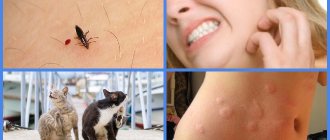
Cat and dog fleas
Cat fleas (Ctenocephalides felis) are biologically different from dog fleas (Ctenocephalides canis), but these differences can only be visualized using a microscope.
Despite their name, cat fleas bite dogs and many other animals, as well as people. In the United States, the predominant share of infection comes from cat fleas, and in Europe – from dog fleas. In the photo, the dog flea is on the left, and the cat flea is on the right.
Why are fleas dangerous?
Massive flea bites greatly annoy people; scratching can cause irritation, itching of the skin, suppuration, and dermatophiliasis. A large number of hungry fleas can lead to anemia and emaciation of animals.
In addition, in nature there are fleas infected with tularemia microbes, tick-borne encephalitis viruses, and HFRS. Fleas of cats and dogs serve as intermediate hosts of helminths: cestodes of dogs and rats.
The main danger in epidemiological terms are rat fleas, which live in natural plague foci and can involve synanthropic fleas in the spread of a particularly dangerous infection.
How fleas bite
Cat fleas are obligate parasites. Both male and female individuals live solely off the blood of the host. This type of feeding is also characteristic of some types of flies. In other parasitic insects, only the female is involved in blood sucking. Fleas are also among the rare insects that require blood throughout all stages of their life cycle. This also applies to larvae, which consume feces of adult fleas, saturated with blood.
Non-motile ectoparasites
Fleas live on the surface of the host's body, rather than inside it, and are therefore classified as ectoparasites (parasitic externally). When sucking blood, parts of the oral apparatus are embedded under the skin of the host, while the body and other parts of the insect's body remain motionless, so fleas are considered sessile ectoparasites. Fleas do not attach to hosts like ticks. Their body is covered with spines, bristles and ridges that prevent the insect from removing the insect from the host's hair.
Ways to control fleas
Often people find it difficult to control these insects. To make it easier to get rid of cat fleas, it is important to detect their appearance as early as possible . Therefore, owners should be attentive to their pets. It is important to note that a pet can become infected in several ways:
- Contact of a pet (even short-term) with a carrier of these pests;
- Fleas can be brought into the house on shoes or clothing;
- A cat or dog can bring these insects from the street.
Once fleas are detected, you must immediately begin getting rid of these dangerous pests. There are a number of measures for this purpose:
- The first step is to treat pets that may be carriers of adult fleas with specialized products. Flea collars, sprays, shampoos and drops work well for this purpose. All these products are available for both cats and dogs.
- Then it is necessary to treat the room where they were found from pests. There are various products available on the market for this purpose. Insecticide concentrates are by far the most popular means of combating these insects. From such a concentrate it is necessary to prepare a solution and spray it around the apartment, paying special attention to places where fleas may accumulate.
- To get rid of surviving larvae, it is recommended to use insecticidal dusts, which need to be scattered in problem areas.
How do fleas feed?
Exploratory samples
Once on the host's body, fleas first look for a suitable place to bite using their palps. The skin is then punctured and the search for the blood vessel begins. The flea injects saliva into the wound with anti-clotting properties, which helps in the search for blood.
A test piercing causes an allergic reaction on the skin, which is why flea bites are often observed in clusters of 3-4 pieces. The abdomen consists of 4 salivary glands, which are connected to the oral cavity. In addition to the anticoagulant, saliva contains a substance that facilitates the penetration of the proboscis into the skin.
Distractions during blood sucking
Fleas are often distracted while sucking blood, this is due to the movement of cats or dogs. Once interrupted, the parasites move and bite nearby, resulting in several bite marks appearing on one area of skin.
Duration of blood sucking
Cat fleas begin sucking blood within 5-20 minutes after attacking the owner. They become saturated within the first 10 minutes. On average, females suck blood for 25 minutes, and males for 11 minutes. Females suck twice as much blood as males.
Digestion
Blood that enters the digestive tract does not flow back into the vessel thanks to the valve, which ensures one-way movement of blood flow, preventing regurgitation. The digestive tract releases components necessary for digestion. The digestive enzymes of fleas are adapted to digest blood.
It is believed that there are gender differences in the digestion process, as female fleas digest blood faster than male fleas. It is important for females to digest blood quickly as they need nutrition and energy to lay eggs.
Adult parasites suck much more blood than they can digest. Because blood passes quickly through the intestines, it is only absorbed by nearby cells in the intestines. As a result, fleas excrete large amounts of feces, consisting mainly of undigested blood. These feces serve as the main source of food for the larvae.
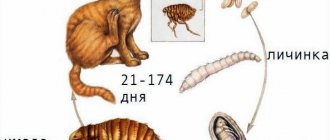
The role of blood in the life cycle of fleas
Fleas feed on blood throughout their entire life cycle. Even larvae need fecal digested blood. Adult insects - females and males - suck the host's blood. Blood is not just food for fleas; without it, mating and reproduction are impossible. Young individuals without blood do not reach sexual maturity: the ovaries of females and the testicles of males remain underdeveloped.
Hungry adults are not capable of mating. Blood sucking stimulates sexual development and further reproduction. Adult insects consume much more blood than they can digest. Blood passes quickly through the intestines, and only part of it is absorbed. As a result, the adults excrete copious amounts of feces in the form of undigested blood.
The larvae live off this feces. In this way, adult insects take care of their offspring. This is believed to be the first step on the evolutionary ladder for fleas to care for the next generation.
Do fleas bite through clothes?
As a rule, they do not bite through clothing. Jeans, socks and even thin fabrics will prevent bites. However, there are a few exceptions. Fleas can bite through thin, tight fabric, such as tights, sweatpants, or yoga pants.
Fleas bite under clothes
Not finding direct access to the skin, they will crawl under clothing and bite there. These parasites prefer to feed in hidden places and suck blood while remaining unnoticed. If disturbed while bloodsucking, they hide in the seams of clothing for up to 24 hours and periodically come out to bite again.
Why Clothing Protects Fleas
According to some experts, although clothing serves as protection against bites, it actually helps parasites. It is easier for a flea to attach to the fabric fibers of clothing than to the bare skin of a person. Once on the human body, bloodsuckers will find a place with an area of skin open to a bite or crawl under clothing to do this. Clothing is a kind of camouflage for them, under which they freely suck blood.
What areas of the body do fleas bite on?
Cat fleas jump an average of 15 cm in height (maximum 20 cm). This height corresponds to just below the human knee. Once on a person, they bite in the place they hit, without significant movement. As a result, bites are usually found on the legs, feet and ankles.
In rare cases, bite sites appear higher; for example, if a person is sitting on the floor, then fleas easily end up in unusual places: in the pelvis, groin, and wrists. Bites on the face are unlikely, except in children.
The best clothes against flea bites in the apartment and on the street
Clothing that does not leave exposed skin is best at preventing bites. Wearing socks and long pants will protect against leg bites. However, there is still access to exposed skin between the socks and trousers; this can be solved by tucking the trousers into the socks.
Repellents for clothing
To stop fleas from attacking clothing, repellents such as permethrin are used. Permethrin is an insecticide, but in low concentrations it acts as a broad-spectrum insect repellent. Permethrin repels fleas, mosquitoes, ticks and biting flies. It binds tightly to the fibers of clothing, so it is resistant to water, washing and drying. Treated clothing repels insects for up to 6 weeks or 6 washes.
What do cat flea bites look like?
Flea bites vary in intensity depending on the human body and the degree of sensitization. Sensitization is an increase in the body's sensitivity to irritants, causing allergies. As a rule, the reaction to insect bites occurs in 5 stages of sensitization, which correspond to the frequency of previous bites.
5 stages of sensitization
- In the absence of previous contacts with parasites, sensitization does not occur. In this case, there will be no reaction to the bite.
- Subsequent stings cause a delayed or late reaction after 24 hours.
- As the frequency of bites increases, both immediate and late reactions occur.
- Continued flea bites on human skin reduce the intensity of the late reaction. After all, only immediate reactions appear.
- Over time, with an increase in the frequency of bites, complete desensitization is achieved in the human body - immunity to insect bites appears.
Young children have a low level of sensitization, and, as a result, flea bites in children cause more pronounced delayed reactions than in adults. Achieving complete immunity in adults and children is rare, since the second stage lasts at least 1.5 years.
Immediate reactions
Hives
Within 5-30 minutes, bites on the body cause hives. Hives are areas that rise above the surface of the skin, framed by a halo of redness. Redness of the skin occurs due to dilation of superficial blood vessels. The areas of urticaria have an irregular shape, but clearly defined boundaries. The diameter of the urticaria areas is 2-10 mm. The urticaria quickly disappears without any significant symptoms of irritation.
Bite marks
Fleas are adapted to pierce the skin without leaving damage. There is little or no bleeding at the bite site. Bites on the human body do not leave marks unless the insect gets into the vessel. Bite marks, represented by red dots called hemorrhagic marks, disappear within 3-4 days.
Delayed skin reactions
Papules
If a person is bitten by fleas, then delayed reactions develop 12-24 hours after the bite. Such reactions include, for example, papules. A papule or nodule is a cavity-free formation that rises above the skin level. Papules are accompanied by areas of skin redness around the formation. The diameter of the papule is 1-3 mm, and the redness reaches 20 mm. In rare cases, a vesicle or bubble forms inside the papule. Also, in the middle of the papule, the color of the skin sometimes turns black, indicating necrosis - the death of the skin area. Papules disappear on the third day, but in rare cases they persist for up to a year.
Flea bites often appear in clusters of three bites up to 3-4 centimeters in diameter. The bites are arranged in a line or triangle. This cluster is humorously called “breakfast, lunch and dinner.”
Bubbles (vesicles)
Flea bites rarely cause blisters on the skin. However, in atypical cases, delayed reactions appear in the form of a vesicle. Initially, the fluid accumulates under the skin in multiple vesicles, and after 2-3 days the vesicles grow and unite into a large vesicle called a bulla. The skin around the vesicle turns red. As healing progresses, the skin darkens and the vesicles disappear.
Secondary infections
Flea bites are sometimes very itchy and, as a result, make you want to scratch. Scratching damages the skin and creates conditions for bacteria to enter, which often happens. Infected bite sites are filled with pus, and phlycterns are formed.
Flycterna is a bubble surrounded by an area of reddened skin, inside of which there is serous or purulent discharge. When there is extensive damage to the skin, abscesses occur.
Pain after flea bites
Flea bites are not painful. In fact, people often don't notice they are being bitten until they see the fleas. As a rule, bites are recognized after a reaction appears on the skin, which may not appear at all, which is why it seems that fleas bite some and not others.
When they bite, they inject saliva into the surrounding skin. Saliva prevents blood from clotting, spreads, and softens the layers of skin. This helps the needle-shaped mouthparts penetrate the skin easily. After bloodsucking, there are almost no traces of damage left on the host’s skin.
Preventing fleas in cats
If you have just gotten rid of annoying parasites or want to avoid their appearance altogether, you need to take a number of measures:
- Bathe your cat regularly with flea-proof shampoo and wash her bedding frequently.
- Periodically inspect the animal for parasites.
- It is not advisable to let your pet go outside, where he can meet an infected animal and pick up fleas from it. After a walk, wash your cat with anti-parasitic shampoo.
- Put a flea collar on your cat.
- Give the animal injections against blood-sucking parasites at the required intervals.
How to distinguish flea bites from bedbug and mosquito bites on humans
In this article, we looked in detail at what flea bites look like. But even with this knowledge, it is difficult to immediately recognize their bites, which are confused with the bites of mosquitoes and bedbugs. The symptoms of a flea bite in humans are indeed very similar to the symptoms of other bites - hives, itching and swelling occur. To learn how to distinguish, below is a table of the differences between flea, bedbug and mosquito bites.
| Symptom | Insect | ||
| Bedbugs | Fleas | Mosquitoes | |
| Bite marks | Small, deep bites with a hole in the middle and an area of redness around it. Blisters may appear around the puncture | Bite marks are medium-sized, hard, red dots. | Small red dots |
| Where do they bite? | Clusters of 3-5 bites form marks on any part of the body | As a rule, 2-3 bites form a mark. The tracks are called breakfast, lunch and dinner tracks. Most often they bite the legs and legs, less often the upper parts of the body | Single bites, dots appear all over the body |
| Appearance time | Bedbugs are nocturnal insects, so bites occur in the morning | Bites appear at any time | Bites appear at any time |
| Itching | Obsessive itching disappears within 1-24 hours | Goes away within 2-3 hours, does not always appear | Intense itching disappears within a day |
| Other typical symptoms | Brown stains on sheets and mattresses appear as a result of accidental crushing of bedbugs during sleep | Sometimes there is severe pain at the time of the bite. It is rare to spot an insect | The flight of a mosquito can be heard, and besides, after a bite, the skin is very itchy |
| Peak insect activity | Insects are active all year round | According to the Canadian Department of Environment, high activity occurs towards the end of summer. | Activity increases in summer and autumn |
The danger of fleas to humans
Cat fleas are dangerous to humans because they are carriers of infectious diseases, their bites can cause allergic reactions, the wounds hurt and there is a risk of their suppuration. If an insect has previously bitten a sick animal, there is a risk of transmitting the infection.
What diseases can cause parasite bites in a cat:
- Entomosis is a skin lesion characterized by itchy rashes. The bite area becomes swollen, ulcers may appear in the throat and mouth, and there is a risk of damage to the central nervous system.
- Dermatitis is an inflammatory lesion of the skin, accompanied by swelling, burning, itching, and blisters.
- Bartonellosis is a serious disease accompanied by rashes on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral infection that is accompanied by intoxication and damage to the membranes of the brain and spinal cord. The disease leads to severe complications and death.
- Helminthiasis is a disease caused by parasitic worms - helminths. Fleas are carriers of tapeworms and nematodes.
Bites are often accompanied by severe allergic reactions that may require medical intervention. When scratching a bite, there is a possibility of infection spreading and the wound becoming suppurated.