Water bugs are found in any body of water where there is no strong current. They belong to the order Hemiptera.
The name fully corresponds to their way of life, since insects spend almost all their time in a reservoir or on its surface. Here they find food, lay eggs, and mate.
Types and appearance of water bugs
To date, scientists have described quite a lot of species of these insects. They have different lifestyles, taste preferences, and appearance.
Water strider bug
The appearance of the water strider is characterized by a small body (from 0.1 to 3 cm) and long limbs.
Many hairs, impregnated with a wax-like substance found on their legs, help them glide across the pond with ease. A relatively large support area and low weight keep them on the surface film of water.
In search of food they have to travel long distances. Hence the name. The front legs are shorter than the hind legs and are designed to hold the prey. These water bugs feed on the larvae of small insects.
Water strider
Water striders are winged, but use their wings reluctantly.
Only unfavorable conditions force them to travel short distances by air in search of a new source of water. They can move on land, but slowly, since the peculiar structure of their limbs makes it quite difficult for them to do so.
Smooth water bug
The main difference between the smooth bug and other species is the hind limbs, which are noticeably longer than the rest and act like flippers when moving. He swims with his back down, raising his upper body above the water, which allows him to obtain the necessary supply of air for breathing through the tracheal tube.
Large red eyes search for prey in the upper layers of the reservoir. They become small fish, mosquitoes and other insects. The bug can dive for the victim, but not deeply. The air supply is only enough for 5–8 minutes. The body of an adult reaches 1.5 cm. The color is most often brown, but the smoothie can change shade, mimicking its environment.
Water bug Gladysh
Developed wings help him search for bodies of water rich in food. He prefers to fly at night. The love of light often attracts these insects to artificially lit areas in the evenings.
A special feature of the smoothie is its ability to make sounds similar to the chirping of a grasshopper.
Streaked water bug
The method of movement of the rower is similar to the smooth one, but it swims with its belly down and rows with its forelimbs, which are longer than the rest. The body length is only 0.8 cm. It received its name for the appearance of the outer integument. To stay under water, the insect clings to plant stems. A bubble filled with air located under the elytra makes it possible to breathe for some time without floating up.
Streaked water bug
Bottle bugs make peculiar sounds that are almost impossible to hear in the wild. But in an aquarium, it is better to hear the singing of this insect if there is silence in the apartment.
Belostoma (giant water bug)
The length of an adult belostoma bug (lat. Belostomatidae) reaches 10–17 cm. It can be found in tropical climates, where it prefers warm, shallow reservoirs that are completely warmed up in the sun. The insect can sit in ambush for a long time without coming to the surface. Its prey includes small fish, frogs, insects and three-keeled turtles. Often the belostoma bug attacks a victim larger than itself, infecting it with nerve agent.
The front legs of the insect have special hooks with which it holds the trophy until the injected agent begins to take effect. Belostoma prefers to use its wings only in emergency situations.
Belostoma
The brown oval body of the giant bug is flattened on top, which allows the males to incubate eggs on it until the larvae hatch.
How dangerous are water bugs for humans?
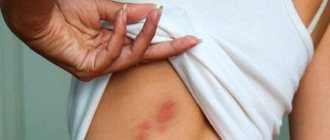
Water striders are the most harmless bugs; they do not threaten humans. People come into contact with them by chance while swimming in bodies of water. Even if they get bitten, they do not suffer from it. To avoid trouble for sure, the bite left by the water strider needs to be treated with brilliant green.
Another thing is the water striders that live in tropical reservoirs. Bedbugs have a sting, and their bite causes severe discomfort. The wound hurts as if stung by a bee or wasp. The affected area becomes numb and the pain lasts for at least an hour. After being bitten by a tropical water strider, an allergic reaction may develop that cannot be treated without antihistamines.
Gladysh is a dangerous water bug. It inflicts painful stings similar to those left by wasps. The giant belostoma eats small fish and frogs. In addition, it bites extremely hard, its bites bring suffering to a person. It is true that insects bite for self-defense. They do not attack people who do not intend to touch them.
Other types of insects leave a foul odor when they come into contact with human hands. Hands smell bad after talking to:
- harmful turtle;
- stink bug;
- Italian shieldweed.
Unless absolutely necessary, you should not come into contact with water bugs. If an insect accidentally enters a home, it is expelled, being careful.
Lifestyle and habitat of water bugs
The vast majority of species of these insects prefer fresh water bodies without current. Since they need oxygen to breathe, they cannot go to great depths and stay in water for a long time. You have to rise to the surface for the next portion of air. Only water striders never dive.
You can meet representatives of this type of bedbugs in any climate zone. Exceptions are giant water bugs, which do not tolerate cold water.
The lifespan of an individual does not exceed two to three years. Insects overwinter mainly on land, hibernating. For example, the smooth water bug prefers to spend the cold season, hiding in the forest litter or tree bark. In spring, the period of searching for a partner and mating begins.
When threatened, bedbugs freeze and appear dead. Some species are capable of secreting a repellent liquid.
Insect habitats
Most species of water bugs live in fresh water bodies at considerable depth. However, they cannot breathe underwater; they have special air sacs, which they replenish when floating to the surface.
Belostomas live in tropical regions and some areas of North America. They are most common in the USA, South Africa, China, Thailand, India, Brazil and Argentina. Other species live almost everywhere.
Danger to humans
Do not be afraid of large insects; water bugs do not pose a danger to humans. This is due to the fact that they compare the parameters of the intended prey with their own and will not risk rushing at such a large predator. However, if the insect senses danger, it may bite.
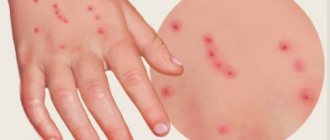
This often happens to children because of their natural tendency to be overly curious. After a bite, water bugs inject an enzyme that prevents the wound from healing quickly. This causes the bite to remain for several days or even a week. In rare cases, an allergic reaction of varying severity is possible.
A more dangerous situation is to encounter a large number of bedbugs during migration. They move from one body of water to another, often for the winter, in groups of hundreds of insects.
More discomfort is caused by the bites of bedbugs that live in tropical waters. The most painful are smoothies. The damage can be compared to a bee or wasp sting. Swelling of the injured limb, numbness and pain may occur.
There are varieties of bedbugs that, upon contact, leave a strong, unpleasant odor on the limbs. These include:
- stink bug;
- Italian shieldweed;
- bug harmful turtle.
Nutrition
All water bugs are predators. Their prey includes small insects, fry, fish eggs, larvae, and frogs. An elastic proboscis allows one to inject poison that has paralytic properties into the victim’s body and suck out biological fluid from it without resistance. Some varieties of bedbugs inject saliva into the caught prey, liquefying the insides, and then suck out the resulting juice, leaving only the shell.
Nutrition
If there is a lack of food, bedbugs can eat each other.
Insect feeding
Small species hunt smaller prey, are characterized by fast movement and high activity. Large ones prefer to attack from ambush, are slow, and spend a lot of time hiding in shelters. Aquatic insects are characterized by a piercing-sucking type of mouthparts. Because of this, all types of bedbugs are unable to eat solid food or bite off pieces of prey.
A bug that has captured prey.
Belostoma prefers to inject a paralyzing poison into the body of a large victim, which does not allow it to free itself. Having secured the prey with its forelimbs, the insect pierces its outer cover with a piercing proboscis and sucks out biological fluids rich in nutrients. Suitable food sources:
- tadpoles, frogs;
- eggs;
- amphibian eggs;
- smaller insects;
- small fish;
- other water bugs.
Reproduction of water bugs and care of offspring
All water bugs lay eggs. The only difference is where they do it. Smooth bugs prefer plant stems, while water bugs will choose algae leaves for their eggs. The most caring ones are the male belostomas. The female lays eggs on the surface of the back, filling it completely. All the time until the larvae are born, the future father takes care of the offspring: protects them from predators, maintains the desired temperature. While fiddling with the eggs, the male Belostoma does not feed, so after the larvae hatch, he quickly dies.
The hatched nymphs differ from the adult only in size. They immediately begin to hunt and after a few molts they are ready to breed.
The harm and benefits of giant water bugs
Just like other representatives of this species, Belostoma is an important link in the food chain. By hunting three-keeled turtles, they help regulate their numbers. If there are a lot of giant water bugs, they begin to eat young valuable fish species.
Belostomas cause trouble for humans when they get into the pool. Their bite is quite painful.
In recent years, Belostomas have begun to be bred on special farms in countries where they are used to prepare gourmet dishes. Fried giant water bug is a delicacy.
Gourmet dish
Giant bedbugs - who are they?
Fortunately or unfortunately, there are no giant waterbugs in our area. Giant water bug is an alien tropical creature. Belongs to the genus Belostoma. Reaches a length of 15 cm. The color is brown with different tints. The terrifying appearance of an insect does not mean that it is dangerous to humans. Giant water bugs have 3 pairs of limbs. The front ones are bent in the form of claws. With them, the predator grabs the prey and pulls it towards itself.
Hunting process and nutrition
Giant water bugs can be found in bodies of water with standing water. The Belostoma giant water bug prefers to hunt at night. Water bugs choose a convenient place and simply freeze. When the victim approaches, the giant bug quickly grabs it with its pincers. Belostoma's saliva contains a substance with a nerve-paralytic effect. The victim has no chance of surviving if the waterbug injection has already followed. Giant water bugs are interested in large insects, frogs, and small fish. The giant belostoma bug itself rarely becomes a victim.
Reproduction
This point requires special attention. Caring for future offspring is completely transferred to the strong back of giant water bugs - papas. The female Belostoma lays 3–4 eggs directly on the back of the male. He does this until there are about 100 pieces there. The back of giant water bugs can easily accommodate this amount. From now on, all responsibility is shifted to dad. The water bug carries them for 2 weeks. Periodically, the giant water bug rises to the surface and exposes its back to warm up. In this way, the larvae avoid the formation of mold and the accumulation of harmful microorganisms. In this form, belostoma resembles a hedgehog.
The harm and benefits of giant water bugs
There is no need to fear for a person’s life or health when encountering this water bug. Belostoma does not hunt humans. In addition, it is preferable for giant water bugs to quickly take refuge in a safe place. However, highly persistent and curious people run the risk of being bitten. Water bugs bite like a bee or wasp. There won't be any big consequences. There will just be redness and swelling. The sore spot will calm down after a week.
On the contrary, Belostoma is considered a very useful bug. Water bugs are the only creature that can calmly deal with pests such as three-keeled turtles. They pose a great danger to the younger generation of commercial fish.
In addition, giant harmless water bugs themselves suffer from human hands. Giant water bug is served fried in Thai restaurants. The demand for such exotic dishes is quite high. Therefore, in some lakes the giant bug remained in small numbers. And on farms they are trying to breed them.
The bug is not always harmful and dangerous to health. Reckless destruction of these creatures is strictly prohibited. Even if a wonderful dish is prepared from a bug. Everything in nature is interconnected! Perhaps, in the era of global warming, such large creatures will appear in our ponds. You need to know how to meet them.
Is it dangerous for humans?
People are not targeted by waterbugs, but they can defend themselves. Their proboscis is able to pierce the human epidermis and inject poison. If there is no strong allergic reaction, then there is no particular threat; it is enough to treat the wound with an antiseptic. The red spot will go away quickly.
The bite of the Belostoma water bug is painful, since the sting penetrates deep into the body and the injected poison has a more powerful effect. If you are bitten, you need to treat the wound and take an antihistamine.
To avoid such an outcome, it is enough not to pick up the parasites and try not to step on them with your bare feet.
How to get rid
Very often, water bugs are found in home ponds and swimming pools. In the latter case, this causes particular inconvenience, since the bites cause the desire to swim to disappear, especially in children. Chlorinating the water will not help in this case.
Many people catch bedbugs using nets, but this is a temporary measure. Since they migrate, if there are other bodies of water nearby, they quickly fly back.
The solution, if the pool is small, is to cover it with a fine mesh during the period when no one is swimming. There are remedies for bedbugs, but they are not safe for humans, and they will have to be used constantly due to migration.
The water bug is a common, but not dangerous insect for humans. It feeds on other smaller ones, including mosquitoes, occupying an important position in the food chain. When visiting bodies of water, it is better not to touch them to prevent being bitten. They pose a danger only to people prone to allergic reactions, which is rare.