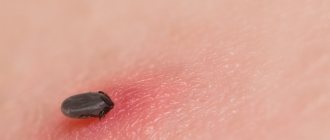
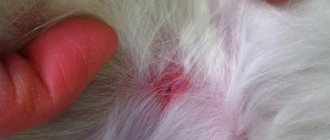
What does a tick bite look like?
The tick attaches to the human body using a hypostome. This unpaired outgrowth performs the functions of a sensory organ, attachment and blood sucking. The most likely place for a tick to attach itself to a person from bottom to top is:
- groin area;
- stomach and lower back;
- chest, armpits, neck;
- ear area.
During a bite, under the influence of tick saliva and microtrauma, inflammation and a local allergic reaction develop on the skin. The site of suction is painless, manifested by round redness.
The site of a tick bite in Lyme disease (borreliosis) looks characteristic - in the form of a specific spot-like erythema, which increases to 10-20 cm in diameter (sometimes up to 60 cm). The shape of the spot is round, oval, sometimes irregular. After some time, a raised outer border of intense red color forms along the contour. The center of the erythema becomes bluish or white. The next day, the spot looks like a donut, a crust and a scar are formed. After two weeks, the scar disappears without a trace.
Video: bitten by a tick, what to do? Urgent Care:
Bite symptoms
The fact is that it is impossible to immediately determine and detect the moment of a tick bite, since it does this absolutely painlessly by introducing natural anesthetics under the skin. However, after a few hours, the following symptoms may appear:
- slight nagging pain;
- mild subcutaneous itching;
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- visible enlargement of lymph nodes;
- rash on the body.
These symptoms indicate the penetration of infection into the blood and the beginning of infection.
Signs and symptoms of tick bites in humans
A tick bite is not accompanied by pain in humans. An attached tick can remain unnoticed for a long time.
Signs of a tick bite appear after two to three hours:
- weakness, drowsiness;
- chills;
- aching joints;
- photophobia.
The brightness of the signs of a bite depends on:
- number of ticks attached;
- individual characteristics of the human body to which the tick has attached.
Strong manifestations of signs of a bite should be expected in the elderly, children, people with a history of chronic diseases, allergies and immunodeficiency conditions.
The first symptoms of a tick bite:
- hyperthermia up to 37-380C. against the background of low blood pressure and tachycardia;
- tachycardia (more than 60 beats per minute);
- itching and rashes;
- lymphadenopathy (enlargement of regional lymph nodes).
The first sign of a tick bite
Finding a tick attached to a person’s body is, of course, the very first and most important sign of a bite. The tick usually bites in places with delicate skin, with a developed capillary system. It is possible to suck on ticks of two age stages: imago (adult form) and/or nymph (one of the larval forms). Visually they are distinguished by the number of limbs:
- imago – four pairs of legs;
- nymph – three pairs of legs.
What other symptoms are there of a tick bite?
Strong responses of the human body to a tick bite manifest themselves in the form of:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- difficult, hoarse breathing;
- nervous reactions in the form of hallucinations, etc.
Temperature after a tick bite
An increase in temperature in the first hours after a bite is a sign of the development of allergic reactions to the saliva of a sterile or infected tick.
After a tick bite, you need to record your body temperature every day for ten days! Fever, diagnosed 2-10 days after the bite, is one of the signs of the onset of infectious pathogenesis.
Features of fever in the main infections transmitted by ticks:
- Tick-borne encephalitis. Relapsing fever is typical. Fever 2-4 days after a tick bite. The temperature lasts for about two days and returns to normal levels. Possible repeated increase in temperature on the 8-10th day and other types of fevers;
- Lyme disease (borreliosis). Hyperthermia is characteristic in the middle of pathogenesis, as one of the secondary symptoms of the disease, combined with migraines, chills, muscle and joint pain;
- Human monocytic ehrlichiosis. Moderate fever begins on the eighth to fourteenth day after the bite and lasts about twenty days;
- Human granulocytic anaplasmosis. Hyperthermia is possible two weeks after the bite.
Fever is common to almost all tick-borne infections, such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Signs of a parasite bite
The tick feeds, remaining unnoticed for a long time, depending on its individual characteristics. Signs of a tick bite are more pronounced if many parasites penetrate the skin.
After detecting a bite mark, it is necessary to determine at what stage of development the tick is. The adult form is called an imago. It differs in that it has 4 pairs of legs. The female feeds on blood longer than the male and can remain on the body for several days. It only takes a few hours for a male to be satisfied. A larva called a nymph can also attach itself to the skin. The larva has 3 pairs of legs.
If a tick is found on the skin, it should be pulled out immediately. Doctors advise not to kill it, but to put it in a jar, which is sent for analysis to identify the pathogen. Since the tick takes a short time to attach itself, timely detection allows you to avoid infection. If the tick does bite through the skin, the patient should be observed by a doctor for 30 days.
The incubation period after a tick bite in a person can last up to 2 months. The rate at which symptoms manifest is influenced by the blood-brain barrier. If it is weak, signs of the disease are detected earlier.
During the incubation period, the disease can be detected using antibody tests and PCR. The first method shows when the infection passed, and the second helps to identify the specific pathogen.
Consequences of a tick bite
Possible consequences of tick-borne infections, in the form of lesions:
- nervous system - encephalitis, encephalomyelitis, various types of epilepsy, hyperkinesis, headaches, paresis, paralysis;
- joints – arthralgia, arthritis;
- cardiovascular system – arrhythmia, blood pressure surges;
- lungs – pneumonia, a consequence of pulmonary hemorrhages;
- kidney – nephritis, glomerulonephritis;
- liver – digestive disorders.
Consequences of an encephalitis tick bite
There are several variants of the course of tick-borne encephalitis.
Favorable outcome:
- asthenic syndrome (chronic weakness) lasting up to two months, followed by complete restoration of body functions;
- moderate disease with recovery up to six months;
- the disease is in severe form with a recovery period of up to two years without paresis or paralysis.
Unfavorable outcome:
- Persistent organic syndrome with a significant decrease in quality of life in the form of motor function defects without progression of symptoms;
- Persistent decrease in quality of life with progression of symptoms (continuous progression, abortive - recurrent).
Contribute to the progression of symptoms: alcohol, stress, overwork, pregnancy. Long-term persistent changes in the form of epilepsy, hyperkinesis are the reason for determining disability groups III, II, I.
Disability is determined by a special medical commission:
- Group III disability: moderate paresis of the limbs, rare epileptic seizures, loss of work skills, significant reduction in professional qualifications;
- Disability of group II: severe paresis, hemiparesis in combination with epileptic seizures, pronounced changes in the psyche, severe asthenia, loss of work activity and the ability to self-care;
- Group I disability: severe motor impairment, frequent Kozhevnikov epilepsy (a type of epilepsy), widespread hyperkinesis in combination with epilepsy, dementia (acquired dementia), persistent loss of the ability for self-care and self-control of behavior, inability to move without assistance.
Diseases from tick bites
Diseases transmitted by ticks include viral, microbial (including rickettsial) and protozoal infections. Such diseases are diagnosed on almost all continents of the globe.
Human viral infections transmitted by ticks:
- Tick-borne encephalitis (territory of Russia, Austria, Czech Republic, Finland, Germany, Hungary, Sweden, Switzerland, Poland, Slovakia, Baltic countries, Kazakhstan, China, Japan, Korea, others);
- Tick-borne hemorrhagic fevers (Congo-Crimean hemorrhagic fever (South of Russia, China, Serbia, Bulgaria, Central Asian countries, Congo, Kenya), Omsk hemorrhagic fever (Omsk, Novosibirsk, Tyumen, Kurgan, Orenburg regions);
- Rare tick-borne fevers (Lipovnik fever (European countries), Kemerovo fever (Kemerovo region).
Microbial infections of humans transmitted by ticks:
- Borreliosis (everywhere in Russia, Eastern Europe);
- Ehrlichiosis (Russia, Eastern and Western Europe, USA, Japan, China);
- Anaplasmosis (Russia, Europe, North America, China).
Microbial (rickettsial) human infections transmitted by ticks:
- Marseilles fever (southern Europe, South Africa, Asia, in areas with a humid hot climate, Crimea, Dagestan, Caucasian coast of the Black Sea);
- Astrakhan spotted fever (Astrakhan, Volgograd regions, Republic of Kalmykia, western Kazakhstan);
- Tick-borne typhus of Northern Asia (Siberia, Khabarovsk, Primorsky Krai, Northern and Eastern Kazakhstan, Armenia, Turkmenistan, Mongolian People's Republic);
- Tick typhus of northern Australia (Queensland);
- Smallpox rickettsiosis (found in Central Africa, Southern Europe, USA);
- Tsutsugamushi fever (Primorsky Krai, Kuril Islands, Kamchatka, Sakhalin, India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Indonesia, Pakistan, Japan, Korea, China);
- Q fever (Regions of the Volga region, Western Siberia, Central Black Earth Region, India, USA, France, Canada, Tunisia, Mali, Morocco, Western Ukraine, Spain, other countries);
- Paroxysmal tick-borne rickettsiosis (previously in Western Ukraine, there is currently no data on its distribution).
Human protozoal infection transmitted by ticks:
Human babesiosis (Scandinavia, France, Germany, Yugoslavia, Poland, Russia, US East Coast).
Let's sum it up
The tick bite itself does not pose a particular threat; its danger lies in the fact that, along with saliva, an infection can enter the human body, which often leads to serious health problems and even death. The most severe diseases are: ehrlichiosis, borreliosis, tick-borne encephalitis and hemorrhagic fever.
To protect yourself from infection, you need to get vaccinated on time, wear closed clothing, use anti-tick sprays and carefully inspect your body after every walk.
What to do if you are bitten by a tick?
The first step is to remove the attached tick. A live tick must be stored/transported at ambient temperature; a killed (crushed) tick must be stored/transported in a thermal container with ice.
Tests for tick infestation are carried out in laboratories of Rospotrebnadzor (they are accredited and certified for these analyses). In some regions, research is carried out by other laboratories; their addresses and telephone numbers can be found on the Internet.
Video: how to properly remove a tick using a thread:
Antibiotics for tick bites
Antibiotics are not always used to suppress tick-borne pathogens.
Antibiotics are not used in the treatment of tick-borne encephalitis (caused by a virus).
Principles of treating a patient with tick-borne encephalitis:
- Bed rest in a hospital for the entire period of fever and seven days after its end;
- In the first three days - human immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis;
- Prednisolone, ribonuclease, blood substitutes - rheopolyglucin, polyglucin, hemodez are indicated;
- For meningitis - increased doses of B vitamins, ascorbic acid;
- In case of respiratory failure - intensive pulmonary ventilation (IVL);
- During the recovery period - anabolic steroids, nootropic drugs, tranquilizers.
Depending on the form of tick-borne encephalitis, an antibiotic may be prescribed as an auxiliary drug to suppress the microflora that has caused complications in the lungs, intestines, kidneys and other organs. The type of antibiotic is selected by the doctor based on the sensitivity of microorganisms to it.
When treating borreliosis (Lyme disease), antibiotics are mandatory! They are used to suppress pathogens. Lyme borreliosis is caused by a microorganism from the group of spirochetes.
Principles of treatment of patients with borreliosis:
- Hospitalization is required for neurological disorders;
- At the stage of erythema (redness), tetracycline and drugs of its group are prescribed. Bacteriostatics (this group includes lincomycin, chloramphenicol, macrolides) prevent the development of later stages of the disease;
- Neurological syndrome can be relieved by intravenous injections of bactericidal antibiotics of the cephalosporin and penicillin series. The group of bactericidal antibiotics also includes aminoglycosides and polymyxins;
- Restoring water balance - blood substitutes, saline solutions, prednisolone, vitamins, drugs that normalize cerebral circulation, anabolic hormones.
As a means of etiotropic therapy in the treatment of tick-borne infections:
- of a viral nature (see list above), antibiotics are not used to suppress the virus; instead, a specific immunotherapy method is used;
- antibiotics of a bacterial nature (see list above) are used;
- protozoans (see list above) use drugs that suppress the growth and reproduction of protozoan microorganisms.
First aid for a tick bite
The victim must be helped to remove the tick, place it in an airtight container and sign the label accompanying the sample with biomaterial.
The suction of a tick provokes an allergic response from the body, sometimes in the form of Quincke's edema.
Signs of angioedema develop over several minutes or hours in the form of:
- swelling of the eyelids, lips and other parts of the face;
- muscle pain;
- difficulty breathing.
This is a very dangerous manifestation of an allergic reaction; you must immediately call an ambulance and try to help the victim until doctors arrive.
At home you can do the following:
- give one of the antihistamines (Claritin, Suprastin, Erius, Telfast, Zyrtec and others);
- provide access to fresh air;
- administer prednisolone (dexamethasone) at a dose of 60 mg intramuscularly.
Diagnostic and therapeutic measures for possible infections are carried out in medical institutions.
Find out more: Folk remedies for tick bites
Where to go if you are bitten by a tick?
It is necessary to perform the following algorithm of actions:
- remove the attached tick;
- submit it to an accredited laboratory to identify infectious agents using the PCR method (see below for how to find out the address);
- donate blood (if necessary) to detect antibodies to ELISA in human serum (details below).
- undergo a course of treatment based on the results of laboratory tests and clinical indications.
Remove attached tick
Tick suction occurs after it attaches to the human body. This process takes from several minutes to several hours. Blood absorption lasts from two hours to several days. The suction is invisible to humans, and a tick that has already drunk blood has a round shape and a gray color.
The attached tick must be removed urgently, but very carefully! It is necessary to protect its abdomen from damage and leakage of hemolymph and human blood. Hands and the wound at the site of the bite should be treated with an alcohol-containing solution (vodka, cologne, alcohol solution of iodine or brilliant green).
Removing a tick using improvised means:
- Throw a thread in the form of a loop around the proboscis (close to the skin), tighten it and slowly pull it out with swinging movements. Instead of threads, you can use nails, two matches and other suitable items.
- Place the tick inside a plastic bag and tie the neck.
- Sign the label for the package (indicate the date, time, place of detection, full name of the person from whom the tick was removed, contacts for obtaining information about tick infestation).
Removing a tick with a special tool:
- Use medical (manicure) tweezers or devices (Tick Twister, Tick Nipper, Pro tick remedy, Trix, Tricked off, others);
- Place the tick in an airtight container (medicine bottle, for example);
- Sign the label on the container (see above).
If you cannot remove the tick yourself, go to the nearest emergency room, emergency department of a medical facility, surgical clinic, or clinic. The list of institutions working around the clock and providing emergency assistance in case of tick bites can be found on the website of the territorial department of Rospotrebnadzor for the corresponding region.
Submit the tick to an accredited laboratory
Tests are carried out free of charge, but be sure to clarify this information. PCR research based on ready-made diagnostic kits AmpliSensTBEV (encephalitis, borreliosis, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis), distributor InterLabService LLC. We need to know when the results will be ready. Usually the same day or the next morning.
Donate blood to detect antibodies
Within 10 days after biting a tick, on the recommendation of a doctor, it is sometimes necessary to donate blood to detect antibodies in a person to infections transmitted by ticks. For diagnostics, the test system “VectoVKE-IgG-strip” of JSC “Vector-Best” is used. Analysis time: 2 hours 30 minutes.
When donating blood, you must indicate the date of vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis (if any). The presence of vaccine antibodies gives false positive results. The information provided will reduce the time required to determine the diagnosis and increase its accuracy.
Carry out immunotherapy as recommended by a doctor
Based on the results of tick studies using PCR and/or blood serum using ELISA, specific immunotherapy is carried out based on the doctor’s recommendations.
- Administration of human immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis is paid!
- Gamma globulin is administered free of charge to certain categories of citizens and on the basis of a VHI policy under the tick-borne encephalitis treatment program (be sure to contact the medical institution specified in the contract within 4 days after the bite).
The time during which specific treatment is possible, the duration, and the frequency of administration of globulin should be obtained from the attending physician. The address of the point of care for encephalitis is indicated:
- in the VHI policy;
- on a stand in the laboratory.
How I passed a tick
I rushed to my clinic, it seemed like I needed to bring a tick and show it, and then they would decide what to do with it. But at the reception they told me that the infectious disease specialist would not deal with such problems, and they sent me to the emergency room at my place of residence.
It’s good that I called there first: at the emergency room they explained to me that since I had already removed the tick myself, it was not to them, but to the laboratory . But I wasn’t sure that it was a tick, it seemed to me that maybe it was some other “animal” that had attached itself to me. At the emergency room they gave me the phone number of the first city infectious diseases hospital. I dialed the number and again voiced my doubts about the insect.
At the hospital they informed me that I was again at the wrong address, and advised me to contact the Moscow Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology, on Grafsky Lane, or the Federal Center, on Varshavskoe Highway.
I called the Moscow center. They listened to me and said that if I don’t know who bit me, then I need an entomologist, and they only take one species for testing, namely ticks. And they gave me the entomologist’s phone number. This is actually a neighboring department.
I called the department, but they told me that the entomologist was on vacation... And they added:
“What do you think, how many entomologists are there in Moscow? Yes, there are only one or two of them!” And this despite the fact that consultation with an entomologist is paid...
But it was necessary to check the “animal”. I had to decide to hand over the insect as a tick. I called the Center on Grafsky again and asked what the delivery procedure was, it turned out:
- submitting a tick for analysis costs 1,633 rubles 12 kopecks
- You can submit it daily until 15:30, and the tick must be fresh - that is, removed from the body no later than five days ago
Photo: Pravda Archive. Ru
The family said that the tick should feel comfortable, for this it needs:
- put it in a container with damp cotton wool so that it does not accidentally dry out
- and then put in the refrigerator
I did so. From time to time I opened the container and made sure that the tick was comfortable - it was vigorously moving its paws.
The Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology issued me a pass, and now I’m already there. The first thing that struck me was the line of people who had been bitten, which stretched down the stairs from floor to floor. And I thought that there were only a few people like me!
But before I stood in this line, I had to stand in two more:
- to the accounting department
- to the cashier
To the accounting department - to conclude an agreement (with a passport), and to the cash desk - to pay for the analysis.
Whom did I not meet in these queues:
- a young pregnant mother of many children with two children
- young couple from the Moscow region
- middle aged man
In short, all layers and all ages. And everyone was somewhat amazed at the queue and the cost of the services. Many said that they were forced to go from the Moscow region to Moscow, because there was nowhere to do an analysis “for harmfulness” on the spot...
When I approached the window, they asked me where the tick came from. I named three places. They were “reduced” to one - this is the program. They gave me a number and told me to call in two days. The tick was checked according to the following parameters:
- tick-borne encephalitis
- ehrlichiosis
- anaplasmosis
- borreliosis.
| Disease | Description |
| Tick-borne encephalitis | This is an infectious disease based on damage to the brain and spinal cord by a flavivirus, transmitted to humans through the bites of ixodid ticks . |
| Ehrlichiosis | This is an infectious disease transmitted by ticks. The main symptoms are myalgia, rashes, fever |
| Anaplasmosis | This is an infectious disease with vector-borne transmission. The main symptoms are prolonged fever with severe general intoxication symptoms. |
| Borreliosis | This is an infectious disease transmitted through the bite of an ixodid tick. It is characterized by damage to various organs and systems: skin, nervous system, heart, joints. |
Prevention of bites and other recommendations
The likelihood of a tick attack on a person depends on:
- epidemiological well-being of the territory of residence;
- a profession associated with frequent presence in the forest or field;
- the likelihood of visiting places unfavorable from the point of view of tick-borne infections.
Prevention of consequences associated with a tick bite is based on:
- vaccination, but this is a preventive measure; it cannot be used if a person is infected;
- specific immunotherapy is a therapeutic measure (administration of immunoglobulin only in case of infection or suspected infection after a bite);
- health insurance to pay for possible treatment;
- using special clothing and devices to prevent ticks from getting on the body;
- the use of agents to repel and kill ticks;
- limiting the number of ticks in biotopes and places where people are likely to be found.
Recommendations for choosing a vaccine
Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of disease; it is indicated for all people living in disadvantaged regions and people professionally associated with forests (drillers, geologists, surveyors, foresters). Anyone who is interested in it can be vaccinated if they wish, provided there are no contraindications.
Primary vaccination is possible from the first year of a child’s life, and then at any age. Adults can be vaccinated with domestic and imported drugs, children are better off with imported ones. In Russia, six vaccine options are available from four manufacturers from Russia, Germany and Switzerland.
Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis produced in Russia:
- The concentrated inactivated vaccine is indicated for use from three years of age and older;
- Encevir (EnceVir), Russia, is indicated for those aged eighteen and older.
Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis produced in Switzerland:
- FSME-Immun Junior, indicated from one year to sixteen years;
- FSM-Immun Inject (FSME-Immun Inject), similar indications.
Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis produced in Germany:
- Encepur Children, indicated from twelve months to eleven years;
- Encepur adult, indicated for ages twelve years and older.
Two vaccination schemes: preventive and emergency:
- Preventive vaccination provides protection against ticks during the first year, and after revaccination – for three years. Repeated vaccinations are carried out every three years.
- Emergency vaccination provides a short-term protective effect. Indication: urgent trips to regions unfavorable for encephalitis.
Vaccination is carried out after a preliminary survey of the patient for allergic reactions, clinical examination, and thermometry. Persons with health problems are not allowed to get vaccinated. There are contraindications and restrictions.
In Russia, “Human immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis” is produced, produced by the Federal State Unitary Enterprise NPO “Microgen”. The drug contains ready-made antibodies to viral encephalitis. It is administered intramuscularly for the purpose of treatment, usually after infection or when there is a threat of infection. Doses and frequency of administration can be obtained from your doctor.
Recommendations for insurance of expenses associated with the treatment of tick-borne encephalitis
It is advisable to recommend insurance as an addition to vaccination or as the only measure if vaccination is not possible. Insurance against tick-borne encephalitis is carried out within the framework of VHI - voluntary health insurance. Payments are provided to compensate for the costs of expensive treatment of tick-borne encephalitis and other similar infections. When choosing an insurance program and insurance company, you need to pay attention to:
- the policyholder has permits for the execution of voluntary health insurance;
- the cost of VHI services and the reputation of the policyholder;
- availability of documents for the right to provide medical and preventive care or an agreement with a person authorized to provide such assistance on behalf of the policyholder;
- Availability of a 24-hour toll-free emergency telephone line.
Recommendations for preventing tick attacks
When going to the forest or out of town, choose suitable clothes in light colors:
- anti-encephalitis suit;
- a jacket (shirt) with long sleeves and cuffs and trousers tucked into socks;
- a hood that fits tightly to the head and protects the neck.
Every hour you need to inspect your clothes from bottom to top to identify ticks. Every two hours it is recommended to examine the body, primarily the armpits, neck, groin, chest and head. You should avoid or minimize being in tall grass at the edge of the forest, along paths.
There are various devices on sale to prevent ticks from getting on the body in the form of insecticide-impregnated mosquito nets, special shoes, clothing, and so on.
Recommendations for using products to repel and kill ticks
For these purposes, repellents and acaricides can be used.
Repellents repel ticks and insects - these products are suitable for application to exposed parts of the body and for treating clothing. The active ingredient is DEET (diethyltoluamide).
Prevention of tick bites and the development of diseases caused by them
You can prevent a tick bite if you follow preventive measures. There are several ways to protect yourself from attacks by these arachnids, which are carriers of diseases dangerous to human life.
Special clothing
When in areas where there is a high risk of tick attacks, you should wear protective clothing. It must meet the following requirements:
- Maximum privacy. There should be no bare areas on the body. Sweatshirts must have long sleeves with cuffs. Pants must be tucked into shoes. Do not unfasten buttons or zippers.
- Dense material. Ticks will not be able to gnaw through such fabrics.
- Light colors. It is difficult to detect a crawling parasite on dark clothes, so clothes should have light shades.
- The presence of a zipper. It provides better protection against ticks from penetrating the skin than snaps and buttons.
There are special suits against tick attacks. They consist of trousers and a jacket. Their feature is as follows:
- Inconspicuous colors for parasites and insects. The costumes are sandy or mottled green in color. These clothes are made from cotton fabric.
- The presence of a special composition that coats protective clothing. This connection neutralizes a tick or insect that has landed on the suit in 5 minutes. Protective suits retain their protective properties for 3 years, after which they require additional treatment with a special compound.
- Cut. Traps are sewn into the jacket and trousers of the protective suit - chemical and mechanical. They work this way: first, the tick lands on fabric treated with a special protective compound. The substances contained in it paralyze the parasite. The arachnid, gradually weakening, moves upward into a trap hidden due to the peculiarities of its cut. The weakened parasite penetrates into a fold of tissue, where its final paralysis occurs. Traps completely eliminate contact of the tick with human skin.
The most popular and convenient models of protective suits are Biostop, Antignus, Helios.
Anti-tick products
Tick protection products are available in various sprays that are applied to the skin and clothing. The substances they contain repel parasites.
There are the following main types of anti-tick products:
- repellent - repel ticks;
- acaricidal - kill parasites;
- insecticidal-repellent - combined-action preparations that repel ticks and, if they come into contact with skin or clothing, kill them.
Repellents are applied to clothing and exposed skin. Such products contain aggressive chemical substances, contact with which the tick tries to avoid. The protective properties of such drugs last for about 5 days.
Repellents include products with the following names:
- OFF! Extreme;
- Reftadim Maximum;
- Gall-RET;
- Biban.
Acaricides contain substances that have a nerve-paralytic effect on ticks. Upon contact with treated clothing, the parasites experience paralysis of the limbs and they fall off the surface of the clothing. Only clothing can be treated with such products: due to the high degree of toxicity, they are prohibited from being applied to the surface of the skin.
Acaricides are presented in the form of aerosols. The most popular are:
- Fumitox-anti-mite;
- Gardex anti-mite;
- Anti-mite breeze;
- Anti-Tick Picnic;
- Gardex aerosol Extreme.
Products with a combined action , insecticidal and repellent, simultaneously protect against ticks and blood-sucking insects. They are applied only to clothing.
Such drugs include:
- Kra-Rep;
- Mite-kaput aerosol;
- Medias-Comfort.
When using chemical repellents, keep the following in mind:
- In conditions of rain, wind, heat, the duration of action of the product is reduced. The same applies to profuse sweating.
- Protective agents should be applied to the skin in ring-shaped strips. Particular attention should be paid to the areas of the knees, waist, ankles, collar cuffs and sleeves.
- When treating clothing and skin, you must strictly follow the instructions for the preparations. For personal safety reasons, it is recommended to use a respirator when applying compositions to clothing.
Other Precautions
To prevent a tick bite, you should stick to the middle of the paths when moving through forests or overgrown areas: ticks usually sit on the side of the paths. After leaving potentially dangerous areas, you should carefully inspect your clothing and skin. You should not bring clothes, plucked branches, berries and grass into the room - they can also contain parasites.
Ticks do not reproduce in residential areas, as they have low humidity levels. However, an arachnid brought into an apartment can bite a person.
When going to an area where ticks may be located, in addition to protective equipment, you should, just in case, take with you devices for removing ticks from the wound, a disinfectant, and an antihistamine.