Sometimes, even after flea treatment, the cat continues to itch. Itching can be caused by drugs of dubious quality, allergic reactions, or scratching on the body. Only a veterinarian can accurately determine the causes and prescribe proper treatment.
Let's find out what additional symptoms will help in making a diagnosis and how to help the cat before the doctor arrives.
Prevention
Prevention of itching in a cat should be based on preventing diseases that can cause itching in a cat.
Prevention of worms in cats. In order for your cat to be healthy and not be able to infect your children, who are constantly hanging around a common pet, it is necessary to promptly prevent the appearance of worms in the cat. In order to prevent helminthiases in cats, you need to fight:
With fleas. Raw fish and meat should be excluded from your cat's diet. Avoid contact of your cat with stray animals. Disinfect your cat's litter box periodically. Store your clothes and shoes in closed cabinets and cabinets. After contact with a cat, especially children, they need to wash their hands thoroughly with soap. Carry out deworming regularly.
Prevention of dermatomycosis. After each walk with your cat, you need to examine its skin for injuries and abrasions. If they are detected, treat with an alcohol solution of iodine, aniline dyes, chlorhexidine, meramistine. It is necessary to carefully monitor the feeding of your pet, and it is necessary to gradually switch to another type of food. It is advisable to purchase feed from trusted and reliable manufacturers. Regularly treat your cat for worms and ectoparasites. Hide household chemicals in a safer place from the cat. In order to prevent infectious dermatitis, it is necessary to carry out appropriate vaccination with an antifungal vaccine - Microderm, Vakderm F, Polivac.
Prevention of scabies mites in cats should be based on the formation of a strong immune system in the cat. Animal owners must organize proper feeding of the animal and normal living conditions. As a preventive measure, immunoparasitan, which is administered to the cat every 3-6 months, has proven itself well. This drug activates the cat's defense mechanisms and protects it from re-infection with ticks. Periodically carries out preventive treatments against fleas and ticks.
In order to prevent stress in a cat, owners should treat it kindly, not punish it for minor pranks, avoid stressful situations during walks, keeping it on a leash away from stray dogs and cats.
Infection with scabies mites
Demodicosis in cats occurs in three forms.
Scaly form.
This form is the mildest form of demodicosis and is most often found in young cats (up to 2 years old). Symptomatically, this form is manifested by itching, focal lesions on the skin, the number of focal zones does not exceed five, redness, dry scales appear on the cat’s ears, eyelids and neck. However, there are no signs of skin lesions on the cat’s paws and back.
Generalized form.
In this form, the disease occurs with massive damage to the skin and is accompanied by the formation of pustules, bleeding wounds, the affected skin is severely flaky, the cat's owners note constant itching, erythema, scratching, and scabs appear. At the location of the tick itself, upon careful examination, we note small elevations, with a crater in the middle, from which, when pressed, a white mass emerges. In cats, lesions are most often observed in the head, neck and muzzle, in the nose, eyelids, and tips of the ears. At the same time, damage to the paws and back is noted. The coat is dull, sticky, seemingly sprinkled with dirty flour, with receding patches. This form of the disease develops very quickly.
Juvenile demodicosis.
In terms of its clinical manifestation, this form of demodicosis is practically no different from the generalized form. The only difference is that juvenile demodicosis in cats is a genetic disease (the kitten is infected in the womb). This form of demodicosis is the most severe for a cat, due to the fact that it causes consistent damage to the cat’s immune system, as well as the entire body.
Additional information about the disease is presented in the article -.
Notoedrosis (pruritic scabies)
– a chronic invasive disease of cats, clinically accompanied by dermatitis in the scalp, itching, scratching and hair loss.
The source of infection is animals with notoedrosis, especially stray cats, dogs, rabbits, as well as rats and mice, which cats are especially fond of. Transmission of the infestation pathogen to a cat occurs through direct contact with an infected animal or through infested care items.
Penetrating into the thickness of the epidermis, itching irritates the nerve endings and injures the basement membrane of the epidermis, as a result of which the papillary and deeper layers of the skin are involved in the inflammatory process. All this causes disturbances in the central nervous, cardiovascular and reticuloendothelial systems. A sick animal scratches the itchy areas, the skin thickens, becomes bald, loses its elasticity, skin respiration is impaired, oxygen deficiency increases, and heat transfer increases.
Clinical picture
. Notoedrosis lesions in cats initially appear on the scalp (on the bridge of the nose, brow ridges, at the base of the ears) in the form of papules and vesicles, which then become crusted. A sick cat develops itching, which is especially intensified in the evening. On clinical examination of such cats, the skin appears dry, thickened, crusty, and dermatitis and hair loss are noted. Such a cat suffers, becomes weak and, upon external examination, looks unhappy. If untreated, the disease process spreads from the head to the back, shoulder blades, paws of the hind and forelimbs. The generalized form of notohedrosis in cats usually develops after 2-3 months. The cat loses weight, the skin becomes folded and becomes covered with dry, gray crusts.
At the beginning of the disease, the sick animal experiences mild itching, the sick cat begins to worry, shakes its head, tries to comb the mite-affected ear with the claws of its paws, or scratch the sore ear on various objects. During a clinical examination of such a sick cat, the veterinarian detects inflammation of the ear canal; serous and sometimes purulent and ichorous exudate is released from the ear canal, which has a sharp putrefactive odor. Sometimes the exudate completely clogs the ear canal and this leads to hearing loss. The exudate released from the ear canal glues the hair of the lower edge of the auricle and, when dried, forms scabs and crusts of gray or light brown color. Sometimes if you lightly press on the base of the ear, you can hear a characteristic splashing sound. When the eardrum is perforated, the cat loses its appetite, its body temperature rises, we notice bow-headedness (the head is turned towards the affected ear), and nervous phenomena appear, including convulsions.
Additional information about the disease can be found in our article -.
Reasons for the development of poisoning
Flea drops are applied to the animal's withers. This place was not chosen by scientists by chance. The pet cannot reach it on its own and lick off the insect repellent.
Below we have collected the main reasons why flea drop poisoning can develop in pets.
- Failure by the owner to comply with the rules specified in the instructions for the drug. You can find a large number of different flea products on sale. They all differ in application rules and action. Before using them, you must read the instructions carefully.
- Bathing the animal during the first few days after treatment. It is this reason that is leading in the development of poisoning of dogs with drops from fleas and ticks. Due to frequent walks outside, dogs are bathed much more often than cats.
- Purchasing counterfeit or expired funds. You need to buy drugs only from official and licensed outlets, veterinary pharmacies or clinics.
- Use of drops in small, weakened or sick animals.
- Applying drops not to the withers, but to another area of the body. In this case, the animal is poisoned after licking the drug. This reason is more typical for cats, since they wash and clean their fur more thoroughly.
- Incorrect selection of the required dosage of drops. The drug is available in different dosages, which depend on the weight of the animal.
- Treatment of kittens and puppies that are breastfed. At the same time, their mother suffers, as she washes them and eats the drug.
- Individual intolerance to the components of the drug and allergies to it. The animal may develop urticaria and angioedema.
Medicines for worms
Here are some medicines for worms :
- " profender ". Sold in the form of drops. Depending on the size of the cat, the cost of the medicine varies. The packaging includes two pipettes and caps. The drug is applied in the form of drops to the withers. After some time, it is absorbed by the skin. Depending on the age of the cat, the dosage also changes. The first use is possible after two months, with a weight gain of 0.5 kilograms. The medicine has no side effects, so it can be used against worms even in a nursing cat;
- " stronghold ". The drug has a basic component – selamectin. It is very effective in the fight against worms. Of all the medicines, it is the most used because it has many positive aspects. After instillation, after 30 minutes you can play with the cat. This substance is very moisture resistant. Two hours after instillation, the cat can be washed in water, and the effect of the drops will remain the same. After 6 weeks, drops can be used in kittens, as well as in cats during pregnancy. The effect of the drug begins on the second day after use. The worms disappear and do not appear for more than a month. This deworming remedy is in great demand;
- " prazicide complex ". Use is allowed for kittens from two months. It should not be used on weakened animals or on cats nursing children. The kit includes only one pipette, so if the animal is large, then one package will not be enough. The remedy is harmless and is applicable for many diseases, including worms. It can be used monthly, and as a means of prevention;
- drops " Bars sport - he ". This medicine is based on substances such as praziquantel and ivermectin. Quickly absorbed into the blood, it moves throughout the body. Already at the age of two months it can be used in cats. A very effective remedy for worms.
We recommend reading: How to Tell if a Large Breed Dog Is About to Give Birth
Preventing Itchy Ears
Itching is caused by various factors, so following a number of prevention rules will help protect your cat from scratching:
- Poison worms in a timely manner. This will also help protect children who constantly play with animals. You should not give your cat raw foods: fish, meat.
- After each walk, inspect the animal for abrasions. Treat detected wounds with iodine or other disinfectants.
- To avoid infection with parasites, the cat should not be allowed to come into contact with other animals.
- Disinfect the cat litter box regularly.
- The transition to a new food should be carried out gradually.
- Do not punish your cat for minor offenses: this will prevent stress.
The very first rule that is strictly followed for any cat is keeping its ears clean. Hygienic procedures must be carried out at least once a week. Since proud, mustachioed individuals really do not like such manipulations with their ears, your pet should be accustomed to this from a young age, that is, from a very early age. Then it will be much easier to clean, examine, and treat your purring pet.
It is also necessary to show it to the doctor if there is any change in the health status of your pet, so that the treatment quickly brings results, and its absence does not cause serious consequences.
Signs of ear disease in a cat
Diseases of the hearing aid have very similar symptoms at the initial stage, by which it is quite easy to determine that a cat’s ear hurts or is very itchy and requires qualified help:
- head tilted to one side;
- the cat rubs and scratches its ears with its paw, sometimes tearing the skin around until it bleeds;
- the pet does not allow the owner to even touch the ear;
- the ears turn red inside, strange dirt and plaque forms in them, which emits an unpleasant odor;
- Sometimes the ear makes a sound similar to squelching when pressed.
In addition to these characteristic signs, if the disease is advanced, the cat’s temperature begins to rise, the pet loses its appetite, and can become extremely restless, even aggressive.
Causes of itching in cats
A cat chews itself and scratches itself when its skin becomes itchy.
There are several reasons that cause this condition:
- lichen;
- helminthiases;
- endocrine system problems;
- failure in the hormonal system;
- influence of stressful situations;
- the occurrence of skin diseases (fungus);
- there are insects in the fur that feed on blood;
- allergic reaction.
First, the animal is checked for fleas. This is the main reason why your pet starts to itch a lot. Flea bite marks persist for about 1.5 months, causing itching. If there are no insects in the animal's fur, it must be shown to a veterinarian.
Lice, lice, mites, flea dermatitis and other parasites that cause itching
Infection with ectoparasites occurs through outdoor shoes. The skin becomes inflamed if there are traces of scratches or small wounds on it.
If they are not treated in time, the animal will scratch them. Suppuration will appear, which will lead to baldness or sepsis. Sulfur ointment or powder is used to treat wounds. The drug in powder form called Yuglone is the most effective and is recommended for use by veterinarians.
Infection with helminths as a cause of itching
If the animal is infected with worms, then:
- the pet itches and licks the anus area because it feels severe discomfort in this place;
- appetite deteriorates, stool changes, changes occur in the digestive tract;
- there are noticeable changes in the cat’s behavior (he is too excited or in an apathetic state);
- the skin is dry and flaky, and the coat becomes dull.
Hormonal and endocrine disorders
- Improper functioning of the thyroid gland. At the same time, the fur becomes tangled, itching and dandruff appear. In some cases, cats go bald.
- Cushing's syndrome. Due to a malfunction of the adrenal cortex, the skin loses its elasticity and becomes thinner. Comedones appear on the back and sides of the animal.
- Diabetes. The disease manifests itself in the form of local baldness, dry skin, seborrhea, and dull hair.
Ringworm, fungi and other types of skin mycoses
Similar symptoms occur when an animal's skin and coat become infected with fungal and yeast diseases. Dermatomycosis does not pose a danger to people; it is treated with antifungal drugs.
If an animal becomes ill with ringworm (trichophytia), then treatment begins immediately, since this disease can also affect humans. In the affected areas, hair falls out and bald patches appear in the form of circles. Therefore, areas that the animal scratches heavily should be carefully inspected.
Infectious skin diseases
Often itching and irritation are caused by infectious diseases:
- Cheyletiellosis (pityriasis scabies) occurs due to infection by a separate group of mites of the genus Cheyletiella. Insects look like small white dots moving around. You can find them along the back.
- Pyodermatitis is caused by bacteria. They infect not only the surface of the skin, but also penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis.
- Notoedrosis is a contagious infectious disease that occurs due to ticks. Itchy mange is transmitted through contact with a cat.
- Demodectic mange is a rare disease spread by ticks.
Ear parasites
Due to improper care, parasites appear in the animal’s ears. Ear mites (otodectes) infect the ear canal and cause severe itching.
An unpleasant odor emanates from the ears, which is accompanied by dark-colored discharge. In the affected areas, the skin becomes red, the animal constantly scratches its ears and shakes its head. Huge wounds appear behind the ears due to constant scratching.
Body temperature rises. The progression of the disease can lead to severe inflammation of the outer ear and parotid space. In such a situation, the cat tilts its head to the side and constantly walks in this position.
Allergy
Your cat may be hypersensitive to the components of the new food. With food allergies, cats typically scratch their faces, scratch their ears, and violently lick and bite their limbs. In this case, the cat is prescribed a diagnostic diet in order to identify and eliminate the “harmful” food component.
So, an allergy can arise as a result of a flea bite (see where fleas come from in domestic cats), and cats, as a rule, begin to scratch their hind limbs, stomach, tail and back.
A cat may also be hypersensitive to the bites of other insects. In this case, the cat scratches and intensively scratches precisely those areas of the body that have been bitten by insects such as wasps, mosquitoes, bees, ants, etc.
A fairly rare type of allergy is a contact allergy. In this case, the pet's itching occurs due to a reaction to an irritant, which usually affects the chest and abdomen area. If scabies is caused by a reaction to environmental substances, then you need to give the cat allergy tests.
In recent years, allergies have increasingly begun to affect animals, including cats. When an allergy occurs, the cat's owners note the following symptoms: hair loss occurs (cat hair loss), dandruff appears, an unpleasant odor emanates from the cat's hair and from the cat's mouth, problems with the ears appear (ear diseases in the cat), the cat itches, sometimes the cat he chews his paws, rubs his nose, licks himself vigorously, and allergic dermatitis appears (dermatitis in cats).
We suggest you read: What does a soldier bug look like?
Causes of allergies in cats:
- dust, mold, pollen;
- food (food allergies in animals);
- flea medications;
- medical supplies;
- hygiene products;
- infection;
- insect bites;
- reaction after vaccination;
- low-quality material (toys, bedding, drinking bowl);
- breed tendency.
Only a veterinarian can correctly identify allergies and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Often, a flea collar can cause contact dermatitis, which causes hair loss, itching, and the cat scratching the area around the neck.
When introducing a new product to the diet or skin and coat care products, cat owners must monitor their pet's behavior. Food allergies manifest as inflammation around the head, anus, and ears. Vomiting and diarrhea occur. Exposure to allergens can cause angioedema and lead to the death of the animal.
Causes of itchy skin in cats and kittens
Absolutely all cat owners have had to watch their pet scratch or lick itself. If this happens infrequently and irregularly or is just a way of daily grooming, no one even pays attention to it. But if the animal scratches, scratches, licks itself constantly, bald patches appear on the fur, and the skin becomes red and inflamed, the owner begins to worry. And not by chance. After all, persistent itching in cats is not a trifle. It can be a symptom of many diseases and will disappear only if its root cause is found and eliminated.
Let's find out why a cat might itch? It turns out that this does not happen by accident.
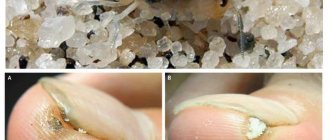
Quite often, fleas are the cause of itchy skin in cats, especially if the animal has an increased sensitivity to parasite bites. In some cats, an allergic reaction can develop even after a single bite, and skin itching can become the main symptom of flea dermatitis. Detecting the presence of parasites is not difficult.
Atopic dermatitis
One of the most common causes of itchy skin in cats is atopic dermatitis. This disease is an increased sensitivity to certain environmental substances. May appear seasonally. For diagnosis, a blood test for antibodies and a skin allergy test are performed.
Food allergies
Food allergies in cats are less common than other types of allergies, but the main symptom remains the same - itchy skin. The disease develops due to an inadequate reaction of the skin to proteins and protein compounds in food. It is quite difficult to identify food allergies; the most common method is an elimination diet.
Treatment. A diet that excludes foods that cause an allergic reaction from the cat’s diet.
Parasitic diseases
Parasitic mites (ear mite otodectes, cutaneous cheyletella and scabies notoedres) can also cause itching.
Otodectosis. A contagious disease characterized by severe ear itching and the presence of black crumbly plaque or serous exudate with an unpleasant odor in the auricle.
Notoedrosis (pruritic scabies).
The disease is manifested by severe itching and the presence of papules on the surface of the cat's head and neck. Over time, the affected areas become covered with a crust that spreads to other parts of the body.
Cheyletiellosis
Characterized by severe flaking of the skin (dandruff), sometimes in the form of papules covered with scales. The animal is experiencing severe itching.
Fungal or bacterial skin infection
The main cause of bacterial skin infection in cats is staphylococcus. Characteristic symptoms: severe itching, rash, skin inflammation, hair loss, pustules.
Yeast fungi, which are part of the usual microflora, under unfavorable conditions begin to multiply rapidly and cause skin problems, including itching.
Serious health problems
Itchy skin can occur due to disruption of the endocrine system, the presence of autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosis, eosinophilic granuloma, etc.).
Symptoms of allergic dermatitis
The presence of ectoparasites is determined by examining the cat, during which fleas themselves or their remains are found on the fur and skin. If it was not possible to visually detect parasites, you can conduct an experiment.
© shutterstock
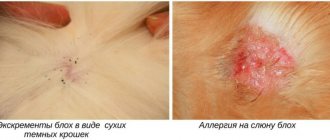
A paper napkin must be moistened with water and rub the skin in the affected area; if pink, red or brown stains appear, this indicates the presence of flea excrement.
The cause of an allergic reaction in a pet is not the fact of the presence of ectoparasites, but a specific protein that enters with saliva during a bite. It is to a foreign protein that the cat’s immune system responds, that is, an allergy.
Fleas do not live on a pet all the time; they drink blood, but prefer to reproduce in calm conditions. Therefore, fleas most often live in the bedding, the rug on which the cat sleeps. These areas must be treated first when ectoparasites are detected in an animal.
The main manifestations of this pathological process include in cats:
- severe itching – the pet constantly itches or bites the fur with its teeth;
- hair loss - especially observed in the neck, abdomen, croup and tail;
- formation of papules - a tubercle forms at the site of the bite, the skin is inflamed and itchy;
- changes in skin and coat pigmentation;
- redness, swelling and inflammation of the skin;
- coughing, sneezing, discharge from the eyes and nose may appear;
- the animal is in a state of excitement, reacts painfully to touch, and aggression may be noted.
© shutterstock
When severely scratching itchy areas of the skin, it is injured, as a result of which pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the body and can cause a secondary infection against the background of flea allergic dermatitis. Until the root cause, that is, fleas, is eliminated, there is no point in treating secondary pathologies, since the therapy will be ineffective or short-term relief will be noted.
The cat is itching
The article discusses the main issues related to scratching pets, and also gives an idea of how veterinarians can solve such a problem, since only they can issue a prescription in such a case.
Common causes of itching in cats are parasites, allergies, fungal or bacterial diseases. Only a veterinarian-dermatologist can recognize the actual cause and help eliminate it.
Before visiting the doctor, your pet can be treated with parasite drops such as Advantix, Stronghold or Frontline. In cases where you are sure that the itching is not associated with lichen, you can also bathe the cat using medicated shampoo.
Why does a cat itch and lick its fur when hunting?
A cat whose desire to mate awakens may experience itching due to increased hormone production. It has been noticed that when an animal licks its fur, it instinctively calms down and gains mental balance.
If your cat itches, scabs appear and hair falls out, what to do?
The appearance of scabs and bald patches on the body of cats is most often caused by fleas and ticks. If this is the case, then it is enough to treat the animal with a high-quality antiparasitic agent.
It is worse if the cat's skin and hair follicles are infected by bacteria or fungus, or when the cause of the itching is associated with an allergic reaction. In such cases, only a doctor can prescribe treatment.
If a cat scratches its neck, back, withers, skin, cheeks until it bleeds, what to treat?
If a cat scratches its neck, back, withers, skin, cheeks until it bleeds, this is a serious reason to contact a veterinary clinic. But even an experienced veterinarian is not always able to immediately, without laboratory tests, diagnose a skin disease caused by itching. Despite the similarity of symptoms, treatment for itching can be completely different and is selected purely individually.
If a cat scratches its eye, what to do and treat?
One of the effective folk remedies to prevent a cat from scratching its eyes is to wash the eyes with a warm chamomile decoction. However, it will be better if your mustachioed pet is examined by a veterinarian-ophthalmologist.
Cats, cats and kittens have itchy teeth, what to do at home
For kittens and older animals whose teeth itch, it is advisable to purchase special chewing toys. With their help, cats will be able to satisfy their natural desire to chew, as well as clean their teeth of plaque and tartar.
Why does a cat itch with a flea collar?
In some animals, the flea collar itself may cause an allergic reaction. In such cases, anti-flea drops and shampoos can help control insects.
Cat itches against a person, carpet, corners, floor
There are perioral glands on the cat's head. When an animal rubs against a person, a carpet, corners or the floor, the secretion produced by the glands remains on them, thus the cat marks the territory, and at the same time its owner.
The cat itches at the base of its tail and rushes around the apartment
Possible causes of itching at the base of the tail and hyperactivity shown by the animal may be flea bites and a peculiar reaction to estrus.
If the kitten scratches its belly
The most likely reason for a kitten scratching its belly is an allergy.
Itching and irritation of the skin can occur not only from food that the kitten’s body does not accept, but also from substances from the external environment, as well as from flea saliva.
Why does a cat itch from flea drops and other causes of itching?
The most common reason why a cat may start to itch is because it has fleas. She begins to behave restlessly, scratching her neck and near her ears. Every caring owner wants to establish the cause of his cat's anxiety, because in addition to small insects, itching can be caused by allergies, otitis media, fungus, and parasites. We found small black dots, there is no doubt - these are fleas. Anti-flea drops are considered one of the popular remedies. But sometimes the cat itches after flea drops. The owner asks a lot of questions: the drops didn’t help, she has allergies, is it worth purchasing additional products, fleas are not visible, but the pet still scratches its neck, why? There are a lot of questions, it is necessary to consider the most common causes of itching in cats.
Possible causes of itching
Often, a domestic cat often washes and scratches its neck behind the ears, its muzzle, tears the skin on its head and scratches itself so that its hair falls out or sores appear until it bleeds and scabs and scabs, and to find out why this happens and how to treat it, first The first thing you need to do is check whether he has fleas or not. If blood-sucking insects or their eggs are detected, you will need to immediately treat the animal’s fur with special preparations.
Even after the parasites are completely eliminated, the body still contains the substance that entered the bloodstream during the bite. Its effect can last from 1 to 2 months, causing the cat to want to scratch the irritated area.
If no fleas were found during examination of the animal, then the cause of the itching may be as follows:
- skin diseases;
- hormonal disbalance;
- allergic reaction;
- endocrine gland disorder;
- lichen;
- the presence of parasitic worms (helminths).
Cause of itching after flea drops
After fleas appear, the cat begins to scratch the body vigorously and injure the thin layer of skin with its claws. There are several reasons why, even after applying flea drops, the cat itches all day long. Among the most common are:
- Penetration of infection. After a pet scratches and injures the skin, pathogenic bacteria and infections can enter it. As a result, the wound begins to fester, become inflamed and itch severely. Therefore, after applying pain therapy, the cat continues to scratch its body. In this case, the owner is recommended to carefully examine the animal and identify areas of injury. To treat wounds, local anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which are prescribed by a veterinarian; in case of severe infection, it is necessary to start giving the cat a course of antibiotics. In the case of a festering or bleeding wound, it is necessary to treat it with disinfectants and cover it with a sterile bandage until the wound is completely healed;
- Stressful state. Many cats, especially small kittens, experience severe stress after their body is damaged by multiple insects that bite painfully and torment day and night. Therefore, after treatment, the kittens continue to itch and make sudden movements at the slightest fright. The condition after therapy may last for several days. At this moment, you should pay more attention to the kitten, pet it and calm it down. If necessary, you can relieve your animal of stress with the help of sedatives, which are sold in veterinary pharmacies without a veterinarian’s prescription;
- Allergic reaction to the active substance. Quite often, after using flea drops, the cat itches. If a careful examination of the body does not reveal small fleas, then the cause is most likely an allergic reaction. Skin itching appears due to the active substance of the drug. In this case, it is necessary to immediately wash the pet and rid its skin of the irritant. If it is necessary to continue flea therapy, you should change the medicine to a more suitable one;
- The characteristic odor emanating from the medicine. Cats are very sensitive to foreign odors. The cat family is very clean and spends a lot of time keeping their fur clean. Quite often, after anti-flea therapy, pets begin to itch in order to get rid of the smell. To get rid of an irritated pet, you need to wash the animal and leave it alone.
If your cat itches a lot after receiving flea drops, then perhaps the cause is the increased activity of parasites on the body. Insects begin to actively run around the cat’s body in order to find a secluded place from the effects of the medications.
Associated symptoms
Along with the main symptom - itching, other characteristic signs of using flea drops may be observed. Among the most common are:
- sneezing;
- cough;
- paw twitching;
- increased activity;
- irritability;
- scratching the body until it bleeds.
Negative symptoms in most cases are associated with an allergic reaction and increased flea activity. In the first case, to alleviate the animal’s condition, it is recommended to give it antihistamines. Diphenhydramine is considered the most effective. Depending on the dosage, you need to break off half or a quarter of the tablet. Then crush it into powder, dilute it in a teaspoon with water and pour it into your pet’s mouth. As a rule, the cat will calm down and go to sleep. After waking up, the symptoms will disappear. If necessary, you can repeat the reception.
In the second case, if the animal begins to actively scratch its body after drops from parasites, then the pet should be given sedatives, for example a little valerian, so that the cat stops injuring the skin. After some time, when the insects leave the body, the symptoms will disappear. To prevent the disease, you should not wait for your pet to be infected by insects, but carry out therapy against parasites on the body in advance.