What is demodicosis
In addition to the medical one, the disease has several names: “rosacea,” i.e., similar to a rose, and “rosacea.” All of them are given for the appearance of the affected skin, which looks like a scattering of pink acne. Disfigured areas are clearly visible on the skin, in which there is a reddened and thickened layer of the epidermis, penetrated by dilated tiny blood vessels, which are called “telangiectasia,” as seen in the photo of demodicosis in a patient.
Most often, foci of the disease appear on the face, which leads to cosmetic defects in women, who develop demodicosis more often than men at the age of 30-50 years. A small number of parasites can also be found on other parts of the body: on the chest, back, neck, etc.
Interesting!
Rosacea is the most common disease among the population of Ireland and southern Italy, but residents of the African continent and China suffer from it quite rarely.
Causes of demodicosis
The causative agents of the disease are microscopic subcutaneous mites of 2 types:
- which parasitizes inside the sebaceous glands of Demodex folliculorum;
- in hair follicles of Demodex brevis in humans and mammals.
On a note!
Sometimes they are called eyelash mites due to their frequent settlement on eyelash hairs, as well as acne glands.
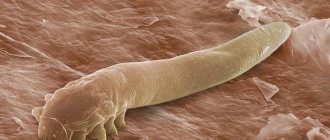
The size of an adult parasite is 0.2-0.5 mm, so it is impossible to see them with the naked eye, but only under a microscope. The tick's body is translucent, has an elongated shape and consists of 2 parts; in front there are 4 pairs of legs for rapid movement at a speed of up to 16 mm/h. The spoke-shaped mouthparts are designed to eat particles of epithelium and secretions from the sebaceous glands. The mite has many scales on its body, with which it attaches to the hair follicle.
Demodicosis mites
The life cycle of the parasite is several weeks. Reproduction occurs through the laying of 20-25 eggs by females in the cavity of the hair follicle, from which 6-legged small larvae emerge after a few days. As they grow over 7 days, they form into adults.
The entire life of demodicosis mites passes under the upper layer of the epidermis, and they come to the surface exclusively to mate or search for a new location. Due to photophobia, they lead an active life at night.
Routes of transmission of demodicosis:
- upon contact with a sick or healthy person who is a carrier of Demodex, which according to statistics constitutes 80% of the planet's population;
- Ticks can remain viable in the environment and survive for some time when exposed to water.
On a note!
Demodexes are opportunistic parasites found in the skin of many people. Their reproduction and subsequent clinical signs of the disease usually appear under favorable conditions.
Factors contributing to the development of demodicosis in humans:
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract);
- disorders and diseases in the endocrine system: hormonal imbalance, diabetes, etc.;
- decreased immunity (after a common cold or due to a long-term illness);
- negative external factors: nervous stress, overheating in the sun, long-term use of medications or hormonal drugs, harmful working conditions, the use of oily cosmetics and allergic reactions, alcohol abuse, unhealthy diet.
Under what conditions does the subcutaneous tick provoke the disease?
Demodecosis capitis is a disease from the acariasis group caused by parasitic mites. There are more than 65 species of Demodex (acne glands), but only three of them parasitize the human body. Microscopic mites feed on sebum - sebum. Therefore, they live in hair follicles and sebaceous ducts, causing hyperactivity of the glands.
Demodex belongs to the group of opportunistic microorganisms and is found in 95% of people. But only in some of them they provoke demodicosis of the head and smooth skin.
Activation of parasites occurs when the body’s immune strength decreases.
Factors that provoke the proliferation of acne:
- psycho-emotional stress;
- dermatological diseases;
- abuse of spicy foods;
- frequent visits to baths;
- vitamin and mineral deficiency;
- excess decorative cosmetics;
- hormonal medications;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- infrequent hair washing.
People with hypersensitive skin, diabetes mellitus, and allergic dermatoses are susceptible to the disease.
When the immune system is functioning correctly, the tick does not penetrate the skin deeper than the basal layer. But excessive sebum production, decreased immunity due to medication and stress provoke activation of demodex.
At a temperature of 30-40°C, the acne gland multiplies quickly. The more parasites there are in the follicles of the scalp, the more pronounced the signs of demodicosis are.
In 8 out of 10 cases, relapses of infection are observed in the warm season.
Symptoms of demodicosis
The disease manifests itself to varying degrees depending on the number of mites and their reproduction process, the type of epidermis and the condition of the patient's body.
Features and signs of demodicosis:
- an inflammatory skin rash that appears on the face, eyelids, and less often on other parts of the body;
- itching in the affected area, which intensifies in the evening and at night, during the period of increased activity of subcutaneous mites.
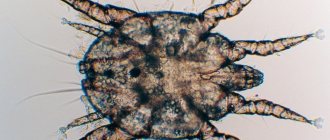
Signs of demodicosis
Classification of demodicosis in humans, code according to ICD-10: B88.0, is carried out according to external signs, which determine the stage of the disease:
- The erythematous form is manifested by the appearance of erythema or redness in some areas of the skin: on the face, the rash is localized on the nose and cheeks, its edges are clearly defined and slightly raised. “Vascular spiders” are formed from small vessels, which, when the face is affected, are clearly visible on the sides of the nose and cheeks.
- Papular-pustular stage - characterized by the appearance of pimples (papules) and ulcers (pustules) up to 2 mm in size, formed due to the overflow of hair follicles with sebum. The ducts are blocked due to the accumulation of parasites. The color of the formations ranges from pink to red-bluish.
- The hypertrophic stage occurs in the absence of treatment, resulting in hypertrophy of the affected areas of the epidermis: pineal growths are formed on the damaged area, the names of which depend on the affected area (rhinophyma - on the nose, metaphyma - on the forehead, blepharophyma - on the eyelids, otophyma - on the earlobe , gnathophymas - on the chin, etc.).
On a note!
Symptoms of demodicosis in children are often disguised as a rash that accompanies adolescence and hormonal changes in a young body. For an accurate diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and get tested for ticks.
Treatment of the disease
Subcutaneous demodex mites can occur in men, women or children, causing a lot of trouble in caring for the affected skin and embarrassment, because it is extremely difficult to hide the consequences of demodicosis. The parasite lives in the subcutaneous layer only where all possible conditions for life have been created. The tick feeds on subcutaneous fat, which is produced daily. Attempts to hide the tubercles characteristic of demodicosis with the help of decorative cosmetics only aggravate the problem. Pores clogged with special tinting agents become inflamed, and sebaceous plugs allow the parasite to multiply many times faster. Both dermatologists and traditional healers can easily answer the question of how to treat demodicosis. Demodectic mange on the body is a disease that people suffered from a hundred, two hundred years ago and fought with the same diligence only with the help of homemade tinctures and lotions.
The treatment regimen for demodicosis includes taking several types of drugs at once, each of which has its own purpose. Killing healthy ticks is not enough, because before infection with the parasite, the necessary prerequisites (negative changes) for the development of a dangerous skin disease have arisen in the human body. The root cause of demodicosis is weakened immunity. Before treatment, you need to know not only how to get rid of demodicosis, but also how to avoid relapses of the disease.
Therapy for demodex consists of:
- local drugs (destruction of parasites);
- immunomodulators;
- complex of vitamins (minerals and amino acids);
- anti-inflammatory agents (prevent the occurrence of allergic reactions - “Tavegil” and “Diazolin”);
- anthelmintics (“Ornidazole” or “Metronidazole”).
The selection of local treatment is guided by the individual reactions of the patient’s body. It will not be possible to get rid of parasites forever in one day; only an integrated approach to solving the problem that has arisen will ensure positive dynamics in the treatment of demodicosis. The course of treatment procedures lasts from several weeks to a year. Ticks that live off the host (human) may appear again, then therapy is repeated.
The most effective means of combating ticks are topical ointments. The instructions for such drugs determine the standard dosage, but the attending physician may change the method of use and the amount of the drug to combat demodex.
- “Demodex complex” is an effective and safe drug that is often used as the main treatment for demodicosis in people of different ages and genders.
- The exclusively natural base of the product does not cause an allergic reaction or side effects.
- “Demodex complex” helps in the early stages of the disease and fights against mites in severe cases of demodicosis.
- For people who have gotten rid of the subcutaneous parasite, it helps relieve symptoms from the first day of use.
Active demodex and its treatment require increased attention, because after getting rid of the mite, the patient will regain his previous appearance and get rid of constant anxiety. Helminthiasis is curable provided that all recommendations and prescriptions of the attending physician are followed.
Demodicosis on various parts of the body
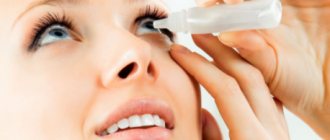
One of the common areas affected by this disease is the eyelids and eyes, when mites multiply in the meibomian glands, i.e. at the base of the eyelashes. The onset of inflammation is usually manifested by severe itching and symptoms of blepharitis, an inflammatory process on the eyelids, and a possible bacterial infection.
The main sign of demodicosis of the eyelids is a whitish border at the base of the eyelashes. If left untreated, eyelashes fall out and the edges of the eyelids become enlarged, causing the patient to experience difficulty closing them.
Demodectic mange on the body
On a note!
Demodicosis of the eyelids in 60% of cases also manifests itself on the face and scalp, and can cause complications in the form of chronic conjunctivitis, abnormal eyelash growth and other diseases.
Demodicosis of the scalp begins as a result of the establishment of a favorable environment on the scalp. The disease is rarely detected due to the fact that the appearance of pustules under the hair goes unnoticed by a person. Distinctive symptom: severe itching in the evening. The skin lumps that appear can be felt by palpating the head.
Demodectic mange on the arms, chest, back, and neck can appear when mites multiply heavily and the disease spreads to other areas of the upper half of the body. It is accompanied by sensations of skin tightening, itching and burning in the affected areas. However, this happens very rarely due to the different structure and functioning of the sebaceous glands on the human body, as a result of which Demodexes do not find nutrition in them.
Diagnosis of demodicosis
If characteristic symptoms of the disease appear, you should contact your doctor for examination and an accurate diagnosis, which can only be confirmed after receiving an analysis from the affected area of the skin and subsequent laboratory testing. The patient submits such a scraping to a skin and venous dispensary or a private laboratory.
Important!
Before taking the test for demodicosis, you should not use cosmetics or wash your skin for 2 days in order to get accurate results.
Under a microscope, biological material is examined for the presence of demodex mites, their eggs or larvae. The diagnosis of demodicosis is made if per 1 sq. cm of skin, 5 adult mites were found; in case of eyelid disease, at least 6 parasites were present on the 1st eyelash.
Diagnostics
Treatment of demodicosis of the scalp begins with proper diagnosis
Even in a healthy person, the Demodex mite lives in the epithelial tissues, so doctors pay attention not to its presence, but to its quantity. The choice of the appropriate examination technique is made by the doctor, since each of the procedures has advantages and disadvantages
Existing methods for diagnosing demodicosis:
- Scraping from the surface of the affected skin - with its help, the affected area of the skin is assessed and the parasite is calculated per unit of skin area.
- Examination of the secretion of the sebaceous glands - part of the mite elements is squeezed out, the skin on the head is partially damaged.
- Superficial biopsy - examines parts of the epithelium and the contents of its glands.
- Skin biopsy followed by histological examination allows you to examine the secretion of the sebaceous glands.
- The study of eyelashes and hair reveals parasites in the follicles; the procedure does not cause much pain.
How to treat demodicosis
Modern medicine presents many effective means and drugs to cure such an unpleasant disease. After confirming the diagnosis of demodicosis, the dermatologist determines a treatment regimen, which consists of complex therapy in several areas:
- Use of topical medications (ointments, creams, sprays).
- Systemic medical products to improve immunity and treat concomitant chronic diseases.
- A program for cleansing the gastrointestinal tract and the entire body of the patient.
- Antibiotics and antiparasitic agents for killing ticks: Trichopolum (tablets, price 100 rubles), Ornidazole (capsules and tablets, price 120-160 rubles), Metronidazole (suppositories, ointment, tablets, price 20-150 rubles) in a course of 10- 15 days. These drugs are contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, kidney patients, and epilepsy.
- Antihistamines to relieve possible allergic reactions.
- Antiseptic solutions for wiping the skin: Chlorhexidine, Hexamine, Hydrogen peroxide, Calendula alcohol tincture, etc.
Drugs for the treatment of demodicosis
Systemic drugs include:
- immunomodulator drugs: Detox (price from 1950 rub.);
- Sodium thiosulfate - has an antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory effect, destroys subcutaneous mites, the cost of injection ampoules is 80-100 rubles;
- complexes of vitamins, minerals, amino acids.
Important!
Local skin treatment is carried out in several courses with breaks; treatment has to be long-term: from 4-6 weeks to 12 months. The maximum positive effectiveness, according to patient reviews, is provided by ointments and creams that contain drying and antiprozoal substances: sulfur, tar, zinc, mercury, etc. They have a blocking effect on the respiratory organs of ticks, which leads to their death.
The most popular ointments:
- Sulfuric, price 20-50 rubles;
- Ichthyol, price 80-120 rubles;
- Yellow mercury (about 670 rub.);
- Ointments containing metronidazole are among the most effective drugs: Klion (350-400 rubles), Metrogyl (180 rubles);
- Benzyl benzoate is a cream with a keratolytic antiparasitic and analgesic effect, destroys mites after the first application, however, the treatment should be repeated after 3 days to get rid of young individuals emerging from eggs, price 20-50 rubles;
- Spregal is an aerosol that causes the death of acne and its eggs, sprayed onto the damaged areas before bedtime, it is recommended to apply on the face with a swab, repeat the treatment after a few days, price 980 rubles;
- Demalan is a cosmetic antiparasitic agent, used to treat demodicosis on the face and eyelids, price 400 rubles;
- Azogel is a drug containing azelaic acid, which has an anti-inflammatory, antiparasitic effect, helps restore the normal functioning of the sebaceous glands; price 400-700 rub.;
- Demazol is an anti-inflammatory cream that improves regenerative and metabolic processes in affected areas of the skin; price 250 rub.;
- Crotamiton - applied after a shower, highly effective against mites, helps relieve itching and inflammation, price 1,400 rubles;
- Stop Demodex cosmetic gel - used to get rid of mites in the eye and eyelid area, relieves itching, swelling and inflammation, restores the skin, price ranges from 180-225 rubles.
Ointments for the treatment of demodicosis
Demodicosis
Demodecosis is a lesion of the skin of the face and outer ear caused by the acne mite (Demodex). This type of mite lives on the skin normally, being a component of opportunistic microflora. It is found in 90% of healthy people. In this case, the number of mites in the follicles does not exceed two or three individuals. Exposure to certain factors leads to activation of the parasite. It begins to actively multiply, the follicle or sebaceous gland increases significantly in size. This leads to the development of symptoms of demodicosis.
A number of researchers believe that the disease more often affects women. Although men also often suffer from this disease. Middle-aged and elderly people are especially susceptible to developing demodicosis. Although the mite does not harm general health, its effect on the skin causes a sharp deterioration in its condition, which continues for years. Over time, the skin condition becomes worse and worse.
Previously, it was believed that demodicosis was incurable and, once it appeared, it tormented its owner for many years. It is now known that the disease is curable, but its treatment is complex and lengthy. It is necessary to approach it comprehensively, because only in this case can you count on a positive result.
Causes of demodicosis Demodex is caused by two types of mites. Demodex folliculorum affects the hair follicles, and Demodex brevis affects the sebaceous glands. They are microscopic in size and feed on the cells of the hair follicles or the secretions of the sebaceous glands. Tick waste products have a strong local irritant effect. In addition, during the period of its activity, which occurs at night, it crawls to the surface of the skin and captures other pathogenic microorganisms with its bristles. Returning back to the skin, it transports the infection there, causing the development of inflammation.
The mite actively reproduces, filling all the space inside the follicle or sebaceous gland, which takes on hypertrophied sizes. The immune system begins to work against the mite population, which further increases inflammation and maintains it.
Risk factors for demodicosis
- Visiting beauty salons - infection often occurs during cleaning or other cosmetic procedures due to insufficient treatment of the instruments used.
- Decreased immunity.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system.
- Stress.
- Pregnancy.
- Excessive passion for baths, saunas, solariums.
- Drinking large quantities of alcohol and coffee.
- Sharing towels, pillows, clothes and other items that come into contact with the skin with people suffering from demodicosis.
- The use of fatty ointments and creams, including hormonal ones.
Symptoms of demodicosis Depending on the type of demodex, damage to the skin or hair (including eyelashes) is observed. By laying eggs in the surface layer of the skin, Demodex causes inflammation, the formation of unsightly bumps, ulcers, and provokes an unhealthy sallow complexion and even early wrinkles. The skin becomes greasy and has a damp shine. It often turns bright pink and flakes off. The disease mainly affects the nasolabial triangle, eyelids, chin, anterior surface of the neck and chest, and ears.
When hair follicles are damaged, eyelashes and hair loss occur. The edges of the eyelids turn red, and scales appear around the roots of the eyelashes. With a long course of the disease, the eyelashes stick together.
In all cases of demodicosis, patients are bothered by painful itching. It becomes much stronger in the evening and at night, when the tick is most active. Sometimes you can even feel its movements under the skin.
Diagnosis of demodicosis At the first symptoms, you should consult a dermatovenerologist or ophthalmologist. Laboratory research methods are extremely important in the diagnosis of demodicosis:
- Skin scraping – do not wash your face or use cosmetics for a day before taking a scraping, otherwise the results may be inaccurate. Skin flakes are placed in a drop of an alkaline solution and examined under a microscope. When ticks are detected, they are counted and, ideally, the species is determined.
- If the eyelids are affected, 8 eyelashes are taken from each eye: 4 from the lower eyelid and 4 from the upper eyelid. They are placed in a drop of alkaline solution or glycerol and microscopy is performed.
Diseases with similar symptoms
- blepharitis;
- acne;
- perioral dermatitis.
Complications of demodicosis
- streptococcal and staphylococcal infections - against the background of weakened skin immunity and synergy with mites, the infection easily enters the skin and causes the development of inflammation;
- conjunctivitis – occurs with demodicosis of the eyelids;
- rosacea;
- papillomas on the eyelids;
- allergic reactions.
Treatment of demodicosis
- acaricidal agents;
- antibacterial drugs – internally and externally;
- antiseptic drugs.
The prognosis for demodicosis is relatively favorable - with a timely diagnosis and proper therapy, it is possible to get rid of the tick. However, relapses of the disease are quite common.
Prevention of demodicosis
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- use of individual cosmetics, puffs and makeup brushes;
- correct diet;
- maintaining immunity.
Nota Bene! During treatment of demodicosis, you must stop using decorative cosmetics, especially makeup brushes. This will prevent the mite from re-infecting and spreading to healthy skin.
Interesting facts Demodicosis can accompany another chronic skin disease - rosacea. With rosacea, demodex is often found in skin scrapings from the affected areas.
Expert: Kobozeva E.I., dermatovenerologist
Prepared based on materials:
- Zatsepina N. D., Maichuk Yu. F., Semenova G. Ya. Eye lesions in demodicosis. Guidelines. – M., 1983.
- Pavlov S. T. Skin and venereal diseases. Directory. – M.: Medicine, 1969.
- Skripkin Yu. K. Skin and venereal diseases. Guide for doctors. – M.: Medicine, 1995.
Cleansing the body and removing toxins
When treating demodicosis at home, it is recommended to carry out therapy with a special diet and the use of medications to remove toxins and cleanse the gastrointestinal tract.
Dietary nutrition involves a complete rejection of flour, sweet, fatty, smoked, and fried foods. It is recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits, cereals (oatmeal, etc.), drink 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day. This will relieve the patient’s body and create unfavorable living conditions for mites.
On a note!
Cleansing the gastrointestinal tract is carried out with the help of absorbent preparations: Activated carbon, Enterosgel, Smecta, Polysorb, etc. They will help remove waste and toxins from the life of parasites.
Treatment with folk remedies
Demodicosis of the facial skin requires timely treatment, otherwise an exacerbation of the disease can provoke severe changes, after which scars and cicatrices remain. There are effective folk remedies that are easy to prepare at home:
- To treat demodicosis, you can use aloe juice diluted in half with water. This remedy relieves itching and discomfort, stops the development of inflammatory processes, and also has a pronounced antibacterial effect.
- Symptomatic treatment of facial demodicosis involves relieving itching and inflammation; for this, you can use herbal preparations at home. The most common folk remedies are decoctions and infusions of chamomile, calendula, wormwood in combination with lemon balm or mint. Use the resulting home remedy to treat demodicosis as compresses or lotions, apply them to the affected skin of the face several times a week.
- Treatment of the disease with celandine juice is effective. A folk remedy based on this plant can be easily prepared at home. The roots of the plant are crushed, mixed with vegetable oil and left to infuse for a week. To treat demodicosis, this home remedy should be applied to the affected skin of the face before bedtime, or mixed with sour cream.
- An effective folk remedy for the treatment of demodicosis of the face is ordinary garlic. A well-known folk home remedy is garlic compress. Several cloves should be crushed into a paste, wrapped in gauze and applied to the affected skin of the face. The biologically active components of such a product have a bactericidal effect, which contributes to the rapid treatment of demodicosis and the prevention of complications.
- Apple cider vinegar may be a simple and effective treatment for facial demodicosis. It is enough to wipe the affected areas with a cotton pad twice a day so that the activity of the pathogen decreases and the symptoms cease to appear.
However, it is worth remembering that treatment of facial demodicosis with herbs and other folk remedies can provoke the development of allergic reactions, and not all such remedies are approved for use in the treatment of children.
Treatment of demodicosis with traditional methods
Therapy using folk remedies takes place in stages: first, the immune system is restored, then the negative effects of mites are suppressed, and then it is necessary to restore and heal the skin by improving its protective properties.
Herbal infusions for oral use:
- make a mixture of herbs from 1 part of plantain leaves, 1 – wormwood, 1 – mint, 1 – yarrow, 1 – tansy flowers, 2 – strings, 1 – nettle; for cooking take 2 tbsp. l of the mixture, pour 500 ml of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes, closing the lid; drink 0.5 tbsp. three times a day before meals, course – 4-6 weeks;
- a mixture of 2 parts of violet, 2 – calendula flowers, 2 – St. John’s wort, 1 – mint leaves and 1 – plantain, 1 – elecampane roots; The drink is prepared from 2 tbsp. l of the mixture, which must be poured with boiling water and left for 30 minutes, filtered, and drunk in the same way.
Folk remedies for demodicosis
Recipes for external remedies for demodicosis:
- Prepare aloe juice and dilute with water in a 1:1 ratio, wet a napkin and place on the affected areas of the skin for 15 minutes. The duration of treatment is 20-25 procedures, done every other day.
- Decoction of 2 tbsp. l linden blossom and 1 tbsp. boiling water, keep in a steam bath for 10 minutes, after straining, use to wipe the skin twice a day, after the procedure, do not go out into the cold.
- Compresses from the juice of ripe tomatoes are made daily for 15 minutes, the course is 20 days.
- Application of Yam veterinary ointment.
- 1-2 tbsp. l dry chamomile per 1 tbsp. hot water, boil for 10 minutes, filter, make compresses alternately with cold and hot decoction 2-3 r. in Week.
- Grind 1 tbsp. l juniper berries, pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 4-6 hours, strain. Use as a lotion 1-2 times a day for 15-20 minutes, pre-wipe the skin with tincture of calendula or eucalyptus.
- Prepare a mass of 100 g of tansy and 400 ml of vegetable oil, leave for 14 days, filter, use as warm compresses 1-2 times daily.
- Grind 3 tbsp to a powder. l wormwood, steam, add 1 tsp honey, 1 tsp alum, 1 tbsp. l vegetable oil, 2 tbsp. l chopped viburnum berries (seedless), mix everything. Apply the resulting ointment to pieces of cotton fabric and apply to the affected areas 1-2 times a day for 2 hours. First wipe the skin with a glycerin solution: 1 tsp per 1 tbsp. water. After removing the lotion, wash with salt water (0.5 tsp of salt per 1 tbsp.).
Treatment regimen for facial demodicosis
Treatment of subcutaneous mites in humans is aimed at eliminating the infection, normalizing the functions of the skin's protective barrier, and eliminating metabolic and hormonal disorders. It is impossible to recognize a parasitic microorganism by external symptoms alone. Before prescribing specific treatment for demodicosis, the doctor must carry out laboratory diagnostics, examining scrapings from the affected areas of the face.
Maintaining personal hygiene measures
Treatment of demodicosis on the face requires careful adherence to certain hygiene standards. While fighting the disease, hot baths, any warming procedures, sauna, solarium, and swimming pool are prohibited. You need to change bed linen and towels more often, and iron them well before use, preferably with an iron with a steam function. It is recommended to wash pillows and bed linen with special antiparasitic additives (for example, with Allergoff, Akaril products). It is also very important to adhere to the following hygiene principles:
- Avoid scrubs, fatty creams, and decorative cosmetics.
- When washing, use cleansers that do not irritate the skin. It is recommended to select them together with a dermatologist.
- Carry out thorough washing in the morning, evening and before each application of local products for the treatment of demodicosis.
- Wipe your face not with an ordinary towel, but with high-quality disposable napkins. Do not apply medicinal products to wet skin.
- Before going outside, use a good sunscreen.
Special diet
When treating demodicosis on the face, it is important to adhere to the dietary nutrition system. It will reduce the load on the intestines, regulate its work, and cleanse the body of toxins and toxic contaminants. During therapy, you should completely avoid alcohol, packaged foods with chemical components, and dishes with a lot of salt, sugar and animal fats.
| Products prohibited for demodicosis | Products recommended for demodicosis |
Junk and heavy food:
| Foods high in fiber:
|
Products with high allergic activity (exclude completely or limit to a minimum):
| Dairy products:
|
| Hard cheeses, rennet cheeses, fatty meats and fish. | Lean meats, poultry and fish - in limited portions. |
| Sweet carbonated drinks, coffee, packaged juices, compotes or fruit drinks. | Green tea, still water without additives, fresh juices. |
Baked goods, flour, sweets:
| Nuts, dried fruits:
|
Carrying out cosmetic procedures
Subcutaneous mites on the face are treated using a number of effective cosmetic techniques. They help eliminate the manifestations of the disease, but are considered only auxiliary methods of therapy, and are always selected individually. Modern procedures prescribed for the treatment of facial demodicosis are represented by the following list:
- microdermabrasion – mechanical peeling;
- laser photocoagulation - treatment of areas affected by demodicosis with pulsed light, a laser is used;
- ozone therapy – treatment of demodicosis with oxygen-ozone mixtures;
- cryomassage – exposure of the skin to cold (liquid nitrogen).
- Abdominoplasty
- How to get rid of nail fungus at home. Quick relief from nail fungus
- Cystitis - symptoms in women, first signs of the disease
The use of local drugs to kill demodex mites
To treat demodicosis on the face or eyelids, ointments, eye drops and creams for local treatment are necessarily used.
Antiparasitic agents:
- Ointment with benzyl benzoate. To get rid of demodicosis, rub three times throughout the day. You can increase the frequency of lubrication up to 5 times. Treatment of demodicosis with benzyl benzoate is contraindicated for pustular infection.
- Permethrin ointment. Apply overnight. The duration of treatment is 14 days.
- Cream "Demazol". Rub into eyelids 2 times a day. The duration of treatment for demodicosis of the eyelids with this cream is 1.5 months.
Antibacterial agents:
- Gel "Baziron". Lubricate the skin 1-2 times a day for 3 months.
- Erythromycin ointment. 1-2 times a day for no more than 14 days.
- Tafazol eye drops. A weekly course is optimal, 1 drop 1-3 times a day.
Taking medications
When treating demodicosis on the face, several categories of systemic drugs are used.
Antibiotics and antiparasitic agents:
- Metronidazole tablets. 500 mg twice a day. The period of treatment for demodicosis with this potent drug is determined by a specialist.
- Doxycycline capsules. 200 mg 2 times a day for the period prescribed by the doctor.
Antihistamines:
- Tavegil tablets. 1 mg 2 times a day until signs of allergy subside.
Immunomodulatory agents, sorbents:
- Immunomodulator "Detox". 1 capsule 2 times a day. The optimal period of use for the treatment of demodicosis is 3 months.
- Sorbent "Rekitsen". 1 tablespoon 3 times a day, diluted in a glass of kefir. Treatment involves taking the powder for a month.
Prevention of demodicosis
There are a number of rules and recommendations that must be followed during treatment in order to get rid of demodicosis forever and prevent relapses of the disease:
- monitor the cleanliness of personal hygiene items and bed linen, change them daily during the treatment period, boil or iron them;
- for the period of therapy, refrain from using cosmetics, going to baths and saunas, sunbathing and solariums;
- to prevent the recurrence of an unpleasant disease, it is recommended to carry out medical and cosmetic procedures during the remission stage: microdermabrasion, i.e. removal of the upper layers of skin along with mites; non-hardware cleansing or peeling of the face;
- Preventive laser therapy is recommended in areas with vascular networks, which will help normalize metabolic processes in the epidermis;
- changing your diet to reduce oily skin.
To successfully cure demodicosis, you should tune in to a long therapeutic process, which depends on the stage and severity of the disease. Feedback from patients and a positive prognosis from specialists allow the patient to hope for a full recovery.