Demodicosis is an inflammation of the facial skin by a microscopic mite. There may also be demodicosis of the eyelids, eyebrows and nose. The parasite penetrates the subcutaneous tissue when a person’s immunity weakens.
Visually, demodicosis on the face looks like ordinary teenage acne, shaped like a red tubercle. More than 70% of people cannot even think that such a terrible tick already lives in their body.
Most often, demodicosis is observed in women due to hormonal imbalances. Also, the appearance of disease in a woman’s body can be triggered by the use of low-quality cosmetics.
Etiology and pathogenesis of demodicosis
The mite that causes demodicosis on the face was studied in 1842. In total, about 70 species of this parasite are known, but only three of them are dangerous to humans, others only harm animals. The size of an adult tick is no more than 0.5 mm. It feeds on human hormones and lard. Afraid of daylight, active in the dark
A female can lay several dozen eggs during her life cycle. New individuals are ready to breed in a couple of days.
At present, it is not yet fully known when the tick begins to multiply rapidly. But in most cases, this is influenced by stress and nervous tension.
Clinical picture
If the immune system is in order, the tick does not cause any inconvenience and is even somewhat useful, because it eats up dead skin particles, helping to renew the epidermis. But if the body’s defenses weaken after suffering an acute illness or during sluggish chronic processes, the tick begins to multiply. It penetrates into the deep layers of the skin, where it causes inflammatory processes. This results in pustules or large, scaly, pinkish areas that resemble rosacea. Usually demodicosis affects the face, but in extensive forms the whole body can be affected. Due to a sharp decrease in immunity, this disease sometimes occurs in women during pregnancy or as a result of severe stress.
Question answer
Is it possible to cure demodicosis?
The main causes of demodicosis
The appearance of demodicosis in the body occurs for many reasons. Very often, ticks appear in people of old age. But there are also the following reasons:
- Using low-quality cosmetics. If you have sensitive skin, choose such products carefully, it is better to consult with specialists several times.
- Improper functioning of the endocrine system.
- Problems in the gastrointestinal tract. Doctors advise sticking to the necessary diet and taking better care of your skin.
- Nervous system disorder. Try not to get into stressful situations. Drink soothing tea and herbs. Take medications only as prescribed by a specialist.
From the onset of the disease until treatment, demodicosis is contagious to others. One handshake can transmit the disease.
Traditional methods of treating demodicosis
There are hundreds of traditional medicines that are used for demodicosis. But they are not able to replace pharmaceutical drugs. Therefore, homemade ointments, lotions, masks and decoctions are used as auxiliary therapy.
Effective remedies for demodectic rash on the face:
- A piece of tar soap is ground on a grater. Mix 2 tbsp. l. shavings with vodka. The creamy mixture is applied to the rash for 20 minutes up to 3 times a day.
- Cosmetic clay. 1 tbsp. l. white clay is mixed with calendula decoction until a paste-like mixture is obtained. Apply directly to problem areas for 30 minutes 4 times a day.
- Compress with oak bark. Boil 1 tsp in 250 ml of water. raw materials for at least 2 min. Gauze is soaked in the liquid and applied to the rashes on the face for 20 minutes. every 3-4 hours.
- Sagebrush. 20 g of herb are boiled in 1 liter of water and left for 3.5 hours in a warm place. Take 150 ml every 3 hours for at least 3 days.
- Castor oil with Trichopolum. 2 tablets are crushed and mixed with 5 ml of castor oil. Apply the product to papules on the face 3-5 times a day.
For the ocular form of demodicosis, it is recommended to wipe the skin of the eyelids with decoctions of tansy and calendula.
Folk remedies are used regularly for at least 2 weeks in a row.
How to properly treat demodicosis
It will take a long time to get rid of demodicosis and forget about this disease forever. Treatment of demodicosis is carried out using a set of measures to improve the immune system and eliminate disruptions of the endocrine system.
Medicines that help get rid of ticks are called acaricidal. The most effective: Demalan, Wilkinson Ointment, Sulfur Ointment, Colbiotsin, Eubetal, Prenatsid, Spregal Cream, Yam Ointment.
There is also a whole series of products against this disease, “Stop Demodex,” which includes hygiene products.
Medicines
Antiprotozoal drugs help well against demodicosis. They act on the nervous system of the tick, and it dies. The tablets must be used carefully; many have contraindications.
The doctor determines the treatment and the amount of drugs.
What does a tick look like, photo
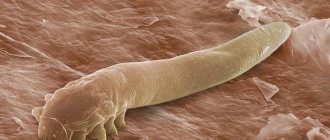
The mite itself looks quite scary - it’s like a machine for digesting fat and dead epidermis, which comes in different types (more than 60), in humans there are two types of demodes, their photos under a microscope are shown below:
- Demodex folliculorum - long individuals that nest in hair follicles
- Demodex brevis is a short, worm-like mite that inhabits the ducts of the sebaceous glands
The mite itself is conditionally pathogenic, that is, as I said above, it requires certain conditions for pathologically rapid reproduction and damage to the hair follicles and sebaceous glands of the face, eyebrows, eyes, and scalp. Sometimes they ask me how contagious this mite is and I ask a counter question: if almost 90% of the world's population is infected
with demodex, but not everyone has
manifestations of demodicosis , the clinical symptoms of the disease are diagnosed much less frequently and only under certain conditions, then how can it be contagious?
Scientists have also proven that subcutaneous mites do not adapt to life outside the host and die in the external environment. Although there are many tips on the Internet on how to avoid getting infected... It's funny. This is a saprophytic (conditionally beneficial) organism that lives on the skin of almost everyone. Here are some more photos under the microscope of a demodex mite:
Perhaps you will find useful an article on a related topic about what chlamydia is, treatment with medication and traditional methods, the reasons for its occurrence, or you want to learn everything about a disease such as herpes zoster, its causative agent and how dangerous it is, about methods of getting rid of it. Good advice awaits you in the article, heel spur - in this case - follow the links. You will learn a lot from the article, which describes acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis.
Advertising MEDICINETEASER
Nutrition rules
If you cleanse the body of toxins and reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract, it will be easier to fight the disease, so experts recommend sticking to a dairy-vegetable diet
It is also necessary to avoid citrus fruits, eggs and honey during the treatment period. It is also better to exclude sweets and baked goods. As for drinks, you should avoid coffee and soda.
Treatment of chickenpox - symptoms and features of manifestation in children and adults. Why shouldn't you scratch chickenpox lesions?Vitiligo - causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis and treatment in the clinic and at home (video + 135 photos)
- Acoustic neuroma
During treatment, the most basic diet is various cereals, vegetables and dairy products. You can eat lean meat in small quantities.
Symptoms of the disease
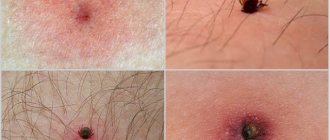
Let's look at the main symptoms of demodicosis. Ticks are able to move throughout the body, but mainly affect only the face, including the forehead, chin, cheeks, and somewhat less frequently, the eyelids, ear canal and surface of the ears, and the head, as shown in the photo below. On other parts of the body, the disease is quite rare.
One of the symptoms characteristic of demodicosis occurs as a direct consequence of the activity of the mite. This symptom is an increase in pores on the skin, the formation of a “loose” surface. This happens due to the multiplication of the parasite. Dozens of individuals simply do not fit in the same place, and the sebaceous gland is stretched, and along with it the skin.
Other symptoms are mainly the result of the body’s attempts to “repel the attack.” Here is a short list of them:
- the appearance of acne in increasing numbers (especially red acne with pus inside).
- increased activity of the sebaceous glands
- discoloration of skin gray
By affecting the skin of the eyelids, mites also cause eyelash loss. The whites of the eyes are also at risk. Unfortunately, if mites are not dealt with, they can also penetrate the inside of the ear, causing constant tinnitus. When such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Demodectic mange causes itchy skin, accompanied by swelling and redness, so it can be easily confused with other skin diseases and allergies. In this regard, it is worth remembering that with demodicosis, unlike allergies, redness with induration always appears first and only then does itching from intoxication begin.
When Demodex affects the eyelids of our eyes , they become itchy and red, scales form at the roots of the eyelashes, a dry crust and plaque appears along the contour of the eyelids, the eyelashes stick together and fall out. The skin gradually loses its elasticity, becomes rough, cracks and peels from profuse rashes. The affected areas thicken, taking on the appearance of scars, with cone-shaped reddish-pink papules emerging from under the crust. Difficulties arise with facial expressions, the nose swells and increases in size.
The advanced stage
of demodicosis of the facial skin is characterized by a yellowish-brown tint of the skin, covered with acne that has turned into ulcers and a puffy, swollen face.
If left untreated, the cosmetic defect of the skin will only get worse and can lead to disfigurement. It is worth understanding that such a skin response is not caused by the activity of microorganisms, but by their waste products , which are very toxic to humans.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of demodicosis, women need to follow the following rules:
- Maintain facial hygiene;
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- Use only proven cosmetics;
- Support immunity with vitamins;
- Get rid of bad habits.
These rules will help maintain healthy skin. To better understand what this disease looks like, look at the photo of demodicosis.
Demodicosis is a complex disease and can become chronic if it is not treated promptly. Also, do not forget that for proper treatment you need to contact specialists.
Appearance of the parasite
Most often, iron ore or iron ore mites, demodex, appear on the skin. Outwardly it looks like a white, translucent worm. Body size does not exceed 0.4 mm. Movement and fixation are carried out by four pairs of limbs. The first are the oral apparatus. The remaining paws have sharp claws. A photo of a subcutaneous mite on the face can be seen below.
The parasite is localized in the area of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. It affects the skin of the face, less often the neck, chest, back, and shoulders. About 4 glands are concentrated in one hair follicle. The main sign of the development of demodicosis is acne.
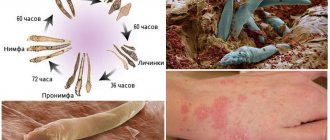
Skin mites on the face go through several stages of development.
- It all starts with a microscopic egg. The female deposits them on the surface of the epidermis.
- After a few days, it transforms into a larva with three pairs of limbs and the absence of respiratory and genital openings.
- The next stage is the nymph, which goes through several stages of its development. On the latter, a fourth pair of limbs appears, the genitals.
- The final formation of the reproductive system is completed in adult ticks - adults.
A photo of a tick on the face at different stages of development is presented below.
On a note!
The subcutaneous mite is present on the skin of every person, but does not cause discomfort and is completely invisible. Acne does not always appear. And only under certain circumstances does it begin to actively reproduce, which causes a difficult-to-treat disease - demodicosis.
Demodex mite at different stages of development