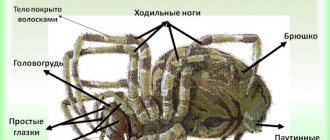
External structure
External structure of a spider
Spiders are heterosexual, and in most species the males are smaller than the females. This is due to the fact that when creating offspring of a female, it is then easier to eat the partner and produce more cubs. At the back are the warts, from which the warts stand out.
Body
The body consists of a cephalothorax covered with chitin, a hard exoskeleton. During its life, it can be updated up to 10 times, and the old one is reset only after a new one is formed under it.
Limbs
Spiders have four pairs of legs covered with small hairs. There are also two pedipalps on the body, which are responsible for the sense of smell. Next to the jaws there are also chelicerae, with the help of which the predator injects poison into the prey.
Interesting fact : thanks to the hairs on its limbs, the spider senses the direction of the wind and orients itself in space.
Color
The main components that determine the spider's color are bilin and guanine. They add brown and white to the body respectively. Also, other shades appear due to the light reflection characteristics of the hairs on the body.
Class Arachnida
Class arachnids , unlike crustaceans, live mainly on land, breathe with the help of trachea and lungs. The class includes three orders, in whose representatives one can trace the process of fusion of body parts. Thus, in the order of spiders, the body is divided into the cephalothorax and abdomen; in scorpions, it consists of the cephalothorax, protomothorax, and posterior abdomen; in mites, all sections are fused into one shield.
General characteristics of arachnids: absence of antennae, four pairs of walking legs, tracheal or pulmonary respiration, permanent perioral appendages - upper tentacles and pedicles.
The cephalothorax contains four pairs of simple eyes, mouthparts, and limbs (walking legs). The most common are spiders and mites.
Spider Squad
A typical representative of the order of spiders is the cross spider. It can be found in forests, parks, on estates, in houses, where they weave large trapping nets from cobwebs. The spider has the first pair of mouthparts - the upper jaws, equipped with sharp, downward-curved claws.
At the end of the claws, the excretory ducts of the poisonous glands open.
The jaws serve the spider to kill prey and for protection. The second pair of mouthparts are the tentacles, with which the spider probes and turns the victim while eating.
Four pairs of jointed walking legs are covered with sensitive hairs. The abdomen of arachnids is larger than the cephalothorax. At the posterior end of the abdomen of spiders there are arachnoid warts into which the arachnoid glands open.
The substance secreted by the glands hardens in air, forming spider threads. Some glands secrete a cobweb that is strong and non-sticky, used to form the skeleton of a trapping net. Other glands secrete small sticky threads with which the spider builds a trapping web. The third glands secrete a soft, silky web used by the female to weave a cocoon.
The spider entangles the victim in the trapping net with a sticky web, plunges the claws of the upper jaws into the prey and injects into it a poisonous liquid that dissolves soft tissues and acts as digestive juice.
Leaving the victim shrouded in web, the spider moves aside, waiting for its contents to be digested. After some time, the spider absorbs the partially digested food. This is how spiders partially digest food outside the body.
The spider's respiratory organs are represented by pulmonary sacs communicating with the environment. In addition to them, the spider has tracheas in its abdomen - two bundles of respiratory tubes that open outward with a common respiratory opening.
The spider's circulatory system is basically the same as that of a crayfish.
The role of excretory organs is performed by the Malpighian vessels; the spider has one pair of them, but they branch.
The hemolymph (blood mixed with lymph) of the spider washes these vessels and metabolic products exit through the lumens, then enter the intestine and are then excreted.
The nervous system is formed by the subpharyngeal node, the brain, from which nerves extend to various organs.
Spiders have numerous and varied sense organs: organs of touch (hairs on the spider’s body and on the legs), smell and taste (on the legs and legs), taste organs are also present on the lateral parts of the pharynx; organs of vision (eight simple eyes).
Some spiders are able to distinguish color, especially those. which look for prey on plant flowers (crab spiders).
Spiders are dioecious animals. Females are larger than males. In autumn, the female weaves a cocoon from a web and lays eggs in it. The eggs overwinter in it, and in the spring they hatch into spiders. Most spiders are beneficial: many small mammals, birds, lizards, and some insects feed on them. Among the spiders there are also poisonous ones - tarantula and karakurt.
They are very dangerous for humans and pets.
Squad of pincers
In most representatives of the mite order, the body does not have a clear division into segments or sections. There are a lot of ticks. Some of them live in the soil, others in plants, animals and humans.
Unlike spiders, flares have an indirect development.
The egg hatches into a six-legged larva, which after the first moult appears a fourth pair of legs. After several molts, the larva turns into an adult.
The red spider mite settles on the leaves of cotton and other valuable plants. It reduces cotton yields and causes plant death.
The flour mite settles in onions and grains. By eating away the embryo of the future plant in the grain, it causes the death of the seeds.
It causes food spoilage in warehouses. for example, various cereals, baked goods, sunflower seeds. Cleanliness and ventilation of the premises where food is stored is one of the main measures to combat flour mites.
The scabies mite (itch) causes the disease scabies in humans.
Females of this type of mite penetrate into the more delicate areas of human skin and gnaw passages in it. This is where they lay their eggs.
Young flares emerge from them, again gnawing passages in the skin. Keeping your hands clean prevents this dangerous disease.
Taiga ticks are very dangerous parasites of humans and animals. When sucking blood, they can infect a person with a serious disease of the nervous system - encephalitis. Under natural conditions, the causative agent of encephalitis is found in the body of wild animals. The role of ticks in the transmission of encephalitis from wild animals to humans was discovered in the late 30s of the 20th century. E. I. Pavlovsky.
Internal structure
Internal structure of a spider
Spiders have a complex internal structure, and several systems continuously function in their bodies.
central nervous system
Consists of the nervous system and brain. The latter is a collection of ganglia. It is responsible for the functioning of the eyes and perception of the environment. The spider's brain is developed enough to analyze and act not only on instincts, but also on existing experience.
Circulatory system
This system is not closed. The heart is located inside the abdominal cavity; the role of its valves is performed by stomata, which close during pulsations. The circulatory system runs through the entire body and into the limbs.
Digestive system
In the process of eating food, the spider's digestive system begins to work. When a predator pulls fluid from its prey, it ends up in the foregut. In it, part of the liquid is absorbed into the walls, and the rest is transported to the stomach. Spiders also have a liver, which is responsible for breaking down food particles.
Interesting: How were dinosaur bones preserved? Description, diagram, video
Structural features
In the external and internal structure of Arachnids there are common features that unite all individuals into one class.
External
External anatomical features are the same for Arachnids from different families.
The main ones will be the following:
- The body consists of a cephalothorax and abdomen. Both parts are connected to each other by a thin stem. The cephalothorax has a clear boundary dividing the body into the head and chest. The first pair of limbs, called chelicerae, is attached to the first.
- Chelicerae serve to capture prey and have a movable claw at the end. In poisonous individuals, poison is released through it.
- The second pair of limbs is called pedipalps.
- There are eyes on the head, some of them are on the front, others on the side.
- Between the chelicerae there is a sucking type oral opening.
- Four pairs of limbs called walking legs are attached to the abdomen. They serve for the movement of the individual and are usually well developed.
- Each leg consists of seven parts and has a pointed claw at the end.
- The abdomen has an oval or rounded shape, and there is a genital opening on the lower part. In males it is slit-like, in females it is surrounded by a peculiar plate of chitin with a process.
The body of spiders is covered with hairs of varying lengths and stiffness. In many individuals, the hair cover extends to the limbs; the hairs are long and very thick.
Internal
The internal structure of Arachnids has its own characteristics.
The main ones will be the following:
- The respiratory organs of individuals are represented by tracheas and peculiar pulmonary sacs, resembling thin plates in structure. Oxygen enters them through the spiracles.
- The circulatory system of individuals is not closed. Blood passes through the vessels and also fills the gaps between organs. The heart is represented by a dorsal vessel located in the abdomen and shaped like a tube with three slit-like openings. The holes have valves.
- The digestive system of representatives of the order consists of the foregut, midgut and hindgut. The anterior one begins with the pharynx, smoothly turning into the stomach. The stomach contains glands that secrete enzymes for the rapid processing of proteins. Spiders have an organ in their abdomen that acts as a liver; it secretes enzymes and facilitates digestion. The hindgut ends in the rectal bladder.
- The nervous system of Arachnids is represented by two nerve ganglia located in the cephalothorax. Nerve endings extend from them to all organs and tissues.
- The sense organs are represented by the eyes, special hairs responsible for smell and touch. Spiders do not have ears or taste buds in the mouth; this function is also performed by hairs located on the limbs.
- The reproductive system is represented by openings on the lower part of the abdomen; paired gonads are located inside. All individuals of the order are dioecious, fertilization is internal.
Typically, spiders have pronounced sexual dimorphism, so it is easy to distinguish between female and male individuals. An additional organ for representatives of the order will be the spinning apparatus, with the help of which animals produce web threads.
Reproduction
Female with spiderlings
The mating season for spiders begins in autumn and lasts until spring. At this time, the male goes in search of the female. Having found a suitable candidate, he begins to perform a special dance that attracts attention. If the female reciprocates, then they retire. After this, the male moves away, and the female begins to wait for offspring. After two and a half months, she lays eggs, and after another month, the young hatch from them.
How do they breathe
Respiratory system of spiders
Depending on the species, spiders may have the following variations of the respiratory system:
- one pair of lungs;
- two pairs of lungs;
- a pair of lungs and a pair of tracheas;
- pairs of sieve and tubular tracheas;
- pair of sieve tracheas.
Getting inside the spider through special holes, oxygen is transported through the hemolymph to the respiratory organs with the help of hemocyanin. The lung sacs are located in the front of the abdomen. They saturate the body with oxygen through the circulatory system. Also behind the pulmonary sacs are bundles of tracheae, which are small tubes. They exit through a single breathing hole. During exhalation, the spider releases the resulting carbon dioxide into space.
Interesting: Are elephants capable of jumping and running?
How do they winter
Some spiders can lead an active lifestyle in winter.
Spiders are able to hibernate in different ways. Some survive frosts in the foliage and bark of trees. Spiders also try to escape the cold by settling in different buildings. In the cold, the predator produces a special chemical that acts as antifreeze. If a female lays eggs before the onset of cold weather, she tries to hide them in a secluded place where the temperature will still remain above zero in the winter.
Interesting fact : in the cold, spiders fall into a state similar to suspended animation. Because of this, processes in the body slow down and they age more slowly.
How many eyes does a spider have?
Spider Eyes
The number of spider eyes varies from 2 to 12 depending on the species, but in most cases there are 8. They are located in such a way that the creature's viewing radius is 360 degrees. Spiders see what is happening around them at about 30 cm. The main task of the visual organs is to notice in time the approach of prey or danger. Also, some types of spiders can distinguish between colors.
In the center of the head is the main pair of eyes, which are larger than the others. With their help, the spider focuses on objects. The lateral eyes are motionless and are needed for additional visibility.
Structural features and description of species
The body of this creature consists of 2 segments, called the cephalothorax and abdomen, which are connected by a stalk. There are simple eyes on the head, there are from 2 to 8. In certain species these eyes are very developed.
Three pairs of warts located on the belly secrete a liquid that closely resembles glue. When exposed to air, this liquid turns into a web.
The spider has 8 legs, and in front there are claws with poison.
Of the more than 40,000 species of spiders, we'll look at a couple of the most famous and interesting.
Did you know? At one time, females of some species of spiders can lay up to 20,000 eggs.
Tarantula
Tarantulas inhabit steppes and forest-steppes throughout the planet. They differ from their counterparts in their enormous size. The body of a tarantula can grow up to 10 cm, and the leg span can reach 30 cm. The female is larger than the male and her weight is almost 100 g.
The structure of the tarantula is no different from other spiders, but it has brown or red hairs on its body and legs. He has 8 eyes. This “baby” lives in earthen burrows up to 30 cm deep and hunts at night.
Its main diet is insects and small amphibians. When threatened, the tarantula bites. Its bite resembles that of a wasp and is not fatal. You can only observe redness at the site of the bite and weakness. Very rarely, breathing becomes difficult and vomiting and nausea appear.
Important! If you are bitten by a spider, you should definitely consult a doctor. In addition to the main danger, spider venom can cause severe allergies.
Are spiders insects or not? Difference between spiders and insects
Spider and Beetle
Spiders are not insects. Despite the fact that they also belong to the type of arthropods, they have a number of differences:
- Spiders have four pairs of limbs, and insects have three;
- spiders have chelicerae with which they inject venom into their prey;
- the head of insects is clearly defined, and in spiders it is combined with the body;
- Insects have only one pair of eyes;
- all types of spiders (with rare exceptions) lead a predatory lifestyle and do not eat plants;
- spiders breathe using pulmonary sacs, and insects use only tracheas;
- Insects have antennae on their heads.
Also, one of the main differences between spiders and insects is the ability to weave webs.
What class do spiders belong to?
The answer to the question: “Is a spider an insect?” taxonomy gives. What class do spiders belong to? Is a spider an insect or not?
Despite the presence of common characteristics, spiders and insects previously belonged to different classes: arachnids (Arachnida) and insects (Insecta). In modern taxonomy, two classes of insects have been identified: cryptomaxillary and open-jawed, combined into one superclass - six-legged (Hexapoda). The class Arachnida stands apart. Is a spider an insect? The answer is no. However, how is it different from insects?
Harmless species of spiders
If the spider's venom is mildly toxic and causes almost no harm to humans, such species are considered harmless and non-poisonous. There are a large number of species in the world, and the main ones are listed below.
Hunter bordered
Border hunter
Lives in swamps and places with high humidity. To hunt, it enters the water and waits for insects and other small creatures to swim nearby on the surface. Feeling the vibrations, the spider breaks away and runs towards the source of the waves to grab its prey. The hunter's length grows up to 2.3 cm, the paw span reaches 8 cm.
Interesting: Why don’t polar animals freeze their paws on the ice?
Flower spider
Flower Spider
The spider has long front legs that can effectively grab prey. Males grow up to 4 mm in length, and females grow up to 9 mm. Females are white, sometimes with a yellow tint on their paws. Males are brown with red spots.
Interesting fact : the spider lives in the buds of different flowers, and its color can change depending on the color of the leaves. This helps to remain invisible while hunting insects.
Knitting spiders
Knitting spiders
Representatives of this species live in fields and prefer to settle near a water source. They spread their nets between branches over a river or pond and wait for various insects to get there. Knitting spiders mainly prefer flies, ants and aphids. Adults stretch up to several millimeters in length.
Haymaker
The Harvesting Spider
has a small round body and long thin legs. The color can be dark brown or with a reddish tint. The haymaker lives both in nature and in residential buildings. Builds webs in well-lit places, because... loves sunlight. Hunts small insects, but can also eat plant foods. It is completely harmless to humans.
Goliath tarantula
Goliath tarantula
An adult can grow up to 30 cm, making this species one of the largest among spiders. The body is covered with hairs, the color varies from light brown to dark colors. Most of the population lives in South America. The goliath tarantula is often kept as a pet. It feeds on insects and other spiders.
Pelican spider
Pelican-shaped spider
Spiders have an unusual shape on the front of their body, which is similar to the head of a pelican. The species lives in Madagascar; the maximum length of adult individuals is approximately half a centimeter. The jaws are quite powerful, allowing them to bite through prey without any problems. They hunt other spiders, and they themselves climb onto their web and attack.
Smiling spider
Smiling spider
Adults grow up to 5 mm, body color can be yellow, green or blue. There are patterns on the back that look like a smile. Eats small flies. Also, the bright color of the predator camouflages it against the background of plants, which makes it invisible to birds and other enemies. The smiling spider lives in Hawaii.
Peacock spider
Peacock spider
Has a multi-colored color that makes it look like a peacock, its body is covered with thin and short hairs. The length of an adult is approximately 4-5 mm. The peacock spider lives in Australia and feeds on insects. It prefers to settle on tall plants, where it weaves a web and waits for prey.
Spiny orb-weaving spider
Spiny orb-weaving spider
The spider is found in the United States, Australia, and the Philippines. The predator has an unusual body shape: it is oval, with six long spines protruding from the edges. Males grow up to 3 mm in length, females up to 13 mm. The front part of the cephalothorax and the spines are painted in a certain color, the back can be white, red or yellow, with dark dots on it. When the spider sits motionless, it tucks its paws under itself and takes the form of a ball.
Interesting: Why is a turtle's shell made of hexagons?
Apulian tarantula
Apulian tarantula
The main part of the population lives in Italy and Spain. As a home, the tarantula digs a hole up to half a meter deep. The size of an individual can reach up to 7 cm. The color varies from red to brown, and there are dark stripes of different lengths on the body. It eats various insects, preferring beetles and caterpillars.
Poisonous spider species
When hunting, some types of spiders use venom, which allows them to quickly and effectively immobilize their prey. The consequences of a bite from some individuals begin to appear almost immediately, while for others only after a couple of minutes. Below are the most common types of venomous spiders.
Karakurt
Karakurt
Spiders have a black body, males have white spots on their backs, females have red spots. Moreover, females become completely dark with age. Karakurt prefers to live in the grass; it weaves its web close to the ground, where insects fall. It can also crawl into rodent holes. Individuals grow up to 2 cm in length.
Cross spiders
Cross spiders
The color of the spider is brown-red, and there are also different patterns in the shape of leaves on the body. Some individuals have a white stripe. Crosses grow up to 3 cm in length, females are larger than males. While hunting, the spider weaves a web in which it catches small insects. The cross is wary of wasps and poisonous flies, because it is afraid of their bites.
Black Widow
Black widow
Adults grow up to 1.3 cm, the body is black. Females have a red, hourglass-shaped pattern on their abdomen. Males have purple paws. Black widows lead a solitary lifestyle and hunt small insects. After laying eggs, females wrap them in webs, making a large cocoon. It is attached to the net and monitored for safety.
Recluse spider
The recluse spider
lives in the eastern United States and is considered highly poisonous. The body of the hermit stretches up to 2 cm, has a brown, gray or yellow color with dark spots. Mainly nocturnal. During the day, the predator hides under stones, and at nightfall it goes in search of insects and other spiders. It can both catch prey using a web and personally pursue it.
Kipling's Bagheera
Bagheera Kipling
One of the few species of spiders that are not predators and feed on vegetation. Individuals live on acacia trees and eat small shoots. The paws of Kipling's bagheera are amber in color, the body has a different color, consisting of black, brown and green. Adults grow no more than a centimeter in length.
White Lady
The White Lady
Spider has a creamy white color, its body grows up to 1.3 cm in length. The main part of the population lives in Namibia, in sandy areas. Most of the diet consists of insects, but predators can also attack reptiles. When hunting, they rarely go further than a few meters from the hole. They are nocturnal.
Interesting: Animal teeth - types, description, names, photos and videos
Types of spiders of medium poisonousness
Among the large number of species of spiders, there are those that release a certain amount of poison during the bite process, but its concentration is not enough to cause serious harm to prey that is several times larger than them.
banana spider
Banana spider
These spiders live in America and are able to run quickly across the surface, which allows them to catch up with almost any prey. The color of individuals can vary from gray to black and white. It feeds on insects and small animals.
Fun Fact : Banana spider venom can be used for therapeutic purposes in the right concentration.
Giant tree spider
Giant tree spider
Also known as the nephilus orb weaver. It grows up to 4 cm in length, with a paw span of 12 cm. It hunts various creatures, from insects to birds. The spider attacks everyone who ends up in its web and cannot get out. Individuals have a wide variety of colors, most often combining black and orange.
Tarantula
Tarantula
The color of this spider varies from light gray to black, the body is covered with small hairs. Tarantulas live in burrows and hunt insects. Adults grow up to 10 cm in length. Currently, 221 species of tarantulas are known, and each has certain characteristics. They live almost all over the globe.
Water spiders.
Relatively large spiders of the genus Dolomedes
, which can run along the surface of stagnant bodies of water and even dive under water, holding on to plants. These spiders feed on insects, fish fry and tadpoles.
The silverback spider lives in Europe, spending most of its life underwater in places where there is little or no current. This is probably the most unusual spider in the world, considering that it, like all representatives of its class, breathes atmospheric air. In the spring, it goes under water and stretches a horizontal network of cobwebs with very small cells between the plants. Then, rising to the surface, it exposes the end of the abdomen, covered with non-wettable hairs. Air collects between them, which the spider, in the form of a bubble held by its legs, drags into the depths and shakes off under its web. It does not allow the bubbles to float up and after repeated such flights it bends into a bell the size of a thimble or even larger, supported from the inside by an air chamber. The spider hides inside it, inaccessible to most enemies, immediately lays eggs, hatches young and overwinters. The bells of the male and female living separately are connected to each other by a bridge made of cobwebs.
Spiders of Russia
In Russia you can meet a wide variety of spiders. It is estimated that the country is home to approximately 2,880 species with specific characteristics. Below are the main and most common ones.
House spider
House spider
This species prefers to live in residential buildings and outbuildings. It eats small insects: bedbugs, moths, flies, etc. If there are no human settlements nearby, it can live in fields and forests, using a crack in a tree or thick grass as a home. The color of the spider is yellow-brown, with a dark pattern on the back. An adult grows up to 1.2 cm.
Orb weaver
Orb weaver
A poisonous spider that lives in nature. The predator climbs trees and weaves a large round web between the branches, into which insects fall, which later become food. Orb weavers can also hunt frogs, rats and other small animals.
Interesting fact : the poison of the orb weaver paralyzes the frog in 15 minutes. For humans, the bite is practically harmless, although there may be discomfort in the affected area.
Argiope arthropod
Argiope arthropod
Males of this species rarely grow more than 5 mm, but females stretch up to several centimeters. The spider is yellow and black in color, which makes it look like a wasp. Argiope is found in central Russia. The spider is poisonous and rarely attacks first in case of danger. Having spread a web, the predator often sits right in its center and does not hide from potential prey.
Interesting: The most popular domestic rodents - list, name, description, photo and video
Hyracantidae
Hyracantids
This species of spider lives in grass and dense thickets and loves temperate climates. Adults grow up to one and a half centimeters. The color is light brown, sometimes there may be a green tint. Chiracantids are nocturnal, do not build permanent housing, travel across territories and hunt insects. The bite is considered highly poisonous.
South Russian tarantula
South Russian tarantula
Grows up to 3 cm, prefers areas with low humidity, mainly steppes. He builds a house in loose soil, digs a hole several tens of centimeters deep. During the hunt, he sits inside and waits. When an insect runs nearby, the tarantula jumps out of the hole and bites the prey. The poison almost immediately paralyzes the enemy, and the spider only has to drag him home.
Silver spider
Silver spider
In Russia, you can find the silver spider in the Far East, Siberia and the Caucasus. The legs and front part of the predator's body are dark brown, the back part is gray. The size of an adult does not exceed 2 cm. The silver spider has a calm character and does not attack without reason. Spends most of its time in water, where it hunts small creatures.
Steatoda
Steatoda
Species is found in the Caucasus and southern Russia; it prefers to settle next to humans and hunt in gardens and vegetable gardens. The spider is black in color with orange-red or gray patterns on the back. It is poisonous, but the bite is not capable of causing severe harm to humans. But it quickly helps to cope with insects.
Black Eresus
The Black Eresus
Spider has a rather unusual color, which makes it look like a ladybug. Eresus lives in the Rostov and Novosibirsk regions. It digs a small hole as a home, to which it is attached all its life. Often the male and female live together to regularly produce offspring. The spider grows up to 2 cm in length.
Solpuga
The Salpuga
Spider lives in the Crimea, has white-yellow legs and a gray body, which is why it is perfectly camouflaged in the sand. It is most active at night and can move quickly. When hunting, it uses long jaws, which help cope not only with insects, but also lizards and rodents. Salpugs grow up to 7 cm in length.
Pouch spider
The pouch spider
is an aggressive predator that is capable of attacking even a large opponent. It has an elongated body of yellow color with a greenish tint. Lives in the Volgograd and Rostov regions. Prefers to live in fields with tall grass, but can also be found near trees. The average length of an adult is 1.5 cm.
False black widow
False Black Widow
The False Black Widow is dark in color and sometimes has red spots on its body. Individuals with light-colored paws are also sometimes found. The spider grows no more than 1.2 cm in length and hunts small insects. Considered highly poisonous. The bite can cause discomfort to a person for 2-3 days. The bulk of the population lives in Dagestan.
Poisonous spiders
It has been proven that spiders are a very ancient form of earthly fauna. And scientists were convinced of this by finding frozen particles of amber, the age of which was measured in millions of centuries. They revealed the remains of a web of prehistoric creatures, which could not be anything other than spiders.
It is also known that their modern descendants instill in people not only disgust, but subconscious, often uncontrollable fear. This is a disease called arachnophobia. Most often it does not have any sound reasons. Moreover, people suffering from it fear harmless little eight-legged creatures even more than plane crashes, car accidents, and even firearms.
The reasons for the occurrence of such a phobia have so far been little studied. But it is assumed that its mechanisms should be sought at the genetic, evolutionary level. Its roots go back to time immemorial, when arachnids were larger and more dangerous, and the distant ancestors of humans were small defenseless mammals. dangerous species of spiders still exist today. We will consider them further.
Karakurt
This is a scary creature. But if you don’t touch him, he usually doesn’t attack people or other mammals. However, its bite can lead to death. It bites through the skin to a depth of only half a millimeter, but injects a very toxic poison. Cattle, camels, horses, and various rodents are especially sensitive to it.
But reptiles, amphibians, dogs and mice react less to it. The poison begins to act immediately, spreading throughout the body within a few minutes. In humans, it causes burning pain, palpitations, pallor, dizziness, vomiting, and later mental instability, confusion, hallucinations, and delirium.
In addition to North Africa, karakurts are also found in the southern regions of Europe, in particular in the Mediterranean and Central Asia, and are sometimes found in Astrakhan and some other regions of southern Russia. Such spiders live in burrows, the passages to which run deep underground.
Such creatures are extremely prolific. And once every quarter of a century or even more often, they experience outbreaks of particularly active reproduction, after which their population increases greatly. The name of this animal is translated from the language of Asian peoples as “black insect”. In addition, it belongs to the family of so-called black widows.
It includes more than three dozen species of black spiders , all of which are poisonous. The color of the karakurt largely corresponds to its name, except for the 13 orange spots on top of its swollen, ball-shaped abdomen. There are karakurts of other colors, including white.
Cross spider
For arachnids, these are rather large animals, with a body length of up to 2 cm. Their chelicerae are not so dangerous and are capable of biting through the skin of mammals only in thin places. And the toxicity of the poison is comparable to that of bees. These creatures received their name for the presence on the upper side of the abdomen of a characteristic pattern in the form of a cross, which itself exists to scare away enemies.
Such spiders live in tree branches, where they weave webs to catch small insects, which is their favorite type of food. Like other representatives of the spider order, they have external digestion, that is, they inject juices into the body of their prey, dissolve it, and then drink it. In total, about 600 varieties of crosses are known, about three dozen of them live in our country.
South Russian tarantula
It is easy to conclude from the name that, like the two previous poisonous fellows, these creatures also belong to the species of spiders that in Russia . And such an event can bring sad consequences. The bite of such a tarantula, as a rule, does not lead to death, although it is extremely painful and can even cause fever.
In the European part of our country, tarantulas live in the forest-steppe zone with a dry climate, in steppes and semi-deserts, and are often found in the Caucasus and the Urals, in Siberia. They dig holes for themselves, which are shallow, no more than half a meter long, vertical tunnels lined with cobwebs. In the vicinity of their home, such unpleasant creatures hunt insects.
Their body size reaches 3 cm, and the color is usually dark below and brownish-red above. In general, the word “tarantula” is derived from the name of the city of Taranto, which is located in Italy. It is in its vicinity that such creatures are found in extreme abundance.