How insects can be dangerous
There are about 625 thousand species of insects in the world, and most of them, when adjacent to humans, do not benefit him.
Insects can:
- Be carriers of dangerous viruses and diseases, such as tick-borne encephalitis, plague, typhoid, diphtheria, sleeping sickness and others.
- Be aggressive towards a person.
- Parasitize on the body of livestock and humans.
- Harm agriculture, eat cultivated plants.
- Settling in a human dwelling, damaging food, furniture and other items.
The most dangerous bugs in the world
It would seem, how can insects harm a person? After all, they are so small and clearly weaker. But there are also hidden threats from beetles. Thus, the most dangerous beetles can carry diseases, harm agriculture and forests, and, in the end, can be simply poisonous.
Here are those insects belonging to the order Coleoptera, which can be considered dangerous:
- Cockroaches. Climbing into garbage cans, sewers, etc., they are carriers of dangerous diseases: typhoid, tuberculosis, dysentery, etc. Getting rid of cockroaches can be very difficult.
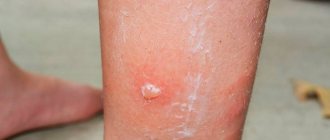
- Blister beetles. They leave a toxic substance on a person’s skin, which causes blisters and abscesses, and if the poison enters the bloodstream, it can cause more serious consequences: kidney and bladder diseases.
- Colorado potato beetles. Perhaps these insects themselves are not the most dangerous beetles in the world, but they can completely destroy nightshade crops, leaving people without a harvest.
- Ground beetles. Some species of these seemingly harmless beetles can spray a stream of caustic liquid from their anus. The distance at which the target is hit is 30-50 cm. If the liquid accidentally gets into the eyes, it can cause severe burns to the mucous membranes and be a threat to vision.
Otherwise, beetles can harm trees and plantings that people cultivate rather than themselves.
Termites
These are insects with a complex hierarchical structure. They are popularly called “white ants”, but they have no common relatives with ants, but belong to the order of cockroaches. They live in Africa and South America, living in colonies. Unlike anthills, the main part of which is underground, termite mounds can rise several meters above the ground.
Humans are not a source of food or a natural irritant for termites, but these insects can harm humans with little or no contact with them. Losses caused by termites amount to billions of dollars per year. Hungry insects completely chew off wooden buildings, eating them away from the inside, which makes it difficult to detect termites in the house early.
Insects are destroyed with insecticides, the wood is treated with special preparations, and in areas with a high concentration of termites, houses are built on stilts broken at right angles under the building itself: termites cannot bend their body in half and simply do not crawl into human habitation.
Caterpillar lonomia
Lonomia caterpillar
Once a year, at the beginning of summer, harmless moths living in the humid forests of South America produce offspring. They lay tiny eggs in the crowns of trees, from which larvae soon hatch. Then “lazy clowns” are born - this is what the aborigines call the most poisonous caterpillars on the planet.
Interesting: Which people are most attracted to mosquitoes? Reasons, photos and videos
The 7 cm long creature is colored brown-green, which allows it to perfectly camouflage among plants. Features of the insect are a white spot on the back, resembling the letter U, and thin bristles covering the body. Each of them has cavities through which poison passes, destroying fibrinogen, a protein contained in human blood plasma.
The slightest touch to a dangerous creature can be fatal. Sharp thorns instantly pierce the skin, and after 12 hours signs of poisoning appear: chills, malaise and headache. Lack of medical care threatens the victim with disruption of the central nervous system, kidney damage and internal bleeding. From 10 to 30 people die annually from poisoning with lonomia toxins.
Lice
Common human parasites that many encountered in childhood. There are head lice, body lice and pubic lice. The head louse is a small translucent insect up to 5 mm long that feeds on human blood. Unlike bedbugs and fleas, it is constantly located on the scalp of its owner.
Insects are very small and fast, so a person detects their presence on the head by the following signs:
- White, tightly seated bubbles appear on the roots of the hair, colloquially called nits. These are lice eggs, which the female attaches to the hair with her sticky secretion. The main locations for nits are the back of the head and the area behind the ears.
- At the site of the bites, you can find traces in the form of red dots that itch very much.
Basically, lice are not dangerous to humans as carriers of diseases (body lice carry typhoid fever, but now they are found only in completely unsanitary conditions). There is an opinion that pediculosis (infection with lice) is a disease of declassed elements and people who do not take care of their hygiene, but this is not so.
Clean hair is much more attractive to lice; they can move onto a person through hugs and other bodily contacts, as well as through household means (using someone else's comb, hair tie, bed linen).
You can cure lice at home - pharmacies offer a wide range of shampoos that kill lice and nits. After using them, all that remains is to carefully comb out dead insects and their eggs from your hair. Folk remedies include hellebore water (often ineffective) and kerosene (effective, but can lead to allergies and damage to the skin and hair).
Human louse
These small parasites that feed on human blood are of two types, depending on where they are located on the body: head and body. Head lice are practically harmless, although cohabitation with them causes considerable discomfort for people. Their bites cause irritation of the scalp, and various infections can enter through the wounds. The body louse is the main carrier of a deadly disease - epidemic typhus.
Black-legged tick
Contrary to popular belief, mites do not belong to the class of insects, but are in the same taxonomic category as spiders. They live in the Northwestern United States; they can also be found in wooded areas of Ukraine, Central and Northwestern Russia.
They feed on the blood of animals, predominantly parasitizing white-tailed deer, biting into the skin with their jaws and securing themselves there with a special sticky secretion. Black-legged ticks are the main carriers of the bacteria that cause Lyme disease, Borrelia.
This disease manifests itself in the form of specific rashes on the skin, a feverish state of the patient, and in the later stages – destruction of bones and joints. Ticks are active all year round, but the risk of being attacked is greatest in the summer.
In order to avoid bites, you should follow some rules when going out into nature:
- Ticks bite in the thinnest and most unprotected places, so the collar should be fully buttoned and the trousers tucked into the shoes.
- It is not recommended to wear flip-flops or sandals; ticks can easily crawl between your toes.
- It is better to choose light-colored clothes for a picnic. It may not be practical, but it is much easier to spot ticks on such clothes.
- Parasites are susceptible to strong odors of spices, so before going out, you can spray your clothes with a decoction of cinnamon, cloves, star anise, or simply put dry spices in your pockets.
- Repellents should be sprayed on tents, backpacks, and all other items that may be useful on a hike.
Second place – ground beetle
Ground beetle
Meeting a ground beetle is especially risky – and this is not in vain. A large black beetle may interest a child or be near an adult, and interest in it may end in failure. The beetle is capable of shooting caustic liquid from the back, and over a considerable distance, up to 50 cm. If the substance gets on the skin, a burning sensation and discomfort will occur. In case of contact with eyes, mouth, or respiratory organs, the risk increases; it is necessary to rinse the affected surface with plenty of water.
Interesting: The largest countries - list, area, names, where they are located, video
Nomadic ants
These insects do not belong to any specific taxonomic order. It happens that even sedentary species of ants can leave their homes. What causes this behavior is unclear, but scientists suggest it could be explained by their complex social behavior.
In Central Africa and South America you can find such living migrating anthills, leaving nothing alive on their way. As in an ordinary anthill, there is its own hierarchy: soldier ants catch prey, and the queen travels with the colony.
Local residents have already adapted to the migration of ants, and when the line begins to approach the village, they take all the livestock from there and leave for a while. After such an invasion, there are no flies or other pests left in the houses, so even such insects bring benefits to humans.
But if you stay in the path of the ants, your pets will be in trouble - the colonies of insects are huge, and they are capable of killing animals hundreds of times larger than themselves.
Nomadic ant
These ants lead a nomadic lifestyle. The whole big friendly family moves from place to place, the journey takes about 2 weeks. The ants make stops only so that the female lays eggs and new members of the community are born from previously formed pupae. The habitat of nomadic ants is the African continent, the countries of Asia and South America. The bite of such a nomad is fatal only to people prone to allergies. Another nuisance from these insects is that they sweep away everything in their path, including livestock.
Wasp
The most dangerous insects in the world can kill a person after the first bite. Wasps cannot be classified in this category, but their bites can be very unpleasant. These hymenopteran insects live throughout the northern hemisphere, excluding the Far North zone. Up to 20 thousand individuals live in families, clearly distributed along the hierarchical ladder.
It is not difficult to distinguish it from a bee: the wasp has a slimmer, elongated abdomen, a bright black and yellow color and a completely smooth body without villi. Wasps occupy an important position in the ecology of natural systems, destroying garden pests - flies, larvae and caterpillars.
Unlike bees, which attack a person only when there is a clear threat to life, wasps are aggressive by nature and attack anyone who frightens and angers the insect with something (bright light, perfume, sharp sounds).
The wasp's venom is toxic to humans; a swelling occurs at the site of the bite, which goes away within a few days; if a person is allergic, the consequences can be more serious - a large rash on the skin, nausea, vomiting. A lethal dose of venom is contained in 700 stings, so in most cases wasp stings are not life-threatening to a healthy person.
9) Poisonous scolopendra
Despite the fact that some centipedes are completely harmless insects, there are also poisonous centipedes. Most of the poisonous centipedes live in tropical forests and deserts. The length of the scolopendra varies depending on the type of family. Some of its species barely reach 15 cm, but larger specimens vary in length from 30 to 45 centimeters. Externally, scolopendras do not look very nice, especially when their size exceeds the norm. Centipedes come in a variety of colors. Most often you can see centipedes of a dark brown or black hue. Scolopendras are not timid creatures and will certainly not run for cover at the sight of a person. Sometimes you can even observe their aggressive behavior. An attack by a centipede on a person is not fatal, but for children a bite can be dangerous. Given the child’s weak immunity, the venom of this creature can cause many ailments. The main symptoms of a centipede bite are: swelling, weakness, burning at the site of the bite, redness, dizziness, nausea and fever. Against the background of a bite, problems such as tissue necrosis, tachycardia and renal failure also develop.
Interesting facts about radiation
Black Widow
The most dangerous insects in the world - black widows or karakurts, actually belong to the class of arachnids. On the territory of Russia it is found in Crimea, Rostov region, Altai region. In particularly hot years, cases of spider bites have been reported in the Moscow region, but this is an exception; as a rule, karakurts never rise so high on the map.
The black widow is a small spider with characteristic bright red spots and a black abdomen, so it is very easy to distinguish it from simple harmless spiders. Karakurts received this nickname due to the peculiarities of mating behavior, when females eat males immediately after mating.
Spiders can be found in ravines and wastelands; they rarely approach human settlements and never attack first. Spider venom contains a dangerous substance called latrotoxin. The first symptoms appear 15 minutes after the bite: a person experiences muscle cramps, nausea, dizziness, and blurred vision.
It should be borne in mind that each organism perceives poison in its own way, and a bite may not always be fatal, but you need to seek help as soon as possible, since death from a karakurt bite can occur within several days.
Hairy caterpillar Coquette moth
The coquette moth lives throughout North and South America. An adult butterfly is not dangerous to humans and their homes, which cannot be said about its larva. A characteristic feature of the caterpillar is the long hairs on its body, which make the insect seem very cute and fluffy, but touching the poisonous spines of this caterpillar hidden in the hairs causes poisoning and burning pain.
These insects live in deciduous forests, settle on trees and feed on leaves and flowers. The caterpillar will not chase or attack a person, so it is very simple to avoid unpleasant consequences from the thorns - do not touch them.
Lonomia
Quite an attractive butterfly. Distributed in the jungles of South America. And completely not dangerous to humans. But its caterpillar is a completely different matter. Lonomy caterpillars hatch in a group, and sit on tree trunks in the same way, perfectly camouflaging themselves as moss. Moreover, they can change their color depending on the environment - on gray moss they will be gray-brown, on green moss they will be brown with green branched shoots. Caterpillars are extremely difficult to spot.
The venom of lonomia is considered one of the strongest; it has a destructive effect on the blood, practically paralyzing the ability to clot. When contacting an animal, a person suffers liver hemorrhages and stroke. It is especially dangerous if contact occurs with several caterpillars. The toxin has an antidote, but it can only help if introduced into the body no later than 15-18 hours after infection. In the future, death may occur.
Rare cases of infection are due to the short period of existence - from hatching to pupation, Lonomia lives for about three spring months. The caterpillar never attacks humans - the poisonous shoots are needed only for protection.
Cockroaches
The red cockroach cannot be called the most dangerous insect, but it certainly can be the most annoying in the whole world. The red cockroach is the most common household pest in our country; several decades ago, these insects lived in almost every apartment building, so it is difficult to find a person who has never fought with them in their life.
The cockroach is a medium-sized insect that lives near humans. Favorite places to live are cracks in walls, floors, and the space under the sink and bathtub. They feed on leftovers from the human table, pick up fallen crumbs, sneak into drawers, refrigerators and spoil food. The lifestyle is predominantly nocturnal.
Insects are very shy, and when the switch is clicked, they usually manage to hide from human eyes.
Cockroaches carry many diseases, such as diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis, and also help spread worm eggs. Some people are so accustomed to cockroaches in their home that they do not consider being around them something dangerous or disgusting, but most still try to get rid of cockroaches as soon as possible. It is advisable to carry out disinfestation together with your neighbors.
Even if the cockroaches did not come into the apartment from them, the insects could have spread throughout the entire house. Special insecticidal aerosols are used to control pests; for preventive purposes, you must monitor the sanitary condition of your home, remove crumbs and food debris from tables, floors and chairs, fix leaking faucets in the bathroom and regularly clean the house.
Rat fleas
The most dangerous insects in the world during the bubonic plague pandemic of the 14th century, after which only 2/3 of Europe's population survived. Fleas, unlike lice, do not live directly on their host, but try to stay close to rat nests, where they can always drink blood.
Rats are not the only hosts of fleas; hungry insects can attack pets and humans . The long limbs of the flea allow it to jump half a meter and quickly move between its victims, and insect bites are very painful and cause the formation of itchy, purulent ulcers on the skin.
Fortunately, today rat fleas, like rats themselves, are rarely found near human habitation, but, despite the increased level of medicine and sanitary conditions, it is recommended to regularly treat pets against fleas with special preparations and put on flea collars.
Wohlfart fly
These insects are common in southern Europe and Russia, northern Africa and China. They belong to the gray blowflies, which are characterized by reproduction in animal corpses. It is this feature that poses a threat to domestic animals and humans, since the fly can deposit its larvae in a wound, cut, or on mucous membranes. As the larvae develop, they begin to eat living tissue and human muscles. Moving inside the body, they cause pain; swelling and suppuration appear in the place where they settled.
Bed bugs
Bed bugs are often found in unsanitary conditions, such as barracks, children's camps, or old apartments. Nothing will stop the insects from moving into a new, clean apartment, because bedbugs go without food for a long time, which allows them to bide their time, hiding in closets, in linen or on other people’s clothes.
A bedbug is a small insect up to 5 mm long that feeds on human blood. The insects themselves have a light brown, translucent color, making them difficult to identify, but when an individual drinks blood, its body increases in size and acquires a rich crimson hue.
Bedbugs settle on the back of mattresses, go out hunting at night, and the next morning a person wakes up to find bite marks on his body. In a healthy person, these are just red dots, without itching or irritation, and therefore people often do not even suspect that an entire colony lives in their mattress.
Also, many bedbugs are carriers of typhoid, anthrax and fever pathogens, but through bites they are not transmitted to humans, because the insect is interested in ensuring that humans can supply it with blood for a longer period of time.
To combat bedbugs, chemical insecticides and heating of apartments are most often used - insects are very sensitive to the temperature of their home, so they die at 50 ° C.
Killer bees
The killer bee (aka Africanized bee) looks very similar to a regular bee, but this killer insect tends to attack more and more often, which is why they pose such a huge threat to humans. They can create nests in places such as car tires, boxes, barns, carriages, etc.
It is known that if these bees are disturbed, they are capable of chasing people at a distance of up to 4-5 km.
If these aggressive bees start chasing you, it is recommended to quickly run away, making zigzag movements. Never try to hide from them by jumping into the water, because they will simply wait for you to come out.
Human gadfly
Botflies are parasitic dipterous insects native to Central Africa. Only one species is dangerous to humans - the human skin botfly. It is noteworthy that the adult insect does not consume food at all, but lives off the nutrients accumulated in the larval stage.
Throughout their short life, and gadflies live no more than a month, their only task is to find a mating partner and lay eggs. The hatched larva secretes special substances that corrode the skin and penetrates inside. With the blood flow, insects can travel throughout the body and even penetrate the brain, literally eating it out from the inside.
The human gadfly is one of the most dangerous insects, as it is capable of infecting the human brain from the inside.
The duration of parasitism is up to 9 months, after which the larva drills a fistula hole in the skin and emerges from the pupa. Within a few seconds, the adult emerges from the pupa and the cycle repeats. Favorite places for laying eggs are the back, stomach and scalp. The main symptoms of a gadfly infestation are a general deterioration in health and weight loss.
If the larva chooses an eyeball, part of the brain or another internal organ as lunch, this can result in death for a person. In tropical countries, you need to regularly treat your clothes with special repellents, even when drying outside, and not dine on food sold on the street.
Predator
Predators are the largest species of bedbugs in the world: the length of an adult individual can reach three centimeters. These insects inhabit almost the entire globe, including Russia. They live almost everywhere: from forest floors to basements and attics of human homes.
They feed on other small insects, lying in wait for them in dark places. When the victim comes close enough, the bug attacks it, pierces its proboscis and lets in a special secretion that dissolves the insides of the insect, after which it sucks them up. The bite of a predator feels like a bee sting; painful blisters may form in its place, swelling and severe itching may appear.
Another type of predator is found in the tropics - triatomine bugs. They bite sleeping people on the lips, eyelids and other parts of the body with thin, uncovered skin, for which locals call them kissers. According to statistics, triatomine bug bites claim more lives than malaria mosquitoes and other insects.
Bullet Ant
They live mainly in the tropics of South America. The way of life is not much different from other species of ants; they live in colonies in nests at a depth of 1 meter. The length of one individual can reach three centimeters; the insect has powerful jaws.
Bullet ants are predators and hunt other insects, spiders and even birds . A person is not a direct target for them, but a colony disturbed by him can attack in self-defense. The venom of such an ant causes paralysis of the limbs and convulsions, but one bite usually does not lead to the death of a person.
Triatomine bugs
They have another, more erotic name - kissing bugs, since these creatures, of which there are 130 species, love to bite a person near the lips. They are widespread in the tropics of South and Central America, Africa, Asia and Australia. These species mainly feed on plant foods, but there are also parasites that drink the blood of humans and large animals. They, as befits bedbugs, attack a person at night when he is sleeping and bite into his lips. It would be nice, because they can still give him the parasite that causes Chagas disease. Up to 12,000 people die every year from such passionate nighttime kisses. The slightest bite, which a person does not even feel, leads to such serious disruptions in the body’s functioning that it is impossible to eliminate it without the help of medicine.
Top 10 most dangerous dogsAccording to most dog handlers, aggression in a dog is not innate, but is formed in the process of upbringing or improper training. Any...
Malaria mosquito
Malaria mosquitoes are widespread throughout most of the world, but are most concentrated in humid tropical countries. On the territory of Russia they live in Western Siberia. Mosquitoes are carriers of malarial plasmodia, the causative agents of a dangerous disease.
Insects feed on the blood of people and animals and transfer parasites from sick to healthy people . It is easy to distinguish a malaria mosquito from an ordinary one: when an insect drinks blood, its abdomen lifts up almost perpendicular to the surface of the skin; in ordinary mosquitoes it is parallel.
There are several types of malarial plasmodia, and each of them causes certain changes in the patient’s body, but the most severe form of infection, common in the African region, causes fever, anemia, enlargement of the liver and spleen, and in 80% of cases ends in the death of the patient.
6) Malaria mosquito (sandfly)
Parasitic malaria mosquitoes pose a significant danger to people. In their genus they have about 10 subspecies of their family. Basically, Indian and African species are more dangerous. These small dipterous insects are carriers of parasites and infections. The malaria mosquito goes through a whole cycle of infection. Initially, he becomes infected with Plasmodium from a human host. The malarial plasmodium then multiplies inside the mosquito. Then the mosquito, after 5-10 days, becomes the carrier of the infection and its main source. There are mosquitoes that carry not only human, but also animal plasmodium. The most dangerous diseases transmitted by malaria mosquitoes are: malaria, threadworms, yellow fever and encephalitis.
African honey bee
The most dangerous insects in the fauna of the African continent are the Africanized bee. This is an artificially bred hybrid that was not found in nature until 1956, when Brazilian geneticist Warwick Kerr crossed common European honey bees with wild African ones.
The scientist planned to breed a new species that would combine the high performance of African bees with the calm disposition of European ones. The experiment did not live up to the hopes placed on it and led to the emergence of aggressive killer bees.
African honey bees differ from their domesticated counterparts:
- They are several times more aggressive than ordinary bees and attack everyone who comes within ten meters of the nest.
- They attack their victims in a swarm and are able to wait for a long time and pursue them.
- After the appearance of an external stimulus, the bees calm down after at least 8 hours.
- They cause enormous damage to apiaries, destroying domestic bees and taking honey with them.
An African bee sting is no more dangerous than a regular bee sting, but the specificity of their behavior leaves the victim no chance: the bees attack and sting in a swarm, introducing a lethal dosage of poison equal to approximately 500 stings.
Fire ants
In terms of lifestyle and habitat, they are very similar to bullet ants, only with the difference that they are 2-3 times smaller. In some South American Indian tribes, fire ants (in the local language - takandir) are used for initiation rites.
The boy receives the right to marry and hunt only after he puts gloves full of ants on his hands and stands firm for 15 minutes, and the ritual must be repeated 20 times. For several weeks before initiation, boys must drink a special decoction of dead ants.
Local shamans believe that this will help boys develop immunity and cope with bites more easily. The solenopsin contained in the venom causes local tissue swelling, paralysis of the limbs, nausea, fever and dizziness. An ant sting feels 30 times worse than a bee sting, and even one dose can be fatal to an allergy sufferer.
Giant Asian hornet
Ordinary hornets do not cause fear to most people, but even locals try to stay away from these Asian giants. In the homeland of these insects - in Japan and Thailand, they are called murder hornets. The length of an individual can reach seven centimeters, it is the world's largest species of hornet known to man.
Insects prefer to live in paper nests made of bark, which they build in light forests or groves. They feed on other insects and attack humans only in cases of obvious threat, but they can harm people in other ways: hornets massively destroy families of domestic honey bees, causing significant losses to beekeepers.
The venom of murder hornets contains a substance called mandorotoxin, which destroys brain neurons and inhibits the activity of the nervous system. The bite itself is also very painful: survivors say it felt like hot nails were being driven under their skin. One dose of poison causes severe swelling and tissue necrosis, and an encounter with several hornets can be fatal for a person.
Megalopyge opercularis
This hairy caterpillar of one of the moth species recently began to be called Donald Trump's caterpillar, for its resemblance to his hair. But the cute and fluffy appearance of this insect is deceiving. The fur, under which the caterpillar's body is hidden, consists of hairs with poisonous spines. If a person decides to pet a caterpillar, he risks receiving a powerful toxic injection. Upon contact with human skin, the thorns dig into it and break, and the poison causes a severe burning sensation. Particularly susceptible people may experience dizziness and vomiting. These insects are common in the USA, Mexico and northern Central America.
Tsetse fly
The tropical forests of Central Africa are home to another deadly insect - the Tsetse fly. It can be distinguished from an ordinary fly by a characteristic pattern on the wings and a large, pronounced proboscis. The real scourge of the African continent is not the flies themselves, but the trypanosomes living in their blood.
Flies feed on blood and become infected from antelopes, and then transfer the microorganisms into the blood of other animals through their saliva. Characteristic signs of “sleeping sickness” are swelling of the lymph nodes, skin ulcers, drowsiness and paralysis. People with trypanosomiasis can suddenly fall asleep while doing simple things, which is why the indigenous people gave it a name accordingly.
There are two forms of sleeping sickness - Gambian and Rhodesian.
The first can occur in humans and primates and lasts up to five years, the second is specific to humans and is acute, destroying the body in six months. More than 2,500 cases of the disease are diagnosed every year in Africa. Sleeping sickness is easily treatable, but the drugs are expensive and inaccessible to the majority of affected people below the poverty line.
| Top insects | Habitat | Danger to humans |
| 1. Black-legged tick | Northern USA, Western Europe, Ukraine | Carries Lyme disease pathogens and feeds on blood |
| 2. Rat fleas | Everywhere | They carry pathogens of various diseases and leave ulcers from bites. |
| 3. Malaria mosquito | Everywhere | Carries malaria pathogens, feeds on blood |
| 4. Tsetse fly | Central and Southern Africa | Carries sleeping sickness pathogens |
| 5. Human gadfly | Central America | Larvae parasitize the human body |
| 6. Fire Ant | South America | Painful venomous bites |
| 7. Bed bug | Everywhere | Feeds on blood and lives in human homes |
| 8. Africanized bee | Africa | Destroy peaceful bees, are aggressive, attack people |
| 9. Black Widow | Southern Europe, South America | The most powerful venom among European spiders |
| 10. Termites | Everywhere | Destroying wooden buildings |
Around the world, tens of millions of people die every year from diseases carried by insects and from their bites, but we cannot turn a blind eye to their benefits. The most dangerous African bees provide local residents with honey, ants destroy other more dangerous pests, and even parasitic insects regulate natural relationships, infecting old and sick animals.
Author: Alexey Simonov
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Diamphidia (Diamphidia locusta)
This is a small bug of light brown color with dark spots. Distributed in Central and Southern Africa. It is believed that this insect has the most powerful poison. However, it is not the bugs themselves that are poisonous, but their larvae. African tribes have been using larvae poison for a long time. Arrows treated with this toxin kill an animal of about 500 kg within a few hours. The poison remains deadly for a year.
The toxin affects the nervous system, and those who have received a portion of the poison are deprived of the ability to move and breathe, so the meat of killed animals is not contaminated, it can be eaten, it is only necessary to cut out part of the carcass near the arrow.
The poison kills a person almost instantly; there is no antidote yet. However, death from this toxin is very rare. The larvae are unsightly and are found in remote areas. They defend themselves and do not show aggression towards the living world.