Treatment
The first stage of therapy is to clean the ear.
A cotton swab with a disinfectant removes plaque, crusts, and scabs. You should not use sticks so as not to accidentally push the secretions deeper. Zoolotions are used for processing:
- "Otifri";
- "Otoklin";
- "Fitolar".
If they are not at hand, disinfecting solutions from your home medicine cabinet will do: furatsilin, potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine, 3% hydrogen peroxide. At the second stage, the ears are treated with acaricidal preparations.
The drops received positive reviews:
- "Tsipam";
- "Surolan";
- "Ectodes";
- "Amitrazine";
- "Demos";
- "Dana";
- "Aurikan";
- "Aurizon";
- "Oricin".
The drug is dripped into both ears, even if one hurts, and distributed over the surface with massage movements.
The treatment is repeated after 5 days. Frontline Spot On and Stronghold drops have a good effect: they are applied directly to the ear according to the instructions.
To prevent bacterial infection, it is useful to treat with the combined preparation “Amidel gel NEO”. It has both acaricidal and antimicrobial effects. Lidocaine in the medicine relieves itching and pain. The gel is inserted with a swab into the ear canal, the ears are gently massaged, and treated twice with a 5-day break.
To support the body's defenses, immunomodulators are prescribed; they help to cope with the disease more quickly. “Immunofan” and “Ribotan” are popular among breeders: it is better to use them on the recommendation of a doctor. In severe cases of the disease, external remedies cannot be used, so the sick cat is given injections of medications containing ivermectin.
From the first day of treatment, it is important to destroy ticks around a sick pet: wash the apartment with acaricidal agents, disinfect objects, wash or replace cat litter.
Pathogens
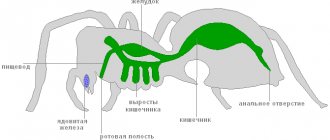
Demodicosis in cats is caused by 2 types of microscopic mites: Demodex cati and Demodex gatoi. The first lives in hair follicles and adjacent tissues, the second - in the superficial layers of the skin. The size of the parasites does not exceed 0.5 mm; they can only be seen under microscope magnification. The transparent body is supported on legs with hooks, the oral cavity looks like a proboscis.
Demodex develops in the body of one carrier and dies in the external environment after 2 hours. An adult gnaws through the epidermis, penetrates the hair follicle, where it feeds on cell breakdown products, sebum and reproduces.
From the egg to the mature individual, the tick passes through the stages of larva, protonymph and deutonymph. The parasite develops in both active and passive forms: in the first it feeds and grows, in the second it becomes motionless. The biological cycle lasts 20–25 days; in 3 months, at least 3 generations of mites develop in the cat’s body.
More often, demodicosis affects animals under 2 years old, elderly and emaciated.
Siamese and Burmese cats are more susceptible than other breeds.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
Ear scabies is a disease caused by mites. Arthropod parasites settle in the hearing organs of a pet, injure delicate skin, and their saliva and feces activate irritation and itching. Insects live only on animals, so people do not become infected.
Arthropods parasitize the eardrum and external auditory canals. They prefer to feed on lymph, blood and skin particles. Like all pests, ticks are very tenacious - they survive without a host on a starvation diet for two weeks. Signs of the disease depend on the stage of its development:
- First 14 days. The pet shakes its head and constantly scratches its ear with its paws.
- From 15 to 20 days. To reduce the intensity of itching, the cat rubs against walls, rough objects and corners. At the base of the passage and on the inner walls of the hearing organs, abrasions, scratches and dark, coffee-like discharge appear. An unpleasant odor appears from the ear, the animal loses its appetite and tilts its head at an angle of 120 degrees.
- The period from the third to the fifth week. The cat has a high body temperature, sometimes there are seizures, convulsions and tremors of the limbs. The swelling is visible to the naked eye, and when you palpate it, a squelching sound is heard. Sticky mucus appears on the fur.
At home, otodectosis in cats, the symptoms and treatment of which are interrelated, can only be diagnosed at the second or third stage. The initial stage takes place in a hidden form and is not always definable. If suspicions arise, veterinarians recommend carefully running a cotton swab along the inner passage of the ear. The contents are shaken onto a black cloth, illuminated with a lamp and examined under a powerful magnifying glass. White dots spreading in different directions are ear mites.
It is much easier to diagnose a disease in a hospital than at home. The specialist carefully examines the pet, identifies primary signs of otodectosis and performs tests. If the animal’s condition allows it, then it undergoes an otoscopy - an instrumental examination of the surface of the auricle and membrane. A positive result and the overall clinical picture influence the choice of therapy.
What ear diseases affect cats?
Most ear diseases are caused by parasites and mites. The next group is various inflammatory processes, accompanied by unpleasant diseases , such as infectious and inflammatory processes, otitis media and other ear diseases. There are also post-traumatic problems. Ear diseases in cats can be roughly divided into several groups:
- Otodectosis. The cause is the scabies mite, which parasitizes inside the ear canal and inner ear area. This is an extremely contagious and serious disease that requires mandatory treatment;
- Otitis and other diseases of the external and internal ear;
- Eczema and dermatitis;
- Hematomas and abscesses. Are a consequence of injuries;
- Neoplasms of various origins and tumors;
- Necrosis of the auricle.
Let's look at each group separately.
© shutterstock
Causes
Ear mites do not appear out of nowhere. When it develops, there is necessarily a carrier and reasons for the activation of the disease. The risk group includes kittens under the age of one year and weakened animals. The former become infected from the mother, and in the latter the pathogen “wakes up” after a malfunction of the immune system. There are three main causes of ear mites:
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules. The presence of people in a living space in street clothes, shoes, irregular washing of the rug at the doorstep. Small pests are found in tiny particles of sand and soil.
- Communication with sick animals. Upon contact with a sick cat, the pathogen travels to the pet directly or through the hands of the owner. Otodectosis does not parasitize humans, but they are its carriers.
- Street walks. Arthropods live in basements and attics, in grass and garbage containers.
The disease progresses individually in each specific case. Its intensity depends on the cat’s immunity.
Often the pest lives unnoticed in the pet’s body for months. At the first serious failure, stress or injury, the insect wakes up and begins to actively “suck” its host.
What is demodicosis
Demodicosis is an intradermal parasitic disease that is caused by a subcutaneous mite - Demodex, it belongs to scabies mites, so synonyms for the disease are “red scabies”, “demodex” or “hypodermic mite”.
Different species of animals and humans suffer from demodicosis, and each has its own tick: that is, a cat suffering from demodicosis is not dangerous to humans.
There are two types of mites found in cats: Demodex cati and Demodex gatoi.
The tick itself is microscopic in size (200-300 micrometers), has an elongated body, divided into a head, chest and abdomen; it also has upper and lower jaws, and four pairs of short legs. It is this structure that determines the features of its existence and life cycle.
Normally, small numbers of Demodex cati mites live in the hair follicles and sebaceous glands of each cat. They become the cause of disease only when the animal’s immunity is weakened.
If a cat has another type of tick - Demodex gatoi, which lives on the skin, then infection occurs through close contact between a sick and healthy animal: when sniffing or when cats rub against each other, or when the cat has access to fragments of skin and fur with ticks. Such a fragment can be brought home by the owner, which is called “on his feet.”
A tick, once on the skin, uses its entire arsenal - a proboscis on the head, an elongated body, jaws, limbs - to gnaw through the surface layer of the skin and, going deeper, penetrates the hair follicle or sebaceous gland. Here, for its life activity, there is everything necessary: the appropriate temperature, secretions (specialized substances) of the follicles and glands, blood, lymph, fragments of dead cells. All these conditions necessary for the life cycle of each tick species are different: from the moment of laying eggs to the development of an adult. In general, this takes 25-30 days.
According to statistics, demodicosis is rare in cats, but the consequences for the animal’s body, the danger to other cats and long-term treatment make this disease very serious and requiring treatment only from a veterinarian. It is important to remember: if a cat has a weakened immune system or has other health problems, the disease will not cure itself.
Features of treatment
An advanced form of otodectosis in cats is very dangerous. If pus gets into the brain, the animal dies in agony. At the same time, related problems arise - bacteria, fungi, damage to lymphatic vessels. Abscesses, injuries and inflammation in the auditory organ lead to deafness, so it is important to start treatment on time.
Basic therapy
The disease gradually progresses, causing discomfort to the animal, so you should immediately contact a veterinarian. All activities take place under the strict supervision of a specialist. In advanced cases, you will have to leave your pet at the clinic. If the condition is not critical, then the procedures are carried out at home in three stages:
- Cleaning the ears. Using a cotton swab soaked in the medicine, carefully remove dark discharge from delicate skin. To do this, use a solution of furatsilin, camphor alcohol or three percent hydrogen peroxide.
- Symptomatic therapy. Special acaricides destroy insects, preventing them from reproducing. To prevent your cat from scratching, you need to relieve the itching and remove the pain. When the course is complicated, infection occurs with secondary flora, which is destroyed by taking antibiotics and antihistamines.
- Strengthening the immune system. To prevent re-infestation, it is necessary to increase the body's resistance. The veterinarian prescribes vitamin therapy (injections, tablets).
Disinfection continues until complete recovery. On average, each cycle lasts a week, and the entire course lasts at least a month. The specialist pays attention to the course of the disease and prescribes painkillers, antimicrobials or antihistamines. Before administering the medicine, be sure to wipe the sink with cotton wool or gauze soaked in warm lotion or chamomile decoction. Both ears are treated, otherwise the mites will move from the diseased organ to the healthy one.
Medicines for ticks
There are many anti-tick remedies, but the most popular are liquid ones. To eliminate otodectosis in cats, treatment at home should begin at the first symptoms. The drug is instilled into the pet’s ear, then the shell is squeezed and lightly massaged.
Kittens are prescribed medications that can cause minimal complications. Most of these drugs cannot be prescribed to animals under 2 months of age. In American Stronghold, the active ingredient is selamectin, which does not cause allergic reactions or poisoning. Russian Inspector Total K is based on fipronil. Both drugs are packaged in a convenient pipette with a long spout.
The Dana brand produces ear drops against ticks in several types. The medicine for otodectosis is packaged in small plastic bottles. It is instilled into both ears every 5 days. The treatment course lasts a month. A complex preparation with fipronil Ultra is applied to the withers and hearing organs.
The domestic product Bars is a light oily liquid with an unpleasant odor, packaged in small plastic bottles with a dropper. The drug blocks the nerve impulses of insects and causes their death. In recommended doses it does not cause poisoning.
Ivermec, based on ivermectin, is produced in tubes and sprays. In addition to the active ingredient, the medicine contains lidocaine and panthenol. In mild cases, treating the ear twice with an interval of 5 days is sufficient. In a neglected state, the number of procedures is doubled. To prevent the pet from licking the drug, a collar is placed around its neck. Ivermec is contraindicated:
- kittens younger than 12 weeks;
- pregnant and lactating females;
- weakened animals.
For minor lesions, veterinarians recommend less aggressive medications. Lightweight Otovedin has a gentle effect on the auricle and does not cause irritation or poisoning.
The drug consists of plant extracts and essential oils, therefore it is absolutely safe. To improve wound healing, Ectodes with propolis is used, and Demos sulfur drops are prescribed to cleanse scabs and pus.
Folk remedies
Herbal medicine is not as effective as drug treatment, and all folk remedies are used as a supplement to the main course. If the cat has serious scratching and swelling, then decoctions and extracts will only worsen the condition. Alcohol is toxic to cats, so it is prohibited to use alcohol tinctures.
Green tea is an excellent remedy to use in the early stages of rinsing your ears. Two small spoons of leaves are poured into a cup of boiling water. A cotton swab is dipped into the cooled solution and then wiped over the skin. Green tea can cause allergies, so experts recommend observing your pet’s behavior. A less aggressive plant is chamomile.
Vegetable and essential oils prevent ticks from breathing, so they are often used in the treatment of otodecosis. Almond kernel extract is used for tissue regeneration.
Causes of demodicosis in cats
For demodicosis, the gender, breed or age of the animal is not important, but some veterinarians, from their experience, speak of a predisposition in Siamese and Burmese breeds.
The following are susceptible to demodicosis:
- cats with weakened immune systems: recent infectious diseases, treatment with antibiotics, hormones; infected with fleas, helminths; having diseases of the endocrine system;
- adult cats over 5 years old and elderly animals;
- cats under 1-2 years old
- kittens taken early from their mother, i.e. those who have not received enough immune bodies from breast milk;
- possible intrauterine infection from mother to fetus;
- cats with a genetic predisposition to demodicosis;
- cats with poor skin condition: damage to the integrity of the skin, inflammatory diseases (including as a result of other parasitic, fungal and bacterial infections);
- cats with genetic diseases associated with weakened immunity.
In addition, the development of demodicosis is promoted by:
- stress, which weakens the immune system;
- Violation of conditions of detention: keeping a sick and healthy animal in close proximity; access to the fur and skin of a sick animal;
- violation of the diet, especially in protein balance.
Preventive actions
Looking at photos on the Internet of otodectosis in cats, many owners are frightened by the complexity and painstakingness of therapeutic procedures. In the early stages, the disease is treated for 7 days, then preventive measures are started. In an advanced state, drug therapy will take at least a month, after which a long rehabilitation and restoration of immunity is carried out. It is important to follow all the veterinarian's instructions.
During therapy, the cat is quarantined, completely excluding its contact with other animals. Owners may be carriers of ticks, so they should not visit friends who have pets at home or pet stray cats. It is necessary to thoroughly disinfect the home and sterilize the sleeping place of a sick pet. It is better to replace the litter with a new one and burn the old one.
A balanced diet will help strengthen your cat's immunity. It is necessary to exclude harmful foods from the menu, giving preference to quality food. If the pet is on dry food, then choose the option for weakened animals. Animals on a natural diet are given more meat and vitamin complexes are required. Immunostimulating injections are prescribed only by a doctor.
The quarantine continues after the cat has recovered. Your pet should not go outside unattended. Pests become active in the warm season (May - September), but they are able to live in basements throughout the year. To prevent the occurrence of otodectosis in cats, you need to apply drops to their withers once every 30 days, which provide protection against ticks.
Prevention eliminates long and unpleasant treatment, so it is necessary to protect your pet from street animals. Every day the cat's ears are carefully examined and cleaned of dirt. They are treated monthly with a special lotion, and disinfected with Amit or Bars once a quarter. You need to regularly wash the entrance mat and your pet’s personal belongings.
Useful materials:
- Skin diseases in cats Causes of spots on the skin of the Sphynx In fact, there are reasons that could explain the change in pigmentation...
- Herpes in cats Who is susceptible to the rhinotracheitis virus? Both cats and cats of different ages and breeds can become infected with the rhinotracheitis virus. Attention! More often...
- Chelavit for cats General information and release form Domestic cats cannot independently control their diet and therefore often…
- Leukopenia in cats symptoms Instructions for use Before drawing the drug into a syringe, it is recommended to shake the bottle until smooth...
Symptoms of ear diseases in cats
Although all ear diseases in cats differ in symptoms, there are also some standard signs. It is important to know that any of them is a reason to contact a veterinary clinic for qualified help.
Here are the typical signs of ear disease in cats:
- the pet scratches its ears, this is caused by discomfort,
- tilts his head to the side, rubs his ear against the surface, tries to shake off or remove something,
- discharge is observed,
- the animal has a lethargic appearance, loss of appetite, no playful mood,
- body temperature rises,
- wounds, purulent formations or tumors are visually visible.
Pathogenesis and routes of infection
Parasites destroy the skin and hair follicles, as a result the hair falls out and stops growing. Waste products are released into the surrounding tissues, irritate nerve endings, and weaken the protective function of the skin. The cat develops dermatitis and a bacterial infection develops. The tick is able to move in internal organs through the lymphatic system.
The routes of spread of parasites have not been precisely established; doctors' opinions are divided. Some call sick animals the source of infection. Others consider Demodex mites to be permanent residents of mammals and humans that do not cause harm, but rather reproduce and disturb in unfavorable conditions.
These include:
- weak immunity due to past infections, viruses, chronic diseases;
- unbalanced diet: lack of fats, vitamins A, B, E;
- helminthic infestation;
- skin lesions;
- fleas;
- unsanitary conditions of detention;
Kittens inherit demodicosis from their mother.
A person cannot become infected; the immune system does not allow feline Demodex mites to pass through.
Inconveniences include minor inflammations when the parasite gets on the surface of the skin; they go away on their own without treatment.