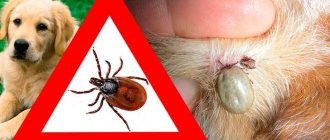
Probably each of us has been bitten by a gadfly or horsefly at least once in our lives. Therefore, we all know firsthand how painful and unpleasant it is. At the same time, the bite manifests itself differently in all people. For some, swelling and itching go away in just a couple of minutes, for others, on the contrary, unpleasant symptoms are observed for several days. What does this depend on? What are the possible consequences of contact with these large flies? What should you do if you are bitten by a horsefly or gadfly? We will try to answer each question listed in as much detail as possible, as well as share other useful information.
Gadfly bite
Quite often you hear: “I was bitten by a gadfly. What to do?". Firstly, I would like to immediately note that this is impossible. The fact is that almost all species of this insect do not have a piercing-cutting type of mouthparts. That is, even if they want to, they will not be able to bite through your skin. In principle, they don’t need this. Adult spiderworts (as gadflies are called in many areas) do not feed or bite! They have enough of the substances that they accumulated while they were in the larval stage.
But what really stings both people and animals (including cattle) are horseflies. For what? To get blood, which, like the same mosquitoes, they need to reproduce.
Why then do you still hear from many people (and even doctors) about cases where gadflies were bitten? This is explained by the fact that people confuse these insects. As a result, horseflies and gadflies sometimes act as synonyms. That is, this is the name of all flies that overcome people, livestock, animals, etc.
For reference! However, the fact that gadflies do not bite does not make them any less dangerous insects. These winged birds are carriers of various infections. They can also lay parasitic larvae, which cause significant harm to the health of their victims.
Who are gadflies and why are they dangerous?
People who do not have special knowledge about the life of insects cannot distinguish a gadfly from a horsefly, thinking that they are the same type of insect.
However, there is a major difference. A horsefly bites a person in order to suck blood, while a gadfly simply seeks thermal shelter. The bite of a gadfly is aimed at depositing larvae under the skin of the victim. Botflies belong to the family of dipterous insects. Their appearance resembles bumblebees. The length of the insect can reach 30 mm. The wings are gray and variegated. The bite of a gadfly or horsefly, as they are popularly called, is difficult for a person not to notice. Some people have no idea how dangerous an attack by flying insects can be for a person. However, the consequences of a gadfly bite can be very serious.
Causes of bites
Since the oral organs of dipterans are not fully developed, when attacking a person, the insect is not able to suck blood. They bite in order to deposit larvae under the skin of a person. Males feed only on flower nectar, while females seek thermal shelter, biting people and laying larvae.
When do they bite?
The main habitat is reservoirs, lakes, rivers and forests. The optimal air temperature for insect activity is from +15 to 32 degrees. These insects also love to live among livestock pastures.
Insect activity begins to appear at the end of the first summer month. They like to fly when the weather is warm and there is no wind. They find the wet human body and the smell of sweat attractive.
How to recognize a gadfly bite?
Many people do not know what a gadfly bite looks like and cannot distinguish it from other insects. However, you should know and distinguish between damages in order to take timely measures.
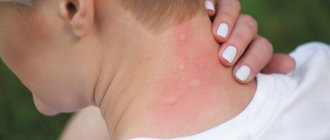
When a gadfly bites, a red spot very quickly appears, which increases in volume and swells. A painful itch occurs. Very often, dipterans attack in a group, then multiple wounds are found on the human body in different parts.
Attention! Gadflies are distinguished by their importunity; they pester the victim until the last moment, attacking it and buzzing aggressively.
What happens if a gadfly bites?
After a gadfly bite, the injury site quickly turns red and severe itching appears. At first, the wound has clearly defined boundaries, then redness and swelling cover a large area on the body. An allergic reaction may occur in the form of swelling, even fever.
It is impossible to miss if a gadfly bites a person, as it is characterized by severe pain, burning and itching. Immediately after the attack, blood will ooze into the wound area and will not clot for a long time, which further attracts other female insects. The person will scratch the skin vigorously.
Allergies are quite rare. However, the condition of the victim should be carefully monitored.
Possible consequences
You can see what the bite itself looks like in the photo. Usually the skin turns red and the area around the wound swells. In this case, itching immediately begins. Even people with not the most sensitive skin want to scratch this area a lot.
After being bitten by a gadfly (or, more correctly, a horsefly), unpleasant symptoms often appear. It could be:
- increased body temperature;
- chills;
- strong pain;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- headache;
- involuntary urination4
- diarrhea.
All this is the result of the human body’s response to substances that penetrated it through a bite. What should you do if you experience any of the listed symptoms? We definitely recommend that you seek medical help immediately. After all, there is a risk of developing a severe allergic reaction, including anaphylactic shock - an extremely serious condition in which you can even die.
Normally, after a horsefly bite there should be no serious consequences. Slight redness on the skin, mild itching and mild swelling measuring about 1 cm² are allowed. In this case, after an hour, positive dynamics should appear - the bite site should stop itching very much, redness and swelling should decrease. If this is exactly what happens, then there is no need to worry. In 2-3 days the wound will heal completely.
For reference! Single horsefly bites usually do not cause negative reactions. Provided that the insect did not sting you in the eyelid, eye area, lip or neck. Bites to these parts of the body are often very difficult to bear - with swelling, enlarged lymph nodes, allergies, etc.
A horsefly is not a gadfly! What it looks like: description, morphology
The bite of a horsefly and a gadfly - there is a difference, and there are many differences.
The horsefly (lat. Tabanidae) is an insect of the short-whiskered suborder of the Diptera family; in Russia it is represented by 176 species. By nature of nutrition it is classified as a predator or saprophage. Females feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals during oviposition, the rest of the time on carbohydrates - plant sap, honeydew - the secretion of aphids, scale insects, etc.
- Male imagoes are not blood-sucking: they feed on plant sap, nectar, and honeydew.
- The female horsefly, which inflicts the bites, differs from the gadfly in its powerful sucking apparatus with a sharp cutting proboscis and highly aggressive saliva.
Externally, horse flies resemble a large fly, and their size is significantly larger than the size of a gadfly. The insect's body is dark, elongated, with a massive abdomen, two pairs of wings, and large, bright and iridescent multi-colored eyes. The main hosts are cattle, less often birds, and for some species – humans.
Among the common ones:
- Lacewings. Dark gray flies with black wings in males, transparent in females, with dark patterns, up to 10 mm in size. They settle near bodies of water.
- Bullfly. A dark brown or gray-brown fly that lives in pastures, on the edges of forests, near rivers, laying eggs in the grass. Size 12-25 cm.
- Raincoat. A small fly, activated before rain, distinguished by a marbled pattern on the wings.
A horsefly bite is comparable to the bite of about 70 mosquitoes in terms of the volume of blood consumed by the insect!
Why a horsefly bite is dangerous: consequences through the eyes of doctors
What does a horsefly bite look like? Characteristic features:
- At the site of the bite, two holes are observed - the main difference from the damage left by bees and wasps.
- The bite is accompanied by severe pain - according to the victims, it is not comparable to the bites of other insects.
- After being bitten by a gadfly (more precisely, a horsefly), almost immediately the skin becomes intensely red, swelling and swelling of a large size, burning and itching instantly develop.
Is the bite of a gadfly (more precisely, a horsefly) dangerous? What are the consequences? After a bite, complications are likely caused by the aggressive composition of saliva: special toxins reduce blood clotting and act as allergens. But the main thing is that saliva carries anticoagulant components, and after a horsefly attack, a blood clot does not form, preventing infection from entering the wound from the outside.
Horsefly saliva contains bacteria, viruses, and can carry parasitic infections - nematodes, helminths, etc.
Insects are carriers of anthrax, filariasis, tularemia, borreliosis, trypansomosis and other diseases.
Among the complications:
- local swelling in the form of a nodule, rapidly increasing, accompanied by pain and itching, inflammatory infiltrate;
- increased body temperature;
- enlargement of the lymph nodes closest to the lesion;
- as a manifestation of allergies - rashes on the arms, legs, torso, less often on the face;
- the site of a horsefly bite can become inflamed and fester as a result of infection, both directly during the bite and subsequent infection of the open wound;
- with numerous bites - a pronounced increase in temperature, allergies, general malaise.
Allergy sufferers are most vulnerable to horsefly bites - multiple rashes are possible, spreading far from the site of the lesion; in people with a weakened immune response, in most cases the temperature rises.
The consequences of a gadfly bite in children are no less serious: they manifest themselves in severe swelling, intense pain, allergies, and general weakness.
How quickly do the consequences of the bite go away (swelling, itching)? Depending on the degree of damage: for example, a bite that occurs without infection disappears without a trace in 3-5 days. In case of multiple lesions, infection, suppuration, the formation of large nodes and edema, it is difficult to predict: a physician should treat the bite.
Horsefly bite: what to do - help with a bite
What to do after being bitten by a gadfly that is not a gadfly at all: doctors advise:
- If possible, squeeze the skin around the wound tightly with your fingers so that blood comes out: this will somewhat reduce the concentration of toxins in nearby tissues. Compression prevents the further spread of allergens and infection and reduces pain.
- Rinse the bite.
- Treat with an antiseptic (from alcohol and brilliant green to iodine, chlorhexidine, etc.).
- Apply the bactericidal patch directly to the wound.
- If possible, cover the area of skin around the bite with ice.
- Be sure to take an antihistamine.
- If any complications arise after being struck by a gadfly, contact a medical facility!
What not to do after a horsefly bite: doctors warn
How to anoint a horsefly bite? Nothing - until the bleeding stops (except for antiseptic)! How to treat? You can smear and apply compresses after the wound has healed, if the site of the horsefly bite is itchy, itchy, or swollen (arm or leg).
It is strictly forbidden to:
- Apply plantain, burdock, green parts of dandelion and other remedies to bleeding wounds: if an incident occurs in nature, an infection is likely to enter the open wound: remember that a bite is the gateway to infection.
- Scratching bites: increased blood circulation spreads toxins and infection into nearby tissues, causing the affected area to become more painful, swelling and itching to increase.
- Apply “homemade” remedies (salt, vinegar, soda) to the still open wound: infection is possible, even greater pain as a result of irritation.
All folk remedies are used exclusively after the wound is closed.
Compresses, lotions, and ointments are applied after a blood clot has formed at the site of the bite, directly on the swelling.
Also: a note to those who have been bitten
- an alcohol compress (vodka) prevents blood clotting - i.e. the wound does not heal, the gates of infection remain open. They are used after the hole has been “closed”; an alternative is brilliant green;
- Iodine can cause burns and cause an increase in infiltration, resulting in further spread of infection.
- the use of dimexide for a gadfly bite is advisable in case of formation of infiltration and voluminous edema; it is contraindicated in case of allergies. The permissible concentration is from 1:4, 1:5 – assigned individually.
First aid
It is precisely in the first seconds after the bite that it is necessary to act correctly and quickly so that the toxins contained in the horsefly saliva do not spread throughout the body, causing severe swelling, burning, allergies and other unpleasant reactions. To do this you need to do the following:
- Apply pressure with your finger or some non-sharp object to the bite site. This will prevent the spread of toxic substances. Just don’t scratch the wound or touch it with dirty hands!
- Next, it would be a good idea to cool the area of skin affected by the insect. Apply ice, a cold bottle, or something else. This will reduce pain and swelling.
- Wash the wound to prevent dangerous bacteria and infections from entering the body. Best with soap. Use cool water.
- Treat the bite with alcohol, brilliant green, iodine, hydrogen peroxide or another antiseptic that you have on hand. Of course, when relaxing in nature, you may not have all this with you. Then use medicinal herbs - chamomile or plantain juice will do.
- After 10-15 minutes, apply antihistamine ointment to the skin near the bite. What kind of creams can be applied? These are Fenistil gel, Elokom, Baneocin, etc.
If you do not do the above, there is a high risk that an abscess will form at the site of the bite, which will cause discomfort. The fact is that a harmful insect often injects pathogenic bacteria and toxic substances under the skin along with saliva.
Symptoms and consequences
Allergy sufferers and children under 5 years of age are very sensitive to attacks by gadflies, so they often experience symptoms of intoxication. In the first two hours, headache, nausea and vomiting, chills, fever, and loss of consciousness are noted. If an insect gets into a blood vessel during a bite or the victim has anemia, diabetes, a hematoma and a long-lasting bruise appear. The most dangerous consequences that require urgent treatment:
- Severe swelling of soft tissues. It is the most common symptom of a gadfly bite in a person prone to allergies. Due to hyperemia, it is impossible to bend a leg or arm, and the resulting rash provokes severe itching.
- Infection with life-threatening viruses. This is evidenced by deterioration of the condition, a strong increase in temperature, impaired vision, hearing, memory, and weakness.
- Anaphylactic shock. The body's reaction, requiring urgent help, occurs in extreme cases after multiple bites or in allergy sufferers. In this case, generalized edema, decreased blood pressure, loss of consciousness, and cessation of breathing and pulse develop.
Attention! A gadfly bite in the eye can cause partial or complete loss of vision. An attack in the face and neck area is very dangerous. The swelling spreads to the lips, eyes, larynx, and tongue. Subsequently, heavy breathing appears, suffocation and asphyxia occur.
Itching, slight swelling, and burning may go away on their own after a few days, but you should not scratch the wound or treat it with aggressive medications. If a person has been attacked by several gadflies, it is better to immediately take antihistamines, treat the bites, and then immediately consult a doctor.
What if a horsefly or gadfly bites a child?
The most dangerous thing is when horseflies bite children. In most cases, a growing body and an immature immune system are not able to cope with insect toxins. Therefore, in children the consequences of a bite can be much more serious. On their delicate skin, areas around insect wounds quickly swell. It even happens that a limb completely swells - hand, forearm, ankle, etc.
After a horsefly bite, a baby often develops redness. In this case, the child experiences severe pain, and the persistent itching forces him to scratch the wound, which is fraught with additional infection. In addition, in most cases, skin rashes occur.
Is all this dangerous? Certainly. Children may develop a powerful autoimmune reaction in response to a bite, the consequences of which are difficult to predict. Therefore, we strongly recommend that after your “meeting” with a horsefly, take your child to the doctor. And as quickly as possible!
What to do if bitten by a gadfly?
To prevent the development of serious consequences after an insect attack, you need to clearly know what helps with a gadfly bite.
The sooner first aid is provided, the fewer negative consequences a person will experience. Therefore, you should clearly know what to do if your leg is swollen after a bite, or redness appears, in order to reduce the risk of an allergic reaction. Also, when going into nature or on vacation near the water, you need to stock up on the necessary anti-allergy medications and painkillers. Folk remedies in the form of herbal compresses help well with a bite, so it is important to foresee everything in advance in order to have the necessary remedies on hand in case of a bite.
Emergency therapy
Every person should know how to provide first aid when bitten by a gadfly. It should be as follows:
- Press on the wound with something hard or with your finger. This will prevent the insect's toxic saliva from quickly spreading under the skin and will reduce pain.
- Apply ice. This will help relieve itching and swelling.
- Rinse the wound under cold water. This will wash away all the dirt from the wound. When washing the wound, use ordinary toilet or laundry soap; it has a disinfecting effect.
- Immediately treat the bite site with a disinfectant to avoid infection.
If a gadfly has bitten the eye, it is also advisable to immediately apply cold to relieve the itching and prevent swelling.
How to treat a bite with drugs?
When emergency treatment is delayed, or a person develops an allergy, drug treatment should be resorted to. If swelling develops from a gadfly bite, we can talk about an allergic reaction. In this case, take antihistamines to eliminate allergy symptoms. Such drugs include: Suprastin, Tavegil, Claritin, Zyrtec and many other pharmaceutical products.
You should also know what to apply to a gadfly or horsefly bite. Ointments that have an anti-inflammatory effect are suitable here: Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone. Such remedies for horsefly and gadfly bites are applied immediately after an insect attack.
To relieve itching from a bite, medications such as Fenistil-gel, Bepanten ointment or Depanthenol are applied to the wound.
Folk remedies
It happens that there are no first aid medications at hand after an insect bite. In this case, you have to resort to treatment with folk remedies. You can use the following plants:
- Plantain leaves. The plant is crushed to a paste consistency and applied to the wound. Plantain will help cope with pain and prevent swelling from reaching large proportions.
- Dandelion leaves. Used as a compress. The leaves should be softened a little and applied to the damaged area. Dandelion will quickly help heal the wound, preventing swelling from spreading to healthy tissue. Has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Mint. Has a calming effect, relieves swelling and inflammation. Will help cope with itching.
It also happens that medicinal herbs are not at hand. You will have to carry out treatment at home. The following tools are suitable for this:
- dilute baking soda in a glass of water, moisten a bandage in the solution and apply to the bite site;
- tomato juice, sour cream, kefir help relieve swelling and cool the affected area;
- raw potatoes relieve swelling and redness well.
Important! It is forbidden to press on the wound to squeeze out the gadfly’s saliva. This will only speed up the penetration of toxins into the blood.
How to treat horsefly bites?
For many people, the wounds heal on their own, and the swelling and redness disappear the very next day. That is, most often no special therapy is required. Treatment after horsefly bites is often necessary for children and people with compromised immunity, serious illnesses, and those who suffer from allergies.
But in any case, the bite site and well-being should be closely monitored during the first two days. Are there any unpleasant symptoms? Then you need to understand whether to carry out treatment at home or seek medical help? You need to start from a specific situation:
- If you suddenly see that the swelling from the bite is increasing and the itching does not go away, then take an antihistamine - for example, suprastin or tavegil. Apply anti-inflammatory ointment to the skin at the site of swelling periodically. You can also apply a compress with dimexide, soda or ammonia to relieve burning and itching.
- If the swelling quickly increases to a decent size, the skin in this place becomes hot to the touch and very dense, you should not limit yourself to home treatment. Go to the doctor right away.
- Has the wound started to fester? This is one of the most unpleasant consequences of a bite. Treatment in this case should be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. If painful bumps have formed, the wound has become suppurated, or gadfly larvae have gotten under the skin, then surgical intervention is necessary.
- If you feel weak, dizzy or your body temperature is above 37 degrees, then you should not self-medicate - go to a medical facility.
- Does your child complain of pain after being bitten by a horsefly? It is necessary to give him a pain reliever (Nurofen, Panadol, etc.) and urgently show him to the pediatrician.
What does the bite site look like?
Each person reacts differently to a gadfly bite. It all depends on age, the state of the immune system, predisposition to an allergic reaction, sensitivity. Two small punctures are visible on the skin; blood oozes through them for a long time. Swelling occurs immediately, after a couple of hours, or does not appear at all.
You can distinguish a gadfly bite from a wasp, bee or bumblebee by the following signs:
- the bite site becomes pale, and a bright red rim appears around the edges;
- tumor growth is observed (swelling of the entire leg or arm is possible);
- the temperature rises at the site of the bite;
- the skin itches and itches.
You should not scratch the tumor; it can become infected. In this case, the gadfly’s bite looks like an abscess. Pus begins to ooze from the punctures, body temperature may rise, weakness appears, and an inflammatory process is observed in the blood.
What you need to know
The overwhelming majority of people cannot accurately distinguish a horsefly (large, often with multi-colored eyes playing with colors) from a gadfly (smaller, less bright), and the assistance that should be provided to the victim depends on this. There are more than 3.5 thousand varieties of large flies that attack humans and mammals.
Most are classified as horseflies (3000 species) and gadflies (50 species). They are quite similar, so at first glance it can be difficult to determine exactly which particular insect this is, even for an experienced biologist.
Subcutaneous botfly - more often causes invasion in humans than other species
Important. The fundamental difference between horseflies and gadflies is that the former feed on blood, while the latter lay eggs under the skin of warm-blooded animals.
Only females always bite. If she manages to lay a clutch, then after a short period of time the larvae begin to hatch under the epidermis.
The duration of the infestation may vary, depending on the type of insect. For humans, the danger is posed by the subcutaneous gadfly (see photo), in this case it lasts about two months - all this time the larvae will parasitize and cause severe discomfort.
Most often, laying does not occur due to noticeable pain at the time of piercing the skin, but in certain cases (deep sleep, intoxication, the inability of a person (for various reasons) to drive away an insect, etc.) the eggs still end up under the skin.
All other types of gadflies are not so dangerous for humans, except in cases where the larvae end up in the eyes, which can cause the development of conjunctivitis and deterioration of the visual analyzer; in special situations, treatment even requires surgical intervention. Most of all, insects bother large warm-blooded animals, but sometimes small rodents also suffer. The larvae infect various organs, and when they accumulate in large numbers in the body, they cause the death of the infected individual.
Causes of bites
Flies go through several stages of development. The female lays a huge number of eggs, within a week larvae emerge from them, and from there pupae. And only then a big fly flies out.
It’s not hard to guess why horseflies bite – everything has to do with nutrition and reproduction. Only females are dangerous. They need blood to lay eggs and maintain vital forces. Without this component, the female will not be able to give birth to new offspring.
The diet is dominated by fresh blood of livestock and wild animals. But if a person appears in the field of view, the horsefly will not miss the moment. Males feed exclusively on flower nectar and do not live long. After fertilization, the females soon die.
Interesting!
One female is capable of laying from 500 to 1000 eggs. The first stage larvae develop on the host body. They are cattle, forest dwellers. The worms feed on blood and after a while fall into the grass, onto the soil, and pupate there. After a few days, it transforms into a fly.
Life of a horsefly
These blood-sucking flies feel good in light forests, fields, steppes, as well as in deserts and on mountain slopes. Horseflies crowd into bodies of water where the necessary moisture is available. The larvae of most species develop in water. Adults spend most of their lives in flight, being well oriented in the area. They love sunny and hot weather, so they are most active during the daytime on summer days.
Nutrition
The diet of a horsefly depends on its developmental phase and gender. Insect larvae consume invertebrate animals that live in water bodies or soil. The food of adult specimens, called adults, varies: males feed only on plant products (nectar of flowers, plant juice) or “milk” from aphids, and fertilized females are literally bloodthirsty.
Females can feed on carrion: the corpses of animals that died 1-3 days ago. Because of this, insects become carriers of infectious diseases.
Reproduction
Caring for procreation and breeding offspring in blood-sucking flies begins in the warm season. The exact period depends on the climate of the area and the specific type of insect. The way horseflies reproduce is identical to the type of reproduction in dipterous insects. Under favorable circumstances, opposite-sex individuals mate, and after some time lay a clutch. Pregnant female horse flies need to feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals.
The development of horseflies takes place in 4 stages:
- Eggs. One female can lay from 400 to 1000 pieces. The eggs have an elongated shape.
- Larvae. They are spindle-shaped and have no limbs.
- Doll. Looks like a butterfly pupa.
- Imago is an adult insect. How long horseflies live depends on the species. But their life cannot be called long: it usually lasts one summer.
The total duration of horseflies from the moment of laying eggs until the death of the imago is up to 4 years.
A very common genus of horseflies, including approximately 400 species of insects with a characteristic appearance.
These are ash-gray flies, 6 to 13 mm long, with marbled wing patterns. They hunt silently and attack in both clear and rainy weather. Rainflies live in Eurasia and Africa.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Laiki: description, photos and character of popular varieties of the breed
An insect goes through a full cycle of transformation: egg, larva, pupa, adult. Life expectancy 1 year. There is one peculiarity: adult gadflies do not receive food. Their existence is possible due to the substances in the body obtained by the larva. The life period completely depends on the temperature and the speed with which the insect creates a “platform” for its offspring.
The female gadfly carefully selects a place on the animal's skin. Areas with less wool are suitable for this. They attach up to 2-3 eggs per hair. This condition lasts from 3 to 20 days. Development phases:
- The larva at the 1st stage grows for several days, then gets inside the victim, thanks to hooks on both sides. The movement goes through the blood vessels, the spinal column and to the fat layer in the direction of the brain canal. The rest is sent to the esophagus and penetrates into the mucous tissues.
- Larvae 2-3 tbsp. move to the back and lumbar region. At the attachment site there are tissue capsules. To develop further, they need oxygen. To receive it, the larvae make special passages through the skin of the animal (fistula). As they develop, they molt and emerge to the surface through ready-made holes in the dermis. After which pupation occurs on the ground.
- The next phase lasts from 1 to 7 days after leaving the animal’s body. The rate of further growth of pupae, depending on humidity and temperature, lasts 33-44 days.
- As a result, the adult fly (imago) emerges within three to five seconds. The insect is ready for new mating and flight.
The short life cycle of a fly (1 year) ends in death; the gadfly does not hibernate in the fall. During the cold winter, the larvae live inside the victim. An adult insect lives very little (3-20 days). By the end of life it loses most of its body weight. In cold weather, the insect almost does not fly. In this case, life is extended by another month.
Adult gadflies are able to reproduce immediately after emerging from the pupa. It is noticed that the mating process takes place in a constant place where they fly every year. After which the females begin to search for an animal to procreate. A large number of eggs each contributes to rapid reproduction. Insects have few enemies, only birds. In southern regions, gadflies mate longer than in northern latitudes.
Gadflies have adapted to live next to many animals. They parasitize small rodents, artiodactyls, the largest rhinoceroses and elephants. Even with a minimal number, due to the high fertility of females, insects multiply quickly in the almost complete absence of enemies.
Horse Gadfly
The equine botfly presents a seasonal challenge because it lays its eggs on the inside of horses' front legs. On the cannon bone, knees, sometimes on the throat or nose.
The eggs appear as small yellow blobs of paint and should be carefully removed during laying season (late summer, early fall) to prevent infection in the horse. When a horse rubs its nose on its legs, the eggs go into the mouth, and from there the intestines. There the larvae grow and attach to the lining of the stomach or small intestine.
Attachment of larvae to tissue causes mild irritation, which leads to erosions and ulcerations. Removing eggs (which stick to hair and fur) is difficult because the bones and tendons are located just under the skin on the bones. They are removed with a sharp knife (razor blade) or coarse sandpaper.
Must be caught before reaching land. If the larvae remain attached, they develop for 10–12 months and leave the body through feces. From time to time, horse owners report seeing botfly larvae in horse manure.
They are cylindrical in shape and reddish-orange in color. After one to two months, adults emerge from the developing larvae and the cycle repeats. You can get rid of gadflies using several types of agents, including dichlorvos, ivermectin, trichlorfon.
What do a gadfly and its larvae look like?
Gadflies live in almost every corner of the planet; in total there are more than 150 species of insects.
In our country, 60 varieties are registered. Usually, gadflies lay their larvae in the body of animals, less often they get under the skin of a person. Dermatobia Hominis - the “human gadfly” lives in the tropics (Mexico, South America, Argentina). In the temperate climate of Russia, Ukraine and the countries of the former USSR, the insect has not been observed. The adult is a special species of fly measuring up to 20 mm. Dermatobia Hominis looks like a small bumblebee: a shaggy body and a bright orange color. The gadfly has a rather large head with pronounced large eyes, a blue abdomen, and small transparent wings.
Insects living in our latitudes usually have a calmer color: dark brown or coal-black, gray-blue. They prefer livestock as a host, but it happens that when they bite, they also infect humans.
The adult does not feed; the supply of nutrients obtained during the larval development stage is enough for the entire life cycle.
The larva after birth is very small. During the phase, it grows several times, reaching 2 cm. Its body has an oblong teardrop shape. Special hook hairs allow it to attach to the skin of animals or humans.
One adult female can reproduce up to 650 eggs, but only 20% are viable.
A species of dangerous gadfly that lives in southern countries.
Adult insects infect animals and people, giving rise to the larval problem. Knowing what a gadfly looks like, you will be able to take the necessary measures in time against flying individuals that carry eggs.
- The body size of an adult varies from 1 to 3 centimeters, depending on the species.
- The body is covered with coarse dark hairs.
- Color - dirty brown, dark brown, black, dark gray, or can imitate the color of bees, but in slightly paler colors.
- On the head there are large eyes in relation to the size of the body.
- The insect has 6 legs.
- The wings are transparent, may have a grayish tint, and are slightly longer than the body.
- Upon closer inspection, cerciform jaws can be seen on the head.
This description applies to all four types of gadflies under consideration. Of course, each of them has additional external features, such as a different number of hairs on the legs, however, this information does not play a role in the context of the fight against these parasites. You can destroy horse, bull, cavitary sheep and Russian gadflies using the same methods.
A species of dangerous gadfly that lives in southern countries.
Symptoms of bites
Not only gadflies attack, but also bees, wasps, and mosquitoes. And it is often difficult to understand exactly which insect left a mark on a person’s body. Although in the case of the gadfly there is no doubt. After an attack, the insect does not fly away, but circles over the chosen victim, choosing a place for a new bite. The marks that remain on the skin of a child or an adult have characteristic features. Thanks to two holes at the puncture site and other features, it becomes clear to any person that a gadfly has attacked. Signs:
- severe pain;
- instant redness;
- intense itching due to toxins entering the bloodstream;
- the appearance of redness and extensive swelling or swelling after the bite of an annoying gadfly.
What can happen immediately after the attack
The bite of a gadfly is dangerous due to the release of toxins into the blood. In a short period of time, they spread to all tissues and organs, leading to general intoxication. Even people who do not suffer from allergies have a reaction to a gadfly bite. Common symptoms observed in most victims:
- high body temperature (above 38.5 °C;
- migraine-like headaches;
- nausea, frequent vomiting, diarrhea.
People with severe sensitivity and a weak immune system may experience anaphylactic shock from the bite of a small gadfly. Often the site of the attack begins to itch unbearably, and a raised papule appears. If a gadfly bites a child, the consequences are not long in coming, since the child’s body does not have high resistance.
Signs of an allergic reaction
The sensitization reaction is the greatest health hazard. When a person is predisposed to developing allergies, in the absence of help with a gadfly bite (if nothing is done), the likelihood of death increases greatly. There are a number of signs that, if detected, require the victim to be taken to the hospital immediately. The issue of hospitalization is the competence of the doctor.
A successful outcome is in the hands of not only the patient, but also those around him. Symptoms for which you should not hesitate:
- the development of extensive edema that spreads quickly;
- the appearance of intense itching against the background of redness of a large area of the dermis;
- acute pain that does not subside over time;
- dizziness that prevents the victim from standing;
- attacks of vomiting, only becoming more frequent each time;
- lethargy, apathy, indifference to everything that happens;
- decreased motor activity, fatigue, weakness.
Please note! In case of a severe allergic reaction after an insect attack, the victim involuntarily empties the bladder and (or) intestines.
Clinical manifestations after a bite
Common reaction to a gadfly bite
Typically, a person is attacked by one or more flies over a period of time. It is quite difficult to drive away the insect; it shows excessive persistence and pursues the object chosen for laying eggs for a long time.
The easiest way out in this case is to go indoors or kill the gadfly. Some species fly almost silently and are able to land on the skin unnoticed, despite their rather large size. At the moment of the injection, a person feels a strong burning pain, which differs from mosquito or wasp bites.
The consequences will be as follows:
- a red dot is visible at the puncture site, there may be no blood or very little of it is released;
- a papule forms around the wound, which subsequently resolves;
- the pain is short-lived, the itching from a gadfly bite can be of varying intensity (depending on the type of individual and the characteristics of the body’s response);
- as a rule, slight swelling and hyperemia forms.
Note. After being bitten by a gadfly, there is no need to comb the skin. This will increase irritation, and harmful bacterial microflora can enter the body through the damaged epidermis.
Gadflies are parasites and before meeting a person they can come into contact with various animals, so it is possible that when the skin is punctured, the wound will become infected with pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, the reaction to the bite will be stronger; suppuration may appear, which is quite painful on palpation.
In this case, the victim should be examined by a doctor and prescribed treatment to eliminate negative symptoms and stop the spread of infection. The cost of self-medication is often prohibitively high, because if timely qualified assistance is not provided, the infection can be severe, and the resulting abscess will need to be opened surgically and cleaned.
The insect injects substances under the skin to which the immune system reacts violently.
In particularly sensitive individuals, clinical manifestations are quite pronounced:
- temperature (febrile or subfebrile indicators);
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- dyspeptic manifestations.
How to protect yourself from being bitten
When planning a trip to nature, you need to wear closed, light-colored clothes with long sleeves that do not have a bright pattern. The fact is that the eyes of horseflies can only distinguish dark or very bright colors well. It has been noticed that light-colored pets are bothered by horseflies much less than their counterparts painted in darker colors.
For country picnics, you should choose places significantly removed from pastures, farms and other places where you can find grazing livestock, since they are always accompanied by clouds of blood-sucking insects.
Horseflies are repelled by the pungent smell of wormwood. By hanging bunches of it near doors or windows, you can be sure that not a single one of them will fly into the house.
By throwing a few stems of chamomile into the fire, you can protect your campsite from annoying bloodsuckers.
A good way to protect against horsefly attacks is a mosquito net thrown over the tent. Horseflies prefer to bite sweaty or wet people, so you should not swim in a pond located in places where these insects are large.
Often, to reduce the number of bloodsuckers, special puddle traps are set up in farmyards by pouring a small amount of kerosene or fuel oil into them. Distributed in a thin layer over the surface of the puddle, these liquids prevent the take-off of insects that decide to drink from them on the fly.
Do not neglect traditional repellents. By scaring off bloodsuckers, they can temporarily save a person from many bites.
After an insect bite, swelling occurs, which causes a lot of trouble for a person. Redness and itching may begin. It is necessary to take timely measures to eliminate these unpleasant symptoms. If your leg is swollen after an insect bite, the treatment method depends on what kind of pest it was. This is discussed in more detail in the article.
Insect bites are most troublesome for allergy sufferers because they experience an allergic reaction and the itching does not go away for several weeks. But this can affect all people.
To facilitate the process you need:
- Treat the bite area with ammonia.
- Wipe the sore spot with vinegar, diluted with soda, vodka and lemon juice.
- Take an allergy medicine.
- Use an ointment with a cooling effect.
- Consult a doctor if swelling does not go away.
Prevention
It is better to prevent an insect attack than to treat negative consequences, therefore, when going to nature to relax, you should take precautions. Of course, a single bite of a horsefly or gadfly will not be fatal to a person; an attack by a group of insects can seriously harm health.
Following simple preventive measures will help avoid unpleasant consequences from the invasion of dipterans:
- Bright clothing and dark colors attract pests. It is better to wear clothes in light colors.
- Insects are active in warm sunny weather. It is recommended to take this into account when planning your vacation.
- It is recommended to wear thick clothing with long sleeves and wear trousers instead of shorts, as gadflies are attracted to exposed areas of the body.
- Insects are especially active in attacking a wet body, so it is recommended to immediately dry yourself with a towel and change into dry underwear when leaving the water.
- Sit for a picnic away from dense forests, rivers and ponds, since these are the habitats chosen by horse flies and gadflies.
- If you are planning a vacation with an overnight stay in nature, then the tents should be protected with mosquito nets, which should be checked for holes.
- Gadflies are repelled by the smell of plants such as chamomile, wormwood, tansy, so you can stock up on plants by placing them near your resting place.
- Use special protective equipment against bites of gadflies and other pests in nature.
So, the bite of a gadfly or horsefly poses a danger to human health, especially if he is susceptible to an allergic reaction, so it is necessary to take precautions when going into nature. Before planning a family vacation in nature, you should think carefully about everything and stock up on pest repellents, especially if you are planning a vacation with children. Well, if a person does become a victim of dipterans, emergency treatment should be carried out immediately to avoid serious complications.