is no grass yet, ixodids can attack even on bare ground.
But even in this case, the parasites do not jump like fleas. Ticks crawl along the ground in search of prey and can easily get caught on the sole of a shoe. Once on the shoe, the bloodsucker climbs up the clothing to the place it needs. In early spring this is the neck area.
Flying ticks
In addition to the belief that ticks jump on people from trees, they are often credited with the ability to fly. To answer the question of whether ticks have wings, it is enough to carefully examine the parasite. It doesn't even have a "seat" for wings.
But another blood-sucking parasite that can fly has wings. The deer bloodsucker, a fly that parasitizes large ungulates, is often mistaken for ixodids that can fly. It rarely attacks people, but it does happen. Important! The bloodsucker has quite a lot of external characteristics that make it similar to arachnids. This parasite is also brown in color. It flies only in search of prey. Having found an object, it sheds its wings and turns into a cutaneous wingless parasite. The fly clings to its owner in such a way that any tick would be jealous. Bloodsuckers live in the same habitat. And they even suffer from the same diseases. Because of these moments, the opinion arose that ticks fly. But the life cycles of bloodsuckers are different. Tick activity begins in spring and ends in autumn. Bloodsuckers are active almost all year round and it is in winter that they have the most crucial period: reproduction.
Common blood-sucking insects fly in spring and summer. In unfertilized bloodsuckers, the years begin in the fall. Having found a host, the fly remains on him throughout the winter. During the cold months, it lays live larvae, which only turn into adults at the end of August.
To summarize, we can say that ticks cannot jump or fly. They either wait for prey on the shoots of bushes, or climb directly from the ground. If a bloodsucker flies, it is a fly.
Do ticks run fast?
Not fast at all. In its entire life, a tick may not crawl 10 meters.
In most cases, the prey itself comes to the hunter. Thus, the bloodsucker does not need the ability to move quickly. It is much more important for him to take an advantageous place for hunting, to latch on, and, probing every millimeter of skin, to find the most tender and safe place to bite.
If you wait for a long time, the tick may decide to move to the nearest source of blood at a distance of up to 100 meters. This will take him about 3 months. Therefore, tourists staying in the forest for a long time should be prepared for the arrival of bloodsuckers.
How a tick attacks and bites
Ticks are guided by smell; they can wait for a victim for a long time. As soon as she passes by, the spider clings to the body or clothing with its paws, and then crawls along the body in search of food, quite meticulously looking for a place for its bite. Having found tender skin, the tick digs into it, releasing an anesthetic substance along with saliva. Therefore, a person often does not feel the attached tick.
Gradually, the head completely sinks under the skin, and the abdomen swells from drinking blood. At this time, the skin feels tight. The tick can attach itself to the victim for 1-2 weeks; after eating, it flies off on its own.
Danger to people
In fact, attacks by these insects are quite common. They live in forest thickets, but in search of food they also visit other territories, so they can be found not only in forest areas, but also in fields. Most often they attack from above, jumping on their heads. This is due to the fact that this way they can cling to the hair and securely attach to the victim. It is impossible to predict the body's reaction to a parasite bite, since everyone experiences it individually.
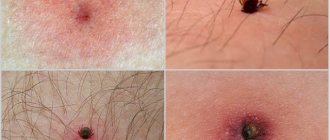
Some people may not notice the bite at all, after which there will only be a small spot of red and color, and after 2-3 days it will disappear. Others, during a bite, feel very severe pain, after which the affected area turns red, inflamed and itchy. Situations are possible when a person has an allergic reaction to the saliva of the parasite and it occurs in a rather complex form.
The affected area becomes inflamed and swelling is observed, accompanied by severe itching. A rash and blisters may appear, and dermatitis may develop. If a person is predisposed to urticaria, he develops edematous dermographism. Symptoms do not disappear quickly and the condition can last up to 3 weeks.
When the body's reaction is severe, treatment with medications is required. It is worth saying that a person tolerates the initial attacks of the parasite quite easily. Since the small amount of toxins that enter the body is quickly neutralized by the immune system. But subsequent bites are quite dangerous and can be tolerated in severe forms.
Studies were conducted that showed that 25% of moose ticks were carriers of dangerous spirotechs. Spirotechans are the causative agent of Lyme disease.
Most often, these bloodsucking creatures attack adults, but do not attack children under 8-10 years of age. This feature is due to the fact that they parasitize large animals. But here it is worth considering that during periods of maximum activity, when they need food, they can attack any victim in order to satisfy their hunger. These individuals can attack a person in groups; there are known cases, and they are not isolated, when about 100 elk ticks attacked one person at once.
Danger to humans
In addition to animals, deer flies also attack people. You can encounter this during the daytime in the forest, when there is no wind. Cases of mass attacks (more than 100 pieces/min.) of insects per person have also been recorded.
Since a tick with wings is based on size, it attacks adults more often than seven-year-old children. The most attractive targets for bloodsucker are moving targets.
After a deer lice lands on a person, it does not move for a couple of seconds, and then quickly begins to look for a place through which it can get onto the body or hair. It is almost impossible to dislodge the insect; it holds on well with its tenacious nails. As soon as the moose fly gets under the clothes, it begins to drink blood. In rare cases, this process begins after half an hour or an hour. The bloodsucker will remain on the body until it is removed.
Different people's reactions to being bitten vary. It depends on individual or acquired sensitivity to the saliva of the parasite.
For humans, the moose fly is dangerous because of its painful bites, which swell and turn red. For allergy sufferers, they can cause irritation throughout the body. In this case, you may need to take antihistamines.
According to observations, the skin reaction of a person who is bitten by bloodsuckers every year is much stronger.
Lice cannot live on a person for a long time; they stay on his body only for 2 days, since human blood is not suitable for them to give birth to offspring. There is no evidence that deer ticks transmit infectious diseases. However, the deer bloodsucker is dangerous to humans because it can cause many skin diseases.
How to remove a parasite
If you find a moose tick on your body, it must be removed as quickly as possible. The right thing to do in this situation would be to contact medical institutions, but if you consider that they attack in nature, then often this is not possible.
In order to remove it yourself, you can resort to the following methods:
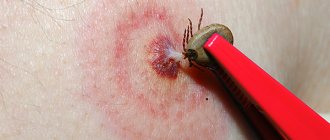
- Tweezers. It is necessary to grab the parasite under the abdomen and begin to twist it clockwise with careful, leisurely movements. It is very important not to make sudden movements, since the body can be torn off, and the proboscis will remain in the wound. If part of the bloodsucker remains under the skin, then inflammation will begin.
- Vegetable oil. They need to lubricate the parasite and the bite site well. The oil does not allow oxygen to pass through, which leads to the person suffocating and sticking his head out on his own. You can also use other fatty products instead of oil.
- Thread. It is necessary to make a loop and put it on the tick, then gently move it from side to side and slowly pull it out.
To be able to identify the infection at the initial stage of infection, the parasite must be submitted to a laboratory for laboratory testing. Such studies are carried out with a living individual, which gives the most accurate results. To do this, after removing it, put it in a glass container and place a piece of damp cloth there to preserve its vital functions.
General description of ticks
Ticks belong to the subclass of arthropods of the arachnid class. The mite order has more than 54,000 species. By size they are classified as small, small and microscopic spiders. Their size allowed them to settle into the top layer of soil, rich in decaying organic matter, which led to such a diversity of species.
Appearance
Ixodid tick photo
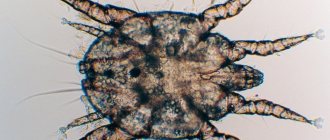
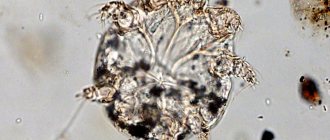
The structure of mites is not diverse. Animal and domestic ticks have undergone some internal changes compared to their wild counterparts. These arachnids have both a non-segmented body and an oval or spherical body divided into an abdomen and head. It is covered with hard chitinous plates or shell. Ticks have 6 pairs of limbs, the first 2 form a kind of proboscis, the remaining 4 are used for movement. The first pair has a claw-like shape; under a microscope, the mite resembles a kind of crab (photo is provided).
All ticks are divided into 2 sexes; development occurs with metamorphosis. Ticks reproduce at different rhythms depending on living conditions. The first stage is the laying of eggs, from which the larvae emerge. During its development, the tick larva molts several times. After the first molt, she enters the nymph stage, after the last she is considered mature (imago). Different types of ticks at the larval stage go through several periods of transformation, marking the next stage of development. Ticks reproduce where they live. Ticks feed on liquid or semi-liquid food.
Nutrition and threat to humans
The vast majority of arachnids are free-living in the natural environment; only a few species of ticks live off humans. Parasites feed on the blood or biological material of people and animals; so-called saprophages consume plant or animal remains. Some types of mites prefer living plants.
House ticks have adapted to living near humans or on their bodies. Most ticks live in natural conditions, including the most dangerous species - the taiga tick (also known as the ixodid tick). It is he who is the carrier of many dangerous diseases. Ticks choose damp places, ravines, and prefer tall, dense grass and shady places. Having a good sense of smell, they set up ambushes along forest paths. Information about where ticks live, what types of ticks are found specifically in your area, which areas are treated and safe, and when the highest tick activity is achieved can be obtained from the sanitary and epidemiological station.
Bottom view of a tick
Ticks are most active in May and June. It is believed that in September the taiga tick and other types of parasites dangerous to humans and animals no longer attack and do not pose a danger. Are ticks dangerous in the fall? In fact, activity directly depends on weather conditions. Warm summers and autumns significantly prolong the period of tick activity, which may end in October, although bites are especially dangerous in spring and early summer. It is safe to say that ticks do not attack or be active in winter in any case, but the full range of “hunting” is recorded from April to November.
At what temperature ticks die depends on the living conditions. When ticks are outside the donor’s body, they can die at a temperature of +7ºС…+14ºС within 2-3 weeks, at +60°С - within an hour. In cold weather, the parasites go into suspended animation and lay eggs in the spring, thereby completing their life cycle. Where ticks overwinter also depends on the conditions and the specific species. In the natural environment, they burrow into the grass and leaves of the ground layer. This allows you to overwinter at the lowest temperatures. Life expectancy, depending on the species and taking into account periods in suspended animation, can reach 10 years.
How dangerous are ticks to humans? The likelihood of transmitting serious diseases acquired from wild animals through saliva is too high. The activity of ticks in the spring-summer period leads to the fact that in Russia 2000-3000 people become infected with encephalitis per year. A tick bite can also cause:
- epilepsy and hyperkinesis;
- Lyme disease (borreliosis);
- nephritis;
- arthritis;
- indigestion;
- blood pressure surges and arrhythmia;
- pneumonia or pulmonary hemorrhage;
- complete loss of legal capacity and ability to move and care for oneself (in the worst cases).
Treatment
There is no single treatment regimen for bites of these bloodsuckers, since different reactions of the body are observed. Remember that when scratching the affected area, various infections can occur, which is also dangerous for complications. After removing the parasite, the bite site must be treated with an antiseptic.
To relieve symptoms, for example, get rid of itching, you can use Fenistil gel, which will also speed up the healing process. For allergic reactions, Suprastin, Zirtex and other drugs are used. The wound must be sealed with a bandage.
If we talk about traditional methods, you can use aloe juice, which will relieve itching and speed up healing, as well as calendula tincture. You can use regular ice, it will reduce inflammation and swelling. Soda is used, which is diluted with water to a paste and applied to the wound.
Preventive measures
In this case, the same preventive actions that we use to protect ourselves from ordinary ticks are effective. Proper clothing that covers the entire body. Jacket with cuffs and a collar close to the neck. The pants are tucked into the socks, and the jacket is tucked into the pants. A headdress is a must.
Avoid bushes and stick to paths and open areas. Check your clothing for ticks as often as possible. Be sure to use repellents that protect against most parasites and are most effective in natural conditions.
Lyme disease does not always present with a rash
Where do ixodid ticks live?
Most often, ixodid ticks are found in dense areas of forest overgrown with shrubs, where the sun's rays do not reach. They especially love neglected forest clearings left in disarray by “black” lumberjacks.
We invite you to read: Shampoo for head lice: a review of effective products
The danger of tick attacks begins with the onset of above-zero temperatures, when the first thawed patches begin to appear, and continues until the end of September. In July their activity decreases slightly.
Why is the deer bloodsucker dangerous for animals?
In large quantities, moose ticks systematically drink the blood of animals, as a result they become restless, stop sleeping and eating normally, as a result of which exhaustion occurs, and the growth of young animals slows down. In addition, regular blood loss can lead to their death.
Deer is the main host and supporter of the deer bloodsucker
The deer bloodsucker can be found on the body of the following animals:
- roe deer, deer, elk, deer - representatives of the family of artiodactyl mammals;
- cattle;
- wild boars, bears, dogs, foxes, badgers, goats, sheep and others - their parasitism was noted.
Insects drink the blood of animals about 15–20 times a day. Sexually mature females feed more often than males. When it comes to pets, it is impossible to specifically prevent the appearance of parasites. A person can save them from the long-term presence of deer bloodsuckers using special aerosols and sprays to kill insects such as flies, mosquitoes, and ticks.
What to do after a bite
If an arthropod was caught “in flagrante delicto,” it is carefully removed, placed alive in a jar, and taken to a laboratory for examination. If traces of an attack are found without the bloodsucker, the irritated area is lubricated with an anti-insect bite remedy.
Help with a tick bite
After an attack by an uncaught tick, a person will have to monitor his health for about a month. The incubation period for some Ixodid-borne diseases can last up to 30 days.
Victims often have questions about whether it is possible to wash after a tick bite. After all, in this case there is a risk of wetting the irritated area. But the bite is not a tuberculin test, although it is similar in appearance. You can safely swim after a tick bite or take a bath
All precautions are related not to traces of an attack, but to the state of human health. If a victim attacked by an arachnid has a weak heart, then the person may not be able to withstand the steam room
Playing sports is not only possible, but also necessary. An attack by blood-sucking arthropods would be no different in consequences from an attack by insects, if not for the delayed consequences. The likelihood of contracting infections from an insect is lower than from an arachnid. An insect drinks blood once, a tick at least 3 times - once for each stage of its transformation into an adult animal. The likelihood that he will first take a treat from a sick animal, and then transmit the causative agent of the disease to a person, is much higher.
How to deal with moose fleas
There are cases that ectoparasites are found in the backyard of a private house. In this case, the area should be treated with chemicals. This must be done carefully in places where grass grows; high growths must be mowed to eliminate the habitat of ticks with wings.
Salmon flies are repelled by the smell of tansy and wormwood, so it is recommended to plant it near the house. Trees and bushes need to be sprayed regularly with water, moisture is the enemy of the deer bug.
It also does not tolerate strong odors, so garlic tincture is used for watering or spraying. There are also special treatment products that do not harm plants and pets.
To prevent contact with a deer bloodsucker, do not neglect safety measures (wear appropriate clothing, use repellents). It is important to take disinfectants and antihistamines with you. To avoid bringing bloodsuckers home, clothes after a walk should be checked for the presence of attached ticks.
How to remove a tick
A tick that has burrowed into the body must be removed immediately; the longer it remains on the skin, the more difficult it is to remove it.
How to remove an ixodid tick yourself:
- Wipe around the tick location with any vegetable (unrefined) or camphor oil. It is believed that the tick does not like these odors, so it can crawl out on its own. The oil also forms a film, which allows the bloodsucker to be cut off from oxygen;
- after 10 minutes, take tweezers and carefully unscrew the tick, rotating the tweezers counterclockwise, since the proboscis has a spiral shape. You can also make a loop out of the thread and carefully pull it up, spreading the ends apart;
- if a black dot is visible in the wound, then the proboscis remains there. It is removed with a needle like an ordinary splinter. To keep the needle sterile, it can be heated over a fire. The bite site should be lubricated with iodine.
Do not crush the tick when removing it; splashes may get on you, which can lead to infection. Ticks that you accidentally brought into the house need to be burned.
Deer bloodsucker in the apartment: how to get rid of it
Moose ticks usually live in nature, since this is where most of the animals they feed are located, however, sometimes they can be found in an apartment or private house. Most often this happens if there is a park, forest, large-scale natural recreation area or nature reserve near your home. The likelihood of moose ticks increases significantly if there are stables or enclosures with mammals in these places.
If you have a deer bloodsucker in your apartment, how to get rid of it you can choose from two options, which are essentially one, just in different designs. We are talking about poisoning parasites with chemicals. This can be done either independently or with the help of SES. In the latter case, you need to order the service of treating the entire apartment from insects, and the problem with bloodsuckers will be solved in just 1 day if you contacted a SES certified by Rospotrebnadzor with many years of experience.
You can try to treat your apartment from parasites yourself using products for exterminating crawling and flying pests with a wide spectrum of action, for example, such as:
- Raid or Raid Max aerosol
- Raptor universal protection against 17 types of insects
- Tsipromal
- Lambda Zone
- Gett
- Xulat
- Contra Insect
- Combat MultiSpray, PowerSpray or SuperSpray
- Medilis Super
- Aerosol Delicia
Bloodsuckers not only crawl and fly around your house, but also directly attack your body and health, so the sooner you get rid of them, the better. It makes no sense to devote time to useless attempts to deal with them using folk or other non-chemical methods, since they will scare off the parasites only for a while, without completely solving the problem.
Ticks do not always transmit disease
Scientists know thousands of species of ticks around the world. Only some of them cause problems. For example, Lyme disease is spread by the elk tick. Mountain tree ticks also pose a danger - they can cause you to get a fever.
In the footsteps of Harry Potter: where a tourist can go to experience the magic for himself
The children forgot to close the door, letting the heat out of the house. Dad came up with a way out
The most interesting animals discovered in 10 years, for example, the dwarf lemur
Thirty percent of people do not develop the characteristic rash. However, other symptoms are still present, such as joint pain or muscle pain, and sometimes meningitis.
Since statistics on this infection appeared in 1991, the disease affects more and more people every year. Moreover, doctors are sure that many people simply do not know about their diagnosis. Some perceive low energy as a result of depression and do not take any steps to treat their Lyme disease.
She didn’t pass by: the kind woman took off her scarf and covered the frozen dog with it
Night in a glass igloo overlooking the Northern Lights: a unique hotel in Finland
Does he look you in the eye? This means he loves: signs that a guy is openly in love
Dogs can also get Lyme disease, but unlike humans, there is a vaccine for them. However, it is unknown how reliable it is. In 1998, there was a vaccine for people, but it was not ideal. It protected against eighty percent of the variant bacteria that causes Lyme disease and required a booster shot. In addition, the vaccine had many side effects, so it was later withdrawn from production.
How to protect yourself from moose lice in the forest?
Now you know that moose fleas are dangerous to humans, so a trip to the forest should be carefully considered. Experts recommend:
- wear clothing that covers the entire body;
- the trouser legs, cuffs and collar must fit tightly, otherwise the moose fly, which we described above as a dangerous bloodsucker, will crawl into the holes towards the body;
- treat your hands, face, and neck with repellents. Typically, moose lice treatment is made with DET;
- apply repellent to clothing. If you have any difficulties purchasing a ready-made repellent, you can use regular tar soap. This remedy for moose lice in the forest will save you no less effectively;
- Bring with you special tools for removing ticks - a lasso handle, a tick gun or an ordinary strong thread. After physically feeling the bite, you need to try to remove the blood-sucking fly as carefully as possible by pulling its proboscis out of the body;
- take hydrogen peroxide and iodine, hand sanitizers and an antihistamine for moose flies in your backpack - the person providing assistance also sanitizes the hands.
Removing the insect will not be easy. It must be remembered that a flat fly is a sticky one, having a body structure in which classical physical methods of fighting do not work. If there is no confidence that the ectoparasite will be correctly extracted, you need to use oily substances. If complications are detected, consult a doctor immediately. It often happens that a moose fly is found in an apartment. In this case, you need to try to drive it out or scare it off with repellent.
If you are bitten by a tick, it will remain on your skin for several days.
The taiga tick is a small spider. Encephalitis ticks do not exist, so they are called because they carry the encephalitis virus. The main carriers are ixodid ticks. How to recognize a tick? It has a thin flat body in the form of a shield, a small head with a sharp proboscis and four pairs of limbs. Claws with suction cups on their limbs help ticks move.
In half of the cases, a tick bite is not accompanied by redness of the skin. Symptoms of a bite resemble those of a cold - chills, fever, withdrawal symptoms. Redness may appear at the site of the bite. If it does not go away, or the temperature rises, it is better to go to the doctor. The latent period of encephalitis sometimes lasts for 3 months. Then the disease develops sharply: severe muscle pain, nervous system disorder, etc. appear.
How to remove a tick
The ixodid tick carries several natural focal infections that affect the central nervous system. The consequences of a tick bite are varied. With a favorable outcome, chronic weakness is observed for two months. In severe cases, irreversible changes may occur: paralysis of the arms, blindness, and death may also occur.
Previously, dust (DDT) was used to kill ticks. They simply sprayed it with dust from an airplane, but then they thought that this would spoil nature, since dust does not decompose well and accumulates in plants and organisms. They also write that if dust enters the human body, it causes detrimental effects on human health.
How to protect yourself from tick attacks:
- Before going into the forest, tuck your pants into your socks and put on thick clothes. It is advisable that the bottom of the trousers and sleeves have elastic. A tick cannot bite through clothing.
- When you return from the forest, carefully inspect your clothes and hang them out in a non-residential area to air. Be sure to examine your body and take a shower.
- A popular way to protect yourself from ticks is to put garlic in your clothing pockets; ixodid ticks do not like its smell.
- Repellent helps a lot; you need to spray it on shoes and pants up to about the knees. But repellents quickly wear off and their effect is destroyed naturally.
- Currently, vaccination is considered the most effective protection against encephalitis, but it does not protect against tick bites. An immunoglobulin injection prevents you from contracting encephalitis, but it does not protect against borreliosis. In addition, vaccinations kill natural immunity.
We suggest you read: What does a mite look like on your eyelashes
? “Mites are a highly profitable business project. The more often tick bites occur, the more money there is for insurers, doctors, drug and vaccine manufacturers, pharmacists, manufacturers of protective equipment, and so on” - this opinion can often be heard, and I agree with it. Not everyone bitten by infected ticks gets sick, I was also bitten, and I simply pulled them out using the methods described above.
Ticks are not mosquitoes that bite quickly and disappear. First of all, the tick crawls over the body in search of an ideal place, and then for about two hours it prepares for the feast - it plunges its head into the skin and injects anesthetic saliva into the blood. Ticks are so small that it is almost impossible to notice. This way the tick can feed for several days, and the females double in size.
The rate of transmission of the disease depends on the virus and the type of tick, but, as a rule, this does not happen instantly. Some ticks transmit the disease in about eight hours, while others take even longer. If you remove the tick from your skin within 24 hours of the bite, you are less likely to get Lyme disease. These bacteria affect a person only one and a half to two days after the bite.
Humans are not the main victim for ticks. They also feed on the blood of mice, birds, rabbits, and deer. Moving from animal to animal, they spread diseases and accumulate various bacteria. It turns out that one tick can carry three diseases at once!
“Your gift was terrible”: what your best friend will never say
10 Best Hotels in Brazil: Hotel Ariau Amazon Towers and More
He left his wife and 4 daughters for her: how did the life of the Kristovsky couple turn out?
Most of these illnesses cause fever, headache, fatigue, muscle pain, and some also lead to a characteristic rash. If it is Lyme disease, a rash appears on the body that resembles a target - with a bright circle in the center and a rim around it. Such signs can appear either three days or a month after the bite.
10 Best Places to Visit in Cuyo: Puente del Inca
Beautiful and little-known destinations in Bolivia: many people don’t know about them
Add to bookmarks: the best breakfast for the whole family – unusual pancakes
In fact, you probably won't get sick even if you're bitten by an infected tick. Only 1 percent of people bitten by a tick develop Lyme disease. If you have saved the tick by removing it from your skin, you can send it for testing to find out what diseases it has carried. If it is a moose tick and it has been on you for more than thirty-six hours, you may be prescribed antibiotics.
This treatment is contraindicated for pregnant women. If you develop flu-like symptoms, be sure to report them to your doctor - they may be a sign of a tick-borne illness.
Ticks do not have a specific active season, but in the summer the danger increases - the whole point is that their number increases. However, it is worth knowing that ticks are active throughout the year, and if the temperature is above freezing, you remain at risk of being bitten. Protective measures should be taken every time you go into the forest.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Traps for Drosophila flies
You can check information about tick habitats in advance. They are most often found on trees growing near open fields. Deer graze in the fields and live in the surrounding forests in order to hide from the field when danger appears, and ticks simply follow the animals. If you find yourself in a dangerous area, tuck your pants into your socks or shoes, and also apply repellent - it also protects against ticks. For maximum protection, you can wear clothing treated with a pest repellent.
Methods for controlling moose ticks
How to deal with bloodsucker? There are several effective methods - industrial and folk.
Terrain processing
Powerful insecticides are used to treat the area. Samples of the first generation caused irreparable harm not only to mites, but also to trees, so they were used only when absolutely necessary. But modern products are absolutely safe for people, indoor plants and pets.
Spraying of chemicals occurs using a special device that breaks down insecticides to the consistency of cold gas. Such steam generators guarantee that poison gets into hard-to-reach areas. At the final stage, hot steam treatment is performed, which does not leave the slightest chance for parasites.
Room treatment
To remove moose ticks from indoors, use liquid carbon dioxide cooled to -50 degrees. No living creature can survive in such cold.
Regular mowing
To protect summer cottages from moose bloodsuckers, you need to mow the grass more often. It is in dense and tall thickets that they most often appear.
Moose ticks, like many other insects, love to live in thick grass, so you need to keep your lawn mowed regularly.
Spraying lawns
Experts advise regularly spraying lawns and trees with ordinary water - ticks hate moisture. To be safe, add alcohol and crushed garlic, a decoction of tansy and wormwood. Planting wormwood or tansy in areas where elk flies are permanent habitats is also suitable.
Using repellents
Before going into the forest, apply a strong repellent that contains DET to your clothing. They have a repellent effect and will not allow ticks to get to the distance you need to jump. An alternative to store-bought products is a bath or shower with tar soap foam.
See also: Moose fly - why it is dangerous and how to fight it (video)
Can ticks fly and are there flying ticks?
Every spring, all nature lovers should be careful, since it is at this time, with the first warm sunny days, that ticks become active. Advice! Among those who have encountered them in the taiga, and sometimes in the Black Earth Region, there is a strong belief that flying ticks exist as a type of ordinary parasite. So do flying ticks exist? You can answer with complete confidence - flying, jumping ticks do not exist in nature. All parasites of this family found in the world hunt and feed, hiding in the grass, they react to the smell of a person.
They also do not fall from trees and bushes, as some people believe. The main reason for these misconceptions is that bloodsuckers strive to rise as high as possible to a person’s head, where they are mainly found later.
As a result, the victim believes that the tick fell from the tree, although quite recently it was just sitting on the grass and then gradually climbed up from the level of the knees onto the clothes.
Ticks also cannot fly. Most often they are simply confused with the “Deer Bloodsucker”, which feeds on the blood of wild boars, deer and other animals. It's not a mite, but there is a slight resemblance. The “deer bloodsucker” is often found in Siberia and Scandinavia, but practically does not attack people if there are wild animals on its territory.
The “deer bloodsucker” has two wings, 8 eyes, and the size of the parasite is 3.5 mm. He looks a lot like a fly. It hunts mainly in the fall, just like the tick, while in ambush.
When the victim approaches, it takes off and heads towards its scent. After a quick capture, the parasite moves to the hairline and begins to drink blood.
It is worth noting that the “Deer Bloodsucker” or “Moose Fly” is not afraid of danger and cannot be scared away. Until it stings a person, it will not stop attacking - this is a feature of this type of blood-sucking species that does not encounter resistance from wild animals.
Her bite is very painful, but she does not bite right away, as she waits a little, trying to gain a better foothold. Once it attaches itself, it is more difficult to remove than a tick.
The bloodsucker sheds its wings, becoming smooth, and it also has very tenacious legs that help it stay on the victim. Moosefly can give the victim Lyme disease, another type of fever. Cases of infection are not recorded due to the great distance of its habitat from civilization. Important! To protect yourself from insect bites, you should use special products and dress properly. For example, innovative insect repellents DEET. They are suitable for both adults and children. They effectively cope with their task, and their price is quite affordable and affordable for everyone.