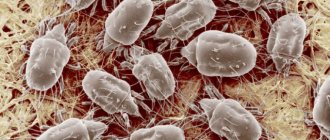
Who are saprophytes
Among arachnids, saprophytes are distinguished, the representative of which is the house dust mite.
It would seem that who can be frightened by things that no one in real life notices, does not notice only because they are negligible in essence, but not everyone is sensitive to them. And this hidden threat is extremely dangerous for each of us. It is enough to be at home or visiting, at work, in the office to simply inhale vital air, and with it many billions of dust particles.
Can you imagine that on one square centimeter there is a miniature periodic table, and this is an integral part of our life, from which there is no escape. Even though the concentration is negligible and cannot significantly harm health, all dust is a habitat for human companions in life - domestic insects, tiny bacteria and organisms.
Dust mites are quite small “animals” and it is very difficult to see them with the naked eye; their size ranges from 0.1-0.5 mm. About 200 species are widespread throughout the globe. Their normal life cycle is about 65-80 days, with the female laying approximately 60 eggs at a time.
The ideal habitat is our apartment with a temperature of +18-25 ° C, because they are not able to independently regulate their body temperature, and air humidity is important, since ticks, having special glands, absorb and evaporate moisture through the skin. Saprophytes and others like them feed on organic substances found in excess in house dust.
In unfavorable conditions, the tick hibernates, covering itself with a protective shell (hypopus), at which time it is very resistant to external influences and is not picky about food and water.
When living conditions change, it emerges from its state and gives life to a new generation. Saprophytes and the like feed on organic substances found in excess in house dust, these are animal and human hair, the remains of various foods, dust from books (cellulose), bird feathers, and a natural wool carpet is just a godsend for them, as well as human epidermis, which is the most delicious morsel. But not the mites themselves, but their waste products, namely their decomposing armored corpses and feces, are the strongest allergens that cause a number of diseases.
Description of saprophytic mushrooms
Saprotrophic organisms (decomposers) are necessary for the environment, as they contribute to the faster decomposition of plant and animal remains. At the same time, they do not leave solid waste, that is, they do not pollute the environment. Mushrooms are typical decomposers; they close the small cycle of substances in nature.
Features of structure and nutrition
The appearance of saprophytes is very diverse. They can be higher:
- tubular;
- marsupials;
- lamellar.
And imperfect:
- Yeast;
- mold.
The first ones may look like ordinary mushrooms, which are known to everyone. They consist of cells that are huge in size (hyphae) and have several nuclei. Together they form plectenchyma, which are divided into distinct parts: a stalk and a cap. However, in some representatives they may be absent or may not have clear boundaries. The watery pulp is covered with a skin that protects from external irritants.
Saprotrophs, like other representatives of the fungal kingdom, feed only on ready-made substances
The voluminous mycelium consists of many thin branches, which is part of the mycelium . The color varies, mostly white, beige, yellow and red-brown.
And if among the higher representatives there are edible species, then imperfect ones are unsuitable for food. Some are used in the preparation of dishes and drinks, and their hazardous properties are neutralized due to storage conditions or further processing. They differ from “traditional” mushrooms in a completely different structure.
Also read: Variety of cap mushrooms: features and description
Most of the body is represented by mycelium, which is well developed in mold and yeast. Consists of multinucleated cells and septa. As a result of mitosis, conidia are formed on the mycelium. These are immobile spores of brown, white, milky or gray color. Shape: spherical, star-shaped, spiral or thread-like, but it is almost impossible to see with the naked eye.
Saprotrophic organisms (decomposers) are necessary for the environment, as they contribute to faster decomposition of the remains of plants and animals
Saprotrophs, like other representatives of the fungal kingdom, feed only on ready-made substances. Like other heterotrophs, their bodies are unable to produce organic ingredients from carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. The food source for saprophytes are:
- Leaves and needles;
- remains of trees, their branches and trunks;
- animal remains, such as horns, feathers and fur;
- straw.
With the help of mycelium, organisms extract nutritional ingredients from the substrate. The peculiarity is that they do not cause any harm to the environment (with the exception of imperfect representatives if a person or animal eats contaminated food).
Gallery: parasitic and saprophytic fungi (25 photos)
Features of parasitic mushrooms (video)
Examples of saprophyte fungi
Edible:
- Champignons are one of the most common saprophytic mushrooms, the family of which includes the following species: umbrellas, puffballs, dung beetles, cystoderms. They have a pleasant and delicate taste.
- Morels belong to the Morschella family. They are named so because of their memorable appearance: the cap of morels resembles the pulp of a walnut or prune.
- The line is from the discine family.
- Cobweb - prefers swampy areas.
All mushrooms must be thermally processed. A person who has consumed a raw product may become poisoned.
- Inedible : Helvella - found in some regions of Russia and CIS countries.
- Life-threatening : pigworts are a common mushroom, unpretentious to environmental conditions. More recently it was included in the list of poisonous mushrooms.
- Deadly to life : toadstools - have many varieties, which are still easily confused by inexperienced mushroom pickers.
Also read: Winter honey mushrooms: description of appearance, location and collection rules
Morels belong to the Morschella family.
Features of saprophytes
Among arachnids, saprophytes are distinguished, the representative of which is the house dust mite. They find their favorite nutrients in dust. It accumulates large amounts of dandruff, hair fragments, food residues, fibers from nightwear, bed linen. Household dust mites are dangerous for a child or adult with weakened body defenses. Insects are found in almost every living space, and they are especially attracted to warm and humid rooms.
House dust mites are not carriers of infectious diseases, do not bite humans, and avoid their presence. The insect's excrement, its body, dries out and mixes with dust particles that a person inhales.
Saprophyte – dust mite
The main habitat of bed mites is house dust. Saprophytes are so small that they can only be seen under a microscope. They feed on keratinized skin epidermis, which is exfoliated daily from the human body, dead remains of skin scales and pet hair, cellulose book dust, fungal spores and other organic compounds.
Ideal conditions for the reproduction of saprophytes are woolen carpets, pile bedspreads, and cotton-based mattresses. But still, the favorite habitat of these microscopic parasites is bedding (sheets, pillows, duvet covers). Saprophytes love a warm and humid environment, which is usually always present in bedrooms.
As a rule, bedding is not washed frequently, and wet cleaning of the floor surface under the bed is not carried out every day. Therefore, bed mites multiply unhindered and secrete a lot of feces, which cause allergies or itchy skin (scabies) in particularly sensitive people.
How to protect yourself from saprophyte mites
It is worth noting here that for these purposes it is convenient to use the recently popular vacuum bags for storing clothes and things. They are very inexpensive and very easy to use. Things stored in them are not susceptible to dampness and moisture; there is very little air in them, which prevents the proliferation of saprophytes. By the way, these bags also reduce the volume of stored items by almost 3-4 times, which is very useful for our small apartments. You can see what vacuum bags for things look like and what they are like here.
Today, unfortunately, there is no 100% way to cure asthma once and for all, but it is quite possible to achieve effective control over it. To do this, firstly, you need to find out and know the factors that cause suffocation in a particular patient - the so-called “triggers”, or in other words, what substances can cause attacks of allergies or asthma, or cause an excessive reaction of the bronchi in the form of their spasm. And secondly, follow the basic rules of hygiene described above. Remember that it is no coincidence that they say “cleanliness is the key to health”!
Saprophytic mite: a dinosaur the size of a speck of dust
Each individual lives on average 4 months, during which time the female saprophyte mite lays up to 300 eggs
These microscopic arthropods from the arachnid family look truly frightening: several pairs of thin legs and a large body with peculiar proboscis. And if you consider that they have an appetite worthy of carnivorous dinosaurs, then the proximity to such monsters becomes increasingly unpleasant. Saprophytic mites feed on dead particles of our skin. It’s good that their size is microscopic, about 0.1–0.5 mm, otherwise we would have much more subjects for nightmares at our disposal.
Each individual lives on average 4 months, during which time the female saprophyte mite lays up to 300 eggs: that is, the scale of the problem tends to grow rapidly. If you take just a few grams of ordinary dust, there will most likely be several thousand mites in it. What can we say about our mattresses, where we ourselves create ideal living conditions for saprophytes. And they need very little: warmth (20–25°C), moderate humidity (60–80%) and... food!
When you go to bed, you provide them with all three conditions. By the way, our ticks are not known for their good manners, so the “restroom” is considered to be the territory where they are currently located. So the habitats of saprophytes are overflowing with their feces, which they produce in quantities approximately 200 times their own weight.
Nature intended such mites as unique assistants to the decomposition process. But having moved from the nesting places of birds, where they originally lived, to human dwellings, saprophytes became a real problem that threatens the health of every person. In total, there are about 150 species of such mites in nature, but the most dangerous “neighbors” are Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and Dermatophagoides farinae, that is, dermatophagoid or pyroglyphoid. They are the cause of problems with a person’s well-being.
What exactly do saprophyte bacteria feed on?
The bulk of microorganisms existing in nature belong specifically to saprophytes. Like people, they have their own tastes and demands for the food they eat, that is, organic substances must contain more/less certain compounds that help them develop and lead active life activities.
For example, some organisms of this class need to consume the decomposing bodies of animals or plants, containing putrefactive compounds, for full life activity, while for others it is enough to penetrate milk, as a result of which its fermentation is observed.
Consequently, for the life of saprophytes the following may be required:
To study the activity of saprophyte bacteria in more detail, no special substances were used. They were launched into whey, meat, yeast and plant media. Each type of microorganism actively absorbed this substance, but if the substrate was not suitable, then the feeding process slowed down.
Where and how do saprophytic mites live?
House dust is the main habitat of saprophytes
Their main habitat is house dust. Ideal conditions for their living and reproduction are created in the bedroom, where it is warm (+20...25 °C) and relatively humid (60...80%). Under such conditions, mites are capable of laying 300 eggs in four months, and several thousand saprophytes live in one gram of dust. If you consider that up to 40 kilos of dust accumulates in a house per year, imagine the full scale of the threat!
Don’t be surprised if after cleaning you continue to suffer from allergies - whole families of these insects live in blankets, pillows and mattresses. At the same time, each person loses 1.5 grams of skin per day (about 2 kilograms per year), which is the main food of parasites. It turns out that we ourselves are an uninterrupted source of food for harmful insects.
Characteristics of parasitic fungi
Parasitism is a common phenomenon. It is not surprising that among mushrooms it has taken on large-scale forms. There are thousands of species that infect their host and lead to its death. They provoke the occurrence of certain diseases in plants, animals and humans.
Features of parasitic mushrooms
Infection of the body begins with the penetration of a spore. These are cells that serve for sexual and asexual reproduction of fungi. Once in the body, it grows. Numerous threads begin to penetrate into the center of the cells and braid them and tissues. Thus, the parasite feeds, which causes the cells to die.
Everything you need to know about mushrooms (video)
Parasites have a high reproduction rate . They are able to destroy their host in 2-3 days (for example, insects) and begin their hunt again. Moreover, the spores remain viable for several years in the most extreme conditions.
Some fungi are adapted to life in terrestrial conditions, others can only exist in the body itself. Because they produce too few enzymes, a particular fungus parasitizes only the body of one species.
It seems that parasitic mushrooms do not bring any benefit, but this is not so. Of course, they cause damage to agriculture and are pathogens, but some mushrooms destroy harmful insects (locusts, flies, mosquitoes). And birch chaga is actively used in the creation of medicines.
You can often find the tinder fungus on the trunks of most trees.
Names and descriptions of edible parasitic mushrooms
There are not so many species suitable for food, but after appropriate heat treatment they completely lose all their negative properties.
Polypores. Walking through the forest, you can often find this parasite on the trunks of most trees. When collecting it, you must be careful, since not all of these parasites are suitable for food:
- Leafy. One of the largest representatives (up to 1 m in width and up to 20-22 kg in weight). Fleshy and thin caps are collected in one disk, from which grows one leg up to 10 cm in diameter. The color is gray, with a yellow or brown undertone. The pulp has a pleasant aroma;
- grey-yellow. It is not a very large mushroom, its maximum size is 30 cm. It should be collected in the spring and only young individuals. The caps resemble fans; when cut, the mushroom is soft and juicy and breaks easily;
- winter. Young tinder fungi are suitable. The small cap (up to 10 cm) is covered with fluff or small scales. The color is white with a gray tint.
Also read: Purple sapling: a decorative miracle and a powerful traditional medicine
Parasites predominantly inhabit living bodies
- Chaga. Prefers birch trees. It looks like a rough growth, so it can only be recognized by its irregular shape, which stands out sharply on the smooth trunk. The color of the mushroom is black-brown, inside it is dark beige. This parasite produces tasty tinctures, but it is not consumed as food.
- Oyster mushrooms. And although these fungi are more often found on tree trunks, they can also appear on adult individuals, parasitizing them. Individuals line up in numerous rows, growing alone very rarely. The wavy caps smoothly flow into thick legs; the color of oyster mushrooms is pale gray with a slight purple tint.
Dust mites and allergies
According to studies, 80% of patients with bronchial asthma are allergic to waste products of saprophytic mites
The word “mite” evokes in most people unpleasant associations with blood-sucking insects, which every lover of walks in parks and forests knows firsthand. Saprophytic mites differ favorably from their counterparts in that they are not capable of directly causing harm to humans. But, unfortunately, the very fact of their existence gives us many problems. The excrement of dust mites is very toxic, they can cause severe allergies (especially in people prone to respiratory diseases), as well as worsen the condition of the skin, accelerating the process of cell death.
Every time you make your bed, mite waste products end up in the air, literally poisoning your life. The too small size of such particles allows them not to settle for a long time, so if there are dust mites in your house, then you inhale a wild mixture of excrement and dead shell particles almost constantly.
According to research, 80% of patients with bronchial asthma are allergic to waste products of saprophytic mites, which sometimes cause the disease. In addition, about 25% of the population of large cities suffers from allergies, the cause or aggravating factor of which are these creatures.
You should not think that simply by changing your bed linen you will immediately be safe. Saprophytic mites often choose habitats where there is less light and unfavorable environmental influences. Therefore, they crawl deeper into the mattress, pillow and blanket, not disdaining the carpet, your favorite blanket and even clothes. In order to counter such a scourge in a timely manner and with the greatest effectiveness, you need to know about the signs indicating the presence of dust mites in your home.
How to find out that saprophyte mites have settled in the house
First of all, you need to pay attention to the first signs of an allergy. These include:
- A year-round runny nose may be a sign that saprophytes have appeared in the house; a year-round runny nose;
- frequent sneezing;
- cough;
- labored breathing;
- lacrimation;
- swelling.
If these symptoms are independent and bother you for no apparent reason (especially in the morning), then it’s time to start fighting invisible provocateurs - dust mites.
Why are saprophytes dangerous?
As already mentioned, the insects themselves are not dangerous; the threat is posed by their waste products, which contain digestive enzymes - the proteins Der p1 and Der f1. As a result, a person may experience an attack of the following diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- atopic dermatitis;
- allergic rhinitis;
- conjunctivitis.
Let's look at some interesting statistics. Every tenth inhabitant of the earth suffers from allergies, and 60% of all such diseases are household allergies. As for children, in Russia 6% of children suffer from bronchial asthma, and the vast majority of them (about 70%) “owe” this disease to tick-borne allergy.
The trouble is that the excrement of saprophytic mites is deposited in the dust and, having risen into the air, does not settle for a long time. They enter the respiratory tract, remain there and cause allergies.
List of diseases that arise as a result of the activity of saprophytes
- damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes, conjunctiva, inflammation, dermatitis and rashes; dryness, itching and irritation of the skin.
- lung diseases, allergic asthma, which can turn into bronchial asthma.
Engaging in self-diagnosis and self-medication is harmful to yourself; it is better, of course, to consult a specialist if you notice a strange cough and runny nose. Cleaning upholstered furniture will effectively remove saprophytes.
Follow the rules of hygiene, often do wet cleaning, vacuuming and changing bed linen. Woolen and fur products - blankets, natural fur, as well as feather pillows - are favorite places for dust mites. Try to beat and dry in direct sunlight more often. The tick is very afraid of low temperatures, so freezing is effective.
Cleaning upholstered furniture will effectively remove saprophytes. Treat furniture with a special product, clean it of dead microorganisms, because their remains are also harmful to the body!
Ventilating the premises and timely wet cleaning will protect your home and your health, preventing allergies!
Why do you need to get rid of saprophytes?
If we are to be absolutely honest, then it is worth admitting that saprophytes themselves do not pose any danger to humans - they do not bite, do not drink blood and do not infect. But the real danger can come from the waste products of these tiny creatures, which contain digestive enzymes, that is, proteins. They are the cause of the development of an allergic reaction in humans, which in extreme cases can result in bronchial asthma, chronic conjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis, the appearance of which is provoked by waste products of saprophytes.
Mites live in places where dust accumulates - furniture, bedding, carpets. Together with the air, saprophytes and their metabolic products enter the respiratory tract and, settling there, cause allergies. When a person with signs of bronchial asthma comes to see a doctor, and it is not possible to explain its occurrence, the option of a dust allergy is considered.
Structure and methods of nutrition
Fungi belong to the species saprophytes or saprotrophs, which form many spores in the process of life. They scatter to surrounding plants or animal remains, facilitating the reproduction and spread of the mycelium. Examples of vegetation that organisms like to settle on:
- cones;
- branches;
- hemp;
- stems of annual grasses;
- needles and foliage;
- feathers and horns.
Different saprophytes or, as they are also called, decomposers, are characterized by different types of substrate on which they settle and feed. So, for the summer honey mushroom, the best food is the remains of deciduous trees. False honey mushrooms feed only on needles. But the white dung beetle miraculously exists in places highly saturated with nitrogen.
How to deal with saprophytes
- If you wash floors, then once a month wipe them with a 10% saline solution (a pack of salt per 10 liters of water). Saprophytes are afraid of wind, frost and sun. In winter, regularly ventilate and freeze blankets and pillows on the balcony, and “fry” them in the sun in spring and summer. Ultraviolet light completely decomposes the waste products of saprophytes in 2 hours.
- Carry out wet cleaning regularly, and then ventilate the apartment well. If you wash floors, then wipe them once a month with a 10% saline solution (a pack of salt per 10 liters of water).
- Saprophytes die at temperatures above +65, so wash bed linen in the hottest water possible and iron blankets.
- Regularly, at least once every 8-10 years, change the mattress - the main refuge of saprophytes. When choosing a mattress, give preference to those that undergo special non-chemical treatment. For various allergies, choose a mattress with coconut filling - mites feel much worse in them.
- The pillow should serve you no more than 2-3 years; no mechanical or thermal treatment of the pillow will get rid of the saprophytes living there and their excrement. Throw it away mercilessly if you value your health.
We should also talk about washing things - this is another way that helps to significantly reduce the concentration of saprophytes in the air. First, you need to wash all your laundry in the hottest water possible. You shouldn’t go to extremes - you still need to pay attention to what type of fabrics are put into the washing machine and whether hot water can be used for them.
There are a lot of detergents on store shelves that help destroy the tiny creatures in question. These include washing powders from the “Sarma” series - they do not contain chlorine and have an antibacterial effect, which has been officially proven and confirmed by certificates.
Saprophytes cannot be seen, they do not have any pronounced effect on humans, but it is reliably known that these small creatures can cause severe allergic reactions.
Examples of edible species of parasitic mushrooms
Among all their variety, there are some that can be eaten. Some of them are familiar to everyone, but there are also species that few know about.
Autumn honey fungus (real)
The most famous and widespread parasitic mushroom. Belongs to the Physalacriaceae family. It has a pleasant smell and taste. Refers to lamellar mushrooms. Young mushrooms have a small cap; with age it can grow up to 10 cm. Its color greatly depends on the place of growth and can be from honey-brown to greenish-olive, but always with a darker spot in the center. The stem of young mushrooms is quite thick, but becomes thinner and dense with age. The color is yellowish-brown, darker in the lower part, which may be slightly expanded, but without swelling. The plates of young mushrooms are white and become very dark with age. A distinctive feature is the ring in the upper part of the stem - the remnant of a white cover, clearly visible in young mushrooms.
It grows on living trees and stumps, sometimes settling on dead wood, in this case becoming a saprophyte. Found everywhere in large groups, prefers moist forests. Fruits from September until frost. Usually there are 2-3 waves of fruiting. The poisonous sulfur-yellow honey fungus is similar to it.
Honey mushrooms can be boiled, fried, dried, salted and pickled.
Autumn honey fungus (real)
Winter honey fungus (winter mushroom)
It is called so because of its ability to bear fruit even in winter during thaws.
Agaric. Having a cap from 2 to 10 cm in diameter, yellow-brown or honey-colored, the outer edge is lighter. The leg is strong, of medium thickness, velvety brown, slightly lighter in the upper part. The plates are light, the cover is missing.
Habitat: northern temperate zone. It grows on living wood and can also invade dead trees. Fruits from spring to autumn.
The mushroom belongs to category 4. Eat pre-boiled. Boiled mushrooms are salted and pickled. Fungi produce a substance called flammulin, which can fight sarcoma. Very popular in the cuisines of Japan and Korea, where it is industrially cultivated.
Scaly
Depending on the color of the cap, there are common flake with a light brown or brown cap, golden flake with a golden cap, and upland flake with a light yellow cap. A special feature of this mushroom is the scales that cover not only the cap, but also the stem. As a rule, they have the same color. The plates are light. These mushrooms grow on trees and rotten stumps, sometimes on the ground, often in large groups. They bear fruit from late July to early October. Scales can be classified as both saprophytes and parasites.
The mushroom has low taste and is consumed after boiling.
Sawfoils
They have another name - panus. Little-known conditionally edible mushrooms. Only young individuals can be eaten. The Panus family is quite numerous. All of them belong to lamellar fungi and grow on wood, mainly coniferous species, and scaly sawfoil can even grow on telegraph poles and sleepers, for which it has another name - sleeper.
Shiitake
Unfortunately, this valuable mushroom is not found in the wild here - it cannot survive our harsh winters. But in China and Japan it is not only a delicious delicacy, but also a valuable medicine. The list of diseases that it can cure is very long. These include cancer, hepatitis, immune deficiency and much more. In a number of countries it is cultivated. At the moment, shiitake is being intensively studied by scientists who have already isolated a number of valuable potent substances from it.
Traditional methods of combating saprophytes
When cleaning woolen carpets, the old “grandmother’s” method works great: lay the carpet out on the snow and knock the dust out of it with a clapper.
In order to successfully fight bed mites, you need to know that saprophytes cannot tolerate both high and low temperatures. Therefore, if possible, one of the effective ways to get rid of unwanted parasites is to expose cotton mattresses to frost in the winter, and expose them to sunlight in the summer.
When cleaning woolen carpets, the old “grandmother’s” method works great: lay the carpet out on the snow and knock the dust out of it with a clapper. A person who cares about his health should regularly wet clean his apartment, wash bedding at high water temperatures, and store sheets, pillowcases and duvet covers in a dry place.
It is recommended to ventilate the pillows periodically and change them after 2–3 years of use, mercilessly throwing them away. Also, once every 10 years, mattresses, a favorite haven for bed mites, need to be replaced. When fighting saprophytes, the main thing is to avoid large accumulations of dust in the bedroom and other living spaces.
Modern methods of combating saprophytes
Of course, we should not forget about the technical achievements of the present time. Every home has a vacuum cleaner for regular cleaning of the room, but, unfortunately, traditional dust collectors, even those equipped with aquafilters, are not able to solve the problem of bed mites. If financial capabilities allow, it is best to purchase a multifunctional dust collection system made in the USA, Rainbow.
Perhaps, today this is the only vacuum cleaner that meets all modern requirements (humidification, disinfection, aromatization) and guarantees removal of saprophytes. However, its cost is quite high.
Such devices are equipped with special filters, an ultraviolet lamp and fans, which create difficult conditions for the reproduction of saprophytes and eliminate the source of allergic dust. If you follow the above recommendations, it is quite possible to protect yourself and your household from uninvited household inhabitants - bed ticks.