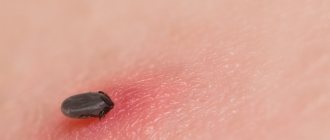
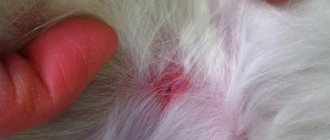
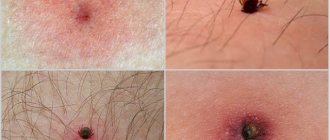
Often a pleasant walk in the forest or park with a great mood can lead to sad consequences. The reason for this may be the bite of an arachnid, namely a tick.
The danger is that you may not notice a tick bite on your body, which can cause diseases such as:
- Encephalitis – inflammation of the brain;
- Ehrlichiosis is an acute zoonotic infectious disease;
- Typhoid is a feverish disease that is accompanied by mental health problems and a rash.
In this article we will talk about the signs and symptoms of a tick bite, as well as the consequences.
Where can a tick bite and in what places?
Ticks are creatures that practically do not move and crawl no more than 7 meters in their entire life.
They are divided into:
- Demodex is the most dangerous species;
- Ixodidae - carry encephalitis.
A tick can bite:
- Ticks live not only in the forest, but also in those places where the grass exceeds 10-20 centimeters in length, this could be an ordinary city alley that has not been treated;
- Ticks live in forests, so the place of infection may be a forest. Those who often go hiking wear completely covered clothing, collect stripes and wear hats. After leaving the forest, they carefully examine each other, and after arriving home, they wash their clothes and take a bath;
- Most individuals are active in late May and until mid-July;
- Ticks love moisture, this has a beneficial effect on growth and development.
Favorite places for bites are:
- Groin area;
- Tissues on the neck and behind the ears;
- Stomach;
- Shin;
- Armpits;
- Inner thigh.
Let's celebrate! Based on the above, we can conclude that ticks bite only in soft tissues, since this is the easiest thing to do. Unfortunately, positive dynamics in treatment is observed in only half of the people with a bite.
How to understand that a tick is encephalitic?
Encephalitis is a brain disease that can be caused by a tick bite.
It is impossible to determine by appearance whether a tick is infected or not; even a doctor cannot do this without taking samples and diagnostic tests, for example:
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- X-ray of the bite area;
- Blood analysis;
- Study of the arachnid itself.
About the presence of encephalitis in the body, they can only say:
- Poor blood circulation in the brain;
- Change for the worse according to MRI results;
- Pallor in the upper body;
- Change in cerebrospinal fluid.
Classification of encephalitis:
- Spicy;
- Chronic;
- Subacute.
How is a regular tick bite different?
The bite is absolutely no different from the usual one; only the consequences that can occur after the bite and removal of the tick from the body can be different.
Causes
The name of the disease fully reflects the cause of its occurrence - an infected ixodid tick is to blame for the disease. The virus that he carries and secretes in his saliva, when examined under a microscope, appears as a spherical accumulation of particles with small protrusions on the surface. This is one of the smallest viruses, its size is half the size of the influenza virus and four times less than the size of the measles virus. But this small and harmful virus, due to its small size, can easily overcome all the protective barriers of human immunity.
Arbovirus is weak when exposed to high temperatures; it dies after just a couple of minutes of boiling. Also, the pathogenic organism does not like sunlight and disinfectants; it easily dies in the environment in sunny weather.
At low temperatures, the arbovirus can live happily ever after, which is why it can remain active in chilled cow's milk if the cow or goat was bitten by an ixodid tick shortly before milking. These creatures love tall bushes, grass, and trees, so a child can be bitten while walking in a forest, field, park, or wooded area.
Symptoms of encephalitis after a tick bite in a person
The manifestation of symptoms of encephalitis can be confused with influenza and colds, as they come in the form of:
- Severe and intolerable headache;
- Weakening of motor muscles;
- Aches in the limbs and back;
- Dizziness;
- Fever;
- Redness of the upper body.
After a creature bites, erythema forms on the body, which subsequently turns red and swells. This symptom may also indicate Lyme disease.
If help is not provided in time, the person will experience more severe symptoms:
- Epileptic seizures;
- Complete inability to move;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Slow speech or no speech at all;
- Memory loss.
- Coma.
Let's celebrate! A person with a disease in the form of encephalitis sleeps little and cannot remain calmly in bright light.
How long does it take for encephalitis to appear?
Some people confuse encephalitis that has already manifested itself with the previous stage of a stroke. This disease, like many others, has an incubation period that ranges from 8-25 days.
The duration directly depends on:
- Number of bites;
- Region (the Far East is the most dangerous).
Note! There are also cases in history when the virus manifests itself already on the first day or only after a month. This virus can be diagnosed immediately by taking certain medical measures.
Temperature increase
The first and most striking symptom is a sharp increase in temperature, which is very difficult to bring down with any medicine. Unfortunately, this symptom can also characterize a common cold, so people do not always go to the hospital on time, thinking that everything will go away on its own.
And only laboratory tests can establish the correct diagnosis, and at high temperatures there are also changes in the brain, which are justified by severe pain in the head.
Such changes include:
- Overflow of blood vessels;
- Formation of necrotic foci;
- Brain swelling;
- Fibrous changes;
- Damage to blood vessels;
- Inflammation of blood vessels.
Different stages of encephalitis
Stages of encephalitis:
- Fever lasts for 5 days.
Appears as:
- Pain in the head;
- Increased temperature;
- Nausea;
- Lethargy.
Meningeal – lasts 203 weeks and is accompanied by:
- Frequent vomiting;
- Photophobia;
- Intractable headache;
- Dizziness.
Meningoencephalitic - severe form is observed for 3-4 weeks.
The symptoms are:
- Hallucinations;
- Memory loss;
- Cramps.
Polyencephalomyelitis - 3 weeks, these days the following is observed:
- Impaired movement of the limbs;
- Muscular atrophy;
- There is no control over your body.
Polyradiculoneurotic – lasts for an indefinite amount of time with:
- Pain in the nerve pathways;
- Paralysis of the upper and lower limbs;
- Tingling.
Note! The duration of the stages can be individual for each person and is associated with the course of the disease and the treatment received.
Factors influencing the length of the incubation period
Incubation period of tick-borne encephalitis
How severe the damage will be and how quickly the incubation period of encephalitis will pass after a tick bite depends on many factors. The fundamental condition is the person’s condition at the time of the bite. If his immune system works in a calm mode and is ready to resist viruses, then this period increases.
Important!
Categories of people with weakened or immature immunity are at particular risk. These are the elderly, children and pregnant women. In this case, the manifestation of the disease may occur within a couple of days after the tick bite.
Also, people who have various kinds of autoimmune diseases and their defenses cannot work at full capacity are predisposed to the rapid reproduction of the tick-borne encephalitis virus in the body.
If a person has an excellent defense system, leads a healthy lifestyle and his body is able to resist even tick-borne encephalitis viruses, then he may not even know about the presence of the pathogen. The body itself will fight the disease and not give any signals. At this time, the immune system will develop special antibodies to the virus, and the disease will be defeated. In this case, it will be possible to find out that after a tick bite the causative agent of a dangerous disease was introduced only by taking a blood test.
Signs of tick-borne encephalitis in children
Children, due to their age, do not know how to protect themselves from tick bites, and adults often forget about the simplest methods of prevention, which include:
- Cloth:
- It must completely cover the skin, regardless of the time of year and weather conditions; accordingly, trousers and sweaters must have adjacent cuffs so that the tick does not penetrate inside;
- Turtlenecks and sweaters must be tucked into pants;
- In turn, tuck the pants into the socks;
- It is necessary to wear light-colored clothing, as it increases the likelihood of detecting a tick;
- It is mandatory to wear a headdress, and for women, collect their hair in a bun and also wear a headscarf.
- Chemicals:
- against insect bites;
- insectoacaricidal drugs that kill ticks.
- Inspect each other every 10 – 20 minutes;
- After the hike, take off your clothes and wash them;
- Take a bath.
Vaccinations are also relevant for children, which can save the baby’s life. They can be done at a certain age:
- From 3 to 11 months, children are vaccinated with EnceVir;
- From one year to 12 years, they are vaccinated with Encepur;
- From the age of 13 you can get vaccinated with FSME-IMMUN.
Or get vaccinated after a bite within 7 hours with emergency vaccination. If ticks are in the house, it is necessary to treat with an acaricidal agent.
But, unfortunately, ticks can also bite a child, transmitting encephalitis, which is accompanied by:
- Weakness;
- Photophobia;
- Headache;
- Convulsions;
- Drowsiness;
- Tongue paralysis;
- Decreased muscle tone;
- Loss of voice;
- Lack of ability to speak;
- Poor appetite;
- Vomit;
- Fever;
- Arrhythmia.
Let's celebrate! Only a doctor can confirm the diagnosis, prescribing the correct treatment based on age.
Consequences and complications of encephalitis
Consequences of a bite:
- Encephalomyelitis is the destruction of the sheath of nerve fibers, which is accompanied by:
- Impaired consciousness;
- Parkinsonism is a neurological syndrome;
- Hemiparesis – unilateral damage to the limbs.
- Myelitis is an inflammation of the spinal cord, manifested by:
- Weakness;
- Fever;
- Numbness of the limbs;
- Lack of sensitivity.
- Epilepsy is convulsions while a person is conscious.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the brain; symptoms include:
- Headache;
- Vomit;
- Lethargy;
- Convulsions;
- Heat.
Complications:
- Memory loss;
- Anorexia is a mental disorder caused by refusal to eat. It seems to a person that he is fat with minimal weight;
- Decrease in the level of intellectual development;
- A disorder of speech function, which can be manifested in the form of slow speech or its absence at all;
- Inability to maintain motor functions.
No one is immune from a tick bite, but you can follow simple prevention rules that can prevent a bite. If, nevertheless, a creature is noticed on the body, it is necessary to immediately contact emergency medical care to establish the correct diagnosis, especially for small children.
Note! You need to know that tick-borne encephalitis does not have a 100% cure; a specialist prescribes only drugs that can support the body and adapt a person to society. And if you immediately consult a doctor after a bite, the virus will not have time to enter the lining of the brain, which will give you a chance for positive therapy.