Why is a tick bite dangerous?
How dangerous are ticks to humans? In addition to the fact that the insect sucks blood from a person, it injects its saliva into the victim’s body, which contains an infection. That is why ticks are the source of a number of serious and dangerous diseases. Many of them are difficult to treat and cause great harm to the entire body. In addition to blood-sucking mites, there are other species that can cause allergies with their bites, as well as severe skin itching. How dangerous are ticks? This is what we will discuss now.
Why is a tick dangerous?
As already mentioned, the tick itself does not pose any danger. The blood that ticks suck from animals is dangerous. It can contain a lot of different microbes, bacteria, viruses. When attacking a person, the tick “injects” infected blood into the human bloodstream, poisoning it. The most common and dangerous disease is encephalitis. This disease affects the nervous system, sometimes causing irreversible consequences. Ticks also carry fever, bolleriosis, and other dangerous diseases.
If bitten by a tick
The bite itself is painless, a person may not even notice it. After a day, the bite site begins to itch and hurt, which is due to the development of the inflammatory process. It is necessary to remove the tick along with its trunk as soon as possible. It is advisable to do this in a clinic, and you should try to save the tick for analysis (according to statistics, only 20% of ticks are infectious). If the bite occurred far from civilization, there is no need to panic. You should try to pull out the tick with tweezers or your fingers, after treating them with an alcohol solution. This must be done very carefully, with twisting or rocking movements, trying not to break off the trunk. If the insect has already burrowed deeply into the skin, you can drop oil or any fat on it to block access to oxygen. If traveling conditions are not favorable, you can cover the tick with a bottle of water with the neck down so that it suffocates, then it will be easier to get it out. If the trunk does come off, it is better to use a heated needle and pull it out like a splinter.
If the insect was successfully removed, you need to place it in a container with a tight-fitting lid and take it to the laboratory for analysis. It is advisable to place a piece of cotton wool soaked in water in the container to deliver the tick alive.
Precautions for people helping with a bite
- You should beware of any contact with a tick, and under no circumstances crush it with your fingers like a mosquito.
- Avoid contact of hands with mucous membranes after removing the tick.
- You cannot burn an insect with cologne or alcohol - then it will simply dry out, and it will be even more difficult to remove.
- When extracting, you need to act very carefully, trying not to damage the insect’s abdomen.
Why
do you need to take a tick for analysis?
For the presence of a source of infectious diseases in the tick. If a person is lucky and the tick turns out to be sterile, then the maximum that a bite can pose is an allergic reaction. If the insect turns out to be infected, the victim should be administered a special serum against tick-borne encephalitis, and the sooner this is done, the better.
Consequences of a tick bite
Unfortunately, they can be disastrous. Encephalitis causes destruction of the nervous system. A person’s limbs may fail, speech and coordination of movements may be impaired. Much depends on the victim’s immunity, but, in any case, such a serious infection can cause serious damage to health.
Other infections, such as Lyme disease or fever, can also adversely affect a person's vital organs. Thus, Lyme disease seriously affects the blood vessels, heart muscle, hearing organs and nervous system.
Prevention of tick bites
Today there are a number of vaccinations that can protect against encephalitis. They are done in the cold season so that the body has time to “accumulate” a sufficient number of antibodies to the infection. Successful vaccination can protect the body 100% even after a tick bite, but it should be remembered that ticks do not only transmit encephalitis. Foreign so-called “express vaccines” are also produced that can quickly form immunity to tick-borne encephalitis. They are done 3 times in 21 days, and guarantee up to 98% effectiveness.
For some reason, in our country people do not like and are afraid of vaccinations. In this case, you will have to defend yourself, and very carefully.
Basic preventive measures for the whole family
- Inspection.
Even if you do not live near a forest, a tick can attack within the city limits - just walk through tall grass. After each such walk, you need to carefully examine yourself and your children. Remember that ticks are very small in size and not easy to spot. - Cloth.
If you go into the forest or go into nature, take care of your clothes. It is important to cover all parts of the body as much as possible, including the head and arms. The cuffs should fit as closely as possible to the wrists so that it is difficult for the insect to get through. Undoubtedly, this is not entirely convenient in the summer due to the heat, but you should still protect yourself in places of particular danger. It is better to choose light-colored and plain-colored clothing - ticks are easy to spot on such clothes. Choose a fabric that is as smooth as possible; it will be difficult for ticks to catch on. It is better to put a hood on your head and as closed shoes as possible on your feet. - Repellents.
Stock up on special insect repellents. Take them with you into nature, updating them periodically. It is best and most convenient to use products in spray form. For children, purchase a separate product according to age. - Caution.
While walking, do not pick off branches or walk on tall grass. After coming from the forest, outer clothing must be removed, shaken out well, and mutually inspect each other. - Vaccination.
If your job involves frequent exposure to nature or wooded areas, it is recommended to get vaccinated. - Mowing the grass.
At your summer cottage or in your yard, mow the grass regularly. Remember that ticks usually attack from the ground, so keep your lawns low. - Keep an eye on the children.
After each walk, carefully examine the child, change clothes every day.
Do not neglect the rules of behavior in nature in the summer. Remember that preventive measures and the ability to provide first aid for a tick bite can cost a person’s life.
Diseases caused by tick bites
How dangerous is a tick bite for humans? Let's look at the diseases transmitted by these insects and their symptoms.
Lyme disease, characteristics:
- constant state of fatigue;
- headache appears;
- the bite site becomes a noticeable wound;
- a red rash appears on the body;
- If treated in a timely manner, it can be easily treated with antibiotics.
Spotted fever, characteristics:
- body temperature rises significantly;
- there is severe pain in the head;
- nausea is observed and vomiting is possible;
- muscle soreness is noted;
- a rash appears on different parts of the skin, most often on the wrists, arms and legs;
- causes serious complications, which may further lead to stroke or impaired renal function.
Tularemia, characteristics:
- body chills;
- a very high temperature rises;
- bothered by headache;
- nausea;
- lymph nodes are enlarged;
- there is swelling in the area of the bite;
- an open wound forms;
- severe consequences are possible, such as pneumonia, peritonitis, gangrene, etc.
Ehrlichiosis, characteristics:
- appears from the first day after the bite;
- constant nausea and vomiting;
- feeling weak;
- Strong headache;
- inflammation occurs in any organ;
- there may be a state of chills;
- the outcome of this disease is unpredictable, since the disease can be asymptomatic, or it can cause serious damage, even death.
Relapsing fever, characteristics:
- heartbeat increases significantly;
- you feel unbearable pain in your stomach and head;
- weakness of the whole body is observed;
- feverish condition;
- Usually cured without consequences, no fatal outcome is observed.
Encephalitis, characteristics:
- the temperature stays around 39;
- there is a fever;
- severe chills;
- weakness of the whole body, muscle soreness;
- there is a pronounced detachment in consciousness;
- severe consequences in the form of meningeal syndrome and paralysis;
- appears three days after the bite.
Babesiosis, characteristics:
- constant feeling of malaise;
- complete aversion to food;
- general fatigue is felt;
- worried about fever and chills;
- anemia develops;
- the disease provokes renal and liver failure;
- profuse sweating.
I would like to note that even if a preliminary vaccination against tick bites has been carried out, it only helps against encephalitis and does not apply to other diseases.
You can see photos of dangerous ticks for humans in the article.
Educational program. How dangerous are ticks?
Author:
Skrypnik Ksenia
3 minutes
1555
How to remove ticks correctly, is there emergency vaccination, and other answers to important questions about ticks.
What kind of ticks are we talking about?
There are more than 40 thousand species of ticks in the world. Despite such diversity, not all of them are dangerous, but only some of them. Ixodid ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases - they lead a parasitic life and feed on the blood of animals. Russia is inhabited by the taiga tick, which is found mainly in the Asian part of the country, and the European forest tick, which predominates in the European part.
Female ticks are much more dangerous than males - they can stick and feed on blood for a whole week. However, males, nymphs, and tick larvae pose a danger.
Where do ticks live?
Contrary to popular belief, in order to become infected with tick-borne encephalitis or another disease for which they may be a carrier, it is not at all necessary to go to the taiga (although the likelihood of infection there is much higher). Ticks are found both in city parks and in summer cottages. They prefer well-moistened places overgrown with grass.
Many people believe that ticks wait for their prey and then jump on top of it. However, more often the tick sits on the top of a blade of grass or a low bush and simply grabs onto someone who passes by. It begins to climb from the bottom up - the tick can reach the head of an adult in 15 minutes.
How dangerous is a tick bite? If I am bitten by a tick, will I get sick?
Ticks can transmit various diseases. They can cause not only tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis, which many have heard of, but also tick-borne relapsing fever, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis and other diseases. The likelihood of infection depends on the region where the tick lives.
The virus enters the bloodstream immediately after the bite, but the first symptoms of the disease may not appear immediately, but after several days or even weeks. It is not at all necessary that you will get sick after being bitten. Firstly, not all ticks are infected, and secondly, only about 5% of those bitten by infected ticks become ill.
Diseases caused by ticks, in rare cases, can be asymptomatic, but more often a febrile state occurs: the temperature rises, headaches, increased fatigue, and joint pain appear. In addition, paralysis, problems with hearing and vision may develop. Many residual effects can persist for several years after the illness.
What should I do if I find a tick on myself?
The tick must be removed as soon as possible - the longer it stays on the body and feeds on blood, the greater the likelihood of infection. It is best to go to the emergency room, where a specialist will remove the tick.
If this is not possible, then you will have to act independently. You need to grab the tick as close to the skin as possible - you can try to pull it out with your fingers, tweezers or thread. It is worth trying to pull out the entire tick. If the arthropod's head remains inside the skin, do not panic, it can be removed like an ordinary splinter.
You should not smear the tick with oil or anything else - this will make it suck blood more intensely and only increase the likelihood of infection. But it is better to disinfect the wound left after a bite.
What to do with the tick itself?
The tick must be placed in a jar, in which you should place a damp cotton wool or gauze, after which you must take it for analysis - where exactly, you can be told at the emergency room or the ambulance service by calling 03. List of laboratories and services involved in the analysis of ticks and Emergency immunoprophylaxis can be found here.
10 days after a tick bite, it is necessary to donate blood to detect tick-borne encephalitis using the PCR method, after 2 weeks - to undergo a test to detect IgM antibodies to the tick-borne encephalitis virus, and another week - to detect IgM antibodies to borreliosis. Remember that ticks can also cause mixed infections; your doctor will prescribe tests to detect them.
How can you protect yourself for the future?
The most effective way to prevent tick-borne encephalitis is vaccination. You can get vaccinated at any time of the year, but you need to remember that vaccination consists of several stages - at least two weeks should pass between the second vaccination and a possible encounter with a tick. The standard vaccination regimen takes at least 45 days, and the emergency one – at least 21. The exact timing depends on the vaccine chosen.
If you are not vaccinated, but emergency vaccination is necessary (or if you have already been bitten by a tick), immunization with a specific immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis is prescribed.
And if there is no opportunity to get vaccinated, why not go to the forest or go to the country?
However, you can try to minimize the risk of being bitten. When going into the forest, you should tuck your pants into your shoes and your T-shirt or shirt into your pants. You need to tie a scarf around your neck and put a hood on your head. You need to examine yourself and your comrades at least once every 15-20 minutes.
You can also use repellents - there are products that need to be applied to open areas of the body, and there are acaricide sprays based on permethrin and alphamethrin, sprayed directly onto clothing. The effect of this treatment lasts for a week.
However, we must remember that neither special clothing, nor anti-tick agents, nor even vaccination can provide 100% protection.
Periods of tick activity
Seasonality is directly related to the activity of ticks and the danger from their bites.
Peculiarities of tick behavior in spring:
- the end of April is considered the beginning of tick attacks on humans and animals;
- in May the number of individuals increases significantly;
- spring is considered the most dangerous period, since during the winter they become very hungry and accumulate a lot of toxic substances;
- the probability of contracting encephalitis from the bite of an infected tick is about ninety percent.
Peculiarities of tick behavior in summer:
- in early June, females actively attach themselves to mammals in order to begin reproducing offspring when they are sated;
- by the end of summer, the harm from tick bites decreases, since they are no longer so hungry and the concentration of poison in saliva decreases.
Peculiarities of tick behavior in autumn:
- in September activity decreases significantly;
- If the autumn is warm, you can get a tick bite in October.
If the summer is very hot, then the activity of ticks noticeably decreases, since they cannot tolerate heat above thirty degrees. These insects hibernate at plus four.
Types of dangerous ticks
Among the mites that cause harm to human activities, the following types are distinguished.
Barn mites, characteristics:
- settle in flour and cereals;
- if they come into contact with a person, they cause an allergy;
- do not stay on the body for long, as they mainly prefer plants;
Bed mites, characteristics:
- found in bedding, carpets and mattresses;
- feed on dead human cells and scales;
- can provoke allergies in the form of rash and itching, and in rare cases cause bronchial asthma.
Dust mites, characteristics:
- live in an apartment on furniture in the dust;
- a person is allergic to them;
Scabies mites, characteristics:
- very small in size, almost impossible to detect on the human body;
- transmitted through touch or common household objects;
- operates directly under the skin, gnawing tunnels in it and thereby causing severe itching.
The most dangerous ticks
2018-09-19 City Disinfection Station
As soon as the first echoes of summer come to the city, all people gather their families and go into nature - what could be more beautiful than a picnic in a park or forest? Not everyone thinks about the danger that threatens among green spaces filled with ticks that are dangerous to health. These arthropod parasites not only silently enter the human body, but are also sometimes carriers of diseases. How can you tell if a tick on your body is dangerous? Can its bite harm the health or even lead to death of the tick victim? Let's try to figure out which ticks are the most dangerous.
Ixodid ticks
Ixodid ticks are the most dangerous to human health and have more than 650 species and subspecies with their own characteristics and dangers to health and life. They are malicious carriers of fatal diseases - tick-borne encephalitis and tick-borne borreliosis. Such parasites live on all continents of the planet, breeding both on trees and on the skin of penguins in Antarctica. The average size of such ticks is 4 mm, but when saturated with blood they grow to 10 mm. In our country, ixodid ticks are a common phenomenon (except in arid areas); they lay eggs, up to 15 thousand at a time, but only a few of them survive and turn into adults, living on average 2-3 years.
Let's take a closer look at the most dangerous ticks of the ixodid family.
Black-legged ticks
The black-legged tick is most often found in forests and steppes. With its bite, it transmits Lyme disease, babesiosis and human granulocytic anaplasmosis to the human body. It is quite easy to recognize such a tick, because it got its name thanks to the black color of its legs. These parasites infect the human body rather slowly; sometimes they can drink blood for 4-5 days. Be careful and carefully examine your body after going outdoors; if you find a tick, consult a doctor immediately. It is worth noting that the main area of distribution of such ticks is the east of North America, so when traveling to this continent, take care of your health and get vaccinated.
Taiga ticks
Such ticks live in the central zone and are becoming increasingly widespread - they are found in forests, fields, thickets of a wide variety of shrubs, in city park ensembles, in suburban green areas and in summer cottages. These parasites are the most dangerous carriers of encephalitis; in addition, through their bite they can also infect you with other diseases. Taiga ticks do not have eyes, but they can easily navigate by the aromas and heat emanating from the body of the victim. They usually wait for a person at a height of up to one meter in the grass, bushes or trees. They are well oriented in space and feel where the paths that are in demand among people are located. Be careful in areas with large crowds of people.
Dog ticks
Despite the name, the dog tick poses a threat to both animals and humans. These parasites carry such dangerous diseases as Marseilles fever and tularemia.
Their distribution center is in Eurasia, but they are also found in Africa and North America. The color of its body will help you distinguish a dog tick - brown with a small spot on the body, the limbs of the individual are darker than the body. The average size of an adult individual is 4 millimeters; a blood-filled individual can reach a size of 11 millimeters.
Dermacentors
You can quite often find this type of tick in forest belts or steppe areas. Dermacentor is a carrier of the most dangerous diseases with fatal consequences. There are several subspecies of this genus of ticks. Brown ticks
Brown ticks are carriers of the most dangerous infections - piroplasmosis and tularemia. Brown ticks are considered quite large - females are 4.3 millimeters, males are 4.8 millimeters. The number of eggs laid by a female depends on her size; they mature in an average of 2-3 weeks. Pasture mites
Pasture ticks carry tick-borne typhus, encephalitis, and Omsk fever. This undoubtedly dangerous type of tick is found mainly in the steppes. These ticks mainly attack animals living in the forest-steppe zone. However, there have been situations when pasture ticks have attacked humans, which is why it is important to treat tents in the forests with special chemical solutions, and to clean the surrounding area of excess plantings.
How to protect yourself and your loved ones from dangerous ticks
The world is filled with dangers even where we do not expect them at all. If you return from a trip to nature, be sure to carefully examine your body and advise your loved ones to do the same. If you find a tick on your body, immediately go to the doctor. It is important to treat the room after such situations - it is not known how long the tick stayed on your loved one’s body, perhaps it managed to lay eggs. The City Disinfection Station will help you here. We will quickly and reliably clean your home of all traces of ticks, and you will forget about these parasites. Call – 8 (800)-707-81-28, we are happy to help you!
Author of the material: Vladimir Egorov
Disinfector Experience in the field for more than 4 years
Which tick is the most dangerous for humans?
Ixodid ticks are considered the most dangerous to human health. It is they who, by attaching and sucking blood, carry many infections. Burying into the skin, the parasites last for several days or even a week, transmitting viral pathogens with saliva. That's why it's important to know what they look like.
Ixodid ticks, description:
- oval shape, the body itself is flat;
- the color range varies from light shades of brown to black;
- covered with durable and elastic chitin, which cannot be crushed, but at the same time, as it fills with blood, it stretches well;
- tick eggs are oval, no more than a millimeter;
- The stages of development include the stages of larva, nymph and imago.
Among all the diseases transmitted by ixodid ticks, encephalitis is considered the most dangerous. It can occur in mild or severe form. In the first case, a person experiences a feverish state, which completely disappears after a couple of weeks. In the second, the brain is affected, which leads to paralysis, mental disorders or even death.
Taiga tick: what does it eat?
The taiga tick is not interested in organic matter; the only thing it feeds on is the blood of people and animals. Food sources for pests can be:
- Wild rodents
- Birds
- Reptiles
- Cats
- Dogs
- Horses
- Livestock
- People
Larvae, nymphs and females of taiga ticks feed on blood. Adult males either do not eat at all or latch on for only 1–2 hours. To reproduce, females need to be saturated with blood in the maximum possible volumes. For this purpose, they can remain on the wearer’s body for up to 2 weeks. Larvae and nymphs are practically no different from adult insects, with the exception of body size - at different stages of development they are in the range of 0.2–0.7 millimeters. Larvae and nymphs need blood to grow.
A tick bite almost always goes unnoticed by humans, so the parasite is most often discovered in an attached state. It is important to remove the tick
and keep it intact for analysis. This will help you avoid possible health problems and begin timely treatment of diseases that could be transmitted through a bite.
Tick habitats
To avoid tick bites, you should know where they live. Ticks prefer to settle and attack their prey in the following places:
- in areas with dense and wet vegetation;
- in shaded areas full of foliage;
- in undergrowth;
- in the meadows;
- at the bottom of ravines full of moisture;
- in thickets near water bodies;
- in the grass on well-trodden paths.
That is why you should be wary of tall grass, from which ticks can jump on humans or animals, and not trees, as many believe.
Danger from ticks
2016-03-29 City Disinfection Station
Many people know about the forest tick, but not everyone knows that the bite of ixodid ticks is dangerous to health. Ticks carry many infectious diseases. Ticks live where there is vegetation. They can be in the grass, on tree branches. You can become infected either through a tick bite or through accidental damage. This happens when the tick is removed from the animal incorrectly.
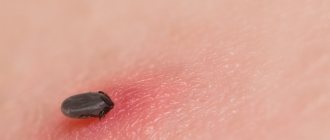
When a tick lands on a bare area of a person’s body, it painlessly attaches itself. Tick saliva contains anesthetic substances. A tick can suck in a mass of human blood that is several times its own weight.
When vacationing in areas where there is a lot of different vegetation, you must take precautions.
How to prevent a tick bite:
1. When going on vacation, prepare clothes in advance that will protect you. The shirt should be tucked into the trousers and the collar and cuffs buttoned. You must wear closed shoes on your feet. Cover the scalp with a scarf or hat.
2. Use special medications while walking. If you do not want to use repellents, then you can use any aromatic liquids (clove-scented colognes, essential oils, spice infusions).
Ticks love to attach themselves behind the ears, on the neck, and in the groin area. In these areas the skin is most tender. You should check your lower back, arms, and legs. Returning from a walk, you need to carefully inspect and shake out your clothes.
From the moment the tick attaches to its bite, it can take from one and a half to two hours, and sometimes more. If you find a tick on your body, you need to remove it immediately. To do this, you need to contact a medical institution. The procedure must be carried out professionally. When removed, parts of the tick's body may remain in the wound, which are also potentially dangerous. If you are far from a medical facility, you will need to remove the tick yourself. It needs to be lubricated with a greasy product that will be at hand. This can be a nourishing cream or butter. Then tie a thread around the tick’s body and carefully, swaying in different directions, without sudden movements, pull it out from the bite site. When pulling, try not to tear off the proboscis, which is deeply strengthened during suction. After removing the tick, treat the wound with iodine or alcohol.
If you are bitten by a tick, be sure to go to a medical facility. The risk of contracting an infectious disease is always present. The extracted ixodid tick is delivered to the laboratory for virological testing.
By following these simple rules, you can safely go into nature and not be afraid of danger from ticks .
Author of the material: Vladimir Egorov
Disinfector Experience in the field for more than 4 years
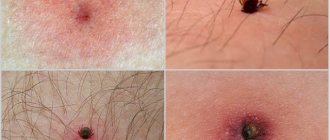
Bite symptoms
The fact is that it is impossible to immediately determine and detect the moment of a tick bite, since it does this absolutely painlessly by introducing natural anesthetics under the skin. However, after a few hours, the following symptoms may appear:
- slight nagging pain;
- mild subcutaneous itching;
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- visible enlargement of lymph nodes;
- rash on the body.
These symptoms indicate the penetration of infection into the blood and the beginning of infection.
How to detect a tick bite
As already mentioned, it is simply impossible to feel an insect bite. Therefore, the best way to understand whether there is a tick on the body or not is a timely examination. Most often, parasites cling to where the skin is soft, then biting through it will not be difficult. They can be found in the following areas of the body:
- in the axillary region;
- on the shoulders and forearms;
- on the inner thighs;
- in the groin area;
- in the place where the elastic band of the pants is located;
- behind the ears;
- between the shoulder blades;
- under the knee;
- in and under the chest area.
Children should be examined especially carefully, because their skin is thin and delicate, which makes it easy for a tick to attach itself to any part of the body. The most important thing is that when you find an insect, do not panic, do not try to brush it off or pull it out.
Self-removal of ticks
You already know how dangerous ticks are if they are not removed correctly. Now it’s worth talking about how to properly remove this dangerous insect. To completely remove the tick yourself, you need to act clearly and carefully, without rushing. There are several effective ways to get rid of this parasite.
1 way:
- a thread is taken and a loop is tightened as close as possible to the proboscis;
- then they carefully pull out the insect, making sure that the head does not come off and get stuck in the skin.
Method 2:
- To remove it you will need regular tweezers or tweezers;
- The tick is clamped and slowly begins to twist in one direction.
3 way:
- take a regular five-cc insulin syringe;
- the beginning of the syringe along with the tube is cut off with a knife;
- the desired area is moistened with water and the prepared syringe is tightly applied to it;
- slowly pull the piston, thereby sucking out the body and head of the tick.
4 way:
- if the head of the tick remains under the skin, then a sewing needle can help;
- it is burned until it darkens, and the bite site is moistened with alcohol;
- the needle is carefully inserted under the head of the tick, then lifted, thereby removing the remains of the insect;
There are several types of devices designed to remove ticks. They ensure that the parasite is completely removed, including the head.
The tick body must be preserved and sent for examination to the nearest SES for infections. The wound left from the bite is carefully treated with antiseptics to avoid additional infections.
Precautionary measures
You already know how dangerous ticks are. Are there any precautions? These tips are familiar to many, and it is simply necessary to follow them:
- Avoid wet areas with tall grass;
- you need to be especially careful during the period when ticks are active (May-June);
- if you are planning a walk in nature, clothing must be appropriate; it is best if it is white, tight-fitting, covering the body to the maximum;
- Don’t forget about a hat, because finding a tick in your hair is very difficult;
- You can first get vaccinated, which can protect you from encephalitis;
- before a walk, treat exposed areas of the body with special anti-tick products;
- upon returning home, you should carefully examine yourself;
- since the tick tries to get to soft places before biting, their inspection needs to be taken more carefully;
- If you are nevertheless bitten by an encephalitis tick, then within three days you need to have time to give an injection of immunoglobulin, which will block the virus.
Follow these rules and be healthy!
Where are ticks found?
For some reason, we are most afraid of tall trees, believing that an insect might fall from there. In fact, the tick lies in wait for its victim in tall grass next to the path or on the lower branches of trees and bushes (at a height of no more than 1 meter).
Parasites are active in the morning and evening hours. In the heat and rain, attacks do not occur, as the insects hide further away.
Most often, you can pick up a tick in the spring or summer. By the end of August, the risk of infection decreases, and by mid-September it disappears completely.