Currently, almost 50 thousand species of ticks live on our earth. Most of this quantity does not pose a threat to human life, but there is one species that affects animals and plants.
The danger is that they may not be noticed on the body or the bite sites may contain diseases:
- Encephalitis;
- Ehrlichiosis;
- Typhus.
Ticks are sedentary creatures that crawl no more than 7 meters throughout their lives. In their functionality and structure, they resemble spiders or scorpions. In this article we will talk about ticks, diagnostic measures and prevention of their origin.
Types of mites under human skin
There are only two types of ticks:
Demodex is the most dangerous species. Ticks are small and have a transparent body, so detecting their bite remains extremely difficult. There are also those ticks that can live on the human body for years and not have any negative effects; they feed with the help of dead cells, which allows them not to die. But in those moments when a person’s immunity weakens, it becomes very dangerous.
The tick begins to act when a person has:
- Stressful situations;
- Long-term state of an empty stomach;
- Being in the cold for a long time;
- Temperature.
The location can be the face and head, as well as the place under the hair.
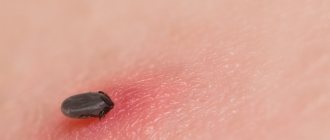
Ixodids are hard ticks that transmit encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain. In order to reproduce, it needs to consume blood. As long as the temperature does not exceed 5 degrees, they are not dangerous. The maturation of the larvae can be extended by several years as well as several months.
Appearance has:
- Black color;
- Hard shell;
Danger of forest ticks for humans
The forest tick is a keeper and carrier of infections that pose a mortal danger to humans. One insect can contain several types of viruses - tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne borreliosis, tick-borne rickettsiosis, ehrlichiosis, babesiosis, anaplasmosis. Pathogens enter the human blood through the tick's saliva, which the tick releases to relieve pain when bitten. The incubation period ranges from two to fourteen days; as a rule, this is a fairly acute infection, accompanied by chills, fever, and elevated temperature. The victim's face becomes redder as a result of hyperemia; in some cases, hyperemia spreads to the entire body of the person bitten by a tick. No one is safe from a tick bite. Ticks are not selective; they bite all warm-blooded animals, without distinction based on gender or age restrictions. The number of fatal cases among people infected with tick-borne encephalitis ranges from 2% to 6%; annually in Russia from 25 to 50 cases of tick-borne encephalitis with a fatal outcome are recorded. The risk of contracting tick-borne encephalitis is negligible; only 2–3% of ticks are carriers of the disease. However, the optimal solution in a situation where a tick has bitten is to remove the insect and submit it to the laboratory for analysis, so that a professional infectious disease specialist can check the parasite for infection in its body.
What is demodex mite?
This type is transmitted:
- Upon contact with a person who already has a tick on their body;
- When using the same things with an infected person:
- Towel;
- Bath;
- Plate;
- Toilet;
- Bed sheets.
- In contact with animals that are already susceptible to the disease.
Good to know! The maximum number of days a female tick can stay is 3 months, in the usual case it is 2 months, after which they die.
What does demodex look like under human skin?
Small in size, up to about 1 millimeter. For a correct diagnosis, it is always necessary to take a scraping, and it is studied in the laboratory, only after this a diagnosis is established and, accordingly, treatment is established.
Photo of a demodex mite on the face
Tick localization locations
Often lives on the scalp, or on other parts of the hair, these include:
- Brows;
- Mustache;
- Head;
- Eyelashes.
Let's celebrate! Many people are already infected with the disease, but it does not manifest itself in any way, but when immunity decreases, it manifests itself in the form of a rash of acne on the face.
Ophthalmic form of the disease
Signs of demodexas on the ophthalmic side:
- Severe itching in the eye area, accompanied by:
- Dry skin;
- Baldness on eyelashes;
- Eyebrow hair loss.
- The inner side of the eye mucosa suffers:
- The eyes get tired;
- It's like sand inside;
- Sticky discharge.
- Vision deteriorates in the form of clarity and percentage;
- The upper part turns red.
Good to know! Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe precise treatment after examining scrapings in the laboratory.
What are ixodid ticks?
Many people know this species; it is distributed throughout the planet. The length of the female is 2 centimeters, but in a hungry state it can be 2 millimeters and has a hard covering over half of the body, but in the male the whole body has a shield. Eggs are laid only on the ground and out of 20 thousand, only 10 units can survive.
If the tick is already infected with encephalitis, then the bite can transmit it through saliva.
How dangerous are ticks?
The danger is in the form of transmission of serious diseases, which include:
- Rickettsiosis – febrile diseases provoked by pathogens;
- Typhoid is an infectious disease that affects blood vessels and lymph;
- Monocytic anaplasmosis is a transmissible disease that affects the blood and its accompanying organs;
- Lyme disease is a skin disease.
How does tick infection occur?
They often wait for their target, strongly attached to the plant with medium legs. The front pair of paws cling to the victim and find a location quite convenient for the tick.
What does the site of an ixodid tick bite look like?
Risk factors
- Ticks live not only in the forest, but also in those places where the grass exceeds 10-20 centimeters in length, this could be an ordinary city alley that has not been treated;
- Ticks live in forests, so the place of infection may be a forest. Those who often go hiking wear completely covered clothing, collect stripes and wear hats. After leaving the forest, they carefully examine each other, and after arriving home, they wash their clothes and take a bath;
- Most individuals are active in late May and until mid-July;
- Ticks love moisture, this has a beneficial effect on growth and development.
Symptoms of a tick under the skin in humans
The mite located under the skin is localized in the sebaceous glands, after which it continues to move to other internal and external organs.
Often subject to such places as:
- Head;
- Back;
- Face.
Urgent contact with a specialist is required if:
- A certain area of the skin turns red or is accompanied by a rash in the form of small red spots; with improper treatment or lack thereof, they develop into papules and purulent pimples;
- There is a feeling of movement or other activity under the skin;
- The skin becomes red and itchy;
- The complexion becomes pale green, as the tick releases toxins and bacteria that poison the lives of both humans and animals;
- If a tick has infected the sinuses, it swells and turns red, which prevents a person from breathing and living in a normal rhythm;
- A vascular network forms on the skin, which is one of the significant symptoms;
- Hair loss, but if measures are not taken, baldness results;
- With infection in the eye area it was mentioned above.
Methods for diagnosing demodex mites
There are several methods:
- Tests in the laboratory - a scraping is performed or a part of the hairline (eyelash or eyebrow) is taken. The laboratory assistant places the material to be examined on glass and examines it under a microscope, and only then makes a conclusion.
Tests are taken only in the first half of the day, since the chance of diagnosing it at this time is much higher. This method will cost from 500 – 1500 rubles, depending on the clinic and the city where the analysis is performed. The good thing about this method is that you study many parts at once;
- The eyelash test is performed only by an ophthalmologist. Using tweezers, take both the upper and lower eyelashes and place them in a test tube. A specialized solution is added to the test tube and the test is performed. The cost varies from 300 to 500 rubles.
- Biopsy - a drop of a specialized substance is applied to glass and attached to the site of a possible bite for 30 seconds. Cost from 1000 to 2000 rubles.
You must first prepare for the tests by refusing:
- Cosmetics;
- Wash your face twelve hours before the procedure;
- Washing your hair;
- Eye drops.
What should I do if bitten by a tick
Do not panic. I'm serious. Remember one simple rule: if you are bitten by a tick, DO NOT PANIC! If you can quickly get qualified help, go ahead! If not, everything in our lives sooner or later happens for the first time. With confident hands we remove the tick from the body. There are several ways to do this.
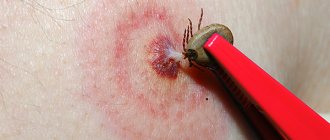
How to remove a tick
1. With your fingers. But not naked. Wrap them in a bandage, gauze, or use a sock. It is important to minimize tick contact with unprotected skin. Grasping the tick as close to its proboscis as possible, carefully unscrew it (like a screw) from the skin. It doesn’t matter which way you twist, the main thing is to keep it parallel to the bite site while removing it. 2. Use thread. Make a loop and place it around the base of the tick's sting. Gently tighten and unscrew the insect from the skin. Do everything calmly, without sudden movements. Usually 1-3 turns and the entire tick is removed along with the proboscis. 3. Use special tools such as tweezers, Klinver, Tick Nipper, lasso pen, etc. But you need to purchase them in advance at a pharmacy or tourist store.
Of the above methods, the last one is the most effective, and the first one is the most risky. I won’t describe the crazy methods, but know that they exist: removing the tick with a syringe, creating a vacuum; smothering ticks with oil; use of soap, etc. No matter how you remove the tick, always remember - you cannot tear off the head. There are salivary glands, and in them all the evil of the world. If you still screw up and the sting remains in the skin, then DON’T PANIC! Pour alcohol into the tick bite area, burn the needle, lubricate it with alcohol and carefully remove the remains from the wound, like a splinter.
I really liked the video on how to remove a tick with a thread, be sure to watch it:
Notice how calmly and quickly the father pulled this arachnid out of his son’s cheek. Well done, this is how you should behave when a child is bitten by a tick!
Where to store ticks
After all the manipulations done, you should have a reddened wound treated with alcohol (iodine, cologne), a live tick (preferably) and washed hands (since tick-borne encephalitis can be transmitted through the gastrointestinal tract). If the “little animal” is alive, we place it in a test tube, vial, or any jar with access to air. My husband wrapped it in a napkin until he got to the pharmacy. There I bought a syringe with a needle, broke off the tip, and placed the tick inside. In this state, Andrei had a chance to keep the insect alive for two days; it was during this period that the tick should be taken to a special laboratory where research is carried out on infection with tick-borne encephalitis viruses. To be completely sure that your new friend will not die before the analysis, you can place him in a clean container (test tube, jar, vial) on a piece of damp gauze, close it tightly and place it on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator. Take it to the laboratory as soon as possible. If the tick is dead, it needs to be burned or poured with boiling water, because Dead specimens are useless for research.
Where to submit a tick
The tick must be taken alive to a special laboratory. If an infection is detected in the laboratory, the patient is given anti-mite immunoglobulin. This type of treatment is called “emergency seroprophylaxis” and is relevant in the first three days after infection. If it is not possible to use immunoglobulin, then antiviral drugs may be prescribed.
Speaking of “special laboratories”. My husband, after going to the emergency department, received the following recommendations: we will take the tick, we will hand it over to the SES, and you will go straight to the emergency room. As it turned out later, there are no laboratories in our city. A week later we called the sanitary and epidemiological station, gave the name and wanted to know the result. The answer was: we don’t do analyses, we need the tick for statistics. So keep in mind that in order to get an analysis for the presence of diseases in your bloodsucker, take it to the laboratory, if there is one, of course, and do not give it to an emergency doctor.
The story with the emergency room is also interesting. The doctor immediately said: “Did you pull it out? What did he come to me? After 10 days the temperature does not rise - everything is fine, but if it rises - then come back.” This is science for those who read this post - engage in educational programs and arm yourself with knowledge. So to speak, help yourself: 10 days after the bite we donate blood for borreliosis and encephalitis. Research method - PCR. After 2 weeks - for immunoglobulins M for encephalitis, after 3 weeks - for immunoglobulins M for borreliosis. With the test results (positive), we go to the doctor. We’re not even walking, we’re flying like a “bullet,” because... the same borreliosis can be treated very well if dealt with in the early stages.
Treatment options
After a correct diagnosis, the specialist prescribes comprehensive treatment, which includes:
Medicines:
- Immunostimulating drugs that help restore the level of immunity in a person, since a certain type of mite manifests itself only when the system declines;
- Antiparasitic medications that penetrate areas of the skin and cause the death of the tick;
- Vascular strengthening;
- Antimicrobial agents, reduce the development of creatures;
- Antihistamines that can protect a person from an allergic reaction.
Procedures:
- Ice treatment, as the name suggests, treats damaged areas with ice;
- Physiotherapy – treatment with currents;
- Ozone therapy – restores immunity.
Traditional methods:
Required:
- Dry chamomile – 2 tablespoons;
- Aloe juice – 250 grams;
- Clean boiling water – 250 grams.
Leave and wet a cloth and apply to the redness for 15-20 minutes.
Required:
- Linden - 2 tablespoons;
- Water – 100 grams.
Leave and wet a cloth and apply to the redness for 25-30 minutes.
Drug treatment for ixodid tick bites
It must be repeated that treatment should only be started if the diagnosis has been correctly made.
Usually prescribed:
- A broad-spectrum antibiotic, 5 to 7 days, is prescribed to block the effects;
- Immunoglobulin - restores the level of the immune system.
Before using any drug, you need to familiarize yourself with:
Contraindications, which may include:
- Heart disease;
- The rehabilitation period after a complex operation;
- Gastritis;
- Ulcer;
- Glaucoma;
- Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding;
- Persons who have an individual intolerance to the components contained in the composition;
- Pancreatitis;
- People whose age is less than 14 years;
- Bladder dysfunction;
- Individual intolerance to components;
- Age up to 14 years.
Side effects:
- Lack of appetite;
- Stomatitis;
- Headache;
- Dizziness;
- Violation of the visual and auditory organs;
- Malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Weakness;
- Arrhythmia;
- Dyspnea;
- The noise that a person hears in the ears;
- Breakdown;
- Vomiting, diarrhea.
Good to know! If one of the symptoms appears, you need to contact an ambulance with the drug that was taken, and also clarify the dosage consumed.
Treating ticks on the face at home
The initial actions when a tick is detected are:
Apply a strong-smelling product to the affected area:
- Alcohol;
- Petrol;
- Sunflower oil;
- Varnish;
This must be done using a rag or napkin by applying it to the affected area for several minutes.
The parasite must be removed slowly, by rocking from one side to the other;
The duration of the tick's origin will affect its size, so you need to pull it out slowly.
Let's celebrate! It is strictly forbidden to pull quickly, as part of the arachnid may remain inside and provoke a purulent process, during which you can get several more serious diseases.
What to do if you are bitten?
What to do if you are bitten by a forest tick? Many people get scared and start doing things that aren’t quite right, dousing the tick with vegetable oil and vodka. It is important to provide first aid correctly, as human health depends on it.
First aid
First aid should be provided by doctors, so it is advisable to go to a special institution so that they can get the forest tick and properly treat the affected area. But if this is not possible, then you should remove the parasite yourself. To do this, you will need forceps, alcohol or chlorhexidine, soap and water.
In almost every pharmacy you can buy a kit that includes tools for extracting forest ticks. You can buy it and take it with you when you go outdoors.
The process itself consists of several stages:
- First, treat your tools with alcohol. The place where the tick sits should also be treated. If possible, wash your hands with soap to avoid introducing another infection through the wound.
- Take tweezers and fix it as close as possible to the head of the parasite. This is very important, because when pulling out a tick, you need to remove it entirely. If the body is torn away from the head, then it will be impossible to get it out on your own. Moreover, as long as part of the tick is under the skin, it continues to poison the human body.
- Having captured the parasite, begin to slowly scroll it counterclockwise. At the same time, you need to pull it slowly and under no circumstances pull it out with all your might.
- Once you have taken out the tick, place it in a container and take it to the laboratory. There they will conduct research and tell you whether the tick was sick and whether the person became infected.
- Wash the wound thoroughly with soap, lubricate it with an antiseptic and bandage it.
Mark the day of the bite on your calendar to monitor whether any symptoms develop and, if so, how quickly.
Once a tick is discovered, action must be taken immediately. No pills, syrups or traditional methods will help. To minimize the possibility of infection, you need to remove the entire parasite as quickly as possible.
Do I need to go to the hospital?
Do I need to go to the hospital after a tick bite? Of course yes! Even if you pulled it out yourself, the doctor should examine the bite site and check whether everything was removed. Moreover, the health station records every forest tick bite, and the victims are under observation for some time (even if the tick was not a carrier of the disease).
A week after the bite, the person who was attacked by the tick must have his blood tested. This should not be neglected even if there are no symptoms, since, for example, Lyme disease develops slowly.
It is necessary to go to the hospital as an emergency if a tick has bitten a person with allergies, immunodeficiency, as well as a child or pregnant woman. Here the clock counts. You should not try to do something yourself, as this can lead to undesirable consequences.