What is demodicosis of the eye?
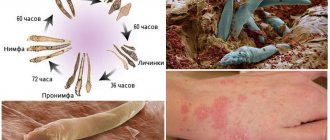
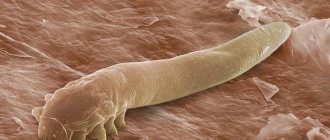
The development of demodicosis provokes the active reproduction of microscopic mites. Its dimensions are no more than 0.3 mm. Therefore, it cannot be seen by the human eye. It feeds on skin that is dying. It usually collects on the edge of the eyelids. This localization is ideal for the reproduction of this parasite. Such mites can remain in the body all their lives and not show characteristic signs.
Against the background of decreased immunity, lack of hygiene rules, and exposure to unsanitary conditions, pronounced symptoms of infestation by this mite are observed:
- severe burning and itching, which is localized in the eyelid area;
- eyelash loss;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- dryness;
- yellow discharge from the eyes.
Symptoms may develop gradually and are not pronounced. Therefore, patients often ignore them and do not consult an ophthalmologist. Such signs occur when specks or small particles get into the eye. Lack of treatment contributes to the development of demodicosis and its spread to other organs.
How to treat demodicosis in the eyes
Treatment of the eyelids of the cornea begins with a visit to an ophthalmologist (in case of skin lesions, you need to go to a dermatologist), who will conduct an adequate diagnosis. Diagnostic measures include only two necessary procedures:
- Donating blood for general analysis;
- Scrapings for microscopic analysis.
In the first case, changes in blood composition are monitored, which changes in a certain way during demodicosis. In the second case, the necessary material for microscopic examination is:
- Horny peeling scales;
- Scraping the fat from the skin;
- Eyelashes (if the eyelids are infected);
- Contents of bubbles (if any).
The biomaterial is processed in a special way, and the mite is detected, and its quantity is determined. Treatment of eye demodicosis in humans requires an integrated approach. To avoid the tick population from reproducing, it is advisable to change a few daily habits:
- Take care to support the immune system;
- Contact specialists if you have diabetes and HIV;
- Do not skip or ignore cleansing procedures. You can use micellar water or herbal infusions. It is not advisable to use scrubs and peels, as they will increase peeling;
- Try to avoid places with high temperatures and humidity (baths, saunas, gyms).
Demodex is treated with three groups of drugs (if we talk about damage to the eyes and face, since one rarely happens without the other):
- Firstly, acaricides (drugs that kill ticks) are needed;
- Secondly, antiseptics (cleanses the skin of pathogenic microflora). They also prevent the addition of any secondary infection that develops against the background of demodicosis;
- Vitamin A in preparations – to restore normal metabolism in the skin.
The treatment regimen for demodicosis of the eyelids and eyes is prescribed individually, depending on the scale of the lesion. But there are several standard medications that are prescribed by your doctor for use:
- Drops that disinfect eyelids and eyelashes (okomistene and vitobact);
- Antiseptic ointments - metrogil and glycoderm;
- Acaricidal solutions and ointments - kill all adults, but do not affect laid eggs. Therefore, it is necessary to apply them for several days in a row to kill the hatching population;
- For the eyes, medicinal drops are needed that will relieve the main symptoms - redness of the whites and proliferation of the capillary network;
- Histamine blockers - in order to reduce the allergic component of ophthalmodedecosis.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of demodicosis of the eyes:
- the disease tends to worsen in autumn and spring (during this period, a decrease in immunity and the development of allergic reactions are often observed);
- exposure to external factors - high air temperatures, hypothermia, radioactive radiation, working with chemicals and household substances;
- consequences of injuries and surgery;
- inflammatory processes;
- diseases of blood vessels, endocrine system, liver;
- bacterial and fungal diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- skin diseases: seborrhea, dermatoses, oily skin type;
- stress, nervous tension;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs.
The disease can be recognized by the following signs:
- stye, which occurs very often;
- severe itching, which may be accompanied by peeling;
- sticking and loss of eyelashes;
- eye fatigue, feeling of heaviness of the eyelids;
- feeling of sand in the eyes;
- swelling;
- increased lacrimation;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- dryness.
If any unpleasant symptoms develop, you should consult an ophthalmologist. This will help avoid the development of serious complications
Symptoms of demodicosis
It happens that people find out about asymptomatic carriers of the disease during a preventive examination. At this point, they are not bothered by symptoms, they do not even have visible signs of inflammation.
Low-symptomatic form of demodicosis
The asymptomatic course of eyelash demodicosis is characterized by periodic severe itching of the eyelids, which is especially noticeable after waking up. In addition, the patient complains of pain in the eyes and sticky discharge. Examination using a special lamp makes it possible to see enlarged eyelash bulbs and the presence of translucent “muffs”. In addition, the conjunctivae of the eyelids turn red.
Demodectic blepharitis
With this disease, thickened and hyperemic edges of the eyelids and peeling of the skin between the eyelashes are observed. Enlarged muffs are visible to the naked eye on almost every eyelash. Problems with the conjunctiva appear, which subsequently degenerate into blephar conjunctivitis, characterized by hyperemic mucous membranes of the eyelids and the appearance of yellow crusts.
Diagnostics
Initially, the patient should consult an ophthalmologist. It is important to listen to the patient’s complaints and study his medical history. After this, a visual inspection is carried out. Biomicroscopy is used to examine eyelashes. This will help detect the presence of scales.
If necessary, additional tests may be prescribed.
If the development of demodicosis is suspected, the first step is to analyze several eyelashes. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor carefully examines the condition of the eyelashes under a microscope. Skin is also taken for analysis. Before this, the patient should not wash or use cosmetics.
It is precisely such surveys that are reliable. This is very important because this disease is accompanied by symptoms that are similar to other pathologies. It is forbidden to independently establish a diagnosis based on general information. If a person is faced with demodicosis, then he may need consultation with specialized specialists: a gynecologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist, immunologist, infectious disease specialist.
What is Demodex ocular?
On the human skin there is a large number of different representatives of opportunistic microflora, which by their existence do not cause him any harm. About 90% of the world's population are carriers of microscopic mites from the genus Demodex and they themselves do not suspect it as long as their number is within normal limits. Failures in the functioning of the immune system lead to a sharp mass reproduction of these parasites.
The demodex mite is a microscopic creature ranging in size from 0.2 to 0.5 mm, whose habitat is the sebaceous and meibomian glands and hair follicles.
An increase in temperature encourages the parasite to take active action, so the exacerbation of the disease most often occurs in the warm season.
Treatment
There is a certain scheme that effectively helps to get rid of this disease. The patient is prescribed a diet, medications, and physiotherapy. Damage to the eyelids and eyelashes is treated with the same methods. Treatment regimen:
- maintaining hygiene;
- massage;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic drugs;
- ophthalmic drops with natural tear substitutes.
The treatment is effective, but long-term. It depends on the complexity of the lesion and the presence of complications. A favorable result can be observed within 1-2 months.
Diet
For this disease, doctors recommend eating large amounts of fruits, berries, and vegetables every day. Foods that increase blood circulation should be excluded from the diet: alcohol, coffee, strong tea, spicy foods.
In addition, you should reduce your intake of sugar and salt. The following foods should be excluded from the diet: citrus fruits, eggs, smoked meats, canned food, fried foods, cocoa and chocolate. It is recommended to replace them with fermented milk products, herbs, and vegetables. Among the drinks, compotes and fruit juices will be useful.
Massage
Massage refers to physiotherapeutic procedures. Additionally, magnetotherapy and electrophoresis are prescribed. You can perform a massage after hygiene procedures and treating the eyelids with antiseptic agents.
The patient must close his eyes. Use your fingertips to make circular movements along the upper eyelid. It is recommended to do it once a day for no longer than 15 minutes. After this, you can notice an accumulation of scales. They are removed with a sterile cotton swab. You can perform a massage only with clean hands.
Drug therapy
For the treatment of demodicosis, drugs of different groups are prescribed. Complex treatment provides a favorable result. It is important to follow the regimen prescribed by the doctor and strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage.
Drops
The use of drops is mandatory. Basically, substitutes for natural tears are prescribed for dryness and for its prevention. The following drops are considered effective: Natural tear, Slezin, Hyphenate.
Gels, ointments, creams
Among the gels I recommend using are Blepharogel and Differin. Ointments are usually prescribed with an antibiotic. For example, tetracycline or gentamicin ointment. Zinc ointment produces an anti-inflammatory effect. Combined creams – Demazol, Demalan. Additionally, you will need to treat the eyelids with an antiseptic solution (Furacilin, Chlorhexidine). It is worth considering that taking medications on your own is strictly prohibited.
The use of pharmaceutical ointments and drugs in the treatment of demodex
After the patient has been tested for ticks, he will be prescribed certain medications for both internal and external use. A person should use only prescribed medications, otherwise the condition may worsen.
The most common external preparations:
- Stop Demodex gel;
- Blepharogel;
- Glycodem;
- Demazol;
- yellow mercury ointment 1-2%;
- Dexodem phyto;
- Amitrazole;
- Benzyl benzoate;
- Demalan cream;
- Recinol;
- Teagel.
Before using the products, the eyelids are prepared by clearing them of accumulated scales. To do this, use tincture of calendula or eucalyptus. After cleaning, after about 15 minutes, the drug is applied to the edges of the eyelids. You need to smear as carefully as possible to prevent the drug from getting on the mucous membrane.
Such procedures must be carried out regularly for 4-8 weeks. After completing the course of therapy, an additional analysis of the eyelashes for demodex will be carried out. If the number of individuals decreases significantly, then the treatment was successful. If the repeated examination does not show significant changes, treatment is resumed, selecting more relevant medications. They also conduct additional testing for immune deficiency.
Prevention
By following simple rules of prevention, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing demodicosis. Key recommendations include:
- Maintaining hygiene rules. Cosmetics must be individual.
- After visiting the bathhouse, it is recommended to wash with antibacterial soap.
- Use your own bed linen and towels. Wash them thoroughly and steam them.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat a healthy and balanced diet, and sleep at least 7 hours.
- The diet should contain a large amount of vitamins to improve immunity.
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. In addition, every person should be examined by an ophthalmologist 1-2 times a year.
Why does it occur
Human skin is an ideal habitat for various microorganisms, and sometimes larger representatives of wildlife, one of which is the Demodex mite.
Parasites do not live on every person’s body, and their activity requires certain conditions.
Risk factors that activate the action of the tick:
- decreased immunity;
- increase in ambient temperature (hot bath, visiting a sauna, prolonged stay on the beach);
- increased humidity;
- hormonal changes;
- frequent stress;
- using cosmetics with a high fat content.
Demodicosis of the eyelids is contagious. There are many sources of infection. For example, contact with infected pets and humans, use of someone else's cosmetics, unsterile instruments in a beauty salon, bed linen (on a train, hostel).