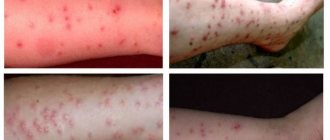
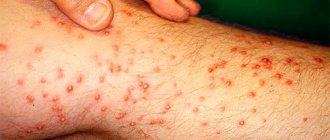
Midge bite
There are two types of blood-sucking insects. Some have a mouthparts designed in such a way that they gently bite through the skin and suck blood using a proboscis. The second group of midges literally gnaws out fragments of skin. This type of insect does not have a proboscis.
A midge bite looks different depending on the structure of the mouthparts. In the first case, it is a small dot on the skin of a dark burgundy color, and in the second, it is a small round abrasion, torn at the edges.
Where do they bite?
The midge mainly bites a person on areas of the skin not protected by clothing (face, forehead, outer part of the foot, lower leg, forearm). But in some cases, insects are able to get under pants or a T-shirt. In this case, bites appear on the upper thigh and stomach.
The favorite habitats of midges are areas near rivers or swamps. This increases the risk of being bitten. Especially in hot sunny weather. But this does not mean that the evening is an ideal time when you cannot become a victim of a midge attack. People often suffer from insect bites after spending a weekend in the country or garden.
Interesting! Old-timers say that during the civil war, a special type of execution was practiced in Siberia. A prisoner sentenced to death was taken to a forest or to a pond. They undressed him and tied him to a tree. A man eaten by midges died a painful death.
How does a bite occur?
Most often, people do not feel that they are being bitten by a midge. On the affected area of the skin, the first signs of a bite appear only after 3-4 hours. Sometimes a person feels symptoms within a day. This is the difference between midges and mosquitoes.
What is in insect saliva?
Simultaneously with biting the skin, a specific anesthetic substance is injected into it. This is one of the components of midge saliva. In addition, at the moment of the bite, poison gets under the skin. The danger is that due to the analgesic effect of saliva, a person is bitten by 5-6 midges at the same time. And this increases the negative consequences.
How and why does edema develop?
The bitten area of skin becomes red and swollen. The swelling is caused by toxic insect saliva entering the bloodstream. It contains a substance that can cause a severe allergic reaction. At first a slight swelling appears. Gradually, the toxic effect of the poison intensifies, and the affected area swells.
What complications are possible after a bite?
Midge bites do not go away without leaving a trace. Even in people who are not prone to allergies, insect venom can cause serious consequences. Reactions to midge poison are divided into local and general. In the first case, it is unbearable itching of the skin, redness and swelling, accompanied by pain. If the lower limbs are affected by midges, then difficulties arise in movement.
Common reactions include increased body temperature, weakness, headache, and swollen lymph nodes. All these are signs of intoxication of the body. If you are prone to allergies, not only the bitten areas of the body may become blistered.
Tissue swelling decreases 3-5 days after the bite. But itching can torment a person for up to two weeks. Scratch marks appear on the skin and often become infected. As a result, purulent wounds appear. When infected with streptococci, signs of erysipelas appear on the skin.
Even if you begin to treat the itching and dark spots from a midge bite in time, marks may still remain on the skin, especially in people prone to keloid scarring.
Further treatment of bites
Even quick elimination of edema cannot prevent damage to the skin. Often, in people with low body resistance to bacterial infections, small wounds begin to fester and turn into multiple ulcers. At this stage of treatment, one cannot do without the use of ointments for midge bites with antimicrobial and antibacterial activity. What a dermatologist can prescribe:
- Levomekol;
- Levosin;
- Tetracycline ointment;
- Syntomycin ointment;
- Erythromycin ointment.
To quickly heal damaged skin, creams and ointments with epithelium-regenerating properties are used:
- Dexpanthenol;
- Panthenol;
- Bepanten.
The use of such ointments helps to quickly restore the skin even after ulcerative lesions without the formation of scars. They have a delicate consistency, are well absorbed and can be used in the treatment of midge bites in newborns and pregnant women.
Recommendation: Pharmacies have a wide range of essential oils of medicinal plants. Preparations made from chamomile, string, mint, lemon balm or sage will help eliminate swelling of the skin. To prepare an external remedy, you need to dilute a drop of essential oil in a tablespoon of water, moisten a cotton pad and apply it to the swelling.
What determines the severity of the reaction to a bite?
The reaction to a midge bite is expressed in different ways. This depends on a number of factors.
Age
Adults tolerate insect venom more easily than children. They more often exhibit local reactions. In childhood, the risk of developing general intoxication of the body increases. Midges pose a particular danger to infants. There have been cases where, with multiple bites, this category of patients developed Quincke's edema.
Immunity
Any toxin can trigger an immune response. If the body's protective functions are weakened, then the reaction to midge poison will be more pronounced.
Increased sensitivity to midge saliva
Sometimes the body exhibits intolerance to the components of insect saliva. This applies not only to midges, but also to other blood-sucking parasites. In this case, the reaction to toxins cannot be predicted.
Pregnancy and lactation
During this period, the immune defense of the mother's body decreases. If before pregnancy a woman reacted to midge bites with redness and slight swelling, then during pregnancy the consequences can be more serious.
Symptoms and pathogenesis
The limbs and neck are most often affected by insect bites. The severity of symptoms depends on the individual characteristics of the organism, the number of bites, and the presence or absence of subsequent infection due to race.
The body's response to midge bites is based on an allergic reaction. Its manifestations can be general and local. It has been clinically proven that the brighter the local symptoms, the less pronounced the general ones. This is due to the body's ability to block the lesion to prevent the spread of toxic substances throughout the body. Common symptoms include:
- tachycardia (rapid heartbeat);
- hypotension (low blood pressure);
- hyperthermia (increased body temperature);
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The palette of local manifestations is more diverse and includes:
- redness,
- soreness,
- burning,
- itching,
- edema,
- rash,
- formation of blisters or papules.
In addition, a midge bite differs from the bite of other blood-sucking insects, such as a mosquito, in that there is a small wound in the center of the area of swelling and redness. Often this wound is subjected to intense scratching, which significantly increases its area and causes the formation of a scab. In addition to the formation of a crust (scab), scratching the injury site can lead to a secondary infection.
The central symptom indicating an allergic reaction is severe itching, which is quite difficult to relieve.
Insect allergy can be accompanied by a serious disease - simulidotoxicosis (a consequence of a midge bite, characterized by the formation of blisters, severe hyperemia and tachycardia).
The body's response to midge saliva is a type 1 allergic reaction, which is based on an increase in the level of immunoglobulin E in the blood serum. Under normal conditions, this type of immunoglobulin is practically not found in the blood; an increase in its level is observed during acute allergic reactions.
What to do if bitten by a midge?
The earlier first aid was provided, the lower the risk of developing severe negative consequences.
First aid
If you are bitten by insects while relaxing in the forest, then first of all it is recommended to wipe the affected areas of the body with any alcohol solution. Then treat the skin with insect bite repellents. Nowadays, few people go on vacation in nature without taking these first aid medications with them.
In the event that a person is susceptible to the development of general allergic reactions that threaten life, he needs to urgently seek medical help.
Treatment of bites at home is carried out using medicines and traditional medicine methods. First aid is aimed at disinfecting the diseased area of skin and preventing the development of edema.
The affected area is treated with an antiseptic. These include:
- chlorhexidine;
- miramistin;
- alcohol solution of boric acid;
- furatsilin solution.
To prevent swelling from increasing, you can apply ice, previously wrapped in a cloth, to the bite site. If this is not done, there is a risk of developing skin frostbite.
Be sure to take any antihistamine tablets.
Relieving inflammation
The inflammatory process appears when scratches become infected. An integrated approach to treatment is required. Antiseptics, as well as ointments and lotions will help remove inflammation.
If there are clear signs of wound infection, the following manipulations must be carried out daily:
- Treat the bite area with soapy water (use 72% laundry soap).
- Lubricate the skin around the inflamed area with any antiseptic. Make sure that the product does not get into an open wound.
- After 1.5-2 hours, apply antibiotic-based ointment to the wound (Levomekol, Levosin, Inflarax, balsamic liniment according to Vishnevsky). It is recommended to smear midge bites at night.
- After the ulcers begin to heal, lotions are added to the treatment complex. Prepare decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus, sage), moisten gauze pads, and apply to sore spots.
Attention! pain has intensified, you should immediately consult a doctor! Of particular concern is the appearance of black spots on the skin. This indicates the development of necrotic processes.
Getting rid of itching and irritation
The poisonous saliva of the midge causes such severe itching that a person may develop a nervous disorder. This symptom is removed using traditional and folk medicine.
Ointments and gels
- Fenistil.
- Sinaflan.
- Psilo balm.
- Momederm.
- Betazon.
- Prednisolone.
- Hydrocortisone.
The first three drugs belong to the group of antihistamines, and the rest belong to the group of steroids. Regardless of pharmacological affiliation, all of these remedies effectively combat itching.
Traditional methods
- Mint toothpaste will help relieve the itching from a midge bite. It is used to lubricate blisters when there is no suitable medicine at hand.
- You can relieve itching with vinegar. It is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10, moistened with a gauze cloth and applied to the affected area.
- Blisters will itch much less if they are treated with cologne or any alcohol solution.
Fighting swelling
At home, baking soda can help relieve swelling. It will also reduce pain and relieve itching. To do this, dissolve 1 tsp in 250 ml of water. baking soda. A gauze swab is moistened with the resulting solution and applied to the bitten area. There are other, no less effective methods of combating swelling, for example:
- apply plantain or parsley juice to the bite site;
- use lotions of essential oils (mint, lemon, lemon balm, santalwood). They are used both in pure form and in solution form. For 1 tbsp. l. of any vegetable oil, take 5 drops of essential oil.
Removal of tissue edema automatically entails a decrease in pain.
Rash and redness
These symptoms are relieved with antihistamines and corticosteroid ointments and gels. The course of treatment depends on the severity of the pathological process, but in any case is no more than seven days in a row.
How to remove swelling from a midge bite?
The midge, or midge, is a blood-sucking insect common in many regions. It feeds on the blood and lymph of the objects of its attack, and when it bites, it numbs the site of skin damage. Often this area of skin becomes inflamed and red, and the unpleasant consequences of the bite are accompanied by other, more serious symptoms. To take timely measures, you need to know how to remove swelling after a midge bite.
First aid and prevention
- The first thing to do is to disinfect the bite site with alcohol or an antibiotic solution (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin).
- Then antihistamine ointment (Fenistil-gel) is applied to the skin to prevent tumors. If there is no ointment, you can treat the wound with brilliant green or a solution of baking soda.
- If the itching is severe or does not stop for a long time, you need to take an antihistamine tablet (Suprastin, Ketotifen, Cetrin, Claritin, Zodak, Zyrtec), even if there have never been any allergies before. This precaution will help reduce the size of the tumor after a bite or prevent its occurrence. It is better to choose 2nd generation drugs (Loratadine, Cyterizine). They, unlike their predecessors, do not have a sedative effect and are better tolerated by patients.
- Also, for severe swelling, you should use hormonal ointments, for example, hydrocortisone ointment. Hormonal drugs of this group have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
To prevent swelling from a midge bite from spreading, you can apply ice wrapped in a plastic bag and a clean napkin to the bite site.
Folk remedies for relieving swelling from a midge bite
Traditional recipes are used in addition to medications and cannot replace them. Most of these remedies effectively relieve swelling after a midge bite.
Traditional medicine recipes:
- Lubricate the bite area with thick foam from laundry soap.
- Apply crushed dandelion, plantain, mint, and bird cherry leaves to the bite site.
- Apply onion pulp to the swelling after the bite.
- Apply toothpaste or menthol rinse balm to the swelling.
- Apply a compress of grated raw potatoes to the tumor site.
Treating complications after a bite
The main complications include:
- increased body temperature;
- weakness and dizziness;
- suppuration of skin scratches;
- the appearance of spots and scars after the wounds heal.
All these negative consequences require symptomatic treatment. Any antipyretic tablets, for example, ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, will help relieve the temperature.
Signs of intoxication are successfully combated by drugs belonging to the group of sorbents (Atoxil, Enterosgel, White Coal).
For inflammation and suppuration of ulcers, the use of antiseptic ointments or solutions is recommended. Miramistin, Methyluracil, Povidone iodine, Betadine, Ranostop have a wound-healing effect.
In addition to drugs purchased at the pharmacy, aloe is used as a wound healing agent. Wash the fresh fleshy leaf well. To cut in half. Remove the pulp with a spoon and place it on a sterile napkin.
Treat the wound with any antiseptic. After 10-15 minutes, apply the medicine and secure with a bandage. Aloe will not only have a wound-healing effect, but also soothe itching and relieve inflammation.
When spots appear on the skin, use such products as bodyagi powder, Bruise off gel, ointments based on heparin and troxerutin.
Sometimes hardenings form at the site of the bites. In this case, absorbable compresses will help. For this purpose, you can use Dimexide. The medicine is diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1:4. Apply a gauze pad soaked in the solution to the bump.
Attention! Dimexide causes burns upon prolonged contact with skin. Therefore, keep the compress for no more than 40 minutes.
Help for face bites
The most unprotected areas of the body are the face and neck. They are often susceptible to midge attacks. Insects love to bite the skin around the eyes and lips. In this case, a person begins to experience unpleasant symptoms within a few minutes after blood contact with the poison.
The eye begins to itch and water. Swelling of the eyelids increases rapidly. An allergic reaction can cause short-term vision loss.
If a midge bites your lip, it increases in size and it becomes difficult to talk.
To minimize the development of complications, first aid should be provided as early as possible.
- Apply antiallergic cream to the affected area of skin. In this case, drugs from the corticosteroid group are suitable;
- To quickly remove toxins, the patient is recommended to drink plenty of fluids;
- Apply a compress of grated potatoes to the sore spot. This product will help cope with itching and cool the skin;
- Parsley juice will help cope with swelling. Wash fresh herbs, chop finely, place in clean gauze and squeeze well. Apply a damp swab to the bite site.
It is strictly forbidden to rub your eyes with your hands. The inflamed mucous membrane is most susceptible to infection. Bacterial flora causes the development of conjunctivitis. If a midge bites you in the eye and the eye is swollen: what to do and how to relieve the swelling, read more in this article.
Products for adults
The main symptom of multiple bites is swelling. In this case, the swelling can be either local or general, that is, spreading to other parts of the body. If the victim’s area is swollen after a midge bite, then you need to immediately apply cold to the sore spot and then treat it with alcohol. Allergic spots need to be treated using both local and internal measures - lotions, compresses, ointments, gels, etc.
The sooner first aid is provided for a midge bite, the sooner the victim’s condition will improve.
Medications
Treatment should be aimed at removing the tumor, reducing pain and suppressing the inflammatory process in the wound. How to remove swelling after a midge bite using pharmaceutical drugs? For this purpose, the following means are used:
- Cynovitis;
- Prednisolone;
- Geoxyzone;
- Fenistil.
Since midge bites in humans cause not only itching and swelling, but also the development of allergies, people prone to allergic reactions are advised to take an antihistamine:
- Suprastin;
- Claritin;
- Zyrtec;
- Zodak;
- Cetrin;
- Ketotifen.
Midge bites on the legs are dangerous because swelling on the extremities persists for two months, which can cause circulatory problems and the development of vascular disease.
If the inflammation is so severe that the patient has formed a scab, then it is necessary to thoroughly wash the wound with warm soapy water, treat it with hydrogen peroxide and go to the hospital. If there is significant deep tissue damage, the doctor will prescribe an antibacterial ointment - Levomekol, Levosin, Syntomycin or Oflocain.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies for midge bites can only be used as a supplement to creams and tablets. The following remedies can be used to reduce itching and swelling:
- Lubricating the sore spot with laundry soap.
- The use of compresses from mashed dandelion, bird cherry, mint and plantain leaves.
- You can also treat the swelling with lemon oil and apply raw potatoes to the wound.
What is strictly forbidden to do after being bitten?
- Do not use household cleaning chemicals to treat the bite area. Only the use of 72% laundry soap without fragrances and dyes is allowed.
- If scratching ulcers appear, they must be handled carefully. Do not allow alcohol solutions to get into an open wound.
- You cannot treat infants on your own. If you suspect a midge bite, a child should be seen by a doctor as soon as possible.
- Corticosteroid drugs should not be used without a doctor's recommendation.
- Despite the itching and desire to scratch, this is not recommended. Scratching is an entry point for infection.
- Corticosteroids should not be applied to an open wound. They cause a burning sensation and slow down tissue regeneration processes.
When is hospitalization necessary?
Medical assistance is required in the following cases:
- The reaction to a bite develops rapidly; available first aid remedies are not effective. It is recommended to contact the nearest medical facility.
- There is a risk of developing anaphylactic shock. You need to call an ambulance.
- Symptoms of intoxication do not subside within 5-7 days when all necessary therapeutic measures are carried out.
After examining the patient, the doctor will decide whether to recommend the patient hospitalization or continue outpatient treatment.
How to protect yourself from bites?
Unlike a mosquito, the midge bites unnoticed. Therefore, it is rarely possible to drive it away from yourself. This means that before going to the country or to the forest you need to take precautions:
- do not apply perfumes that have a persistent sweet smell to your body and clothes;
- leave as little exposed skin as possible;
- give preference to clothes made from natural fabrics;
- use repellents that repel blood-sucking insects. The products must be reapplied after the expiration date specified in the instructions;
- The smell of food attracts midges. Therefore, when sitting down to have a snack, make sure that there are no exposed parts of the body;
- In an apartment you can also become a victim of a midge attack. Especially if the house is located near a pond or forest. In hot, dry weather, it is recommended to use electric fumigators. When choosing a product, pay attention to ensure that it repels not only mosquitoes, but also other blood-sucking insects.
Summer is a wonderful time of year. It would be unwise to spend it in stuffy rooms, fearing troubles in nature. If you take all the necessary preventative measures, you can enjoy fresh air throughout the summer.