Definition
Lice are insects that parasitize the skin of mammals. Their body is flattened and includes three sections: head, chest, abdomen. Males are slightly larger than females. They have a piercing-sucking type of mouthparts that allow them to suck blood through small punctures in the epidermis. They manage without wings.
Attention! Science knows about 500 species, but only three of them can live on the human body: body, head, pubic. What types of lice are there, what is their difference, you will find on our website.
Nits are lice eggs covered with a protective shell. They are an elongated white capsule, the size of which does not exceed 1 mm.
These insects are dangerous to health as they are carriers of various diseases.
Routes of infection
Lice are transmitted from one person to another by contact: it is enough to stand next to the carrier or use his personal hygiene products. People who are at risk are:
- spend a lot of time in public places;
- often go on long trips;
- touch other people's hair, clothes, combs, etc.
You can become infected while visiting any standing body of water, since these insects are able to stay on the surface for some time.
One of the common misconceptions is that lice only appear on those people who do not follow hygiene standards. Practice shows that anyone, even the cleanest person, can become infected with parasites.
We recommend reading: where do lice on a person’s head come from.
Prevention methods
Preventing head lice is quite simple. It comes down to observing basic rules of personal hygiene. Those with long hair are advised to wear a ponytail or tuck their hair under a hat when using public transport. You should also not use extraneous hats, towels, hygiene items, or combs.
If infection cannot be avoided, it is necessary to prevent the further spread of head lice. Bed linen, towels, and hats should be boiled and ironed. How to treat an apartment for head lice? To do this you need to use special tools. They are sold in hardware stores.
After infection, it is important to undergo examination by a dermatologist, who will prescribe therapy, and notify contact persons in the garden, school, and relatives about the disease. The recovery process should be regularly monitored by a specialist.
Life period
Incubation period
After contact with the human body, the louse lays an egg coated with a special substance. The shell protects the contents of the capsule from mechanical damage and exposure to chemicals. The entire structure is tightly attached to a thread.
On average, nit development takes seven days. Throughout the entire period, the egg does without food and oxygen.
When the week comes to an end, the larva appears. She is unable to immediately leave the capsule, so she chews through it, while simultaneously accumulating carbon dioxide in the lower part of her body, which pushes it out. In appearance, it does not differ from a nit in any way except for its size.
You can find out how long the incubation period of pediculosis in humans is on our website.
Stages of larval development
After hatching, the parasite attaches itself to the hair and begins to actively feed. The transition to the next stage of development can take from one to ten days. Over time, the larva begins to look more and more like an adult, but its size is still small and its reproductive system is undeveloped. When the first stage comes to an end, the future louse sheds the old chitinous shell and becomes covered with a harder shell.
After this procedure, a nymph is formed, which goes through two stages of development. Each of them ends with a moult. The chitinous shell is not elastic, so when it becomes too small, it is shed. The evolution of the nymph lasts five days. At this stage, the reproductive system is formed.
The transformation of a nit into an imago (adult) takes about 16 days. The period increases if living conditions are unfavorable.
Features of reproduction
Parasites can begin to reproduce within a few hours after the completion of the last stage of evolution. The mating process takes from 20 to 70 minutes. The female receives seed material, which is stored in the abdomen and used as needed.
She has no need to enter into contact with her partner again, since these reserves are enough for the entire life cycle. The male dies 7–10 days after mating.
The future larva forms very quickly; as it moves along the oviduct, it becomes covered with a dense protective shell. After 24 hours, the female glues the nit to the hair or fabric, depending on the habitat. This happens as follows:
- The louse clings to a thread or hair with its paws using claws located at the ends of the paws.
- Strains the abdominal wall and squeezes out a little sticky substance.
- An egg hatches from the back of the abdomen and is placed in an already prepared area.
- The adhesive substance hardens, forming a reliable shell.
How lice reproduce, their rate of development, read on our website.
Important! It is much easier for parasites to reproduce when their owner is not trying to get rid of them. The female does not have to wait for a suitable partner to appear, so the process of laying eggs goes faster. Stopping the insect population in this situation becomes much more difficult.
How long do they live
The lifespan of a louse usually does not exceed 46 days. This indicator may change up or down depending on the sex and type of animal.
Parasites survive by consuming the blood of their host 2 to 6 times a day. Without a power source, they cannot last more than 55 hours.
Lice never feel hungry, so sucking blood is a way for them to calm their instinct.
What do lice and nits eat on a person’s head?
As already mentioned, head lice feed on blood. And they have a wonderful appetite. During the day, one louse can suck from 0.5 to 0.65 mg of blood. In 24 hours, the insect feeds 4-5 times, and the process of consuming food takes on average 5-10 minutes. This is due to the special structure of the louse’s body; it is absolutely not adapted to long-term fasting. As a result of the absence of food, even a short period can lead to the death of the insect.
At all stages of development, the head louse feeds only on human blood . Due to its special structure, the parasite is able to pierce the skin and pump human blood into its abdomen.
REFERENCE! There is an opinion that lice are capable of absorbing hair and skin microparticles, but it is unfounded, since it has been proven that these parasites cannot digest solid food.
However, other members of the lice family can feed on fluff, skin particles and hairs.
Thus, lice found on the human head feed only on blood, with the exception of the larval period. Nits do not feed on anything at all until they are fully mature.
Types of lice
As already mentioned at the beginning of the article, there are three types of lice that can live on the human body:
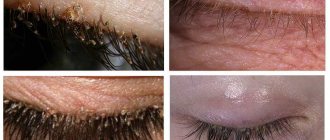
- Pubic - live on the hairy part of the pubic area, the scrotum. Less often - on eyelashes, mustache, back, chest, beard.
- Clothes - live on the skin (in the neck, shoulder blades, lower back), in the folds of bed linen and clothing.
- Head - based on the hair of the scalp.
Type 1 parasites are transmitted primarily during sexual intercourse. The second and third - through everyday use. Habitat and mode of distribution are not the only differences between species.
The size of the pubic insect does not exceed 1 mm. Life expectancy for individuals of both sexes is 30–31 days. During this period, the parasite practically does not tear itself away from the food source. The female lays larvae no more than 26–30 times during the entire period.
The body louse is the largest. The length of its body can reach up to 5 mm. The male lives for 4 weeks, the female for 1.5–2 months. They feed 2-3 times a day. The female manages to make up to 295 clutches until she dies.
The head variety of parasites feeds twice a day. The duration of the life cycle does not exceed one month. These insects are medium in size - 2–4 mm. The female leaves offspring approximately once every 6 hours, by the end of the period - 120–140 clutches.
One clutch of pubic louse consists of 1–2 eggs, body louse 8–10, and head louse 2–4. The number of larvae that a female can lay depends on her size.
We recommend reading: what types of lice there are, their similarities and differences.
What do lice and nits eat in nature?
If a louse is deprived of its owner, it quickly dies under natural conditions. This is due to the lack of food for the insect. As mentioned above, lice cannot live long without food, so they die outside the host. Death occurs within a few hours. Therefore, it is worth saying with confidence that far from living organisms, lice cannot feed on anything other than blood.
Conditions of death
Insects do not tolerate cold well. They can easily withstand temperature drops to zero, but at temperatures below 20 °C they die within 30 minutes. Capsules with larvae maintain performance at a normal level.
A parasite can die from cold only if it is separated from the host’s body. Therefore, to combat body lice, wet clothes are hung out in the cold.
The optimal temperature for the proliferation of parasites on the body is 30 °C. If there is a significant deviation from this °C indicator, females stop laying eggs, and the development of nits slows down. When the figure reaches +45–50 °C, adults die within half an hour, but the eggs remain viable.
The larvae are protected by a durable shell, so they are not afraid of normal exposure to low or high temperatures. They also continue to gradually develop after they enter the water. To destroy them, it is necessary to create conditions under which the nits will find themselves in a stressful situation due to sudden changes in their habitat. This method is used to treat clothes and linen against body lice: they are ironed or boiled.
At what temperature lice and nits die, you can find out on our website.
Important! Changing the temperature regime is not suitable for getting rid of parasites that live on the human body. In this case, the best way to create unfavorable living conditions for lice is to use special products.
Insecticides
Insecticides are chemical substances designed to kill various insect pests. They usually paralyze the animal's nervous system, which ensures its rapid death. But there are remedies that work differently: they deprive parasites of the ability to breathe. Preparations of the second type cannot harm nits in any way, so they are used as one of the components of the complex.
Vinegar
Acetic acid is a popular folk remedy for lice control. Mixed with water, it dissolves the substance with which the egg capsules are attached to the hair.
The acetic environment is also unfavorable for adults. They do not die, but lose the ability to hold on tightly. After such treatment, it is easy to get rid of parasites and their clutches during combing.
Insects are also afraid of other organic acids: cranberry, lemon, grape juice.
Kerosene
Kerosene was used to remove lice in times when there were no safer options. It was applied to the infected hair, a plastic bag was put on top and left for 30 minutes. Kerosene poisoned the adults and partially dissolved the capsules of the larvae, which is why they could not continue to develop normally.
Smells
Using their sense of smell, parasites find a source of food, a mate for procreation, so they are sensitive to pungent odors. You can take advantage of this weakness by adding essential oils to your body and head treatments. Best suited for these purposes:
- tea tree;
- rosemary;
- mint;
- lavender;
- menthol;
- cypress;
- eucalyptus;
- bergamot.
You can add up to 5 drops of essential oil to shampoo or water for rinsing your hair, and no more than 1-2 to products intended for application to the body. The strong smell will not kill the insects, but will make them rather lethargic so that combing them out will bring maximum benefit.
Read on our website which natural oils are effective against lice and nits
The easiest way to create an environment unfavorable for pubic lice is to shave off the hair on which they live. This method is also suitable for getting rid of parasites that live on the head, but modern medicine offers many means that allow you not to make such a sacrifice.
Effective shampoos against lice and nits:
- Paranit;
- Veda and Veda-2;
- Nix;
- Hygia;
- Pediculen ultra;
- Nit Free (Nit Free);
- Does tar shampoo help against lice and nits?