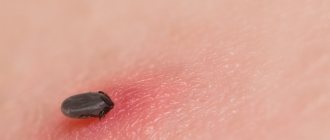
Due to changes in natural and climatic conditions and a decrease in intensive control of harmful insects, a favorable environment is created for the reproduction of the tick population. If earlier tick bites were rarely recorded, now cases have become more frequent.
Ticks live in tall grass and on the foliage of trees. If they could previously be seen only in dense plantings and forests, today, even walking through low-growing grass, you can become a victim of a dangerous insect. Children are included in a special risk zone.
Ticks are not harmless insects; the consequences of a tick bite on a person can be unpredictable. In many cases, complications occur. In this regard, you need to know more about:
- why a tick bite is dangerous, so that if necessary, you have an idea of what to do after a bite;
- what is first aid for a child or adult who is bitten by a tick;
- what complex diseases carried by ticks can worsen human health;
- what measures to take to prevent malignant viruses and bacteria from entering the body through the blood.
The threat of tick bites to humans
The main danger after a bite is that ticks carry infectious diseases that affect the nervous system. Many of them can remind themselves for years with a negative effect on the body. Therefore, it is so important to protect yourself and your family from a seemingly minor problem that can develop into a major health problem.
Knowing what diseases ticks carry, you can promptly detect signs of their manifestation if proper attention was not paid to the tick bite. The list of such ailments is constantly growing, the most common are:
- Q fever - the disease is recognized by such signs as high temperature up to 40°C, weakness, headache, joint pain, profuse sweating, sleep disturbance;
- typhus - makes itself felt by fever, damage to the central nervous system and blood vessels, intoxication of the body;
- tularemia - manifested by fever, damage to the lymph nodes and intoxication of the body;
- Lyme disease (borreliosis) – affects healthy areas of the skin, the central nervous system, the cardiovascular system, the musculoskeletal system, and is also manifested by high fever, headache, chills, weakness, intoxication;
- tick-borne encephalitis - manifested by intoxication, fever, damage to the brain and spinal cord, negatively affects the central nervous system, and can be fatal;
- ehrlichiosis – characterized by high body temperature, chills, headache, intoxication, skin rash.
These diseases have very similar symptoms; in many cases, the type of infection can only be determined after laboratory tests on the person who was bitten by the tick.
Infectious diseases transmitted by ticks cannot be cured on their own, but require immediate hospitalization. Therefore, if you are bitten by a tick, you should seek help from a medical facility, where they will help you remove the tick, treat the wound, and also tell you where to take the tick for analysis in order to determine it as a possible source of infection transmission.
Only a tick analysis helps to make a reliable diagnosis, identify a developing infection and direct treatment in the right direction.
It is advisable to take laboratory tests after a tick bite even when the person does not feel any particular discomfort. The infection affects the body gradually; if you give up on tests, you can create favorable conditions for the deterioration of your health.
Treatment after a tick bite takes a long period of time. Therefore, doctors recommend sounding the alarm immediately after its detection.
How to recognize a bite?
Not always, if a tick has attached itself, it is detected in the process of feeding. The thing is that painkillers that enter the bloodstream along with the parasite’s saliva make the insect’s bite and the process of feeding on blood completely invisible to humans. The feeding time of ticks can vary significantly. Male ticks, as a rule, remain on the human body for only a few hours, while females can suck blood for many days, increasing in size by more than 10 times during their feeding.
In the process of feeding, the abdomen of an embedded tick becomes clearly visible because it significantly increases in size. However, if the tick has already completed its feeding and has left the skin, it is possible to guess that this particular parasite has attacked a person only by indirect signs. At the site of the bite there is a small wound, reaching 1 mm. Redness and swelling may appear around the wound. Considering that similar manifestations are observed with bites of other less dangerous insects, people often do not pay attention to these symptoms. That is why you need to know what symptoms appear first when viruses and spirochetes are transmitted through the saliva of a tick. Symptoms such as increased body temperature, general weakness and fatigue, which appear approximately 3-7 days after going to the forest or other place, can make you wary.
Where does the tick bite?
Ticks can bite exposed areas of the body, but it is possible that these insects can penetrate under clothing. Most often, the favorite areas for tick bites are the neck, the area behind the ears, the scalp, armpits, lower back, abdomen, even the groin area; genital bites are not excluded.
The tick bites unnoticed; people do not experience any pain or discomfort, since the insect injects an anesthetic substance into the blood. Ticks dig into the skin, first penetrating the upper layers of the epidermis and gradually going deeper.
The most common places of bites
A tick can bite on any part of the body, but they have “favorite” places - doctors were able to identify them by analyzing a large number of cases of tick bites. Most of all, parasites love areas with thin skin, namely:
- popliteal fossae (absolute leaders in the number of bites, because the skin there is very delicate);
- head, back of neck;
- elbows, shoulders, backs of hands, armpits, palms;
- groin area;
- Feet.
Parasites rarely bite on the back area, since the skin there is thick and more difficult to bite through.
Symptoms and signs of a tick bite
Symptoms after a tick bite in a person begin to appear within a few hours. People complain of physical ailments such as:
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- muscle weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- profuse vomiting;
- hallucinations;
- change in coordination of movements;
- temperature increase;
- skin itching.
If any of these symptoms appear after a walk in a park or forest, you should immediately examine your entire body for ticks. This should be done slowly, carefully examining each area. Often a tick bite is found quickly.
At the same time, you need to understand that the danger is posed not only by an insect that has already clung to the skin, but also by a tick brought on clothing, which is looking for a spot for a hook.
The symptoms that appear after a tick bite in a person in the absence of medical care can worsen every day.
What does a tick bite look like on the body? The main signs of a tick bite are:
- dotted red spot;
- skin irritation;
- the presence of an insect body embedded in the skin;
- Sometimes a lump forms after a tick bite.
Mark of a tick bite
If the circle around the tick is pink, then this most often indicates an allergic reaction of the body to the saliva of the insect, but if the bite site becomes bright red, and red circles in the form of eczema spread throughout the body, then this indicates an infectious dangerous bite .
If you are bitten by a tick, you need to measure the spot with a ruler and observe its changes until you visit the doctor, if you cannot provide first aid at home.
Red circles from a tick bite are a sign of infection
Who shouldn't be afraid of ticks?
The situation is quite paradoxical, but representatives of both sexes should study the signs of a tick bite. Although insects are more likely to choose women as a source of food, men are similarly susceptible to attacks. When tracking their target, ticks rely on their sense of smell. In most cases, the stronger sex has a more pronounced and pungent body odor. Men produce more sweat, which will be an additional factor in attracting aggressive insects.
Regardless of gender and age, absolutely everyone should be afraid of ticks. You should not neglect the likelihood of contracting the disease, since any insect can be a carrier of the virus. There is an unpleasant fact that ticks that carry Lyme disease search for food sources several times more actively.
How to help with a tick bite at home
The first question that arises when a tick bite is detected is what to do at home?
First aid for a tick bite is to remove it. This is very difficult to do in cases where the insect has managed to penetrate deeper into the skin. The site of the tick bite must first be disinfected.
How to treat a tick bite? It is recommended to treat with iodine, brilliant green or alcohol; in the absence of such available means, ordinary vodka will do. After disinfection, a thin thread is taken, a tight lasso is made from it around the tick’s proboscis, the ends of which must subsequently be pulled tight and the insect slowly swung. This manipulation allows you to remove the tick without damaging its body.
If the insect's head remains in the skin, this means that the infection continues to spread throughout the body. Instead of thread, you can use tweezers or a special medical pin.
Under no circumstances should you make sudden movements when removing an insect; the tick bite is very itchy, so the bitten person must be patient and not move until the tick is removed.
After removing the insect, the bite site may itch for a week or more, so it is recommended to take antiallergic medications. If the tick bite itches severely even after taking antihistamines, you should consult a doctor.
The wound formed after a sterile tick bite heals quickly after it is removed; it is treated with iodine or brilliant green until complete healing. The bite of an infected tick tends to fester and in this case it is impossible to do without the help of a physician.
How to properly remove ticks from skin
You can try to pull the tick out with your hands if it has not yet fully fixed itself and after several rotational movements you will be able to pull it out. If the first method does not produce results, you should use tweezers or, even better, reverse tweezers, which allows you to grab the tick at the very base of its head, which will not allow you to tear off its body. Before removing the tick, turn it several times to loosen its grip.
If you don’t have the necessary equipment at hand, you can use a thread tied in a loop. The loop is placed over the tick's head and pulled together with a gentle movement, after which they gradually pull and loosen it until it comes out.
Video: How to properly remove a tick - three simple ways
If you are in the city, it is best to seek help from a clinic so that an experienced doctor removes the parasite correctly and treats the wound, while examining the tick itself to identify infections or the absence thereof.
Also in many pharmacies you can purchase a special tool designed for removing ticks; it allows you to fix the tick by the head, turn it and pull it out, without the risk of damaging the insect.
If the head of the tick remains in the skin, don’t worry, take a disinfected needle and use it to remove the remaining parts of the tick, then disinfect the wound with iodine, hydrogen peroxide or alcohol.
Drug treatment for tick bites
- The bite of a sterile tick does not pose a threat to health. In such cases, treatment is not prescribed, only the procedure for extracting the insect is performed.
- If the tick is a carrier of diseases, then in each specific case individual therapy is carried out with the help of appropriate medications prescribed by the attending physicians.
- Often, patients are prescribed specific immunotherapy, when immunoglobulin is injected into the body from a tick bite, if there is suspicion of the spread of a viral infectious focus or its laboratory confirmation.
- Antibiotics for a tick bite are prescribed when bacterial infectious diseases transmitted through blood are detected.
- Ailments caused by protozoan microorganisms are treated with drugs that suppress their reproduction.
Diseases such as borreliosis and encephalitis are the most common in the CIS. Their treatment is long-term. Therapy is aimed at restoring proper functioning of the brain, central nervous system and circulatory system.
Borreliosis (Lyme disease) and encephalitis require unconditional hospitalization and hospital treatment. People who have been bitten by an infected tick are sent to infectious disease clinics to undergo laboratory tests.
Lyme disease
Borreliosis is a disease caused by bacteria, so antibiotic therapy is effective in its treatment. Whereas encephalitis is a viral disease and cannot be treated with antibiotics.
Bites from infected ticks can seriously undermine human health, including disability or death. Diseases transmitted through blood by ticks to humans disrupt the functioning of the liver, kidneys, joints, lungs, and digestive system, so during treatment, doctors use complex therapy aimed at restoring the functioning of the entire body.
The most common diseases transmitted through a tick bite.
| Disease | The causative agent of the disease | Tick vector | What does it look like? |
| Virus from the Flavaviridae family | Ixodid ticks: I. ricinus, I. persicatus | |
| Spirochete -Borrelia burgdoferi | Ixodid ticks:
| |
| Virus of the Nairovirus genus, Bunyavirus family | Ticks sort of Hyaloma
|
Source: policemed.com
- Tick-borne encephalitis is an infectious viral disease transmitted through tick bites, characterized by fever and damage to the central nervous system, often leading to disability and death. On average, symptoms of the disease appear 7-14 days (5-25 days) after infection. The onset of the disease is acute; more often the patient can indicate not only the day, but also the hour of onset of the disease. In most cases, the disease ends in complete recovery. With focal forms, a large percentage of the person will remain disabled. The period of incapacity for work is from 2-3 weeks to 2-3 months, depending on the form of the disease.
- Ixodid tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) - This is an infectious disease transmitted through the bites of ixodid ticks, characterized by damage to the nervous system, skin, joints, heart, the disease is prone to chronicity. If the tick is removed no later than 5 hours after the bite, the development of borreliosis can be avoided. This is explained by the fact that the causative agent of the disease, Borrelia, is located in the intestines of the tick and begins to be released only when the tick actively begins to feed, and this occurs on average 5 hours after penetration into human skin. The prognosis for life is favorable. If started late and improperly treated, the disease becomes chronic and can lead to disability. The period of incapacity for work is from 7 to 30 days, depending on the course and form of the disease.
- Crimean hemorrhagic fever is a severe viral infectious disease transmitted through tick bites, characterized by fever, intoxication and bleeding. The disease belongs to a number of dangerous infectious diseases. Late hospitalization and incorrect diagnosis and treatment often lead to death. The mortality rate is 25%. The period of incapacity for work is from 7 to 30 days, depending on the form of the disease.
Animal tick bites
Ticks are blood-sucking insects; they bite not only people, but also domestic animals and livestock. What should you do if your animal is bitten by a tick? Of course, provide first aid - treat the bite with disinfectants and try to remove the tick. To do this, you will need an assistant who will hold the animal and distract it from the procedure. A qualified veterinarian can help rid animals of ticks.
Tick in animal fur
If a puppy is bitten by a tick or a cat is bitten by a tick, the condition of the animals changes rapidly. They become lethargic, lose their appetite, and are inactive. Several ticks can get caught on an animal's fur at the same time; their simultaneous bites can even lead to the death of pets.
If animals are bitten by infected ticks, they also become a source of spread of dangerous diseases.
How do ticks reproduce?
Reproduction of forest ticks occurs after full saturation. After fertilization, the female must feed on blood for about 10 days to produce offspring. At one time, she is capable of laying 5,000 eggs, which in the first stages after birth are located on low plants. Then, after the larvae emerge, they need to find a host - a vertebrate animal that will supply them with blood. This is what will allow the larvae to turn into nymphs (more adult individuals). The growth doesn't stop there. To become an adult, ticks again need to find a victim and drink blood. The period during which the parasite grows from a larva into an ordinary adult tick is determined by two years. Under favorable conditions, it is reduced to 5-6 months.
Preventing tick bites
- To protect themselves from danger from possible tick bites, many people use vaccination against infectious diseases such as borreliosis, encephalitis; the body’s protection lasts for three years, after which revaccination is performed.
- When visiting wooded and bushy areas, you should give preference to clothes with tight elastic bands on the sleeves, tight-fitting collars, hoods that protect the neck, workwear with a sliding surface, and knee-length rubber shoes. Pants must be tucked into shoes. It is recommended not to visit forests and forest plantations without a hat.
- Don't get carried away with walking through tall meadow grass.
- Ticks are repelled by special repellents that are sprayed on clothing and exposed areas of the body. It can also be lotions, creams, gels or pencils.
- Since ticks can settle in a garden plot, it is recommended to mow the grass more often, trim tree branches, thoroughly clean the area in the off-season, and treat harmful garden insects using special toxic preparations.
Preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of tick bites. But, if a tick bites you, despite all the precautions, then there is no alternative to going to the nearest medical center. You should not be negligent about tick bites, and when you find them, you should remember that professional help from a doctor is the best solution in the current situation, which will help maintain the health of both adults and children for many years.
Where can you find ticks?
All districts of the Leningrad region and some districts of St. Petersburg, as well as 13 of the 18 territories of Karelia are infected with tick-borne encephalitis.
The North-Western region (in particular St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region, as well as the Vologda, Arkhangelsk, Novgorod, and Pskov regions) are endemic for tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. Tick-borne encephalitis is common in Siberia, Altai, Sayan Mountains, the Urals, and the Far East.
Lyme disease can be contracted through a tick bite in the forests of the Kaliningrad, Leningrad, Tver, Yaroslavl, Kostroma, Perm, Tyumen regions, and in the Komi Republic. In the Urals, Western Siberia and the Far East, ticks carrying borreliosis are found in pastures and forests along rivers.
You can see a complete list of endemic regions and areas on this website.
The probability that a tick in the Leningrad region is infected with encephalitis is about 1-2%, and borreliosis - 7-10%.
Where can I submit a tick for analysis?
If the victim managed to remove the tick in the hospital, the animal must be sent to the laboratory to be tested for infection. If the tick is removed at home, it is necessary to place it in a small jar along with a moistened piece of gauze or cotton wool so that it does not dry out. It is definitely worth considering that the tick must be alive, this is the only way the study will be carried out. Usually, all tests can be carried out at the sanitary and epidemiological station or special epidemiology centers, the addresses of which can be precisely clarified with the ambulance.
What should I do if bitten by a tick?
If you find a tick on your skin, you should immediately go to the nearest emergency room where first aid will be provided. The parasite should be submitted to a laboratory to find out whether it is a carrier of diseases. If there is no hospital nearby, then you need to, following all the rules, remove the tick yourself. The parasite stays on the skin for half an hour to two hours, so during this time it can be detected and removed. Under no circumstances should a tick be crushed or pulled out; only twisting it will help get rid of it.