Description and features
The class of arachnids is diverse and includes a huge number of species. Scientists number them somewhere around one hundred thousand. Spiders are only one of the orders of this class, and despite their relatively small size, it is not for nothing that they are considered far from harmless creatures. This especially applies to representatives of the migalomorph infraorder.
Specimens of this type are usually larger than their relatives, and also differ in the structure of their oral chelicerae (the word itself is translated literally: claws-whiskers, which says something about their purpose and structure). In these spiders, they are associated with poisonous glands that open in them, ducts.
The family of tarantula spiders is part of this infraorder. Its members are very large. It happens that the leg span reaches 27 cm and even exceeds these figures.
All species of tarantulas are venomous, but with varying degrees of toxicity. Some are almost harmless, but most should be considered quite dangerous. As a rule, their bite cannot be fatal for a healthy adult, but it causes acute pain and can cause convulsions, fever and even hallucinations.
When defending itself, a tarantula can shed hairs from its paws, which leads to allergic reactions in humans.
In addition, the effects of the poison of the described creatures can be lethal for children and small animals.
Fortunately, such living organisms are practically never found in Europe, except that some species live in Portugal, Spain, Italy and areas close to these countries. However, as for other continents, the range of these spiders here is quite extensive.
After all, they almost completely inhabit the south of America and Africa, and are widespread in Australia and on the islands adjacent to this continent.
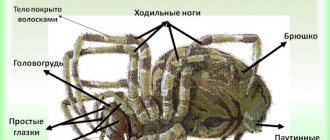
In the photo of the tarantula, you can see that the appearance of such creatures is unique and exotic. The shaggy long legs of such spiders make a particularly strong impression. Moreover, purely visually, it turns out that these creatures have six pairs of limbs. They are covered with bright, thick and significant hairs.
But upon closer examination, only four pairs of legs turn out to be, and four more processes, shorter and located in front, are the chelicerae and the so-called pedipalps.
The colors of such spiders are striking and amaze with their exotic colors, but the range of colors becomes especially rich after the tarantula moults . This is a very interesting and characteristic process for such living beings. Their body is built from the cephalothorax - the front part and abdomen, connected only by a jumper. They are covered with a chitinous exoskeleton - a special shell.
This is a frame that retains moisture during the heat, and like armor that protects from damage. During molting, it is discarded and replaced with another. But it is precisely at such moments that the animal grows intensively, increasing its parameters sometimes almost fourfold.
During molting, tarantulas can increase significantly in size
Such creatures boast four pairs of eyes, they are located in the front. The pedipalps serve as organs of touch. Chelicerae are used primarily for hunting and defense, but also for dragging prey and digging burrows.
And the hairs on your legs should be considered more than just decoration. These are finely structured organs that capture smells and sounds with their inherent sensitivity.
Feeding the tarantula
Spiders do not eat very often: an adult spider requires food once a week. The best size food is equal to the spider's abdomen, but it may try to attack larger prey, especially if it is very hungry.
They feed on various insects:
- locusts;
- crickets;
- cockroaches of various types;
- mealworms;
- Zophobas larvae.
For adult tarantulas, even food such as large Madagascar cockroaches, small frogs and even mice are suitable.
Suitable prey must be alive and moving, and then the spider will begin hunting for it. He will happily chase her across the entire surface of the terrarium and experience excitement. This is a natural behavior that is beneficial for him.
It is worth remembering that adult vagans can go without food for a very long time - for several weeks, and with good health they can go hungry for months, up to one year. At the same time, you need to always have unlimited water nearby. Of course, there is no need to specifically go on hunger strikes for them, but you shouldn’t worry that the spider is starving. You can increase the period between feedings to 8-10 days. You shouldn't feed them too often.
The second name of the tarantula spider from the genus Brachypelma is the Mexican red-haired tarantula spider.
With young individuals everything is different. They grow actively and need food much more often than adults. It is advisable to feed them once every two days, and the youngest ones constantly, never limiting their access to food. There should be something edible in the terrarium at all times.
By the way, small tarantulas do not need that much space, and they can even be kept in small containers. This will make it easier for them to find food.
Molting can be called a special period for each spider - its body prepares for it in advance and adapts subsequently. Therefore, some time before the start of the process, you need to stop feeding the insect. You can resume feeding a few days after molting.
Kinds
This family has many representatives, including thirteen subfamilies, divided into a huge number of species (according to official data, there are about 143 of them). The characteristics of their representatives are very characteristic, so the most interesting varieties deserve special description.
1. The Goliath tarantula is a creature famous for its size, which, including the length of its legs, is about 28 cm. Previously, such a specimen of the planet’s fauna was considered the largest of the spiders.
But the very beginning of the 21st century was marked by the discovery of Heteropoda maxima, a relative in the order that lives in the tropics and is a couple of centimeters larger than the Goliath, which means its size is not limiting.
The color of such a spider is brown, sometimes with shades of red or light colors. Such creatures live in the swamps of South America. The weight of males of the species can reach up to 170 g.
Goliath is considered the largest tarantula spider
2. Black and white Brazilian tarantula spider . Representatives of this variety are slightly smaller than the previous one. Their sizes usually do not exceed 23 cm. They are famous for their intensive growth and bright, elegant, although black and white coloring.
The spider has an unpredictable and aggressive character. Often such creatures hide among stones and under tree roots, but sometimes they crawl out into open areas.
3. Metallic tarantula (arboreal) is also a remarkable species that is found only exclusively in southern India. But in this case, the spider stands out from its relatives not at all in its size, growing no more than 21 cm, but in its brightness and bewitching, fabulous beauty.
Its body and paws are blue with a metallic tint, decorated with wonderful patterns. Such creatures, uniting in groups, live among rotten old trees.
4. Smith's brachypelma is a species found in the southern United States and Mexico. The size of such spiders usually does not exceed 17 cm. The color can be black or dark brown with the addition of red and orange areas, in some cases decorated with a yellow or white border; The frequent hairs on the body are light pink.
This species does not have a toxic poison and is not considered particularly aggressive.
In the photo is the Brachypelma Smith spider
As for the size of the tarantula , this has already been mentioned. But the parameters were given earlier taking into account the leg span. However, the body itself of the largest spiders is about 10 cm in size, and in small species it can be less than 3 cm. It should also be mentioned that tarantulas change their color with age and as they mature.
Arachnid limbs
In fact, many people, when asking the question of how many limbs a spider has, mean only its legs. But the limbs include not only the legs, but also other parts of the body. This representative of the fauna has a feature that people often do not notice. It's all about the forelimbs, called tentacles. Yes, they look like paws, but they have a different function, or rather two:
Leg tentacles are clearly visible in large species. These include: the tarantula theraphosa blond, the South Russian tarantula, nephila and others. In large arachnids, you can also notice chelicerae - strong protruding jaws located in front of the mouth. This part of the body is also a limb. Chelicerae allow them to defend themselves from opponents, pierce through the victim, and in some cases dig and tear holes in the ground.
Chelicerae are also needed to inject venom (for those who have it) into the victim, as if a scorpion were using its sting. The claws also have another name - pedipalps. Males use them to fertilize females.
Lifestyle and habitat
Different types of such spiders take root in a wide variety of geographical areas and conditions. Among these representatives of the fauna, settlers of arid places and even deserts are known. There are species that prefer equatorial forests with their tropical humidity.
Arboreal tarantulas spend their days on bushes and trees, in their crowns among the branches. They weave webs and roll them into tubes. Others prefer solid ground and find shelter in this environment. There are quite a few species of spiders that dig holes for themselves that go deep underground. They cover their entrances with cobwebs.
Tarantulas can live in burrows (burrows) and trees
In addition, the habitat of these creatures largely depends on the stage of development of the individual. For example, as a larva, it spends its days in a hole, and when it grows up it begins to go out onto the ground (this happens in semi-arboreal and terrestrial species). That is, the behavior pattern of these spiders may change as they grow and mature.
Regarding the growth stages of such living beings. Newborn spiders that have just emerged from eggs are called nymphs. During this period of development, they usually do not need food.
Next, the nymphs, undergoing a couple of molts, during which rapid growth of the body occurs, turn into a larva (this is what spiders are called until they reach adulthood).
The hairs covering the body of such creatures are saturated with poison. For their owners themselves, this is a very useful acquisition they received from Mother Nature. Tarantulas use such fur shoots to protect nests by weaving them into webs.
Also, anticipating danger, they spread poisonous hair around themselves, thereby providing themselves with protection. If they enter the body through inhalation, even a person may experience painful symptoms: weakness, suffocation, burning - all these are signs of an allergic reaction.
Tarantula spiders are not particularly mobile. And if they break this rule, then only if there is a good reason. For example, female tarantulas, if they are well-fed, can sit in their shelters for several months. But even hungry individuals are motionless and patient. They are in their ambushes and stalk their prey.
Spider behavior
This species has many differences from other spiders in the genus Brachypelma. For example, he loves to dig holes and does this at home, if the substrate layer allows. For this reason the insect is called a burrowing spider. However, he is not always inside the hole and quite often goes for a walk on the surface of the earth.
If there is insufficient humidity, the spider may have problems with molting.
Its character may be different. Many experienced experts say that keeping a tarantula is not recommended for beginners , as it behaves aggressively and unpredictably. Indeed, some individuals show aggression even for minor reasons, immediately taking a stance and trying to bite. However, this does not always happen, and quite a few representatives of the Vagans species have a peaceful, calm disposition.
If you want to breed these arthropods, then you need to pay attention to the fact that bad character is a hereditary trait . If at least one of the parents is its carrier, then there is a high probability that all offspring will inherit it. Therefore, for breeding it is necessary to carefully select individuals with the most suitable behavior.
Those who have already got a not-so-good-natured tarantula should hope that the character will change after molting. But under the influence of the next moult it can change back.
Nutrition
It is in connection with its feeding habits that such a spider received the name: tarantula . And this story happened at the end of the 18th century in Venezuela, when a group of scientists discovered a huge spider in the tropical forests, eagerly eating hummingbirds.
Then even one of the expedition members, Maria Merian, made a colorful sketch of a tarantula, impressed by what she saw. And he soon made it into the newspapers, creating a certain fame for all the spiders of this family, which became the reason for the name.
In reality, the organisms of such spiders are not often able to digest bird meat. That is, such cases do occur, but rarely. Basically, these creatures eat insects, small arachnids, and can even encroach on their own relatives.
Tarantulas are active predators and can even eat their own relatives
But they are definitely predators. They ambush their victims. And to catch them, pre-prepared traps are used. The diet of these spiders includes: birds, small rodents, frogs, in some cases fish, as well as smaller prey - bloodworms, cockroaches, flies.
Reproduction and lifespan
tarantula spider matures faster than any of the females, but after that it lives no more than a year, and if it manages to mate, then even less. His readiness to have offspring can be guessed by his characteristic external signs. Firstly, bulbs are formed on his pedipalps - natural vessels for sperm.
Males also develop special hooks called tibal hooks, which play a certain role during mating. These devices are needed to hold the partner, as well as protection from her, since the chosen ones of spiders can turn out to be very aggressive individuals.
With the help of arranged webs and hairs on the body, the tarantula senses everything around
In preparation for a meeting with the “lady,” males weave a special web, secreting a drop of family fluid onto it, then grab it with hooks and begin searching for a partner.
But even when the spider is there and responds to the call, showing consent with all her appearance, intercourse does not occur without performing the required rituals. Without them, spiders are unable to determine whether they belong to the same species. This may include bodily shaking or paw tapping. Each variety has its own mating movements.
The intercourse itself can be instantaneous, but sometimes it lasts for hours. And the process consists of the male’s pedipalps transferring his sperm inside the partner’s body.
Such games are completely unsafe for spiders. Some of them may suffer even before copulation if the couple does not get along with each other (this happens more often in aggressive species). And after the act itself, the male usually flees for his life, since if he does not show agility, he may well end up eaten by a hungry female.
Next, the process of egg formation occurs in the spider’s body. And when the time comes, she forms a nest of cobwebs, where those same eggs are laid. Their number varies, in some species it is in the tens, and in others it reaches a couple of thousand.
After completing this, the spider makes a special spherical cocoon and incubates it. This period lasts differently for different species (it can last twenty days or more than a hundred). Moreover, the female can guard her offspring with aggressiveness and zeal, and can even eat the entire farm if she is hungry.
That's the nature of spiders. From the mentioned cocoons, nymphs first emerge, molt and grow, turning first into larvae and then into adult spiders.
Nature has given females a longer lifespan than their male counterparts. Spiders are considered the champions among arthropods in terms of lifespan. The record is 30 years old. But, strictly speaking, the duration of the life cycle depends on the species, and is sometimes measured in ten years, but in some varieties it is only a few years.