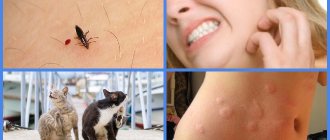
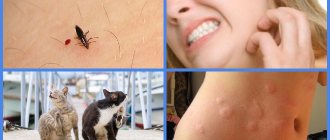
Who do parasites bite?
To maintain their vital functions, lice and fleas feed on the blood of representatives of the animal world, including humans. At the same time, the type of “nutrition” of parasites is different. At the nit stage, fleas develop a digestive system that can “receive” the blood of any warm-blooded animal:
- cats;
- dogs;
- rabbits;
- person and others.
Lice parasitize exclusively on the human body. This feature is explained by the way of life. Fleas, unlike lice, move by jumping. Therefore, this species is able to move from one warm-blooded animal to another. Lice lack this feature, and therefore are forced to adapt and feed on the blood of a specific host.
How to get rid of parasites
Both lice and fleas, once identified, require control. Fleas are difficult to kill . Their elimination includes several stages:
- destruction of parasites on the victim affected by them;
- residential treatment;
- treatment of common areas;
To kill fleas on dogs and cats, special animal shampoos are used. Various drops are also used: Barrier, Neo, Blochnet, Dana Ultra. There are special anti-flea collars for animals.
IMPORTANT! All nooks and crannies in a house or apartment, bedding and rugs of pets must be thoroughly vacuumed and washed using insectoacaricidal agents.
For the treatment of premises, preparations such as Raid, Get, Raptor, Clean House, Dichlorvos can be used.
The fight against pediculosis is simpler . You can purchase numerous products at the pharmacy to help you get rid of lice.
Therapy includes two stages:
- destruction of adult parasites;
- eliminating nits.
Almost no medications have any effect on nits . They are removed manually or a special comb with fine teeth is used. When treating head lice, it is also important to thoroughly wash and boil all clothes, underwear and bedding.
If signs of pediculosis are detected, you should consult a dermatologist . He will prescribe medications that help eliminate parasites, for example, Butadione or Full Marks. The products are available in the form of shampoos, ointments, gels, sprays, and solutions. Therapy can also be supplemented with folk remedies. Medicines are applied to the scalp and hair and remain for the required period. Then the products are washed off, and dead parasites and nits are combed out. After a certain time, the treatment must be repeated to destroy newly hatched insects.
Do you understand the difference between lice and fleas?
Not really
Lice and fleas cause a lot of trouble. But if you quickly determine their presence and take the necessary measures in a timely manner, you can soon forget about the existence of parasites. The choice of antiparasitic medications today is quite wide. Lice are somewhat easier to deal with than fleas, but in both cases you need to start treatment as early as possible.
- about the author
- VK profile
Habitat
Parasites can look (color) differently depending on their habitat. Lice and fleas inhabit almost every continent on planet Earth. You can even meet these little nits in Antarctica. Typically, adult individuals try to parasitize a person or animal. These are particularly favorable places for breeding. The best temperature is 15-30 degrees Celsius. In the cold, parasites feel vulnerable and do not find fresh blood to feed on. Often they choose particularly polluted places containing dust and debris. These are basements of apartment buildings, abandoned industrial premises, attics, cracks, chips in walls or floors.
In nature, they can choose trees, foliage, stumps or snags (especially for reproduction). At the same time, they are looking for a host to parasitize. They settle in the hairline and live until exterminated.
Means for combating larvae
Worms are destroyed with the same drugs as adult insects. The product is 100% effective when detecting areas of accumulation. In this case, powders, solutions, and aerosols are used. Folk remedies give good results.
Frequently used concentrates with a high degree of effectiveness are Executioner, Tetrix, Cucaracha. They mainly give preference to aerosols. The most popular brands are Raptor, Raid, Clean House, Combat, Dichlorvos, Karbofos.
Vinegar, turpentine, and kerosene are used as folk remedies. There is no point in fighting worms with herbs and repellents - they are insensitive to this matter. Powders and dusts also give poor results because they act when ingested.
The fight is being carried out comprehensively. Because it is necessary to destroy both adult parasites and their offspring. You should pay attention to the pet, otherwise the premises or animal will be re-infected and you will have to do everything all over again.
Harm from parasites
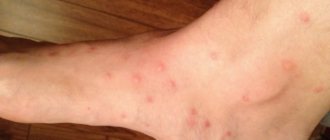
Because lice and fleas gain access to blood by biting through the skin, they leave red and itchy patches on the body. Such consequences are explained by the body’s allergic reaction to external influences. With increased skin sensitivity, a bite can lead to more serious complications, including dermatosis.
flea under a microscope
The danger of lice lies in the fact that this type of insect is considered to be a carrier of typhus. The infection is now highly treatable.
Louse
Fleas, due to the nature of their life activity, are considered more dangerous pests. By parasitizing warm-blooded animals, insects are capable of transmitting various types of infections. Fleas that live on the bodies of rats or cats walking outside are considered more dangerous. This type of parasite is also capable of transmitting helminths. Flea larvae and adults release worm eggs into the human blood during bites.
What diseases are transmitted?
Attention! When a bite is made, each individual injects a specific liquid. Pathogenic bacteria can get in with it. Such bacteria can cause various diseases.
Let's call them:
- Plague.
- Pediculosis.
- Worms (tape and others).
- Salmonellosis.
- Listeriosis.
- Encephalitis virus.
- Pathogenic fungus.
- Typhoid fever.
- Anthrax.
The risk group includes homeless citizens and animals looking for temporary shelter. Unsanitary conditions and dirt provoke the proliferation of small parasites, for which this is an excellent place to live.
Danger to people and animals
Fleas and lice are carriers of diseases, often very serious ones.
- Lice. These bloodsuckers are divided into the following types - body, head and pubic. The body louse can be a carrier of typhus, an epidemic of which in the last century destroyed the lives of thousands of people. Relapsing fever, the plague is carried by head lice. Pubic individuals are currently at the stage of extinction, thanks to the fashion for hair removal of intimate areas. Since lice live mainly on people, they pose a danger primarily to them.
- Fleas. They are considered more dangerous than lice as carriers of infections due to their “omnivorousness”. They can feed on blood from both humans and animals. Therefore, they become infected with various diseases more often. Fleas are also carriers of helminth eggs, which easily pass into the victim’s blood when bitten by an infected insect. Fleas pose a danger to both people and animals.
Important! The most dangerous parasites are considered to be rat fleas, which prefer to feed on human blood when killing mice in attics and basements.
Danger
They say that we owe the terrifying plague epidemics to rats, namely the fleas that lived on them. To this day, rat fleas are considered the most dangerous. They are the carriers of plague vibrios, causative agents of tularemia, pseudotuberculosis, salmonella, brucella and other equally dangerous diseases. And as if this were not enough, fleas carry hepatitis B and C and are transmission links for parasitic worms.
Both head and body lice can transmit such a terrible disease as typhus and infect humans with bacterial diseases.
How are pediculosis and flea infestation diagnosed?
Each insect bite is accompanied by itching and burning. This can cause inflammation. This is called symptomatology. It includes:
- Dandruff.
- Severe rash in the affected area.
- The presence of living or dead insects in the hair.
- The appearance of dermatitis or other skin lesions.
These are the reasons why citizens turn to doctors for help. To confirm the diagnosis, a diagnosis is needed, which is carried out like this. First, the doctor checks the areas behind the ears and neck for lesions. Carefully probes and examines the scalp. The main tool here is a comb. This process is the same for adults, children, and animals. If there are sufficient grounds, the doctor prescribes complex treatment (this is the most effective).
Lifestyle Differences
Photo - difference between fleas and lice
Knowing the difference between lice and fleas, you can choose effective methods for treating head lice and controlling pests without consulting a doctor. Small insects are characterized by the following features:
- permanent habitat - hair on the human body;
- localization - mainly near the hair shaft;
- move quickly.
The following features are characteristic of fleas:
- move by jumping, covering a distance of up to half a meter;
- constant migration from one medium to another;
- the ability to survive and reproduce outside the host's body.
Differences between fleas and lice can also be traced in other parameters.
Fighting methods
Fleas and lice behave differently, and therefore the methods of combating representatives of each type of pest will be different.
If we talk about fleas, they are quite difficult to kill. The fight against them involves several stages, and simultaneous ones. The following must be processed:
- pets;
- their rugs and houses;
- rooms of your apartment.
In order to get rid of lice, the premises are not treated - the fight in this case is based on the destruction of adult individuals and nits living in the hair, as well as boiling clothes and bed linen.
What are the similarities?
The similarity between the pests in question is that lice and fleas consume the blood necessary to maintain life. Lack of access to nutrient fluid provokes the death of the insect colony.
Another similarity between lice and fleas can be seen in the consequences that occur in the carrier of the parasites. The bites leave red, itchy spots on the body. A large colony of adult individuals can cause an allergic reaction and intense intoxication of the body with corresponding symptoms. Scratching (often unconsciously) of bite sites increases the risk of secondary infection and the development of a purulent process in the tissues of the epidermis.
The third similarity is that bloodsuckers, in the absence of a constant source of food, are capable of falling into suspended animation. In this state, insects remain viable. Anabiosis lasts more than a year. If at the end of the specified period the insects do not encounter a food source, the parasites die.
Appearance
Having determined how a flea differs from a louse in its lifestyle, it is worth considering the appearance of the insects. Such knowledge helps to develop a pest control strategy. Since lice and fleas look different, each insect should be considered separately. The first ones are distinguished by the following features:
- body flat on the sides;
- small size;
- gray (translucent) color or red (after saturation);
- short legs.
The second insects are distinguished by their large size and brown body with long hind legs.
What does a flea look like?
Parasites live mainly on animals, but sometimes they are not averse to tasting human blood. The flea's body is flat, brown or almost black. The insect has several pairs of legs, the hind limbs are especially strongly developed, with the help of which the flea makes jumps up to one and a half meters high. You can see the bloodsucker with the naked eye; unlike lice, the flea is somewhat larger and much more mobile.
Fleas on a dog
Insects do not reproduce on their host; parasites prefer to lay eggs in secluded places (behind baseboards, on the fleecy part of carpets, inside the upholstery of upholstered furniture). The development cycle from egg to larva ranges from several weeks to 1.5 months. After hatching from the egg, the larva begins to feed on the excrement of adults, which contains undigested blood of the victim. Under favorable conditions, after 20 days the larva turns into an adult insect.
Flea larvae do not feed on human or animal blood and cannot bite their hosts. Small worms live mainly on the bedding of domestic animals, in secluded corners of human homes.
Lice
Small, grayish insects belonging to the order of lice beetles. Based on where they live, lice are usually divided into two types: hair lice and body lice. These two species separated quite recently, no more than 70 thousand years ago. Therefore, when living in one place for a long time, they easily switch to another species. For example, a head louse can become a body louse and vice versa. You can distinguish one species from another visually if you have good eyesight. The body louse is almost white in color and more elongated in format. Head lice are considered safer because they are not carriers of dangerous infectious diseases.
How are lice different from fleas?
Although lice and fleas are blood-sucking parasites, both males and females of both species participate in the bloody orgy. They have many differences from each other.
- These parasites belong to completely different species. Although both of them suck blood, lice belong to the species of lice and always nest on human hair and never change their donor to another species. A louse will not drink the blood of your pets, while a flea, in the absence of feeders, will happily feast on your blood.
- They can also be distinguished by their appearance, although this can only be seen under a microscope. The louse is larger than the flea, its shell is gray, and fleas wear a black and brown outfit. It's impossible to see, but fleas have eyes and lice are blind.
- The appearance of the bites also varies:
The difference in lice, flea and bedbug bites - Lice differ from fleas in their lifespan. If the lifespan of an adult louse is a little more than a month, then the flea can last a year and a half. Both males and females feed on blood.
- These insects even reproduce differently. A flea throws eggs from its belly, as they say, to whomever God sends, and a louse leaves its offspring next to itself in a person’s hair.
- And most importantly, lice live only on a person’s hair or clothing; fleas climb onto a person or animal only to bite. They prefer to hide in more secluded places.
In conclusion, I would like to note that if you follow simple hygiene habits, the chances of encountering these parasites are low. The main dangerous factors: children's groups and nearby dwellings filled with migrants. As for pets, be sure to carry out anti-tick treatment for pets going outside. The substances included in acaricidal preparations kill not only ticks, but also fleas of various species.
If you find an error or inaccuracy, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Reproduction
Effective control of bloodsuckers is impossible without knowledge about the mechanisms of their reproduction. Thus, lice prefer to live and reproduce in one place - the human head, only in close contact with the scalp of another person, moving from their home. They also lay their eggs on the hair in fairly small quantities - 150 eggs in 50-60 days. After a week, the nit (parasite egg) becomes an adult.
Fleas look for more secluded corners to lay eggs and rarely breed in habitats. They prefer animal bedding, carpets and rugs, upholstery of upholstered furniture, places under baseboards and floor crevices. Flea eggs take a long time to mature - from 14 days to several months, depending on conditions. The egg first hatches into a larva and only then does it develop into an adult. During its life, an adult is capable of laying 600 eggs, from which viable offspring emerge that feed on any organic compounds. Therefore, the fight against their destruction should not be limited to their habitats.
Important! Based on all of the above, it is worth explaining that it is easier to destroy lice - they will completely die when treating the hair on the head. And you still have to look for areas where fleas accumulate and reproduce.
Fleas
The main features of parasite reproduction include:
- Jumping bloodsuckers rarely lay eggs or mate on the host's body. They do this in secluded places that are located near the target;
- flea eggs should be looked for and destroyed not only on the animal’s cover, but also in other places;
- after a certain period, a worm-like larva emerges;
- larvae can be in places where the owner sleeps and rests;
- after a certain period the larva pupates;
- After the parasite emerges from the cocoon, it acquires the ability to live fully.
On average, the complete transformation cycle under suitable conditions is 3-4 weeks.
How fleas reproduce and their lifespan
No less pressing is the question of how fleas reproduce. The process of flea reproduction is quite complex and is associated with a very intricate structure of the genital organs. At the very beginning of mating, the female climbs onto her partner’s back and pulls into herself his genital organ, which in a passive state can be up to one-third the length of the insect’s body. The genital organ penetrates the female's spermatheca within 10 minutes. Sexual intercourse occurs within 10 hours.
In the question of where fleas come from, you need to know that many species, when saturated with blood, begin to reproduce. Fleas can reproduce by laying eggs. The female produces eggs in a small amount, up to 8 pieces, this is done for successful reproduction. Over the course of its entire life cycle, a flea can lay about 500 eggs. Eggs laid on the host's hair develop within two weeks. A larva emerges from the egg and hides in the host’s skin or in nests and burrows. They feed on various remains of undecomposed blood. Molting occurs three times during the entire period, the larva wraps itself in a silk cocoon and pupates. Different types of fleas emerge from their cocoons at certain times of the year.
It is impossible to give an exact answer to the question of how long fleas live, since for different species the lifespan can be from two months to one and a half years.
Body structure
How to recognize fleas and lice? Paying attention to their appearance.
- The flea has a body flattened on the sides, while the louse has a flat body.
- The size of the first will be slightly larger than the second.
- Lice have short walking limbs with small “hooks” - hooks at the ends. With their help, individuals are attached to the hair. Fleas have long legs, especially the racing pair.
- The integument of fleas is brown: from light to dark shade. While lice are colored gray, and their chitin is translucent.
The color of lice will vary depending on whether they are full or hungry - when filled with blood, their body becomes much darker: from burgundy to black
Feeding of parasites
The main diet of blood-sucking insects is blood (whether it is a person, a kitten, or a dog). The flea feeds on the blood of animals (regardless of their species or subspecies). Very often it can parasitize a person (adult or child). The louse settles only in human hair and folds of clothing.
A constant flow of food helps maintain the life cycle and helps maintain life expectancy. Unlike mosquitoes, these insects do not leave the donor for a long time. If no control measures are taken against them, then they can annoy the owner and torment him for a long time.
Lifestyle
The difference between fleas and lice is that the latter parasitize only in human hair, without leaving their habitat. This applies to head and pubic lice. Clothes live in the folds of linen and clothing. Fleas can exist anywhere. In the apartment, basement, in the yard, moving freely and looking for new habitats and breeding places. They do not become attached to a warm-blooded animal, although they feed on its blood. Fleas move in jumps up to 0.5 meters high and long. Whereas lice crawl in the hair and do not leave their shelter. Only 10% of the total number of fleas in the house live in the fur of cats and dogs. The rest settle in more secluded corners.
Distribution routes
The ways in which lice and fleas spread are different. What is the difference? The difference in distribution suggests 2 options. In the first case, insects independently colonize the areoles for reproduction (this happens rarely). In the second option, relocation occurs as a result of physical contact.
For example, if parasites inhabit a non-residential or residential building, then their eggs are found almost everywhere. When they come into contact with their habitat, they adhere to the object and are transported with it to a new place. Along with the eggs there may be larvae and adults. The object can be a person’s clothing, personal belongings, a bag of garbage, or animal fur.
Important! Animals transmit blood-sucking insects to each other through tactile touch. This is rubbing with fur, exchanging leashes or collars. Parasites are transmitted from person to person according to the same principle. This is friction with clothing, use of other people's personal belongings, through bedding.
Important! Lice and fleas are good at hiding when they see an aggressor. With their luggage they can migrate to another city or even country. After reproduction, the population increases several times. The propagation process will repeat again. Chemical or natural control methods help reduce this population.
How to fight and prevent fleas?
If fleas have been detected on your pet, then you must urgently use a product designed to kill them. These can be various sprays, shampoos, collars. Particularly popular are flea drops on the withers, for example, Stronghold for fleas, sold in many pet stores. To prevent fleas from appearing on your pet again, you should put an anti-flea collar on it.
But this will not be enough, because there may be flea eggs in the room where the pet lives. After some time, the adults that hatch will be able to move onto the pet again. To prevent this from happening, you need to thoroughly clean the apartment. Treat areas where eggs accumulate with hot steam. These include the animal's bedding, upholstered furniture where he likes to be, and other favorite places of the pet.
Knowing some features of the life of insects, you can make the destruction of fleas in an apartment several times faster and more effective, as well as prevent their reappearance.
Routes of infection
The spread of parasites such as fleas and lice is always a sign of social crises. Large overcrowding and lack of basic hygiene skills lead to the widespread spread of these parasites among the population.
Another factor contributing to infection by these parasites is migration processes, especially from epizootic-prone areas.
Lice
Head louse is transmitted by contact with hair, by using hair care products of an infected person (comb, hairpins, etc.) and by wearing other people's hats.
Body fleas are spread by touching clothing, by wearing belongings of a sick person, and even by close bodily contact. This disease can be caught in public transport, crowded places and child care institutions.
Fleas
You can become infected with this parasite almost anywhere. Thanks to its jumping ability, a flea can jump on you on public transport, from the ground, or come on your pet after a walk. In urban environments, residents of the lower and upper floors are at particular risk. Fleas often love attics and basements; they have their own blood donors: birds and rats.
lice eaters
This type of ectoparasite has a slight resemblance to lice in appearance. They also constantly parasitize pets, unlike fleas, which use mammals only as a source of food. Lice eaters differ from lice in having a gnawing type mouthpart and a more massive head.
Insects have three pairs of legs, with which they are firmly fixed to the body of the animal. Color varies from yellowish to gray. It is not the blood of mammals that is used as a source of nutrition, but particles of skin and wool. The incubation period for eggs is 3 weeks. Each female is capable of laying up to 70 eggs at a time. Thus, the rate of reproduction of parasites is very high.
The presence of parasitic insects can be determined by some characteristic signs:
- itching and irritation appear;
- Bald areas are observed on the pet’s body;
- there are areas of scratching and inflammatory processes in the damaged skin;
- possible development of dermatitis.
How to choose drugs against ectoparasites
Regularly treating your pet with insecticidal preparations can help relieve the animal of unpleasant symptoms, maintain an impeccable appearance of the coat and protect it from the dangerous consequences of infection. Before purchasing products, you should consult with a specialist. The veterinarian will determine which insects caused the deterioration of the animal’s condition and select a drug. In especially severe cases, complex treatment may be required, including elimination of symptoms of concomitant diseases (dermatitis, eczema, allergic reactions, helminthiasis).
Among veterinary drugs, the following dosage forms are distinguished:
- shampoo.
“Lugovoi” is suitable for treating pet hair and killing parasites, and “4 with a tail” has a short-term repellent effect, that is, it scares away ectoparasites from cats and dogs; - collar
(“Leopard”). It is used for therapeutic and preventive purposes against lice, lice, fleas, and ixodid ticks. Provides protection for up to 4 months; - spray
(“Bars”, “Bars forte”). Products in this form are convenient for use and help protect the animal from insect attacks for up to 1 month; - drops on the withers
(“Bars”, “Bars forte”). Ideal for unruly dogs or aggressive cats. The product is applied to the withers area and provides protection for up to 1–2 months.
Before choosing an insecticidal or insectoacaricidal drug, you must consult a specialist, and before use, read the instructions.
What are the similarities?
The similarity between the pests in question is that lice and fleas consume the blood necessary to maintain life. Lack of access to nutrient fluid provokes the death of the insect colony.
Another similarity between lice and fleas can be seen in the consequences that occur in the carrier of the parasites. The bites leave red, itchy spots on the body. A large colony of adult individuals can cause an allergic reaction and intense intoxication of the body with corresponding symptoms. Scratching (often unconsciously) of bite sites increases the risk of secondary infection and the development of a purulent process in the tissues of the epidermis.
The third similarity is that bloodsuckers, in the absence of a constant source of food, are capable of falling into suspended animation. In this state, insects remain viable. Anabiosis lasts more than a year. If at the end of the specified period the insects do not encounter a food source, the parasites die.
Main similarities and differences
Having considered how fleas differ from lice, we can highlight the main parameters by which it will be easy to determine who exactly you are dealing with and what method of control to choose to destroy parasites. Let's start with the differences:
- a flea is larger than a louse - the body size of an adult can reach 4 mm;
- lice do not have racing legs, and therefore cannot jump, but they move very quickly, covering about 20 cm in 1 minute;
- fleas can multiply and develop in any secluded places, while lice are “attached” to the body of their owner;
- lice parasitize exclusively on humans; fleas, in the absence of a permanent provider, can feed on the blood of other warm-blooded animals;
- The color of chitin also differs - in the former it changes from gray to almost black as it becomes saturated, in the latter it always remains brown.
As for the similarities, first of all, this is nutrition - for these parasites the main and only source of saturation is blood. After bites, the affected areas begin to itch, leaving painful wounds that can easily become infected. At the same time, without food, both fleas and lice do not live long, and under unfavorable conditions they can fall into suspended animation, thus preserving vital energy.
On a note! By hibernating, bloodsuckers can exist for about a year or more!
With their appearance, fleas and lice cause considerable discomfort to their “breadwinner”, and therefore the fight against them must begin immediately. If you do not take steps to eliminate pests in time, they will very quickly increase the number of their colony, which will complicate the process of their destruction in the future.
Treatment options
To combat lice, pharmaceutical preparations are used. Treatment is also divided into 2 stages:
- Destruction of adults.
- Extermination of eggs and larvae.
The eggs are removed by hand or using a thick comb. Good remedies against lice and nits are special ointments, lotions, shampoos and sprays.
The principles of their work are as follows:
- These drugs have a detrimental effect on the nervous system of insects due to the presence of fenthion, malathion, permethrin and other substances in their composition. Their significant drawback is their ineffectiveness against nits and the mandatory re-treatment.
- Such products block the access of oxygen due to the formation of a film on the surface being treated. They contain components such as cyclomethicone and dimethicone. They effectively fight human lice at all stages of their development.
Expert opinion: Anna Pavlovna Stepanenko, a therapist with 15 years of experience. The use of insecticides to combat head lice in children is allowed only after they reach 2 years of age. In addition, such substances are contraindicated for pregnant and nursing mothers and allergy sufferers.
However, preparations that form a silicone film are suitable for everyone, regardless of age or predisposition to allergic reactions. However, it is recommended that children under two years of age have their hair cut to get rid of lice. This is due to the fact that it is inconvenient for fairly mobile young children to apply the composition to the surface of the head and comb out parasites.
The following drugs are most often used to eliminate head lice:
- Medifox. It contains permethrin. It comes in different forms. You can choose a gel applied to the hair and skin, or a concentrate that is diluted and used for a long time.
- Para Plus. It is a spray that affects all types of lice, regardless of their stage of development.
- Pedilin. Sold as an emulsion, gel or concentrate. It is quite effective due to the content of 2 types of insecticides.
- Lavinal. Available in the form of shampoo and aerosol.
- Nok. A safe drug that can be used even during pregnancy.
There are many more ways to combat these parasites. Your doctor will help you choose the right drug. In some cases, it is necessary to combine several types of medications.
To properly treat your head for lice, you need:
- Before use, test a small amount of the product to determine if you are allergic to it. The drug is applied to the wrist or the inside of the elbow several hours before the procedure.
- Thoroughly ventilate the room during and after the procedure.
- To avoid contact of the product with the skin of the face and eyes, use a special visor.
- Distribute the product evenly throughout the hair.
- After applying the product, cover your head with cellophane film to enhance the effect.
- Leave the product on your hair for as long as indicated in the instructions. If unpleasant sensations occur that are difficult to endure, you should wash off the product.
- After completing the procedure, rinse your hair with a vinegar solution. It dissolves the substance with which the female attaches eggs to her hair.
Dead larvae, eggs and adults are combed out of the hair using a thick comb. If this is not done, they can remain on the head for a long time.
Effective treatment
Products for the treatment of head lice should be easy to use, effective, safe for humans, and not cause resistance in insects. Paranit meets these criteria.
The active components of the product are dimethicone and mineral oil; they clog the respiratory openings of the parasite and nits, which leads to their death.
“Paranit” is not addictive to ectoparasites of lice and can be used repeatedly. The product is gentle on hair and scalp. The drug is available in the form of shampoo, lotion, and aerosol. For pregnant women and children over 1 year of age, a special form “Paranitis Sensitive” has been developed.
Pediculosis is not a problem if you have proven, reliable remedies at hand, such as Paranit. The drug will get rid of parasites, while maintaining hair and health.
Getting rid of blood-sucking insects
There are several methods to combat blood-sucking insects. These can be both folk remedies and medications. Let's present the most common and effective ones.
Methods of destruction using folk remedies
Nits cause as much inconvenience to humans as they do to any animal. This technique has a wide range of effects. Folk natural remedies can rid the entire house of “uninvited guests.” Plants such as wormwood, lavender, incense, garlic, as well as lemon and pine needles are suitable here. The strong smell emanating from them drives away fleas and lice for a long time. You can combine them with other methods to enhance the effect.
It is also recommended to use infusions and decoctions of wild rosemary, tansy, and hellebore. To do this, you need to put the shoots with leaves in a small saucepan (you can take several varieties), add water and wait for the water to boil. The decoction should be cooled and used for its intended purpose. If you add grated tar and laundry soap to it, you can rinse bed linen and bedspreads in it for disinfection purposes.
Drug treatment
When affected by lice, fleas, and other blood-sucking parasites, itching, burning, pediculosis, and dermatitis (from frequent scratching) may appear. Such ailments are common not only to people (including children), but also to animals (especially those with fur). For insect bites, lindane, pyrethrium, and allethrin are used to treat lesions. Sometimes doctors even use mercury ointment or Vaseline. The list also includes:
- Creams or gels with menthol.
- Tar or laundry soap.
- Nittifor.
- Foxylon.
- Pedilin or Nyuda.
- Paranit.
- Para Plus.
- Butadione, Levamisole, Albendazole (tablets).
This is only a small part of the medications used to combat parasites. Distinctive features of these funds are the pricing policy, the area of influence, and the shelf life of the effect. There are many products on the market to choose from.
Disinsection of premises
To combat blood-sucking insects, as well as for preventive purposes, premises are disinfested. It does not matter whether it is residential, industrial or basement. For such purposes, special chemicals are used. They are sprayed over a specific distance using a spray gun or installation. To do this, it is recommended to wear protective clothing, a mask and gloves. There is a risk of poisoning. There are several products for this purpose.
Attention! Chemicals should be used strictly in accordance with the directions indicated on the packaging.
Let's comment on them:
- The first stage will require wet cleaning using vinegar, bleach, ammonia or chlorine.
- Then use Dichlorvos, Karbofos, Tetrix, Raptor or Raid, Executioner, Clean House, Get (do not ignore corners, cracks, holes).
- After treatment, it is recommended to ventilate the room, wipe the walls and floor with a soda solution.
Important! This is the basic principle of action when disinfesting any premises in case of suspicion of the existence of parasites.