What's happened
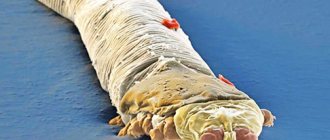
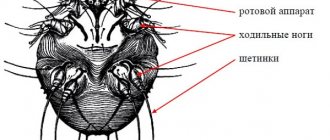
Demodicosis is a skin pathology that occurs due to the actions of the demodex mite, which parasitizes the upper layers of the epidermis. This microorganism is present on the heads of approximately 97% of the world's population. What a subcutaneous hair mite looks like can only be seen from pictures with multiple magnifications. Since the microorganism reaches only 0.06 mm in width and 0.3 mm in length.
There are 2 types of demodex:
- Short. The mite most often affects the ducts of the sebaceous glands.
- Long. The mite parasitizes the hair follicles on the head.
Attention! This microorganism performs an important function: it removes dead skin and inhibits the activity of a number of bacteria. But when favorable conditions arise, Demodex begins to multiply, resulting in symptoms of the disease.
Causes
The main reason for the development of demodicosis is considered to be weakened local immunity. also occurs against the background of:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- severe stress;
- metabolic disorders;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- frequent visits to baths, saunas, solariums;
- hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- skin diseases.
The risk group includes people with endocrine pathologies, as well as people who regularly consume alcoholic beverages.
Causes, routes of infection and provoking factors
The study of demodicosis has shown that in addition to a decrease in immune defense, there are other reasons that cause this pathology. One of the important points is the physiological state of human skin, namely, how correctly the sebaceous glands function, what is the composition of their secretions, as well as concomitant skin diseases and hormonal imbalances.
External influences on the hair and scalp also often lead to the development of the disease. Women are at risk of demodicosis because they constantly use various chemical reagents, as well as other aggressive substances found in cosmetic products for hair and skin.
These masks, gels, shampoos and paints disrupt the functioning of the sebaceous glands, dry the skin, which provokes a decrease in local immunity, and hence the development of pathology.
Immunity can protect a person from the occurrence of this disease, but only if it is strong enough. In this case, after the tick releases metabolic products, defense mechanisms are triggered and toxins are neutralized. When the body is weakened, they are unable to eliminate this problem; all the signs of demodicosis appear.
Reasons for decreased immunity:
- Imbalance of hormones in the body.
- Incorrect use of cosmetics, use of low-quality cosmetics products, exceeding the permissible standards in applying them to the hair.
- Long-term therapy with antibacterial drugs and hormonal drugs.
- Poor diet, excessive consumption of sweets, foods with large amounts of preservatives, as well as low-grade dyes.
- Drinking large amounts of drinks containing caffeine.
- Bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Excessive consumption of salty and spicy foods, as well as chips and fast food.
- Abuse of thermal procedures in saunas, baths, solariums, frequent hot baths. In warm weather, ticks begin active life.
We must not forget about the possibility of infection with a tick from another person, therefore the use of other people's hygiene items, combs, towels and other things is contraindicated. After shaking hands with people or being in public places, you must wash your hands. A sick person constantly scratches his head, and pathogens remain on his fingers, which are easily transmitted through shaking hands.
People diagnosed with demodicosis of the head and other parts of the body are not considered infectious and do not need to be isolated, since every person has the parasites that cause the pathology. It is important to control the activity of these mites through the above measures.
In addition to the described human-dependent reasons for tick activation, there are also pathological reasons:
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- AIDS and HIV infection;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- trichomoniasis;
- depression and other emotional disorders;
- metabolic disorder;
- frequent colds and viral diseases;
- infectious and other chronic diseases.
In addition, children can be included in the risk group for such a disease, since their immune system is not yet sufficiently developed. Elderly people are also more susceptible to demodicosis than others, since their bodies are weakened due to age-related changes.
Symptoms
The first signs indicating the onset of the development of pathology appear in the so-called prodromal period. At this stage, demodicosis manifests itself in the form of hot flashes, which are characterized by the following symptoms:
- feeling of heat;
- redness of the skin (due to dilation of blood vessels);
- red spots have clear boundaries.
The appearance of hot flashes is caused by the influence of provoking factors (alcohol, smoking, etc.). The occurrence of such symptoms indicates that a person has a predisposition to demodicosis.
The following symptoms are observed with demodicosis:
- intense itching in the affected area;
- dandruff;
- swelling of the skin;
- intense hair loss;
- unpleasant odor from the head.
Important! Without treatment, the affected area increases. This can lead to facial skin infection.
Is demodicosis of the head completely curable?
Complete cure of demodicosis is possible only with complex treatment. It should be understood that eliminating the causes that led to the proliferation of the parasite will not lead to the destruction of existing individuals - they must be combated with antiparasitic agents.
For your information. According to statistics, 10% of people who have overcome demodicosis become ill with it again. This can be caused by a relapse of existing chronic diseases, poor diet, alcohol abuse and smoking. In addition, re-infection is possible.
Stages of development
The nature of the clinical picture in this disease is determined by the stage of development of the disease. After the mite colony is reactivated, the pathology goes through 3 stages:
- Erythematous.
- Papular-pustular.
- Hypertrophic.
At the initial stage, the skin in the problem area begins to turn red. But unlike the prodromal period, the symptom occurs for no apparent reason and does not disappear for several days.
At the second stage , papules appear, and in the case of a secondary infection, pustules or ulcers appear.
The hypertrophic stage of pathology development is characterized by thickening of the skin and the appearance of growths. Such disorders are diagnosed when the facial part of the head is affected.
Diagnostics
Demodicosis is characterized by clinical manifestations that occur with other pathologies. Therefore, before starting treatment, it is important to differentiate these diseases. The final diagnosis is made based on the results of the following examination methods:
- Scraping from the problem area. Used to assess the severity of the lesion.
- Analysis of secretory fluid. Allows you to detect the presence of parasites in the scalp.
- Superficial biopsy. Using this method, not only the presence of parasites is determined, but also the affected area. Material for biopsy is taken from different parts of the head.
- Hair analysis. It is carried out to detect parasites in the follicles.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Symptoms of demodicosis on the head appear as soon as the hair mite begins to actively reproduce. At this time, the subcutaneous parasite releases many toxins into the body that cause allergies. Redness and severe peeling of the skin, itching and acne along the hairline are all the result of the activity of a subcutaneous parasite. With demodicosis of the scalp, the hair quickly becomes dirty. During this period, the sebaceous glands, the ducts of which open into the hair follicles, intensively produce sebum.
Symptoms of demodicosis of the head appear gradually, so a person always has a chance to see a doctor who will help start proper treatment in a timely manner.
Often, due to such signs of demodicosis as itching and flaking of the skin on the scalp, a person simply begins to treat dandruff with the help of special shampoos. Such treatment does not give positive results, and sometimes even worsens the course of the disease. Because of this, there is a need to urgently consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis.
Often, the pathology in question can occur in representatives of the fair half of humanity due to the use of cosmetics and hair dyes that contain aggressive chemicals.
Diagnostic methods that help detect subcutaneous mites on a person’s head are:
- Analysis of scalp scrapings allows you to identify areas affected by subcutaneous mites, count the number of adult mites, the eggs they lay and the number of larvae.
- Study of the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the head - analysis of the sebum secreted by the sebaceous glands gives an idea of the number of mites living deep under the skin of the scalp.
- Superficial biopsy of the scalp - a histological preparation is made from a fragment of skin, then the behavior of the demodex mite is studied using a special microscope.
- Follicle analysis - a bulb removed from the hair follicle is examined under a microscope for the presence of demodex mites.
Repeated testing can increase the reliability of the results of any analysis.
Treatment
Treatment of demodicosis is carried out using local and systemic drugs. In the treatment of pathology the following are used:
- Sulfuric ointment. It burns individual areas of the skin, simultaneously destroying parasites. The product should be applied to the problem area 3 times a day.
- Trichopolum. Acts directly on tick DNA. Trichopolum is approved for use by pregnant women. The drug is available in tablet form.
- Botox injections. The substance injected under the skin blocks the functioning of individual glands, as a result of which the parasites do not receive nutrients and die.
- Clotrimazole, Tetracycline. Suppress the reproduction of parasite colonies, simultaneously destroying fungal microflora.
- Streptocide. Recommended for the treatment of demodicosis in children. The Streptocide tablet must first be crushed and applied to problem areas.
In addition to the above drugs, the following are additionally used in the treatment of pathology: ichthyol ointment, Amit, Benzyl benzoate.
Attention! In case of secondary infection, treatment should be supplemented with creams based on tetracycline antibiotics.
Treatment of demodicosis of the scalp
A patient can only find out how to get rid of the symptoms of demodicosis on the head by visiting a dermatologist.
Demodex is activated against the background of other diseases, so patients often have to go to see other specialized specialists - a psychologist, a gastroenterologist. Taking into account the results of the examinations, a patient with demodicosis is prescribed a comprehensive course of therapy. Its goal is to eliminate the causes and signs of activity of the subcutaneous demodex mite and strengthen the body's immune defense.
Medicines for ticks in ointments and tablets
Hair demodicosis is treated with external and oral medications:
- Sulfur ointment 10%. Apply to clean, dry scalp in the morning and evening for a week (can be 3 times a day). The scalp is very sensitive, so sulfur ointment is diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio. Wash off after 3-4 hours (earlier if severe discomfort) with warm sterilized vegetable oil, then wash thoroughly with antiparasitic shampoo. The product has antiparasitic, antipruritic, antiseptic and exfoliating effects for demodicosis of the head. The medicine is contraindicated in children under 3 years of age, and during pregnancy it is used only with the permission of a doctor.
- Permethrin ointment. Larvae and adults of the subcutaneous demodex mite, which causes demodicosis, quickly die after the first treatment procedure. The drug has low toxicity for humans. Contraindicated in children under 3 years of age, pregnant and lactating women. Ointment for demodicosis is applied to the scalp in a thin layer with massaging movements. Wash off after 12-24 hours with warm water and soap or shampoo. If the treatment of demodicosis is not effective enough, the procedure can be repeated only after 2 weeks.
- Metronidazole and Metrogyl gel. The drugs cure demodicosis of the head without relapse. Metronidazole tablets are taken according to the following scheme: 21 days - 3 times a day; 14 days - 2 times a day; 7 days - 1 time per day. At the same time, Metrogyl gel is applied to the skin every day (morning, afternoon and before bedtime). The head should be washed only with tar shampoo. Peppermint or tea tree oil will help relieve irritation after the procedure; apply it to a clean scalp. After a month, it is advisable to repeat the course of treatment.
- Purified sulfur. It is recommended for oral administration during the break between courses of treatment for demodicosis of the head, but only with the permission of a doctor. Along with meals, 250-500 mg of sulfur 2 times a day. The drug cleanses the body of toxins.
- Erythromycin, Levomycetin or Tetracycline. Antibiotics in tablets are prescribed if demodicosis is accompanied by a bacterial or fungal infection. The doctor prescribes the dosage to patients individually.
Metronidazole, like antibiotics, can destroy intestinal microflora. Such drugs cannot be taken without probiotics (useful bacteria) - Linex and Hilak-Forte contain them.
Treatment and care shampoos
It is not possible to cure mites in the head with shampoos alone, so they can only be used as auxiliaries:
- Demodex Complex is a completely natural shampoo. It is used for both treatment and prevention of demodicosis. The product contains plant components that have an antiseptic, antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Demodex Ovante. The active components of therapeutic and prophylactic shampoo are antiparasitic and antifungal substances - sulfur and zinc. The product also contains vitamins and natural oils, due to which the shampoo strengthens local immunity.
- Tar shampoo is a cheap alternative, but no less effective, to expensive products for demodicosis of the scalp. Shampoos based on birch tar (911, Babushka Agafya, Finnish) are not only afraid of demodex mites, but also fungal and bacterial infections. Therefore, the remedy is especially effective for complications of demodicosis.
The manufacturer indicates how to properly use shampoos for demodicosis in the instructions supplied with them.
Drugs to restore immunity
Treatment of demodicosis on the head is not complete without medications that must be taken orally.
The drugs suppress the activity of demodex mites and at the same time further weaken the immune system. Therefore, to strengthen the body’s immune forces, patients with demodicosis of the head are prescribed:
- vitamins of group B, as well as C, PP;
- increased dose of vitamin A and E (Aevit);
- iron - Sorbifer Durules, Actiferrin, Ferroplex;
- calcium gluconate - often intravenously;
- phosphorus - Phosphrene, Calcium glycerophosphate.
Taking general strengthening medications must be supplemented with proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle. Otherwise, it will not be possible to calm demodex for a long time.
Folk recipes
Treatment of demodicosis of the head at home is carried out using kerosene, tar, badyagi, infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs, garlic-based masks and other components.
Elecampane root hair mask
How to prepare: pour 20 g of root into 250 ml of boiling water, simmer covered in a water bath for 15 minutes, let steep for 5 hours. Strain.
How to use: moisten the scalp with the decoction, put a plastic cap on wet hair. After 60 minutes, rinse your hair with regular warm water. Carry out the procedure daily in the morning and evening until recovery.
Result: the plant contains acetic and benzoic acids, which have a detrimental effect on the causative agent of demodicosis. The decoction relieves inflammation, relieves itching and redness.
Concomitant treatment
The success of therapy directly depends on the state of the immune system. To strengthen the latter, you need to include healthy foods in your daily diet and drink vitamin complexes. In addition, the patient must:
- restore psycho-emotional state;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- normalize hormonal balance;
- treat chronic inflammatory pathologies.
In the absence of effect from drug therapy, treatment of demodicosis is carried out using the following methods:
- Cryotherapy. The method involves applying cold to problem areas of the skin.
- Laser removal. Provides quick removal of ticks.
- Skin treatment with Dorogov's antiseptic simulator. This remedy is used only in specialized clinics.
Symptoms of demodicosis can be relieved with zinc ointment. In this case, you cannot use several drugs at the same time. This combination can cause severe complications and reduce the effectiveness of treatment.
Hair care
In case of demodicosis, it is necessary to abandon the usual shampoos in favor of tar soap and “talk” - prepared in a pharmacy and consisting of dimexide, trichopolum and other medications. Spregal is also used, which inhibits the nervous system of ticks.
You can take care of your scalp and hair during exacerbation of pathology using the following shampoos:
- Demodex Complex;
- Stop Demodex;
- Demodex Ovante;
- Munting.
Birch tar should be added to hair care products. The substance has a positive effect on the skin, suppressing inflammatory processes. To quickly get rid of ticks, you can treat problem areas with kerosene for three days. This method cannot be used for inflammation of the dermis.
Treatment for hair mites
As already noted, demodex can live in human hair follicles of the eyelids and, being under the inhibitory influence of the body's defenses, do not cause any problems. Only when the quality of such immune forces decreases does the tick begin to actively feed and reproduce, which ultimately leads to a characteristic clinical picture. Read more about tick larvae here.
Treatment of demodicosis should be aimed at controlling the spread of the mite. Many treatments involve the use of ointments that are applied to the base of the eyelashes at night, since this is when mites can crawl to the surface of the skin to replace one hair follicle with another.
The current popular treatment for hair mites is a whole scheme of techniques aimed not only at destroying all forms of mite development, but also preventing its further spread.
First of all, various special scrubs are used to remove dead eyelashes. The affected areas are then treated with tea tree and macadamia nut oil to try to kill the mite eggs as well. This type of treatment can be carried out at home without the prior approval of a doctor, but it must be remembered that some medications can cause allergic reactions, so before using them fully, you need to apply a small amount and observe for a while.
Treatment and prevention strategies for demodicosis include:
- Use mild shampoos on the scalp and eyelashes every day.
- Cleanse your face twice a day with a non-soap cleanser.
- Various scrubs periodically remove dead skin cells, both on the eyelids and in case of acne.
Possible complications
Demodecosis gives complications when the pathological process spreads to the front part of the head. In such circumstances, the patient is concerned about:
- conjunctivitis, against the background of which visual acuity decreases;
- the appearance of a whitish coating on the eyelashes;
- sticking of eyelashes;
- acne;
- frequent styes in the eyes;
- spider veins.
Be careful! As the pathological process progresses, the patient develops: rhinophyma on the nose, metafina on the forehead, blepharophyma on the eyelids, otophyma near the earlobe, gnathophyma on the chin.
These growths are benign neoplasms that significantly spoil a person’s appearance and often require surgical intervention.
Prevention measures
In order to prevent demodicosis, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- do not use other people's things;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- promptly treat pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system;
- support immunity;
- use scrub or peeling no more than once a week;
- in winter, take vitamin complexes with selenium and zinc;
- quit smoking and alcohol.
Demodecosis responds well to treatment. The pathology does not cause serious complications, but causes severe discomfort. If you follow the rules of prevention, you can achieve stable remission of the disease.