Characteristic symptoms
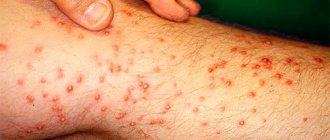
A photo showing what scabies looks like on the body clearly demonstrates skin rashes with the obligatory presence of the tunnels described above, areas of redness, and sometimes pustules.
Additionally, the patient is accompanied by unbearable itching, which intensifies at night - during the activity of the subcutaneous mite. IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
Signs and symptoms of scabies in a typical course
Among the many forms of the disease, the typical form of scabies predominates. Itching, a characteristic rash and the presence of scabies are the main signs and symptoms of scabies, which has a typical course.
Itching with scabies
Itching is a characteristic symptom of scabies. It occurs as a result of gnawing passages by female ticks, which occurs most likely at night, as well as allergies to tick waste products. Its intensity is influenced by the neuropsychic status of the patient, the number of parasites, the effect of medications used by the patient, the level of sensitization of the body to the waste products of mites - feces, oral secretions and secretions of the oviduct glands. In clean people, the intensity of itching may be insignificant.
Itching occurs in the evening and intensifies at night, disturbing the patient's sleep. Chronic itching leads to neuropsychiatric disorders.
Sometimes itching in adults occurs in places where scabies mites do not spread (skin of the face and neck, soles and palms, upper back), which is due to its reflex nature.
If itching bothers not only the patient, but also his family members, you should immediately consult a dermatologist.
Rice. 5. Itching and rashes are the first signs of scabies.
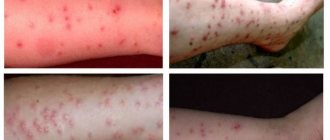
Scabies rash
The scabies rash consists of follicular papules and vesicles. When scratched, linear lesions of the skin (excoriation) appear, often covered with blood crusts. When a secondary infection occurs, pyoderma (pustular skin lesions) develops.
Elements of a rash during illness
Follicular papules appear at the locations of the follicles, where the larvae settle after emerging from the scabies ducts and remain there until they molt and mature. Papules of follicular origin are small in size (up to 2 mm in diameter), scattered, merging in places. They are localized on the flexor surfaces of the upper limbs, anterolateral surfaces of the torso, anterointernal surfaces of the thighs and the skin of the buttocks.
Vesicles (bubbles with liquid) are small in size (up to 3 mm). They are located isolated, mainly in the areas of most frequent infection - the hands, wrists and feet. When a secondary infection occurs, the vesicles turn into pustules (vesicles with purulent contents).
The main role in the development of papules and vesicles is played by sensitization of the body to waste products of mites.
Rice. 6. Follicular papules, vesicles and the presence of scabies are the first symptoms of the disease.
Rice. 7. Scabies on hands. It is in the epidermis of the skin that the female lays the bulk of her eggs, which, when scratched, fall out and, together with the larvae, are spread throughout the body.
Symptoms characteristic of scabies
- Ardi's symptom is characterized by the presence of pustules (vesicles filled with pus) and purulent crusts in the elbow area.
- Gorchakov's symptom is characterized by the presence of purulent and bloody crusts in the elbow area.
- The Michaelis symptom is characterized by the appearance of a pustular rash and bloody crusts in the intergluteal fold, extending to the sacrum.
- Sezari's symptom is characterized by the appearance of scabies that rise above the surface of the skin, which is clearly visible on palpation.
With scabies, the appearance of the rashes is less important than their location, since the rashes associated with the disease are very diverse. A more important sign of scabies is the location of the rashes and scratches.
Rice. 8. Ardi-Gorchakov’s symptom for scabies.
Typical sites of scabies rashes
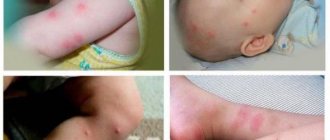
- In a significant proportion of patients, the rash is located in the interdigital spaces and lateral surfaces of the fingers, as well as in the area of the wrist joints.
- In half of men, the rash is localized on the genitals (foreskin and glans penis) and lower abdomen.
- Much less often, the rash is localized on the feet, torso and buttocks.
- Even less commonly, the rash is localized on the skin of the legs and arms (except for the feet and hands).
- In 10% of cases, the rash is localized on the mammary glands (around the nipples) in women.
Rice. 9. The interdigital spaces, the lateral surfaces of the fingers and the areas of the wrist joints are the main places of settlement of scabies mites.
Rice. 10. Scabies rash is often recorded on the anterior wall of the abdomen and the anterior inner thighs.
Rice. 11. Fertilized females reach the genitals of men not only through close contact with a sick person, but also through their own hands.
Rice. 12. In some cases, the disease causes a rash in the intergluteal folds.
Itching that occurs in the evening and at night is a constant and main symptom of scabies.
Scabies
After fertilization, females immediately gnaw through the stratum corneum of the epidermis and penetrate the skin in places where the stratum corneum has the greatest thickness, lower temperature and where there is no or minimal hair - the area of the hands, wrists and feet. Regeneration processes in the thick stratum corneum occur slowly, which is why the larvae of scabies mites have time to hatch and are not rejected with the horny scales of the epidermis.
Scabies is accompanied by the appearance of scabies. Scabies are a pathognomonic sign of the disease. They are performed by female parasites in the evening and at night. Scabies burrows are located at an angle to each other, in each of them the females lay one egg. One female gnaws 1 - 2 tunnels per night. It advances at a rate of about 2.5 mm per day. The length of the passages ranges from several millimeters to several centimeters. In each of the passages, the female gnaws a hole at the top intended for the exit of future larvae to the outside.
Scabies ducts have a curved appearance and a whitish color. They rise somewhat above the surface of the skin. In the front part of the passage there is a female. It is visible through the epidermis in the form of a black dot. The thinner the stratum corneum, the better the female is visible.
Hands, wrists, male genitals and feet are the most common locations for scabies.
Rice. 13. The female makes scabies in places where the thickness of the stratum corneum is greatest, the temperature is low and the hair is minimal.
Rice. 14. The back part of the passages is gradually removed (exfoliated) during the process of regeneration of the epidermis. But some scabies can persist for up to one and a half months.
Rice. 15. Scabies burrows contain the female, eggs, empty eggs, excrement and sometimes larvae hatched from the eggs.
Rice. 16. The photo shows typical locations of scabies burrows.
Causes of scabies
Scabies is caused by the scabies mite (itcher). It is a parasite belonging to the mite family. Itch reproduces on the surface of the skin of humans and animals and feeds on its cells.
Infection can occur through direct contact (for example, with your hand) or indirectly, that is, through the sharing of certain household items, for example, towels, bed linen, plush toys. Outside the host's body, scabies mites can live up to 3 days.
The dependence of the occurrence of the disease on socio-economic conditions, gender or age of the patient has not been confirmed.
However, it has been found that in unsanitary conditions the infection spreads faster and easier.
Closed crowds of people: like schools, nursing homes, hospitals, create favorable conditions for the occurrence of numerous infections.
Often the first source of infection is people with weakened immunity, for example, those undergoing treatment with immunosuppressive drugs or carriers of HIV infection.
A rare but serious and contagious form of scabies is Norwegian scabies. This type of scabies is easily transmitted through bedding and clothing. Animals cannot spread human scabies.
Norwegian scabies
It is one of the types of scabies. Represents a major challenge for diagnosis and treatment.
The incidence of this type of scabies has been constantly increasing in recent years.
Norwegian scabies most often attacks older people and people with weak immune systems.
Skin changes take on a different picture than with the classic form of scabies. They appear as erythematous lesions with increased keratosis of the skin.
Diagnostics
You can suspect a scab based on typical clinical signs and the characteristic localization of the process, which is described above. The following methods are used to confirm the diagnosis:
- coloring the skin with iodine tincture: in this case, the tick burrows turn brown
- skin scraping using 40 percent lactic acid
- mite detection using a videodermatoscope
- removal of the tick from the epidermis and its microscopy
These are the types of diagnostics for infection with scabies, plus known symptoms.
How to quickly cure at home with folk remedies
It is best to use acaricidal medications to get rid of scabies mites. They guarantee 100% cure.
But if you can’t quickly get an appointment with a dermatologist (tomorrow is Sunday, or there is no regular bus from the village to the hospital in the regional center), you can slow down the mass spread of itches throughout the body using ancient recipes.
The effectiveness of vinegar
An acidic environment helps inhibit the growth of parasites, so you can use apple cider vinegar to significantly reduce their population:
- For a day or two (before visiting the doctor), you can thoroughly lubricate the skin covered with the rash 2 (3) times a day.
- Do not rinse off.
An unfavorable environment prevents females from laying eggs and disrupts the metabolic processes of the larvae, causing most of them to die.
Garlic-oil mixture
Recipe:
- Boil 250 ml of vegetable oil (from sunflower, mustard or flax) in a jar (0.5 l) in a water bath over low heat.
- Pour chopped garlic (50 g) with this emulsion.
- Leave for a day.
- Skin damaged by itching should be lubricated 2 times. in a day.
The effectiveness of this product is due to the powerful antiparasitic properties of garlic and the binding properties of the oil (it deprives ticks of proper breathing and prevents rapid movement).
Ash
In former times, people mixed aspen ash with sulfur powder in equal parts.
They settled it in water (the result was a thick mixture). The concentrate was rubbed once a day on the arms, legs, and stomach, where the rash had formed.
To completely cure scabies, 4 days of such procedures were enough.
Tar
What explains the effectiveness of using birch tar for scabies? The substance inhibits all vital functions of ticks:
- Deprives breathing and nutrition.
- Prevents individuals from mating.
- Interferes with the process of laying larvae.
- Does not allow you to gnaw through tunnels.
- Tar is usually mixed with sulfur powder in a 2:1 ratio.
You can apply it directly to the skin where the rash is and a little nearby (covering a 2 cm circumference).
Early treatment
The main principle of scabies treatment is that the entire skin should be treated with drugs, regardless of the location of the disease. The exception is the scalp, which is rarely affected by scabies.
Although scabies can be treated at home, therapy (including the medications used) must be prescribed by a doctor and carried out under his supervision.
You should also follow the recommendations listed below:
- Nails should be cut short.
- Rub in the preparations by hand.
- The preparations are rubbed in in the evening, since the mite is active at night.
- It is necessary to wash before starting the course of treatment and after its completion, but it is not recommended to do this during the period of therapy.
- All family members of the patient and his cohabitants are subject to preventive treatment, even if they do not have symptoms of scabies.
The most common drug for scabies is benzyl benzoate, which is available in the form of emulsions. It is applied to a clean body, to all areas except the face and scalp. But the emulsion is prohibited for use by pregnant women and during lactation.
Lindane cream is also used, which is rubbed into the skin 2 times a day. Aerosol forms of drugs are also used, which are especially well suited for prophylactic treatment of the skin of the patient’s cohabitants. Speragel is available in the form of a spray; its main advantage is that it is suitable for treating pregnant women and young children.