The yellow sak spider or Heiracanthium is a typical representative of predators. It feeds on small insects - aphids, mites, caterpillars, moths. The most colorful species live in tropical countries with warm, humid climates. In the former CIS countries and Russia, the spider is found in the summer. Lives in the forest, in fields, forest edges, orchards, orchards, and city parks. The spread of the yellow spider was facilitated by climate change and hot, long summers.
Photo and description of appearance
The predatory sak spider is small in size. The body of an adult is only 10 mm. The limb span is 25 mm. Females are several times larger than males. The body consists of the abdomen and cephalothorax. Covered with a dense shell. 4 pairs of legs, forelimbs help to grab the prey and hold it during feeding.
The abdomen is bright yellow. Slightly darker than the paw. The cephalothorax is massive, red-brown in color. Powerful jaws, pointed and rounded at the end, catch the eye. With this piercing weapon, the predator breaks the shell, the chitinous cover of the victim, and then injects poison.
On a note!
There are 8 eyes on the head, which are clustered together, but the spider’s vision is poor. The organs of smell and touch located on the limbs help to navigate the environment. The golden sak spider senses the approach of a victim or enemy by vibrations in the air, web, and smell.
The male has a yellow-brown coat, not as bright as that of the females. The size of the spider, including its limbs, barely reaches 15 mm. The main mission is to fertilize the female. After which the arthropod dies.
A photo of the saka spider is located below. You can examine the features of the body structure, color, and powerful jaws of the predator.
Yellow spider sak
Biological characteristics
In official biological language, argiope belongs to the family of orb-weaving spiders. This family is characterized by the production of a large circular catch net with a pronounced spiral stabilimentum in the center. This section of the web is clearly visible in ultraviolet rays, which are distinguishable by many insects, and therefore the stablimentum is so attractive to various insects and beetles.
Reference! Stabilimentum - threads of the web that form a zigzag pattern.
Appearance
According to the description, the Argiope spider really looks like a wasp or a zebra. The body of the arthropod clearly shows an alternation of black and yellow stripes, however, this is characteristic only of females. Males of this species are small and inconspicuous.
Argiope Brünnich spiders exhibit pronounced dimorphism. The female has a body size of 15-30 millimeters in length, while the male Argiope barely reaches half a centimeter.
Spreading
This striped black and yellow spider mainly inhabits the middle and southern regions of Europe and Russia. But recently, thanks to climate warming, argiope has begun to be found in the northern regions. There is information that our spider was seen in the Moscow and Nizhny Novgorod regions, and even further north.
Lifestyle
The usual colony of Argiope settles in forests or meadows. where there is a massive number of potential casualties. The number of one settlement is usually about two dozen spiders.
A yellow striped spider weaves its webs in the twilight evening. He spends no more than one hour making his trap. After the web is woven, its owner is placed in the center of the network and, taking the shape of the letter "X", awaits the victim.
It should be noted that the Argiope catching net is very beautiful; it is distinguished by the presence of a pronounced circular shape and small cells, through which even the smallest mosquito cannot break through.
Nutrition
The zebra argiope spider feeds on the insects that fall into its web. These are mainly numerous Orthoptera, although various flies or mosquitoes often find themselves in the web. The spiders inject poison into them and entwine them with cobwebs, then they suck the juices from the victim’s body, which has begun to dissolve.
Reproduction
The female reaches the age of sexual reproduction after the last molt of her development. During mating, the female wraps a web around the male, and if he fails to get out, then his fate is unenviable - he will certainly be eaten.
And the female will then weave a large cocoon, into which she will place her numerous eggs, which she guards with the care of a loving mother.
At the beginning of autumn, the spiderlings emerge from the cocoon, and, being attached to the webs, are carried by the wind around the area, thus creating new colonies of spiders.
Attention! Flying webs during Indian summer, among other things, are a way for spiders to spread in open areas.
In other cases, the female can lay eggs, and there are up to a hundred of them in one cocoon, in late autumn, and the young spiders hatch and settle with the arrival of spring. The female herself does not overwinter, but, having laid eggs, dies.
What does a spider's web look like?
The spider does not spread its trapping nets in the form of a canvas, typical of many arachnids. Sak makes a bag out of dense web threads into which the victims are caught. A similar cocoon is weaved after fertilization to lay eggs. Often the web blocks the entrance to the shelter. The predator is engaged in weaving webs at night, and during the day it sits quietly in the chosen place.
The yellow sac spider is a poisonous arachnid.
Yellow sac spiders are regularly found in close proximity to human settlements, often appearing in houses, tourist centers and forest recreation areas.
These spiders have a cytotoxic venom that causes swelling and pain that lasts for 7-10 days.
Although necrotic bites are quite rare, it is nevertheless necessary to know that yellow sac spiders can be quite aggressive, especially females, in protecting eggs and nests.
Painful bites are neutralized with antitoxins; for this, victims turn to doctors.
Currently, yellow sac spiders do not have any special protection status. This is a pretty common look.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Reproduction
The lifespan of a female is 1 year. The mating season begins in mid-summer, and towards the end the female lays eggs. For laying, it initially forms a cocoon-bag from its own web. At one time, the spider lays up to 600 eggs. The young take several weeks to develop. The female holds the cocoon near her, ensuring safe formation.
After birth, the cubs of the saka spider live with their mother for a long time. Initially, she provides them with food and teaches them to hunt. During the entire period of growing up, spiders go through up to 7 molts, each time increasing in size.
Interesting!
At the last stage, the genital organs are formed, the body acquires a characteristic color. Adult Cheiracanthiums eat the mother and begin to reproduce themselves.
Danger to humans
All real spiders are poisonous, otherwise they would not be able to absorb food. But few of them are dangerous to humans. Representatives of the Lycosidae family cause fear with their size and appearance, so it is not without reason that they are included in the rating of the most terrible spiders. But whether wolf spiders are poisonous or not is a relative question. Among them are species of varying degrees of toxicity. It is common to fear tarantulas, which even gave rise to the Tarantella dance, according to legend.
In fact, the toxicity of this family of arthropods living in temperate climates has been greatly exaggerated. The bite causes local irritation, characterized by short-term pain, itching and redness.
Tropical species are more dangerous. Their bites cause:
- edema;
- prolonged pain;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- rapid pulse.
The bite is also not fatal, but to alleviate the consequences, you should consult a doctor.
Nutrition, lifestyle of a spider
The yellow golden sak is nocturnal and hides in secluded places during the day. Caterpillars, aphids, and moths become its food. The spider waits for them in the shelter, and then attacks with lightning speed. With its powerful jaws, the spider gnaws through the chitinous cover and injects poison.
Yellow spider sak
The toxic substance affects the nervous system and paralyzes the muscles of the insect. The predator injects saliva into the wound, which liquefies the insides of the prey into a broth and leaves the prey for several minutes. After some time, the spider returns, sucks out the insides, leaving only a chitinous covering of the insect. The same fate awaits an insect caught in a web.
Do Argiopes bite?
There is a category of people who definitely need to stick their hand somewhere: into an anthill, into a bee hive or a wasp’s nest. Such inquisitive characters do not ask questions about whether certain representatives of the fauna bite; they can experience everything first-hand.
For the rest, we inform you that if you put your hand into a web, intentionally or accidentally, the spider will immediately react and bite. The sting of argiope is quite painful and comparable to that of a bee or aspen. The fact is that the wasp spider has quite strong jaws, and it is able to bury them quite deeply under the skin. In addition, do not forget about its poison.
Many people ask whether Argiope Brunnich is poisonous or not? Of course it is poisonous, because with its poison it kills its victims. Another thing is that in most cases this poison is practically not dangerous for humans.
Is sak poisonous or not?
The yellow spider Heiracanthium has poisonous glands and injects a toxic substance into the wound of the victim. For a person, the dose of poison is extremely small, so there is no danger to life. A predator rarely attacks people when they encroach on its own life. However, the likelihood of being bitten increases if the spider gets under clothing or is accidentally crushed by a bare foot or hand.
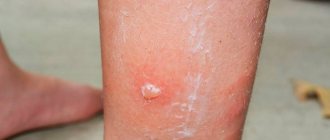
After a bite, unpleasant symptoms appear:
- pain;
- burning;
- redness;
- edema;
- blisters;
- suppuration.
For days the bite site hurts and burns. The next day, the painful sensations are replaced by itching.
People prone to allergies, with weakened immune systems, and young children may develop general symptoms of intoxication.
- headache;
- weakness;
- difficulty breathing;
- vomit;
- abdominal pain;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased blood pressure;
- change in body temperature.
Local symptoms disappear on their own after a few days; if there are signs of intoxication, you should consult a specialist. The likelihood of a severe allergy increases if the spider has bitten repeatedly or there have been several of them. There have been no recorded deaths following a saka bite.
On a note!
If you find a Heiracanthium spider in the house, you should not make sudden movements or try to crush it. The arthropod jumps well and instantly delivers a bite with its powerful jaws. Initially, you should cover the predator with a jar, bucket, or any container that comes to hand. Carefully cover with a sheet of paper, take it outside, and shake off the container. If you decide to kill a predator, spray it with any insecticide.
What to do if you are bitten by a spider?
The bites of most Cheiracanthium spiders cause a local reaction, which is accompanied only by skin redness and slight swelling. In this case, it is enough to wash the wound with soap and water and apply a cold compress. You can also prevent the inflammatory process by raising your hand up.
To exclude the possibility of deterioration in health, it is necessary to take an analgesic (regular paracetamol is sufficient).
If the above options do not help, you should immediately go to the hospital.
The lifestyle of spiders of the genus Cheiracanthium in natural conditions has not been sufficiently studied. But well-known research works suggest that their venom is the most toxic among arthropod venoms in all of Europe. Therefore, you should be careful in places where spiders may be located and under no circumstances try to touch them with your hands if you find them.
Benefit
The poisonous spider is recognized as an active destroyer of agricultural pests. During the season, one small female eats more than 2 thousand caterpillars, adult moths, and aphids. Nobody specially lets yellow sakas into the territory, but if they appear, they are in no hurry to use insecticides. Spiders cause little harm to humans; people suffer through negligence. But the benefits for the environment are enormous. Predators regulate the number of harmful insects that eat plants, crops, and trees.