What is lice?
Pediculosis is a term that refers to the process of infecting a person with lice. The causative agent of the disease is the louse (Pediculus humanus capitis). The incubation period for head lice lasts about 30 days. Upon completion, a person may notice the following symptoms of lice infestation:
- • skin itching;
- • rash on the body;
- • scratching for bites
Upon visual inspection, lice eggs and adult lice can be detected on human hair.
Usually there are no difficulties during diagnosis. Specialists are able to diagnose pediculosis at the initial stage of development of the disease. A person himself can notice changes in his body. When bitten, a louse secretes saliva, which, if it gets into the wound, can cause itching or discomfort.
How long do lice live in bed linen?
The lifespan of adult lice in the feeding environment is approximately 30 days. At this time, females can lay about 90 eggs. After an incubation period of 7 to 10 days, the nits hatch and after another 10 days they develop into adults and the cycle repeats again. Outside the host's head, an adult louse can live only 2 to 4 days at a temperature of about 23 degrees Celsius and 1 to 2 days at a temperature of 30 degrees. Nits without a host can live up to 10 days, but they will not survive at temperatures below 20 degrees.
No matter which method you use, be patient. Lice can be very stubborn, so you may need to take precautions for several weeks to make sure you get rid of every single lice.
[youtube.player]
Pediculosis is a disease that affects both adults and children. Infection with parasites is not the most dangerous problem for human health, but it creates discomfort and many unpleasant moments. In this regard, the question of how long lice live outside the head is decisive in the development of tactics for the treatment and prevention of head lice.
Features of the life of lice
The life cycle of a louse lasts about 40 days and consists of three stages:
- • egg or nit;
- • a larva that goes through three molts;
- • adult.
The first two stages of parasite development last about 15 days. When transitioning to the 2nd stage - into the larval state, it can already feed on human blood, but will be able to reproduce only when transitioning to the 3rd stage, when the genital organs are formed.
Lice reproduce by laying eggs. The female is able to lay them regardless of the mating process, but unfertilized eggs do not develop further and do not enter the larval stage. She can mate soon after she hatches from the nit.
The female lays from 4 to 8 eggs per day, depending on the subspecies of louse, so the parasites multiply rapidly. Over the entire life cycle, each female lays up to 329 eggs.
The insects are protected from above by a hard shell and are oval or pear-shaped. The color of these parasites can be white or with a yellowish tint; less often they are found with a barely noticeable pearlescent tint.
At the front end of the nit there is a cap, which opens when the larva is born. At the lower end, an adhesive secretion is released, with the help of which it is securely attached to the hair. The larva is a nymph that emerges from an egg, similar in appearance to an adult, differing from it only in its smaller size and the absence of genitals
When the ambient temperature drops to +20 °C, the activity of lice decreases. They are not able to lay eggs, the development of the larvae slows down, but the insects do not die. As a result of a decrease in temperature to +10 °C, lice leave their host because they cannot live in such conditions. When the temperature rises to +30 °C and above, the lice die. Low temperatures can also be fatal for parasites, but it is impossible to say with certainty at what temperature lice and nits die in the cold
Getting rid of lice at home: chemistry will help
There are a number of chemical agents to effectively combat head lice. We list them depending on the type of lice.
Pediculosis
Helps against head lice:
Ointments, shampoos and aerosols sold in pharmacies. For example:
- Use 5% boric ointment (boric petroleum jelly), permethrin and serormercury ointments, 20% benzyl benzoate cream. But under no circumstances should these products be used for pustular skin lesions. They are also not indicated during pregnancy, allergies to any of the components of these drugs, respiratory diseases, and children under 5 years of age.
- Shampoos can be either water-based or permethrin-based. They are usually applied to dry hair, wrapped and washed off with warm water after a certain time.
- Aerosols are quite convenient, but also more expensive. They are used in much the same way as ointments.
Shampoos for head lice
Among the folk remedies most often used:
- 9% solution of table vinegar, diluted half with water.
- Tar soap (effective due to the creation of a highly alkaline environment).
- A mixture of sunflower oil and kerosene (1:1), this mixture is smeared on the hair, followed by wrapping and rinsing.
- A mixture of laundry soap and kerosene (1:1), which is diluted with water (1:10) before applying to hair to obtain a suspension of lower concentration.
- Cranberry juice is used against nits. Its acidity destroys the shell of the eggs and makes them easier to destroy.
A word of caution! It should be remembered that treatment with toxic substances (for example, using kerosene or karbofos) should be carried out with extreme caution to avoid poisoning and worsening the condition. So, when asking the question “How to get rid of lice at home?”, remember safety!
It is also recommended to subject bedding and other items of clothing to heat treatment (boiling, steaming).
against body lice , but the most important thing in this case is thorough and complete disinfestation of linen and bedding, outerwear and even the entire home. It is produced both chemically and by exposure to high temperatures (evaporating things, boiling them, treating them with a hot iron, etc.).
Things after chemical treatment and subsequent washing should be hung, for example, on a balcony, ensuring their ventilation and access to open sunlight.
get rid of pubic lice (phthiriosis) using a pyrethrin-based aerosol, which turns out to be very effective against lice. After spraying the drug onto the affected areas, after 30-60 minutes it is washed off with running water and soap or shampoo.
Pubic lice
It is also recommended to shave your pubic hair and armpits; you can treat the affected areas with 5% boron ointment (but be careful with severe lesions). In general, if you have phthiriasis, it is advisable to consult a competent doctor so as not to create additional problems for yourself.
Once again, things will need to be treated, including bedding, linen and outerwear, chemically or thermally.
Where else can lice live?
The human louse parasitizes humans. There are three types of insects known to cause head lice:
- 1. The head louse is named after its habitat, which is the hair of the human body. The head, mustache, and beard are the places where head lice live. Females of this species of parasites lay 4-8 eggs per day, over the entire life cycle - about 140 eggs. After one mating, the female lays eggs daily for 1-1.5 weeks.
- 2. Body louse – linen or bed louse. This subspecies parasitizes the human body, feeds on his blood, accumulating in the folds of bed linen. A body louse can lay 6-14 eggs per day, and about 300 eggs over the entire life cycle. Linen lice are common in all places where people live.
- 3. There is another type of lice that affects humans: the pubic louse, or flat louse. The main habitats of the parasite are the pubis, the scalp of the genitals and the anus. Ploschita can also settle in the armpits, chest, abdomen, eyebrows and eyelashes. Infection occurs as a result of direct contact with insects, and much less often through underwear.
If you know where lice live, you can promptly detect the appearance of parasites on your body and get rid of them. The most serious epidemiological danger is body lice.
Can lice live on people other than humans?
Yes, lice can live outside the human body. However, this is their forced state, and not the usual one. Insects can move on any surface and even withstand slight pressure. For example, if they are covered with sand or pebbles on the beach, they will still survive and make it to the surface. A louse can easily crawl a distance of up to 50 cm, or even more. They cannot fly, but they crawl quite quickly. This explains the high risk of catching lice even without close contact with an infected person and without using his things. It is enough to spend some time at a distance of half a meter from a patient with lice or from his personal belongings for the parasite to reach a new victim. And even if there is no source of danger nearby, the louse may simply be nearby, so there is no guaranteed way not to catch lice.
But being outside a person's head or genitals is a temporary period. The insect will strive to get to the food source; it should receive food 4–5 times a day. Without food, it can live in the most ideal conditions for up to 4 days, but more often than not, 2 days is the critical time for being outside the human body.
The ideal temperature for lice to live is 30–36 degrees, which is why the parasite prefers the human body. These insects also tolerate air temperatures above 23 degrees. When the temperature drops below 10 degrees, the parasite will live no more than 24 hours. In case of frost, it will not last even a couple of hours. If the air temperature exceeds 39 degrees, the insect will also die.
How to avoid getting lice?
Absolutely all people can become infected with lice, regardless of age, gender, social status and race. Since lice can neither fly nor jump, you can become infected with lice only through direct contact with insects
Head lice mainly affects school-age children, and body lice affects people who do not have a permanent place of residence and lead a chaotic lifestyle. Pediculosis pubis occurs in people who are promiscuous, as well as in those close to them.
To avoid becoming infected or to reduce the risk of contracting head lice, you should avoid staying in crowded places where close contact occurs. It is also necessary to observe measures to prevent lice infection.
Who can get infected and how?
Considering how long lice live on clothing, it is logical to ask the question of the likelihood of contracting head lice through non-contact means.
It is possible to become infected with lice without contact with a sick person. Possible paths include:
- Body clothing, if worn by an infected member.
- Combs or other hair styling materials.
- Scarf, cap, hat worn by the patient.
- Use of public swimming equipment.
- Swimming in a river (insects remain viable in fresh water for up to 48 hours).
- Swimming in the pool (if an infected person swam in it before).
- Operation of common objects in groups - kindergarten groups, camps, etc.
Prevention
Prevention of head lice comes down to following these rules:
- 1. Maintain personal hygiene.
- 2. Regular examination of the head and other parts of the body.
- 3. Wash your hair and body with soap at least once a week.
- 4. Weekly change of bed linen.
- 5. Regular combing of hair.
- 6. Thorough cleaning of premises, keeping household items in a clean condition.
- 7. Washing clothes and bed linen at the maximum permissible high temperature.
- 8. Ironing things with an iron and treating them with steam.
Effective treatment
When a person knows where lice live, it is necessary to carry out effective control against them. To destroy these parasites, products based on plant extracts, essential oils and chemical compounds are used. In dermatology, a remedy against pediculosis such as “Paranitis” has proven itself well. It is based on a component called dimethicone and mineral oil.
This drug is a low-hazard compound, but it has a fatal effect on lice. On the lateral surfaces of the body of these insects there are 4 pairs of spiracles, through which air enters the respiratory system. “Paranitis” is evenly distributed throughout the hair and clogs the spiracles of nits, larvae and adults. The product has several forms of release - lotion, shampoo and spray.
If you notice the first symptoms of lice, you should immediately contact a dermatologist. The sooner treatment is started, the faster you can get rid of the disease.
How does pediculosis manifest?
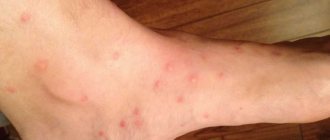
Signs of pediculosis do not appear immediately, but after a few days, when the number of parasites becomes large enough. Symptoms of the disease are:
- severe itching in the back of the head, temples and behind the ears with head lice, in the groin area with pubic lice infestation, in the neck, stomach and back with linen lice;
- the consequence of unbearable itching, which is especially intensified in the evening and at night, is scratching, which causes the formation of grayish-blue spots, wounds, suppuration and crusts;
- a rash in the form of red spots appears at the sites of lice bites;
- an infectious disease is characterized by the presence of nits resembling dandruff on the hair (when infected with pubic and head lice), and dead nits are more faded and not as watery as live ones;
- children become restless and capricious, adults irritable.