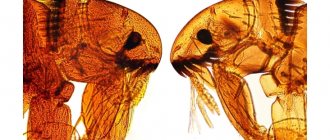
What do hornets look like? (photo and description)
These representatives have different height parameters from 18 millimeters to 35. One of the largest is 55 millimeters in length. In their structure, one can note a large head and a prominent crown. The compound eyes are located at the back. The color of the head is presented in a wide color palette - from black to yellow. They are also characterized by a striped belly, thin wings, strong jaws and large eyes.
Why are hornets called that?
The roots of the word come from the Latin Vespa crabro (literally translated as “hornet wasp”). The common hornet is a species of large wasp that lives in Europe. It is larger in size than the common wasp, but smaller than the Asian hornet. In everyday life, hornets are called differently: “pirates”, “winged corsairs”. If we consider the meaning of the word hornet, then it means “evil man”, “obstinate”, Old Russian (srshen), Russian cer - Slavic (strashen), Polish (szerszen). In the 19th century, the genus Vespa was divided into two genera: hornets (vespa) and wasps (vespula), which means small wasp.
Hornets lifestyle
It is very interesting to watch how hornets live. Colonies live in hollow trees, occupy empty beehives, and attics of houses. The house consists of horizontally molded honeycombs in the amount of 5-7 pieces. Moreover, up to five thousand eggs are laid in each of them. The highly organized life of large wasps allows them to protect their offspring and survive enemy attacks. Special “guards” notify other relatives that danger is approaching, and the whole family rushes to attack. Defense weapons are toxic and, in severe cases, can be fatal.
Hornets eat insects
Attention! A hornet sting in humans is characterized by painful sensations and causes allergic reactions, although the sting itself does not remain in the wound. This is partly due to the dose of poison introduced into the body. In some insect species it is about 2 mg. Compared to a bee sting, this is more than 2 times more. The severity of the bite is also affected by the subspecies of hornet that caused it. The substance of the Asian hornet is considered the most dangerous and toxic.
Spiders, mosquitoes, caterpillars, dragonflies, bees, flies, and butterflies that live next to large wasps in nature are potential “contenders” to be eaten at one fine moment. Hornets lead a 24-hour lifestyle. This explains that they also catch nocturnal insects for food, as a result of which the daily “catch” of an entire family of “pirates” can reach up to half a kilogram of live food. For gardening, captured pests in such quantities are a significant help from huge wasps, which cannot be said about apiaries. Hornets catch bees, climb into the hive and feast on honey. The damage to beekeeping is enormous. A hornet that is not noticed in time can single-handedly destroy a bee colony.
Interesting. It would be incorrect to say that live food is consumed by adults. For growth and development, the larvae need food from finely chewed insects, while the adult hornet is content with flower pollen, their nectar, as well as ripe pulp and juice of fruits and vegetables. The fed larvae themselves secrete a sweetish sticky substance, which the worker wasps feed on in unfavorable weather.
Where do hornets live?
The main part lives in the North of the globe. They can be observed in many parts of the planet. These insects have adapted well to warm Asian countries. European hornets live in agricultural areas, as well as in forests, thickets of groves, and large bushes. They like to build nests in toilets, on verandas, and in summer houses. They are also easy to find under stairs or in window openings. The vespin subfamily, living in the mountainous regions of Japan, is one of the most dangerous. In the Primorsky Territory of Russia you can find several species of these insects.
What do hornets eat?
They love rotten trees and stumps. But their favorite food is rotting berries. They prefer foods that contain a large amount of sugars (tree sap).
They can feed on other insects (wasps, bees, grasshoppers). They kill them with their poison and then chew them with powerful jaws. Hornets attack apiaries, destroying entire colonies. They are attracted to the scent of honey bees. Some types of hornets look for dead insects and are even ready to feast on food waste (meat products, fish).
Reproduction
As soon as the weather changes and the sun begins to warm up, the female hornet is actively looking for a place to hatch her eggs. She flies over large areas in search of shelter to start a family. As soon as it finds a convenient corner, it immediately begins building a nest. Each egg has its own sector. After a few days, a small individual will hatch from it. She chews the lid and gets out. Long before winter, the female breeds offspring, which will continue the work of the uterus.
After fertilization, the males die. Then the old queen dies, and after some time, the individuals that were not fertilized die. Fertilized hornets overwinter and then create their own nest. Only thanks to a well-coordinated organizational system in the hornet family, reproduction is successful. The division of duties (females, males and queen) allows feeding, building and raising offspring in a harmonious system.
Hornets are different: friendly and dangerous
The average weight of hornets is 2 g, with males being twice as small as females. Small transparent, mica-like wings cover the body. Vespa hymenoptera insects live only a few months (males), and about 12 months for females. Before their death, the males fertilize the queens and die themselves. Fertilized females, capable of producing offspring, fall into suspended animation, staying there through the winter and waiting for the warmth of May, when the air warms up to 10 degrees.
The “head of the family” is the uterus. This is a female capable of reproducing offspring. She is a prime example of how hornets hibernate. If the males die with the onset of cold weather, the female wasps find a quiet, warm place to survive. The spring months are spent busy with arranging the nest, building honeycombs, and caring for the larvae until mid-summer. When they mature, they themselves become protectors and providers of food for the newly emerged larvae and the queen. A colony of hornets, in which individuals live together for only a few months, consists of a “creator” - the queen, work “horses” (hornets), young queens and males that do not have stings.
Building a nest
An individual that has survived the cold season becomes the founder of the nest with the arrival of spring. Soon the female finds a safe place for herself high in the mountains or inside a tree. Then he arranges his place in the rooms where people live and in wooden outbuildings. Gnawing on woody species and crusty formations, insects build their houses from numerous steps. The wood goes through the stage of processing into a papyrus product. Such multi-level houses resemble products made from a thin napkin. You can see such structures in old trees, bird houses, barns. The color scheme of such designs can be varied. Brown stripes go with bright colors. Some of them look like an oval shape. But some are also round in shape. The size of such a structure is 700 by 400 mm.
Quite often, people compare the homes of hornets to a blotter nest, comparing the similarities with paper production. The main initial product for construction is thin tree cover and branches of young trees, well processed by hornets. Sticky saliva acts as a fastening material. Once applied to the house, it dries and hardens. The result is a rough, rough wrapper. The poor appearance of the structure is explained by the fact that the hornets build their houses from rotten wood. Some representatives of insects build their burrows with intricate labyrinths. They can be found deep in the ground or in forgotten animal holes. The depth of the hole can be about 60 meters.
Hornets nests
Hornets nest
Insects create nests by chewing wood into papery building material.
The color of the nest may vary:
- brown
- yellow
- yellow-white
- beige
Often nests can be seen on roof eaves and under decking, tree hollows, birdhouses, caves, and attics. Outdoors, hornets usually build nests high above the ground, such as in trees, on utility poles, or in dense bushes.
Most often the nest is discovered in the fall when the leaves have fallen, by which time most of the hornets will be dead or dying, leaving only the queen to hibernate and survive the winter.
Where do hornets spend the winter?
Hornets cannot tolerate extreme cold. But they carefully prepare for the winter. They set up their burrows on the property, at the dacha - wherever they can find shelter. How do insects manage to survive the winter and shelter from wet weather? Only the queens prepare for a long winter sleep. They play the role of leader in the family. For the female, the important point is to survive the winter and then lead her clan. It is also safe to hibernate. To do this, she has to stock up well on nutrients. Finding a good shelter can be considered a necessary condition for the survival of the uterus. Finding a safe place for the winter is a crucial moment in the life of the uterus.
To ensure ideal wintering conditions, you need to choose a quiet corner. Any option may be suitable except warm and cozy houses where people live. Since the warm temperature in the house can awaken the female earlier, and she will begin to build a nest. This scenario will lead to bad consequences. It will be difficult to find not only wood for the nest, but also food for the offspring. The uterus under such conditions is doomed to death. An important factor in favorable hibernation is stability, without sudden temperature changes. A large number of females die during harsh winters when there is little snow. They become easy prey for birds. As a result, most die.
Features of nutrition and reproduction
Adults consume nectar from flowers and can attack other people's hives to search for food. In addition, they consider berries and fruits a delicacy - they often turn them into an unsuitable form for further consumption.
If we talk about new offspring, then the nutrition here is a little different - their diet should include animal proteins for full development. The adult insect catches small flies, wasps and bees for feeding. After this, they thoroughly chew the prey, and the resulting composition is given to the larvae. The larvae thereby thank them with a substance that has a sweet taste - hornets really like such drops.
At the beginning of the autumn period, the female begins to search for a home in order to breed new offspring. The female observes tree insects to select the smallest species, then attacks the queen of the nest. If she wins a place to live, she acquires new hornets that have dark brown or blue wings.
But it is worth noting that the nest can contain a large number of soldiers who fiercely defend the right of their queen to rule the colony.
After the queen changes, the individual secretes a special substance that helps it disguise itself as a dead queen. As a result, the working representatives of the family accept her as their queen and continue their normal lifestyle.
After this, the female lays eggs, from which larvae eventually emerge; they are fed by the working individuals of the colony until they mature. Next, the mating process takes place, after which some of the hornets die. The females leave the nest and begin searching for a new home.
It is rare to encounter a situation where hornets independently build a nest where they live in complete peace. This is possible provided that there are no other people’s nests near the habitat. A long search can lead to mass death of the family.
How long do hornets live?
Hornets differ in appearance (body size) and perform different tasks and functions. In autumn, males begin the process of fertilization, after which they soon die. Working individuals have a short lifespan - no more than three weeks. The female lives the longest - about a year. Working females and males do not live long. They grow up at the end of summer, and in the fall (early September) most of the individuals die. The surviving insects survive only until the first cold weather. Males are needed by the family only for fertilization. After mating they live only a few days. The female is able to withstand the cold and live in hibernation for up to a year. In the second winter, its life cycle ends and it dies.
Life cycle of a queen hornet
Despite the fact that the queen lives no more than a year, during this period she manages to lay hundreds of eggs. Her life follows a certain cycle. Viable young females appear in the hive in late summer and early autumn. Together with them, males born from unfertilized eggs also grow up. By that time, the colony has reached its maximum size.
There can be several hundred hornets in a nest. Mature females and males leave the home to mate. After this, the males die, and the seed transferred to the female is stored in a special section. It will be stored until winter is over.
This is interesting! The queen actively feeds during the last days of autumn, when the weather is still warm. This allows her to stock up on food for the upcoming winter.
In November, life in the hive calms down, because almost all the workers die. Old housing will not be reused. Once the colony survives the cold months and emerges, it will begin building a new home for the family. Not all insects manage to survive until spring.
Hornets usually hide in:
- walls of wooden buildings;
- cracks;
- in tree hollows or under their bark.
Nutrients accumulated during the autumn months are used sparingly due to the transition of the insect body into diapause. This period is characterized by a slow metabolism.
For it to occur, two conditions are necessary: a decrease in daylight hours and a decrease in air temperature. Diapause increases the hornets' body's ability to withstand any external influences. But this condition does not save females from potential predators. Insects hiding in tree hollows are often discovered by mammals and birds, which subsequently eat them.
With the onset of spring, young females wake up from hibernation and begin an active search for food. The main source of food for them is insects. As soon as fruits ripen on the trees, the hornets' menu becomes more varied. The future queen begins to fly around the territory to search for a new place to build a hive.
A suitable option in this case might be:
- areas under the roofs of residential buildings;
- tree hollows;
- birdhouse;
- depression in the soil.
To make the first comb for laying eggs, the queen collects tree bark and chews it. She usually arranges from 40 to 50 cells. Alone, she can make a nest the size of half a soccer ball. The female lays eggs purposefully. The peculiarity is that some of them are fertilized, while others are not. From the former, females emerge, which can later turn into queens, and from the latter, working individuals are born.
Types of hornets
There are several dozen popular species. Hornets are part of the wasp family. They have a lot in common, but have a number of distinctive features that set them apart from other individuals. There are 23 species of hornets. The most common types:
- Common (living in Europe): brown, body length 35mm. It is distinguished by two bright stripes on the lower part of the body. It is well known to Russian gardeners and beekeepers, but was recently brought to the USA and now lives there.
- Black hornet (Dybowski): stripes on the black back are yellow (predator color). The wings are brown. Length 35mm. Few people are familiar with this type of hornet. Listed in the Red Book. They live in the Amur region, Transbaikalia and Primorsky Krai.
- Giant Asian: its body length is 6 cm, has a large wingspan. It is distinguished by its bright head and striped back. lives mostly in Asian spaces. It is also found in the mountains of Sri Lanka, as well as in India and Taiwan. It has a large sting about 6mm. The bite is dangerous and contains a toxic substance. One of the largest in the world.
Some of the most dangerous hornets are Asian hornets, called “killer” hornets. - Japanese hornet (Japanese): a subspecies of the giant hornet called the "sparrow-bee" lives on Sakhalin. Large yellow head, large eyes, adjacent to them are 3 ocelli. The bite is painful and has dangerous consequences, as the venom contains toxins.
- Eastern: has the most elaborate coloring of all types. It is distinguished by a wide yellow stripe on its belly. Bright red with a crimson tint to the wings and body. One of the many species that tolerates heat well. Well adapted for living in deserts and steppes. Originally from North Africa.
- Philippine hornet: has a black color. Another name for the species is Lamentable. It is dangerous because it produces highly toxic poison. The bite is very unpleasant. The main habitat is the Philippine Islands.
Where live?
They live in regions with temperate climates, the largest number of these representatives being in Europe. Also, some species live in North America, North Africa, and Asia.
To equip his colony, he builds nests that can have more than 10 tiers. They live in a family in which there is a queen, female (working individuals) and males.
Let's take a closer look at the design of the sockets:
- Nests can be round, oval or pear-shaped.
- Have several tiers.
- Outwardly, it resembles crumpled corrugated paper, the surface is rough.
- Regarding color, it can be completely different, beige, yellow, brown and purple.
- Dimensions may also vary; such a design can reach 40 cm in width and up to 70 cm in height.
To build their home, insects use soft wood fiber; they chew it, which makes it possible to obtain a sticky and pliable building material.
The place for construction can be chosen completely differently, in trees, under a roof, in a cave, in hollows, there are species that build nests underground. In the photo you can see what the nest looks like.
Differences between a hornet and a wasp
These individuals are easily distinguished not only by size. The main difference from the wasp is its large, impressive jaws, unlike representatives of wasps. The coloring is slightly different. In the hornet it is more diverse. It is larger in size and has a hairy fluff. The hornet is distinguished by its movable whiskers and crown. There are similarities, but the wasp has a narrow waist.
How dangerous are hornets to humans?
Hornets can pose a danger to people in some cases. To protect themselves, the hornets gather very quickly; for this, the individual releases a special substance - an alarm signal. Other individuals can react to it and fly to the aid of a comrade and attack the offender en masse. Therefore, you should not touch the hornet in vain.
The mortality rate from hornet stings is very low, but the risk is still present. In addition, each subsequent sting will be worse tolerated by the body, because immunity to the poison is not developed, but on the contrary, the negative reaction intensifies.
Hornet sting: harm of poison and consequences of toxic effects
The bite of this insect is more painful than a bite from a bee or wasp. It all depends on the individual body’s ability to tolerate pain. If a sting occurs, it is advisable to help the person as quickly as possible. Hornets have a needle with which they can pierce the human body repeatedly. Individuals from Asia are more poisonous than European ones. The bite is accompanied by sharp pain with severe swelling. May cause: severe pain and hemorrhage followed by suppuration.
Does the hornet bite or sting?
The hornet has powerful jaws. His bites are very deep. The wounds take almost a week to heal. When attacking a person, hornets use a sting that leaves scars in the form of dots, but they can also simply bite with their claws. The poison is dangerous because it is toxic and can poison the body. The bite is very painful and the consequences can be unpredictable. Elderly people, children and allergy sufferers are especially at risk. Swelling and inflammation can appear instantly after an insect attack, and suppuration is also possible. Signs of poisoning are characterized by nausea and severe dizziness.
Bites pose the greatest danger to those people who have an allergic reaction. They can worsen a person’s condition from several hours to 2-3 days. The bite is dangerous because the body of a person with allergies does not fight well against the effects of the poison. As a result, large swelling and difficulty breathing may occur. In some cases, people lose consciousness. The insect venom contains histamine, which most often causes a person to feel unwell, up to and including anaphylactic shock. Fatalities are caused by neglect of medical care and delayed first aid.
Hornet-human interaction
The insects look quite menacing; females up to 35 mm in size can frighten any person. But, despite their menacing appearance and the presence of a sting, hornets try to avoid contact with people. Insects are not attracted to jam on the table or other sweets, so they do not have to be driven away like annoying wasps. Workers and young queens are dangerous only near the nest. They selflessly defend their colony, and at any sign of a threat they mercilessly sting everyone within a radius of 2-3 meters.
A family of hornets settled in a remote corner of the garden can be beneficial. Predatory insects are capable of destroying a large number of tree pests - caterpillars, butterflies, flies, beetles and spiders. The total weight of caught food reaches 500 grams.
Attention. Due to frequent cases of destruction of hornet nests, in some places the insects were on the verge of destruction. In Germany, ruining a colony is punishable by a fine of 50,000 €.
The Hornet Queen is the center and foundation of the family. All functions of procreation are assigned to her. Premature loss of the queen is irreparable; the colony is doomed to slow extinction.
What to do if bitten by a hornet?
Usually people have little idea what to do if they are bitten by an insect or do not have enough knowledge to provide first aid. The appearance of severe pain is not a sign that the human body is subject to destruction. You need to know that insect venom contains components that have a strong effect on nerve endings. Therefore, the pain shock can be pronounced. In a normal situation, it is quite difficult to predict the consequences of a bite; each person’s body reacts individually. For some, a bite can only cause pain and swelling, while for others it can end in disaster, including asphyxia, loss of consciousness and even death. If bitten, first aid must be provided immediately. Inaction is unacceptable!
- The first necessary condition that you need to remember is that there is no sting in the wound, only poison.
- Try to remove the poison by sucking it out.
- Treat the bite site with a solution of citric or acetic acid.
- Try washing with any soap solution.
- Treat the wound with an alcohol-containing solution or hydrogen peroxide.
- After this, you need to apply cold with wet sugar. This reduces the risk of poison spreading throughout the body.
- You should not drink alcohol after a bite. This will cause even more swelling and worsen the person’s condition. Bites to the neck and head area are very dangerous.
- From folk remedies, you can use the juices of plants such as dandelion, plantain or soda solution. Onion and garlic cloves are also suitable for treatment.
Signs of an allergic reaction from a bite:
- severe headaches;
- elevated temperature;
- cardiopalmus;
- hard breath;
- pain in the abdomen.
If you have these symptoms, you need to take painkillers in tablet form. This reduces the effect of histamine. You also need to drink a lot of water to reduce poisoning.
It must be remembered that if none of the methods help with a bite, and the condition begins to worsen, call a doctor immediately.
Reaction to a hornet sting
If someone is stung multiple times or has a severe allergy to insect venom, systemic reactions may occur that can affect the entire body. Typical symptoms and reactions to bites:
- Strong pain
- Redness
- Swelling around the bite site
If a person is allergic:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Cold extremities
- Blue discoloration of the neck, eyelids, face, ears
- Attacks of suffocation
- Swelling of soft tissues
- Red spots on the body
- Loss of consciousness