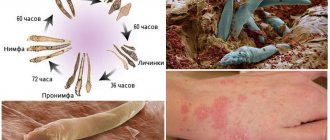
What causes the disease
The subcutaneous mite lives on the human head almost constantly, but does not cause aggravation in healthy people.
Severe symptoms occur with a sharp decrease in immunity when the parasite affects the deep layers of the skin. Also, the activation of the Demodex mite depends on the functioning of the sebaceous glands of the head, the endocrine system and the general resistance of the body. Factors contributing to the proliferation of hair mites in humans:
- hormonal disorders;
- long-term use of antibiotics and corticosteroids;
- chemical effects on the scalp;
- incorrectly selected hair care products;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- unbalanced diet with a predominance of salty, smoked, spicy foods;
- lack of vitamins;
- psycho-emotional overload;
- menopause or reaction to taking hormonal contraceptives.
It has been established that the Demodex parasite on the head secretes a special enzyme that affects the composition of human sebum and causes swelling of the skin. With strong immunity, inflammation and swelling go away on their own. But when the parasites are activated, their number increases to thirty pieces in one sebaceous gland. This contributes to the manifestation of symptoms of the disease on the skin.
Demodex mites can be transmitted to others through direct contact, but the patient does not need to be isolated. In order for the disease to be transmitted to another, a number of factors must coincide, creating favorable conditions for the activation of the parasite.
Demodicosis of the scalp: what is prohibited to use
If the scalp is affected by glandular glands, you should not use traditional hair care products. Shampoos and conditioners must belong to the medicinal series.
Be sure to read:
What does a subcutaneous mite look like: causes and symptoms of the disease, how to quickly cure it
In addition, visiting saunas and solariums is strictly prohibited - the head should under no circumstances overheat. In addition, the consumption of smoked, spicy, fried, sweets, coffee, soda, which have a negative impact on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the state of the immune system as a whole, is contraindicated.
Causes of demodicosis of the head
According to scientific research, it has been proven that iron mites can be found on almost any healthy person. However, the development of demodicosis can begin only when optimal conditions for reproduction are created for the mite. Most often this happens when the local immune defense of the skin is reduced: in such a situation, the parasite has the opportunity to penetrate deep into the layers of the skin.
In addition to the state of immune forces, the physiology of the skin also plays an important role: the function of the sebaceous glands, the composition of sebaceous secretions, concomitant pathologies of the skin, dependence on hormonal balance, etc. The external effect on the scalp is also of considerable importance. For example, demodicosis can develop in women who too often use various chemicals and aggressive cosmetics for their hair and skin.
As we have already said, the tick settles deep in the skin, where it is able to actively reproduce and release larvae outward. If you try to remove manifestations of demodicosis yourself, then you can spread the pathogen on your fingers and hands almost throughout the body.
According to the latest experimental studies, the development of demodicosis can be briefly characterized. During its life, the iron mite secretes special enzyme substances that can affect the composition of human sebum. In particular, a specific substance is released that causes swelling of the skin. If local immunity works, then the swelling stops. With a decrease in immune defense, as well as with an increase in the number of parasites to three dozen in one sebaceous gland, a person develops clinical symptoms of demodicosis.
What could be the causes of demodicosis of the head, or, in other words, what can provoke active reproduction of the mite:
- hormonal imbalance;
- long-term treatment with hormonal drugs and antibiotics;
- poorly chosen cosmetics;
- unhealthy diet, with a predominance of sweets and chemical components (preservatives, dyes, stabilizers, etc.);
- abuse of strong coffee and tea;
- excessive consumption of salty foods (chips, crackers, nuts), pepper;
- frequent smoking and drinking alcohol;
- too frequent chemical exposure to the scalp.
The Demodex mite can be transmitted from one carrier to another, both with household objects and through handshakes and other direct contacts. However, this does not mean that a sick person should be isolated from society. Let us repeat once again that the causative agent of the disease is present on the skin of almost all people, but demodicosis of the scalp develops only when conditions favorable for its life are created.
Symptoms of demodicosis of the head
In most patients, symptoms of demodicosis appear in the head area, although the development of the process on the chest and upper back is not excluded.
Demodectic mange most often occurs on the head due to the fact that the most active sebaceous glands are located here, which are very sensitive to changes in immunity, hormonal balance and the general condition of the body. Among the main areas most often affected by demodicosis are the area of the nose, forehead, upper eyelids and scalp.
Symptoms of demodicosis of the head begin with the appearance of rosacea - persistent erythema, in which swelling and redness of the skin surface is observed. Along with rosacea, acne, nodules, pustules (rosacea) and telangiectasias appear in large numbers.
The most typical picture of demodicosis is:
- persistent redness of the skin;
- the appearance of a rash on the face and scalp, in the form of papules (nodules), pustules (vesicles with purulent contents), acne or pimples;
- thickening of the skin on the affected area;
- the appearance of a visible vascular network;
- itching, irritation, skin tightness.
Demodicosis of the scalp can be manifested by the appearance of profuse dandruff, itching, and pimples on the skin in the hair growth area. This phenomenon is often observed with endocrine disorders (for example, during menopause, when taking hormonal contraceptives), with hypovitaminosis, psycho-emotional stress, and abuse of alcoholic beverages.
Misfortune never comes alone
The activity of mites of the genus Demodex in the sebaceous glands of the skin is observed in a disease such as seborrheic dermatitis. This is a chronic inflammation of the skin in those areas of the head and torso where there are many sebaceous glands (including the scalp).
On a note! A certain role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis belongs, in addition to demodex, to the fungi Pityrosporum and Malassezia (the causative agents of pityriasis versicolor).
Other diseases whose symptoms worsen when demodex is activated:
- pustular or demodectic folliculitis;
- allergic and atopic dermatitis;
- rosacea or rosacea;
- acne (acne);
- psoriasis.
Young men and men are more susceptible to seborrheic dermatitis and acne, since their bodies produce more androgens - hormones that regulate sebum production. Rosacea is more common in women under or after 30 years of age
The diseases listed in the list are accompanied by pathologies of the endocrine glands, nervous system, and digestive tract.
The cause of acne under the hair can be not only demodicosis of the scalp. The same symptoms are observed in diseases of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland, changes in hormonal levels, intoxication of the body, and gastrointestinal dysfunction. Before treatment, you must be tested for demodicosis.
Forms of demodicosis in humans
Depending on the nature of the manifestations on the skin, several forms of demodicosis are distinguished, the symptoms of which are characteristic of the corresponding diseases. Not to be confused with these diseases!
Acneform form
The acneiform type of demodicosis is characterized by the appearance of papules and pustules on the facial skin, which are similar to acne.
Rice. 16. Demodectic mange of the face in women. Acneform form of the disease: papular (photo on the left) and papulopustular (photo on the right).
Rosacea-like form
The rosacea-like type of demodicosis is characterized by the appearance of papules against a background of diffuse erythema. Demodex brevis (short mite) causes the appearance of inflammatory infiltrates and granulomas in the deep layers of the dermis, which are similar to the granulomatous form of rosacea.
Rice. 17. Rosacea-like form of demodicosis: in the form of diffuse erythema (photo on the left), granulomatous form (photo on the right).
Seborrheic (erythemo-squamous) form
The seborrheic form of demodicosis is characterized by the appearance of redness and rash on the facial skin, accompanied by lamellar peeling.
Ophthalmic form
The ophthalmic form of demodicosis occurs with damage to the eyeballs and eyelids. Redness, dryness, irritation, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, fatigue are the main symptoms of eye demodicosis. Itching of the eyelids, redness and swelling of their edges, the appearance of scales or crusts on the eyelids are the main symptoms of demodicosis of the eyelids.
Rice. 18. Demodectic mange of the eyelids. Lamellar peeling is clearly visible (photo on the left). On the ciliated edge of the eyelid, scales form a “collar” around the eyes (photo on the right).
The role of demodex mites in the formation of androgenetic alopecia
There is an assumption that the presence of mites in the hair follicles aggravates the development of androgenetic alopecia. During inflammation, T-lymphocytes are activated, which induce collagen synthesis, resulting in fibrous degeneration of hair follicles.
Rice. 19. Demodicosis of the scalp.
Primary demodicosis
In primary demodicosis, inflammatory skin elements resolve after antiparasitic therapy. About 40% of cases of primary demodicosis develop in patients suffering from rosacea.
Primary demodicosis is characterized by:
- the onset of the disease over the age of 40 years;
- The areas most often affected are around the mouth, eyes and outer ear;
- inflammatory elements are located asymmetrically and are accompanied by itching;
- acne and rosacea are absent;
- high content of mites on the skin;
- positive effect of the antiparasitic treatment.
Symptoms
The disease in most cases manifests itself in the area of the head, where the sebaceous glands are located, which strongly react to the general dynamics of the body, but the process can spread to other areas, for example, the chest. Mostly the hairy part, nose, upper eyelids, and forehead are affected by the disease.
Signs of cephalic demodicosis begin to manifest themselves with the formation of rosacea, characterized by swelling and persistent redness of the skin. Other symptoms:
- rashes on the face, scalp (pustules - purulent blisters, acne);
- compactions (lumpy);
- manifestation of a pronounced network of blood vessels;
- dry skin, severe itching.
The disease also manifests itself as dandruff and pimples in the hair area. This is especially typical for endocrine system disorders (menopause, taking hormonal drugs), stress, alcohol abuse, hypovitaminosis. The hair looks unkempt, remains greasy even after frequent washing, and smells unpleasant due to mite infestation. Often the patient experiences their loss.
Without treatment, the disease will quickly spread to nearby areas of the skin, and then to the entire scalp. This will be manifested by additional signs:
- conjunctivitis, reversible loss of vision;
- whitish coating on eyelids, eyelashes;
- peeling, redness of the facial skin;
- morning sticking of eyelashes;
- manifestation of “barley”;
- acne with segmental pustular formations.
If in the initial stage the disease is easily curable, then in the advanced stage it is much more difficult to cope with it.
Secondary demodicosis
Secondary demodicosis develops against the background of diseases accompanied by a sharp suppression of the immune system (HIV infection, leukemia, etc.), long-term use of corticosteroids and cytotoxic therapy, or develops against the background of acne and rosacea, complicating their course. This form of the disease is registered in 33% of patients with acne.
Secondary demodicosis is characterized by:
- the disease appears at any age;
- lesions are widespread;
- presence of anamnesis and clinical picture of relevant diseases.
Papulopustular rashes on the skin of the face are a reason for diagnosing demodicosis.
Rice. 8. Demodectic mange on a woman’s face.
Local therapy of demodicosis of the scalp
In addition to oral administration, metronidazole and ornidazole tablets are used for self-preparation of chatterboxes. This is the name for suspensions that contain alcohol, soluble and insoluble drugs.
Demodicosis of the head and face - treatment with talker:
- take 6 tablets of metronidazole mixed with the same amount of streptocide and mumiyo;
- grind the substances and add ½ cup of diluted medical alcohol (50°);
- Shake the mixture well before each use;
- apply directly to pimples under the hair on the head and face;
- leave on your head overnight.
An external remedy with metronidazole is Metrogyl gel, which treats demodicosis, oily seborrhea, acne and rosacea (the price of the drug in the pharmacy is no more than $2). Analogs for the active substance: Rozeks cream, Nidaza gel.
The acaricidal drug permethrin, which destroys ticks, is included in the Nitifor cream and lotion, Medifox emulsion, and Nyx cream. In most cases, a single application of permethrin lotion or ointment to the scalp will kill the mites.
Causes, routes of infection and provoking factors
The study of demodicosis has shown that in addition to a decrease in immune defense, there are other reasons that cause this pathology. One of the important points is the physiological state of human skin, namely, how correctly the sebaceous glands function, what is the composition of their secretions, as well as concomitant skin diseases and hormonal imbalances.
External influences on the hair and scalp also often lead to the development of the disease. Women are at risk of demodicosis because they constantly use various chemical reagents, as well as other aggressive substances found in cosmetic products for hair and skin.
These masks, gels, shampoos and paints disrupt the functioning of the sebaceous glands, dry the skin, which provokes a decrease in local immunity, and hence the development of pathology.
Immunity can protect a person from the occurrence of this disease, but only if it is strong enough. In this case, after the tick releases metabolic products, defense mechanisms are triggered and toxins are neutralized. When the body is weakened, they are unable to eliminate this problem; all the signs of demodicosis appear.
Reasons for decreased immunity:
- Imbalance of hormones in the body.
- Incorrect use of cosmetics, use of low-quality cosmetics products, exceeding the permissible standards in applying them to the hair.
- Long-term therapy with antibacterial drugs and hormonal drugs.
- Poor diet, excessive consumption of sweets, foods with large amounts of preservatives, as well as low-grade dyes.
- Drinking large amounts of drinks containing caffeine.
- Bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Excessive consumption of salty and spicy foods, as well as chips and fast food.
- Abuse of thermal procedures in saunas, baths, solariums, frequent hot baths. In warm weather, ticks begin active life.
We must not forget about the possibility of infection with a tick from another person, therefore the use of other people's hygiene items, combs, towels and other things is contraindicated. After shaking hands with people or being in public places, you must wash your hands. A sick person constantly scratches his head, and pathogens remain on his fingers, which are easily transmitted through shaking hands.
People diagnosed with demodicosis of the head and other parts of the body are not considered infectious and do not need to be isolated, since every person has the parasites that cause the pathology. It is important to control the activity of these mites through the above measures.
In addition to the described human-dependent reasons for tick activation, there are also pathological reasons:
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- AIDS and HIV infection;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- trichomoniasis;
- depression and other emotional disorders;
- metabolic disorder;
- frequent colds and viral diseases;
- infectious and other chronic diseases.
In addition, children can be included in the risk group for such a disease, since their immune system is not yet sufficiently developed. Elderly people are also more susceptible to demodicosis than others, since their bodies are weakened due to age-related changes.
Diagnosis of demodicosis of the head
Since the iron mite can be found in almost any person, when diagnosing demodicosis of the head, attention is paid not to the presence of the parasite, but to its number. For this reason, several diagnostic methods have been developed, each of which has its own pros and cons. The choice of diagnostic method is determined by the doctor individually.
| Diagnostic method | Advantages of the method | Disadvantages of the method |
| Scraping from the affected area of the skin. | Allows you to estimate the affected area and make calculations per unit surface. | It is impossible to estimate the number of parasites that are inside the sebaceous gland. |
| Analysis of sebaceous gland secretions. | The parasites that are inside the sebaceous gland are squeezed out. | The integrity of the skin is damaged, making it impossible to assess the entire surface area. |
| Surface biopsy method: a special adhesive substance is applied to a clean glass, with which the glass is glued to the affected area of skin for 60 seconds. As the adhesive substance dries, the surface epithelium and elements of the contents of the sebaceous glands remain on it. | In this way, you can obtain analysis from different zones and surfaces, and then calculate the scale of the damage. | Sometimes this method cannot be used on some areas of the head. |
| Skin biopsy method with further histology. | The contents of the sebaceous gland can be extracted. | The integrity of the skin is damaged, making it difficult to assess the condition of a large surface. |
| Analysis of extracted cilia and hair. | The only diagnostic procedure that allows you to detect mites in the hair follicle. | Sometimes the procedure may be accompanied by some pain. |
Which doctor treats demodicosis of the head?
First of all, you need to visit a dermatologist, who will give you a referral for tests and, based on their results, select a treatment regimen. For large areas of damage not only in the hair, but on the face, neck and back, the help of a dermatocosmetologist may be required. This is the doctor who determines your skin type. He will be able to select medicinal and cosmetic products and use them to treat problem areas. If the cause of the disease is poor immunity, the patient is referred to an immunologist. If hormonal disorders are suspected, an endocrinologist joins the treatment.
Treatment or a vicious circle?
Drugs that help some patients may have the opposite effect on others. It happens that improper treatment of demodicosis of the head leads to increased activity of mites and bacteria in the skin. The consequence is the appearance of new acne, increased seborrhea, peeling and even hair loss. After successful treatment of demodex of the scalp, the proven hair growth stimulating product minoxidil 15 iisolutions will help you restore hair.
Attention! Demodex of the scalp and inadequate treatment of the disease cause a person a lot of anxiety, he becomes nervous, and his health worsens even more.
The proliferation of parasitic mites, pathogenic and opportunistic microbes is a sign of weakened immunity. The appearance of inflammatory elements, in turn, reduces the natural turgor of the skin, it becomes dull and thinner.
Adequate care will help break the vicious circle in which the results of treatment are offset by the use of poor-quality hygiene products or a dirty hair brush. When using medicinal and cosmetic products, the natural mechanism of protecting the skin from parasites is restored, the process of keratinization of the epidermis and the functioning of the sebaceous glands are normalized.
How to treat
Before eliminating the problem, it is necessary to identify the causes that caused demodicosis of the head.
To do this, infected people are prescribed a comprehensive diagnosis of the body: a biopsy of the affected areas of the skin, examination of the secretions of the sebaceous glands, scraping from the surface of the epidermis, histology of biological material (in rare cases).
Immunity restoration
To recover and prevent re-exacerbation of the disease, those infected need to restore the body's defenses.
Otherwise, effective therapeutic methods will bring only temporary results.
The list of measures used to treat demodicosis on the head includes:
- restoration of a person’s emotional state;
- change in diet;
- correction of hormonal levels;
- elimination of all chronic disorders;
- giving up bad habits (alcoholism, smoking, sedentary lifestyle);
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
Drug treatment
Taking medications is necessary to destroy the parasite and reduce the severity of symptoms of demodicosis. As an antiparasitic agent, experts often prescribe the antibiotic Metronidazole (0.5 g 2 times a day).
The course of treatment with the drug is up to 1.5 months, depending on the severity of the disease and signs of its manifestation.
To consolidate the results obtained, Metronidazole is taken 2-3 weeks after the end of the main course of therapy. The drug has a minimal list of side effects and contraindications.
To enhance the results of antibiotic therapy, purified sulfur is also prescribed for oral administration: 500 mg with meals, 2 times a day.
To treat mite-affected areas of the skin, ointments with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects are used:
- ichthyol;
- sulfur;
- Benzyl benzoate;
- Wilkinson.
If pronounced signs of allergic reactions appear, it is better to use zinc ointment or a drug that has a similar effect.
Important information! For the treatment of demodicosis of the head, the use of several drugs for local treatment of the affected areas of the epidermis is prohibited.
When used in combination, creams can form aggressive compounds that are dangerous to the epidermis.
If during an illness pustules or other signs of a secondary infection appear on the head, then it is necessary to use creams with an antifungal or antibacterial effect.
Traditional methods
Alternative therapies are considered quite effective. If demodicosis is at an early stage, then with the help of such home remedies you can completely cure the disease.
We must not forget that before using any such treatment method, you must consult a doctor.
Traditional methods:
- Birch tar mixed with olive oil and grease. All ingredients must be combined in equal parts and mixed well. The resulting product will have a thick consistency like an ointment. Apply the medicine to the scalp at night, during the most active phase of the parasite’s life. In the morning, rinse your hair well with medicated shampoo.
- Apple cider vinegar. For therapy, regular apple cider vinegar available in the kitchen is suitable. This product should be used to lubricate the problem area of hair and skin, especially in areas of rashes. Manipulations should be carried out along the hair growth line, along.
- Herbs can also destroy the mite that causes demodicosis. It is not difficult to prepare a decoction. Take dried plants in equal parts: chamomile, juniper, wormwood, calendula, mix. Pour two tablespoons of the resulting mixture into a liter of boiling water, leave for about an hour, and strain. Rinse the hair and skin underneath with a warm decoction, thoroughly spreading the product over the entire surface of the head.
- Drinking herbal infusions is also very useful for this disease. This method will help to establish digestion processes, enhance metabolic processes in the body, and improve the health of the patient’s body. You can prepare a decoction from chamomile and calendula or mix both plants. Take 1 teaspoon of herbs and pour 1 glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain. Drink the resulting infusion throughout the day.
Even using medications prescribed by a doctor, you should not abandon traditional methods. If there are no contraindications to their use in the form of allergies, then this will not harm, but will enhance the therapeutic effect and speed up recovery.
Shampoos
Shampoos will eliminate the symptoms of demodicosis of the scalp: itching and flaking of the skin, the formation of ulcers and erosions on the surface of the epidermis, etc.
The following cosmetics are used for topical use:
- Demodex complex. The drug is used for both treatment and prevention of parasitic disease. The product is intended to combat demodicosis pathogens and helps against dandruff.
- Demodex Ovante. The drug contains natural ingredients and is produced by an American company. The product for combating hair mites includes eucalyptus oil, birch extract, sulfur, and a vitamin complex. The shampoo is prescribed for the treatment of pathology for people suffering from allergic reactions. To eliminate the symptoms of demodicosis, Demodex Ovante is used for 1 month.
- Demodex stop is a shampoo used to combat demodex mites and some types of fungal microorganisms. The product is applied to the scalp 2 times a day.
- .Manting is a Chinese-made shampoo containing antiparasitic substances.
Many of the shampoos for demodicosis contain the same components as medicinal ointments. The difficulty of treatment with shampoos lies in the need to constantly wash your hair.
Many anti-hair mite products also have a strong, unpleasant odor, which makes hygiene procedures difficult.
Diet
To achieve stable remission of the pathology, doctors prescribe a special diet to patients.
The nutritional rules are structured according to the type of treatment table No. 5, which excludes the consumption of alcohol; spicy, salty, fried and smoked foods.
Only with an integrated approach to combating pathology will the hair mite not make itself known again.
The food consumed during the treatment of demodicosis must be easily digestible so that all the body's forces are spent fighting the parasite.
Nutritionists include the following on the list of recommended foods: cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products. Lean meat and fish are not limited to the diet.
Birch tar - a natural remedy for demodex
Many medicinal and hygiene products include birch tar, which contains the resinous substance betulin, phenol and other aromatic compounds. The shampoo for demodicosis of the head is called “Stop Demodex”. This is a line of medicinal cosmetics, which includes birch tar components, as well as sulfur, herbal extracts, essential oil and urea.
Action of birch tar:
- antiparasitic;
- antiseptic;
- disinfectant;
- sebum regulating;
- anti-inflammatory.
Attention! Phenol in tar has a pungent odor and is a toxic substance. Caution must be exercised.
Birch tar for cosmetic use can be purchased at a pharmacy and added to your shampoo. This component is included in Vishnevsky's ointment, sulfur-tar ointment and other pharmaceutical products used to treat boils, acne, and fungus. Soap and shampoo with tar help with seborrhea, demodicosis, acne, dandruff and hair loss.
Rules for caring for the scalp and hair during treatment
In the process of treating demodicosis of the skin, certain rules should be followed. Shampoo alone will not cope with the attack of parasites. Therefore, it is necessary to wash your hair with a medicinal product, and then reinforce the result with folk methods. Due to the fact that mites are most active in the evening and at night, it is best to treat the skin during this period.
Products in the form of scrubs are not recommended for use more than once every 7 days, so as not to disturb the natural oil balance of the skin and not damage it. Infusions of eucalyptus, oak bark, buckthorn, elecampane, and wormwood have a beneficial effect on the scalp and hair. Your hair should be washed daily. During treatment, hair coloring and perming should not be done.
Treatment
It is possible to achieve the greatest effect only with an integrated approach, when folk remedies are used along with traditional methods (pharmacy medications).
Local therapy
To carry it out, special shampoos are used, among which the most popular are:
- Demodex Complex. Effective for treatment and prevention, removes dandruff, reduces the number of parasites.
- Demodex Ovante. American shampoo. Contains extracts, oils of various plants, sulfur, zinc, vitamin supplements. The content of natural ingredients allows it to be used by those who have allergic reactions. Treatment – at least 30 days.
- Stop Demodex. Destructive for ticks and fungi. It is recommended to wash your hair daily.
- Munting. Contains natural plant components. Prevents parasite activation and improves skin condition.
In addition to medicated shampoos, ointments are used. They are more difficult to apply and also have an unpleasant odor:
- Benzyl benzoate.
- Ichthyol ointment
- Sulfuric ointment.
Tar soap is also used.
All pharmaceutical preparations help reduce the parasite population and eliminate dandruff. They are recommended to be used comprehensively, in combination with medications and a set of vitamins that strengthen the immune system. Trichopolum tablets have an effective effect on ticks. The course of treatment is up to 45 days. Antibiotics are prescribed if the disease is accompanied by a purulent infection.
Traditional methods
In complex therapy, traditional methods of treatment are very effective.
Popular recipes:
- Birch tar. Mix in equal proportions with olive oil and purified grease until thick. Apply to the affected areas before going to bed.
- Castor oil. Take 20 ml and mix with two metronidazole tablets. The ointment is rubbed into the skin at least three times a day.
- Apple vinegar. The areas affected by the rash are wiped.
- Wormwood decoction. Pour 4 tablespoons of the plant into a liter of boiling water. They insist for five hours.
- Aloe. The plant juice is diluted half with water. Rubs into hair roots. Leave for 30 minutes. Treatment – twenty sessions.
With an integrated approach, recovery will come much faster.
Is demodicosis of the head completely curable?
Complete cure of demodicosis is possible only with complex treatment. It should be understood that eliminating the causes that led to the proliferation of the parasite will not lead to the destruction of existing individuals - they must be combated with antiparasitic agents.
For your information. According to statistics, 10% of people who have overcome demodicosis become ill with it again. This can be caused by a relapse of existing chronic diseases, poor diet, alcohol abuse and smoking. In addition, re-infection is possible.
How to prevent relapse
There is no specific prevention of parasitic infection. But to reduce the likelihood of exacerbation of the disease, you should:
- eat a balanced diet;
- treat allergic dermatoses in a timely manner;
- use antibiotics only on the recommendation of a doctor;
- limit the use of hormonal contraceptives;
- use shampoos containing tar and zinc;
- undergo vitamin therapy twice a year.
In 89% of cases, tick activation occurs in autumn and summer. To avoid relapses of demodicosis, during this period you must adhere to a dairy-vegetable diet. If sanitary and hygienic rules and recommendations of a dermatologist are observed, exacerbations of parasitic infections are not observed.
Prevention
Prevention of demodicosis of the head includes avoiding the use of other people's personal hygiene products. Also, to prevent pathology, it is important to monitor hormonal levels and prevent vitamin deficiency.
For sleeping, it is recommended to use pillows and blankets with synthetic fillings. Since hair mites and other microorganisms settle in them less often.
Pillowcases and duvet covers of a patient with demodicosis must be ironed with a hot iron on both sides.
Prevention of the disorder also includes: giving up bad habits, normalizing work and rest schedules, rational nutrition, and wearing protective hats in the hot season.
Demodicosis of the head can only occur against the background of several predisposing factors, for example, infection with a hair mite and weakened immunity. For healthy people, the microorganism does not pose a threat even if it accidentally comes into contact with the skin.
The fight against the disease is carried out comprehensively and includes: normalization of nutrition, the use of products for treating affected areas of the skin (creams, ointments and shampoos), oral administration of antiparasitic drugs, and the use of alternative medicine.
Particular attention is paid to the prevention of demodicosis, since the disease tends to worsen.