With the beginning of spring, in April - May, young raspberry shoots begin to grow. However, among the young strong stems you notice wilted, bent tops of the shoots. Many gardeners think that this is due to lack of moisture or some kind of plant disease. In fact, it is a raspberry fly. The danger from proximity to the pest is that the fly lays its larva inside the stem. Subsequently leads to the death of the plant. How to deal with the raspberry fly and whether it is possible, read more in the article.
What harm does a raspberry fly cause?
The fly itself does not cause much harm to the shoots, but the larvae it lays pose a great danger to the plant. It affects the very first, strongest shoots. The crimson stem fly pierces a young stem in its upper part and lays eggs there. Sometimes it’s difficult to see the puncture, it’s quite small, but if you look closely you can see a hole and unhealthy dark tissue around it.
After 5-8 days, larvae develop from the eggs, small white oval worms up to 2-3 mm in size. The larva begins to move down the stem, eating away the middle of the stem. Naturally, the nutrition of the tops is disrupted. First, the leaves hang on the shoot and wither, and later the shoot dries out and dies. If you break the stem, you can see a larva there - a worm, as in this photo.
The larvae spend the winter in the upper layers of the soil, where they pupate, and with the onset of warmth in early spring, a new generation of flies crawls out of the ground. During the season, one fly can lay up to 90 eggs.
Description of the pest
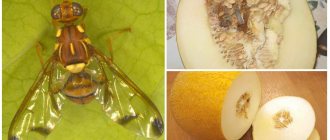
The raspberry (stem) fly is a small (up to 7 mm) sized insect with transparent wings, a gray body and two brown spots on the sides of the head, reminiscent of eyes. Its larvae spend the winter in the soil at a depth of 6-7 cm. When the temperature here reaches +12-+13°C, they pupate and after 8-9 days turn into mature individuals that fly to the surface.
Related article:
How to get rid of spider mites in a greenhouse - useful tips
The period of mass flight and reproduction can vary depending on the weather: it usually lasts about a week, but in cool and rainy conditions it stretches to 20 days. In the regions of the middle zone, these processes usually occur by the end of April to mid-May. Raspberry flies feed on flower nectar, dew, and the sweet secretions of other insects.
What harm does
An adult stem fly does not pose a threat to raspberry bushes: it does not gnaw on them and is not a carrier of infections. The greatest harm occurs during the period of laying eggs, the number of which from one female reaches 60-90 pieces. They are located on the apical leaves of young shoots, which gradually begin to fade. After 8-9 days, larvae emerge from the eggs - gray-white worms about 5 mm in size. They penetrate the soft stems of plants, gnawing passages for themselves and reaching the base of the shoots. After 12-16 days, they turn into adult caterpillars, descend into the soil and entangle themselves in a barrel-shaped brown false cocoon, from which a new generation of insects will emerge next spring.
Related article:
How to permanently get rid of aphids on the site? TOP 5 reliable ways
If a pest appears on the site, it is important not to miss the initial stage of the attack, otherwise you may lose most (up to 80%) of young healthy shoots. In remontant varieties, the formation of berries occurs on the fruit stems of the first year, therefore, in the event of a raspberry fly attack, the number of fruiting shoots will decrease significantly.
How to recognize
The first sign of damage is drooping of the tips of the shoots, as water and nutrients cease to flow to them. Later, the stems acquire a bluish tint, the leaves wither from top to bottom, the plants stop growing and dry out.
You can verify the presence of a pest by examining a cross section of the stem - passages appear in it, which the larvae make inside. When longitudinally dissected, the larva itself can be seen.
Related article:
Folk remedies for aphids on roses
Favorable conditions for defeat
The following errors can contribute to the appearance of stem flies on raspberry bushes:
- Wrong neighborhood. Blackberries, meadowsweet, and meadowsweet are also susceptible to insect attack, so you should not place raspberries next to these crops, or near raspberries from neighboring areas.
- Thickening of plantings . It is important to periodically trim the bushes, since with high planting density, the task of digging up the surface layer of soil where the pest overwinters becomes more difficult.
- Problematic fertilizers. Infection can occur when humus is used as mulch, where insect larvae are located.
- Damage to aphids. The honeydew secreted by it can attract raspberry flies to raspberries. If you don’t take any measures to destroy the first one, you won’t have to wait long for the second one to appear.
- Lack of preventive spraying . They should be carried out in the spring when the buds are swelling, especially when there is a mass reproduction of insects due to favorable weather conditions.
Related article:
Getting rid of the Colorado potato beetle without chemicals
Control measures
To combat flies, chemical, biological and folk remedies are used.
Insecticides
Chemicals are used both for preventive purposes and to combat flies. It is important to remember that insecticide treatment is carried out in calm weather, preferably in the morning or evening, when the sun is low. Treatment can be carried out during the day, but in cloudy weather. Such restrictions are necessary so that after treatment, sunburn does not form on fragile leaves. Of course, such preparations cannot be used before rain.
Working solutions of these products are used to treat leaves and stems against flies and the soil under bushes to destroy the larvae.
The following tools can be used for processing:
- Karbofos is a moderately toxic drug; for use, 60 g of the product is diluted in 1 bucket of water. You must be careful if there are beehives nearby, as the drug has a detrimental effect on bees;
- Iskra is a broad-spectrum drug, including against the raspberry fly. 1 tablet of the product is diluted in 10 liters of water;
- Atellik - sold in 2 ml ampoules and 5 liter canisters. Before diluting the product, you must follow the instructions for use. Due to the strong toxicity of the drug, it can be used no more than twice per season;
- Condifor is a highly effective, low-toxic product; when processed, it seeps through the surface of leaves, stems, and roots. Protects the plant from flies for two weeks, so repeated treatments are required.
- Fufanon-nova is an effective systemic insecticide. The solution is applied according to the instructions, 1 ampoule is diluted in 5.5 liters of water.
All insecticides are poisonous, so when working with them, you must be careful and wear protective clothing, goggles, and gloves.
Biological drugs
- Fitoverm - the drug acts on a large number of flying insects. The effect occurs if the drug enters the gastrointestinal tract of the insect, but does not affect the larvae and pupae, since they do not feed. This product is safe for bees. The drug is diluted according to the instructions, the leaves and crown of bushes and trees are treated. After application, the solution must be used immediately. Harvesting can be done no earlier than after 2 days.
- Agravertine is an alcoholic extract of the soil fungus streptomyces. Once in the gastrointestinal tract of an insect, the drug begins to act within 12 hours, paralyzing the insect and causing its death after 3 days. The solution is applied according to the instructions and used immediately after its application. The effect of the drug is especially effective in hot weather.
Prevention
As you can see, the raspberry fly is very dangerous, and the fight against it can take a long time. And in order to avoid troubles and prevent re-infection, it is necessary to act competently throughout the season. The quantity and quality of the harvest will depend on this.
Prevention is quite simple:
- regularly inspect the bushes in your raspberry patch and pay special attention to the condition of young shoots;
- if you know that there is definitely a raspberry fly in the neighboring area, then it would be useful to carry out preventive treatment with the drug “Karbofos” or “Actellik”;
- in spring and autumn, dig up the area and immediately collect all plant debris;
- Before winter, it is advisable to hill up all the bushes and cover the soil around them with mulch from compost or peat.
Remember, if you follow all precautions throughout the season, you can protect your raspberry tree from pest attack. And even if an infection occurs, do not give up, because now you know the methods of combating the raspberry stem fly. They are effective and easy to implement.
Folk remedies and caring for raspberries
Proper and timely care of raspberries will prevent larvae from laying in the stems and will prevent larvae from developing in the soil. What is raspberry care?
- As soon as the first shoots begin to appear, inspect the raspberry tree once a week. When you see wilted young shoots, you must immediately cut them out and be sure to burn them. Cut the stem at ground level and even a little deeper into the ground;
- To repel flies, the bushes are irrigated with a solution of baking soda (2 tablespoons per bucket of water) and irrigated before the berries begin to set. For this purpose, someone sprays the bushes with mustard solution, which also helps;
- To prevent the raspberry fly from laying eggs, it is necessary that the larvae do not hatch into adults in the spring. For this purpose, mulching is carried out with a layer of at least 8 cm. Plant residues, peat, and sawdust are used as mulch;
- Remove old branches and young weak growth in a timely manner. They take on useful substances, the return from them will be minimal. The remaining young stems will take up more nutrients, grow stronger faster and cope better with pests and diseases. In addition, thickened raspberries are an ideal environment for flies;
- Treat raspberries in advance with biological preparations, they are harmless and effective, act on other pests, but are safe for bees;
- In the fall, after harvesting, collect fallen leaves, loosen the soil under the bushes; in loose soil, the pupae will freeze faster in winter. Loosen the soil carefully so as not to damage the root system. You can treat the soil with some insecticide.
Don’t forget to feed the bushes in the spring, then in the summer they will delight you with a bountiful harvest of sweet berries.
You can order the most productive raspberry varieties from the Gardens of Russia NPO.
I wish you a good harvest!
Characteristic
As you can see in the photo, the raspberry, or stem, fly is a small insect with a pubescent body and a pair of transparent wings.
The dimensions are insignificant - the body length of an adult does not exceed 7 mm. The larva is a worm-like caterpillar, with a pale off-white body color, the size of which is about 5 mm. The larva has no legs; the mouthparts are located between the two anterior segments of the body. The adult caterpillar encloses itself in a barrel-shaped false cocoon that is brown in color. The parasites overwinter in this cocoon, usually in the top layer of soil. In May, when the substrate in the areas where the larvae are located warms up to +12…13°C, they pupate. Development in the pupa lasts about 7-9 days, after which adult flies emerge, whose years last from 8 to 10 days. In cold and rainy weather, the flight may take a little longer - up to 20 days. Under such conditions, most pupae die.
Emerging mature flies feed on flower nectar, dew and sugar secretions of other pest insects, after which the females lay eggs. They usually place eggs on the tops and in the axils of not yet formed leaves, young shoots and in the root shoots of raspberries.
The fertility of female raspberry stem flies is 60-90 eggs. Development in the egg takes from 5 to 8 days, after which the larvae emerge. Young growth bites into the middle of young stems and makes spiral and ring-like passages. The apical parts of damaged stems gradually wither, turn black and die over time. After 12-16 days, the larvae stop feeding. They gnaw through the stem and use the passages they make to descend into the soil for the winter. There they entangle themselves in a false cocoon and remain until spring.
On a note! The number of raspberry stem fly is limited by many predatory insects, especially ground beetles!