What is a web?
Spiders are one of the oldest inhabitants of the planet; due to their small size and specific appearance, they are mistakenly considered insects. In fact, these are representatives of the order of arthropods. The spider's body has eight legs and two sections:
- cephalothorax;
- abdomen.
Unlike insects, they do not have antennae and a neck separating the head from the chest. The abdomen of an arachnid is a kind of factory for the production of cobwebs. It contains glands that produce a secretion consisting of protein enriched with alanine, which gives strength, and glycine, which is responsible for elasticity. According to the chemical formula, cobwebs are close to insect silk. Inside the glands, the secretion is in a liquid state, but when exposed to air it hardens.
Information. The silk of silkworm caterpillars and spider webs have a similar composition - 50% is fibroin protein. Scientists have found that spider thread is much stronger than caterpillar secretion. This is due to the peculiarity of fiber formation
Nutrition
The main diet consists of insects of different sizes. The spider's trapping nets catch flies, wasps, hornets, grasshoppers, locusts, caterpillars, and butterflies. Snakes, frogs, toads, and mice get entangled in large, strong webs.
Cross spider
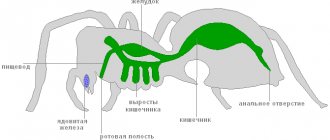
There is no internal digestive system, food liquefaction occurs externally. The spider bites the victim, injects poison that paralyzes the muscles and immobilizes the prey. The cross releases saliva into the insect’s body, envelops it in a web, and waits for several minutes. In 5-20 minutes, the insides of the prey turn into a liquid mass, which the predator sucks up.
The living creatures described are carnivorous. In addition to the flies and mosquitoes already mentioned, aphids, various midges and other small representatives of the insect world can become their prey. If such a prey falls into the net of a given predator, then he has the opportunity to feast on it immediately.
But, if he is full, he is able to leave food for later, entangled with a thin adhesive thread. By the way, the composition of such a “rope” is somewhat different than the thread of a spider’s web. Further, the spider hides its food supply in any secluded place, for example, in the foliage. And he eats it when he feels hungry again.
These spiders have a very excellent appetite. And their bodies require a lot of food. The daily norm is so high that it is approximately equal to their own weight. Such needs force the described representatives of the animal world to work accordingly.
Cross hunters, lying in wait for prey, sit in ambush with virtually no rest, but even if they are distracted from business, it is for a very short time.
These creatures digest their food in an extremely interesting way. This happens not inside the body, but outside. The spider simply releases a portion of digestive juice into the body of the victim, wrapped in a cocoon. In this way it is processed, turning into a substance suitable for consumption. Next, this nutrient solution is simply drunk by the spider.
It happens that the nets placed by these eight-legged creatures catch prey that is too large for such a baby to handle. The spider tries to get rid of such problems by deliberately cutting off the threads of the network connecting itself.
But if the threat does not stop there, for the purpose of self-defense he is quite capable of successfully using his chelicerae against what are, from his point of view, huge creatures. For example, a frog a quarter of an hour after its bite may be completely immobilized.
But are cross spiders dangerous for humans or not? Actually, the poison of these creatures does not produce irreversible changes on the body of all vertebrates. On people, due to the small amount of toxic substances produced by these arachnids compared to human size, they are not able to have a serious effect. The bitten subject feels only mild pain, which subsides fairly quickly.
Where does a spider's web come from?
On the abdomen of the arthropod there are outgrowths - arachnoid warts. In their upper part, the channels of the arachnoid glands open, forming threads. There are 6 types of glands that produce silk for different purposes (moving, lowering, entangling prey, storing eggs). In one species, all these organs do not occur at the same time; usually an individual has 1-4 pairs of glands.
On the surface of warts there are up to 500 spinning tubes that supply protein secretion. The spider spins its web as follows:
- spider warts are pressed against the base (tree, grass, wall, etc.);
- a small amount of protein adheres to the selected location;
- the spider moves away, pulling the thread with its hind legs;
- for the main work, long and flexible front legs are used, with their help a frame is created from dry threads;
- The final stage of making the network is the formation of sticky spirals.
Thanks to the observations of scientists, it became known where the spider’s web comes from. It is produced by movable paired warts on the abdomen.
Interesting fact. The web is very light; the weight of a thread wrapping the Earth along the equator would be only 450 g.
Poisonous or not
The venom of the brown cross contains heat-labile hemolysin, which has a negative effect on blood cells.
However, its dose is so small that it can only harm small animals. A spider bite is not dangerous for humans, but minor discomfort may occur if you are allergic to animal bites.
At the site of the bite, minor pain and itching occurs quickly. To quickly relieve these symptoms, you need to wash the affected area of skin with soap and apply something cold, ice if possible, then apply ointment to relieve inflammation.
Important! The spider never attacks first - a bite is possible if there is accidental contact.
The poison is toxic to invertebrates and vertebrates. It has an effect on the body of rats, mice, humans, and rabbits. Sheep, horses, guinea pigs, and dogs are resistant to poison. For insects and invertebrates, a crusader attack is fatal. Animals experience temporary deterioration in well-being and external irritation.
The Crusader is not dangerous to humans. When it sees people, the spider tries to hide unnoticed. However, if there is a threat to its own life, it can bite. There are 2 small spots left on the body. Initially there is pain and burning. The next day, suppuration occurs. In people with weakened immune systems and children, after a spider bite, their general health worsens. Weakness, nausea, headache, dizziness, and abdominal discomfort appear. The condition returns to normal in a few days.
How to build a fishing net
The wind is the spider's best assistant in construction. Having taken out a thin thread from the warts, the arachnid exposes it to an air flow, which carries the frozen silk over a considerable distance. This is the secret way a spider weaves a web between trees. The web easily clings to tree branches, using it as a rope, the arachnid moves from place to place.
A certain pattern can be traced in the structure of the web. Its basis is a frame of strong and thick threads arranged in the form of rays diverging from one point. Starting from the outer part, the spider creates circles, gradually moving towards the center. It is amazing that without any equipment it maintains the same distance between each circle. This part of the fibers is sticky and is where insects will get stuck.
Interesting fact. The spider eats its own web. Scientists offer two explanations for this fact - in this way, the loss of protein during the repair of the fishing net is replenished, or the spider simply drinks water hanging on the silk threads.
The complexity of the web pattern depends on the type of arachnid. Lower arthropods build simple networks, while higher ones build complex geometric patterns. It is estimated that the female crosstail builds a trap of 39 radii and 39 spirals. In addition to smooth radial threads, auxiliary and catcher spirals, there are signal threads. These elements capture and transmit to the predator the vibrations of the caught prey. If a foreign object (a branch, a leaf) comes across, the little owner separates it and throws it away, then restores the net.
Large arboreal arachnids pull traps with a diameter of up to 1 m. Not only insects, but also small birds fall into them.
What does it eat?
The main thing in the spider's diet are small insects. During the day, the female absorbs food in an amount equal to her weight. When an inedible insect gets into the web, the spider gets rid of it by breaking the threads.
He also tries to avoid flies and wasps, which can lay eggs on other animals. Hunting occurs in two ways: in the center of the web or from a nearby shelter.
The predator is not able to immediately consume food, so it quickly injects aggressive juice into the caught prey, places the prey in a cocoon and waits for the victim’s insides to turn into a nutrient solution. This process takes approximately 1 hour, after which the spider sucks out the prey, leaving the cocoon behind.
Purpose of the web
Fine nets are not only insect traps. The role of the web in the life of arachnids is much broader.
Catching prey
All spiders are predators, killing their prey with poison. Moreover, some individuals have a fragile constitution and can themselves become victims of insects, for example, wasps. To hunt, they need shelter and a trap. Sticky fibers perform this function. They entangle the prey caught in the net in a cocoon of threads and leave it until the injected enzyme brings it into a liquid state.
Arachnid silk fibers are thinner than human hair, but their specific tensile strength is comparable to steel wire.
Reproduction
During the mating period, males attach their own threads to the female's web. By striking the silk fibers rhythmically, they communicate their intentions to a potential partner. The female receiving courtship descends onto the male’s territory to mate. In some species, the female initiates the search for a partner. She secretes a thread with pheromones, thanks to which the spider finds her.
Home for posterity
Cocoons for eggs are woven from the silky web secretion. Their number, depending on the type of arthropod, is 2-1000 pieces. The females hang the web sacs with eggs in a safe place. The cocoon shell is quite strong; it consists of several layers and is impregnated with liquid secretion.
In their burrow, arachnids weave webs around the walls. This helps create a favorable microclimate and serves as protection from bad weather and natural enemies.
Moving
One of the answers to why a spider weaves a web is that it uses threads as a vehicle. To move between trees and bushes, quickly understand and fall, it needs strong fibers. To fly over long distances, spiders climb to elevated heights, release a quickly hardening web, and then with a gust of wind they fly away for several kilometers. Most often, trips are made on warm, clear days of Indian summer.
Where does it live?
The species is distributed throughout Europe, with some species found in North America. Favorable living conditions are high humidity, high temperature, and the absence of direct sunlight. Ideal habitats are coniferous forests, swamps, edges, hedges. Less often they settle in meadows, fields, gardens, vegetable gardens, outbuildings, and residential buildings. There are about 30 species of crosses living in Russia and the CIS countries.
Habitat: damp and damp areas. The greatest likelihood of encountering it can occur in places where a large number of trees grow, where they stretch their webs, as well as along the banks of reservoirs and even in the attics of various buildings.
Did you know? 2.5 billion years ago the first spiders appeared on Earth, which gave birth to more than 30 thousand species of spiders that live almost everywhere today.
More than 30 species of spiders live in Russia and the former CIS countries, including Ukraine. This species of arthropod is a hermit predator, and the main feature of its behavior is an extremely negative attitude towards its own kind. At night, these arthropods weave their hunting webs, and during daylight hours they hunt their victims.