Bed bug
House bugs live near people. The human home contains a source of food, a place where parasites live and reproduce. Here are the most favorable conditions for their existence in terms of temperature and humidity. The appearance of the insect changes depending on saturation. A hungry bug has a rounded size of 2-3 mm and a flat body, less than 1 mm. After drinking blood, it swells up to 8 mm and becomes vulnerable to crushing. Bedbug larvae (nymphs) are hardly noticeable due to their size, but the pain of their bites is the same as that of adult bloodsuckers.
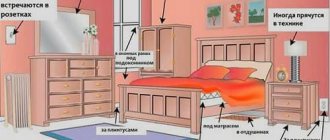
Favorite habitats for parasites are cracks in furniture, bedding, and behind wallpaper. They can be found anywhere they can hide before nightfall. A neglected apartment with unsanitary conditions and a palace can equally be a breeding ground for bedbugs.
The blood-sucking “neighbors” are nocturnal: from 3 a.m. to 8 a.m. One female can lay up to 300 eggs in 20 days. After 3-4 days, a larva appears, which after a week turns into an adult insect. Bedbugs settle in colonies, where mating occurs, eggs are laid and larvae appear. Infestation of a room by bloodsuckers is indicated by a specific bedbug odor from excrement, larvae, and an enzyme secreted by the glands of adult individuals.
What is the danger to humans from the presence of bed bugs?
So, why are bed bugs dangerous for a particular person? Let's figure it out. A simple bed bug, which you can remove from your home even on your own, essentially cannot be considered the source of any infectious disease. The house bug (or bed bug) is a type of bug that classifies these insects as incredibly common synanthropic blood-sucking parasites that are ectoparasites of humans and small warm-blooded animals. In other words, answering the question: why are bed bugs dangerous, we can say with confidence - first of all, because they feed on human blood.
It must be said that, despite being considered a source of infection, the bug is still capable, over a fairly long period of time, of preserving pathogens of various diseases in its own body. Pathogens that may well, under certain circumstances, be transmitted to humans through blood. Such diseases, in particular, include:
- Viral etiology of hepatitis B.
- Tularemia.
- Plague.
- Q fever and others.
Of course, medicine has described extremely rare cases of dangerous infectious diseases developing after a house bug bite, just as in extremely rare cases, malaria occurs after a mosquito bite. However, it is simply unacceptable not to know these facts.
In addition, we should definitely not forget that the bites of a domestic bug themselves can cause considerable harm to a person. Let's figure out whether a bug bite is dangerous for humans and what is its harm? Since bed bugs are nocturnal parasites - those that prefer to eat at night, they can take away normal sleep and disrupt a person’s proper rest. Naturally, all this, in turn, can have an extremely negative impact on the functioning of a person’s nervous system, on his mental and psychological health, and even on his overall performance.
“Traces” from the visit of night vampires
Girl after bedbug bites
How to recognize if there are uninvited guests in your home? Bloodsuckers prefer to bite thin-skinned people. The main targets for their attacks in the apartment are women and children. Children who are defenseless against bloodsuckers suffer the most from bedbug bites.
The bloodsucker selects unprotected areas of delicate skin:
- on the neck;
- face;
- feet;
- stomach;
- back;
- hands.
The insect has a proboscis with two channels. Having pierced the skin in the area of the capillary, the bloodsucker injects a disinfecting enzyme there. For this reason, a person does not feel the moment of the bite. Another feature of the bloodsucker is that bedbugs bite one after another, in one line. Bite marks resemble a chain of red spots located at a distance of 2-3 cm from each other. This is explained by the fact that the parasite does not have such a long proboscis as other blood-sucking insects, and it drinks much more blood than a mosquito or flea. The bug saturates itself, sequentially moving from one skin bite to another.
The bite mark of an adult bedbug looks like a round, swollen spot with a visible bite site in the center. If you do not scratch the damaged areas, the itching goes away after a few hours, and instead of a spot, a red dot remains. Children react most painfully to parasite attacks. Their skin reaction is more acute: the spots have a larger diameter, itch more, and can merge into a solid swollen mass. A bedbug victim is attacked at night by several insects simultaneously. If this is a small child, the favorite “dish” of vampires, then the number of bites can reach several dozen.
Hungry bugs attack people not only at night, but also during daylight hours.
In this case, bloodsuckers are not picky and bite everyone indiscriminately. Bedbug larvae are more aggressive. In order for them to complete their cycle, they need to be satiated at least once. In addition, nymphs do not have an anesthetic enzyme in their saliva, and the moment of biting is sensitive for humans and is more painful subsequently.
Can bedbugs carry AIDS?
HIV is the human immunodeficiency virus, AIDS is acquired immune deficiency syndrome, that is, AIDS is a consequence of HIV infection entering and remaining in the body for a long time. Therefore, the question of whether bedbugs can transmit AIDS is not entirely correct. In the context of transmission of the virus through bites, we can only talk about HIV.
In scientific studies, HIV was found only in the bodies of insects along with drunk infected blood. No traces of infection were found in the excrement or saliva. After entering the body of a bug along with food, the virus persisted in the insect for a maximum of 8 days; all attempts to transmit HIV to experimental warm-blooded animals through bites failed. In light of these experiments, the human immunodeficiency virus is most often not even included in the lists of probable diseases that can be transmitted through bedbug bites. According to the data available today, the HIV virus cannot leave the insect’s body in any known way in order to be transmitted to someone else.
Threat to human health
Why is a bedbug bite dangerous for humans? Insects are not carriers of infectious diseases, including hepatitis and HIV. The danger of infection arises only if the bloodsucker simultaneously bites a sick and healthy person. Bedbugs in an apartment pose a different kind of danger.
Health problems arise in the event of an allergic reaction to the saliva of a blood-sucking insect in the form of:
- rash;
- swelling of the nasopharynx;
- bronchospasm;
- headache.
With multiple bites, children or allergy sufferers may develop anaphylactic shock.
Are bites dangerous if you are not allergic to them? If the bedbug colony is not combated, attacks by hungry vampires can lead to the development of iron deficiency anemia. One bloodsucker sucks up to 7 ml of blood per night.
An adult will experience blood loss if 20-30 bedbugs bite him every night. For an infant, an attack of 3-5 bedbugs is enough for his well-being to deteriorate. Itchy pain makes children capricious, their sleep and appetite are disturbed. Psychological discomfort, sleep disturbance, irritability - this is what bedbug bites are dangerous for humans.
Bedbug bites: danger and consequences
Not so long ago, people believed that the main danger posed by bloodsucking insects was the appearance of itching and scabies on the body. But in addition to the fact that bedbugs bite a person, they also feed on his blood. Itching does not occur at the moment of an insect bite, but after it feasts on blood. At the moment of the bite, the insect injects a special substance into the victim’s body that prevents the process of blood clotting, called a kind of anesthesia.
After an insect bite, a small red spot begins to form on the body with a visible dot in the center. It is these spots that cause itching, but a person can attribute these bites to a mosquito attack. People may not be aware of the presence of bedbugs in their apartment, since these blood-sucking insects are active at night and sleep during the day. Before biting a person, a bug chooses a place where the skin is thinner. One bug can make up to 5 bites per night, which often depends on the age of the insect. In addition, some bedbugs are so fastidious that they feed exclusively on the blood of young people or children, where it is much easier to bite through the skin. But this is only an assumption of scientists, which has no practical confirmation.
Let's find out why bedbug bites are dangerous, and what consequences they carry? First of all, bites affect a person’s health and well-being:
- signs of inflammation appear at the bite sites;
- mental problems and nervous system disorders arise;
- a person may experience allergic reactions to insect bites, which manifest themselves in various forms;
- a decrease in hemoglobin levels in the blood, which often occurs in children and pregnant women;
- rapid fatigue and decreased performance.
Bedbug bites can cause an allergic reaction, especially for children, due to their fragile bodies
But these are only the main types of dangers of bites from domestic bloodsuckers. What are the consequences of such bites, and what they can lead to, we will consider further.
- Inflammatory processes. One bite from a parasite does not pose a danger to humans, which is not to say about their widespread occurrence. If dirt or infection gets into the wound, the problem gets worse. The wound will turn into an abscess, which may break out until treatment measures are taken. If the abscess is not treated, it can result in inflammation or blood poisoning.
- Allergic manifestations. A negative reaction of the body can manifest itself in the form of the following signs: sneezing, rash, swelling, runny nose. Sometimes these symptoms make it difficult to recognize bloodsucking insect bites. Allergic reactions can be complicated by the development of anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema.
- Mental disorders. It is normal for a person to not tolerate small blood-sucking parasites. Facts of bites on the body provoke the development of nervous breakdowns, fear, and somatic ailments in a person. Complications of a mental disorder can result in entomophobia.
If on the first night you find several bites on your body, then it is possible that the very next day you will be bitten by a whole colony of these blood-sucking parasites. If this happens, you should immediately consult a doctor who will help you avoid the development of unpleasant consequences of a brutal attack. Due to allergic reactions, a person can die if timely assistance is not provided.
Signs of a bedbug infestation
The fact that blood-sucking insects have appeared in the apartment can be judged by several signs. First, you need to be able to distinguish bites from bedbugs from the bites of other bloodsuckers: fleas, forest ticks, scabies mites, midges, mosquitoes. How can you tell if it's a bug bite?
Pets carry fleas
Fleas bite during daylight hours and at night. Bites are single, chaotic, pain persists for 3-5 days. The source of fleas is pets. If a cat or dog is itching, it means they have fleas. The habitat of ticks is a forested area. The tick bite is insensitive. A tick that has sucked blood remains in the thickness of the skin. The site where the tick entered becomes very swollen and painful. A tick can be removed non-surgically until its head disappears. The scabies mite makes its subcutaneous passages more slowly than the bug. Midges and mosquitoes rarely attack outside. The pain from their bites is felt immediately and does not go away for several days.
Multiple red spots or a chain of them, discovered in the morning, indicate the appearance of bedbugs in the house. The frequency of appearance of characteristic traces confirms the assumption of bloodsuckers.
The glands of bedbugs secrete a special enzyme, which becomes noticeable when there is a large concentration of insects. In addition to skin lesions, traces of the presence of bloodsuckers are noticeable on bedding. Blood stains from crushed insects, traces of their excrement, and blood leaking from the wound stain the bed. A hungry bloodsucker is difficult to crush: he has a strong shell and a quick reaction. Having drunk blood, it increases in size several times and becomes vulnerable. In insect habitats, bedbug eggs, remains of skins after molting, and excrement are found.
How to improve your health after bedbugs
First of all, you need to take care of proper care of the affected areas of the skin; this can be done at home. The damaged area is washed with water and treated with alcohol or medicinal tincture. If inflammation occurs, ice or some cooled object wrapped in cloth or gauze is applied for a while. Bite areas are treated with aloe juice 2-3 times a day.
Cream “Triacutan”.
If an allergic reaction occurs, antihistamines such as Loratadine, Diazolin will be required. Local manifestations of allergies are reduced when Triakutan or another product prescribed by the doctor is applied to the abrasions.
In addition to treating damaged skin, you should restore the nervous system, get enough sleep, drink herbal tea with lemon balm, chamomile and thyme. Tablets “Glycine” and “Novopassit” help reduce irritability. The listed methods will only work after the complete destruction of insects in the house.
To improve immunity, it is useful to take vitamins, eat vegetables and fruits more often, take daily walks in the fresh air, play sports and avoid stressful situations.
Methods for controlling bedbugs
You can get rid of it using chemical, hygienic and natural factors. Each of these methods has disadvantages that do not allow bloodsuckers to be expelled from the home once and for all.
Chemical method
Means and methods of getting rid of bedbugs
Treatment with insecticides is effective if it is simultaneously carried out in adjacent rooms (in apartments on the site and on the floor). You can carry out this procedure yourself or call specialists from the SES. This method does not affect bedbug eggs. Repeated disinfestation is required after 2 weeks.
Hygienic way
A vacuum cleaner and a steam cleaner are suitable for this purpose. Insects caught in the dust bag are then destroyed. When exposed to steam, bloodsuckers die on the spot, as they cannot withstand temperatures above 50 degrees. Disadvantage of the method: the inability to treat all places where adults and larvae accumulate.
Real risks from bedbug bites
The human body's response to stings varies. Physical signs are absent or expressed as allergies. When people experience severe itching, they scratch and damage their skin. The path opens for infection. Ulcers form that require treatment.
Bedbugs do not infect humans with diseases. Their presence in an apartment causes more moral concern, but some problems from insects do exist.
Psychological discomfort
If bedbugs have just settled in an apartment, there are few of them and they rarely come out in search of food. Adults live for 10 days by drinking blood. When they get hungry, they go for food again.
The female lays eggs daily, from which voracious larvae emerge. This conveyor belt does not stop; soon, every night another wave of insects is sent out for blood.
Sleep is disturbed because there are bugs nearby that will start biting. The pain from this is practically not felt, but the fact itself is unpleasant. Prolonged cohabitation with parasites can cause mental disorders in some people: phobia, nervous tics, panic.
Insomnia sets in, causing unrestrained behavior during the day, irritability, and persistent fatigue. Children feel more pain from bites. The child often cries, becomes capricious and irritable, which affects the psyche of the parents.
Allergy
The saliva that bedbugs release onto human skin for pain relief is a strong allergen. The bite sites in most people are covered with red, swollen bumps. Outwardly they resemble mosquito bites, but the itching is much stronger.
Rarely, but a general allergy of the body occurs. It is accompanied by severe swelling, breathing problems, arrhythmia, and changes in pressure. A doctor's intervention is required; consequences can even result in death.
Children whose immunity is not yet sufficiently developed react especially sensitively to bedbug bites. Allergies are much more common among them. Thin skin reacts sensitively to bedbug bites; the wounds merge into a continuous rash, which causes incredible suffering to the child.
Pregnant women react very poorly to insect attacks. Due to reduced immunity, the likelihood of general allergies increases. Women experience stress and suffer from insomnia, which negatively affects the unborn child.
When there are a lot of bedbugs in a house, they constantly attack people in search of food. Their immunity decreases. If someone suffers from somatic diseases, the temperature rises, and they often get sick.
Constant bites provoke the development of anemia. This does not threaten a healthy person, but the sick, elderly and small children may well suffer.