- about the author
- VK profile
Svetlana Tarasova
Hairdresser-stylist with more than 8 years of experience, expert in the field of haircuts, styling, hair care, coloring.
Hair parasites – lice – often appear in children and adults. Contrary to popular belief, this scourge affects not only those who poorly observe the rules of personal hygiene. What types of lice appear in humans, and how to deal with this unpleasant phenomenon, you will learn from our article.
The main types of lice that a person can have - official names
There are many types of lice. There are more than 500 varieties of these parasites in mammals alone. Three can be found in a human home:
- Head louse;
- Cootie;
- Pubic louse.
Head louse
Pediculus humanus capitis is one of two species of human louse. This species lives on the hair of the head, as well as in the mustache and beard. The legs of the head louse are adapted to live on hair that has a circular cross-section.
The parasite's body is dark gray in color and small in size. A louse, settling in a person’s hair, feeds on his blood. After drinking blood, the color of the body changes to red or purple. The length of the adult parasite is 2-4 mm. Females usually have a larger body size. She lives for about 1 month, laying 5 eggs per day during this time. Eggs (nits) are attached to the base of the hair and mature in 7-10 days. After the grown louse leaves the egg, it is left hanging empty by a thread. 6-10 days after this, the young insect reaches sexual maturity.
Head louse is not as dangerous to humans as, for example, body louse. The fact is that she does not tolerate diseases such as typhus. However, after a parasite bite, saliva enters the wound, which causes itching and irritation (pediculosis). In this case, the likelihood of any infection entering through damaged areas of the skin increases.
Cootie
Pediculus corporis (or Pediculus humanus corporis De G. var. vestimenti) - this insect usually lives in the folds and pile of human clothing. This is where the louse reproduces and lays eggs (nits). Moving from clothing to skin for a while, the insect feeds on human blood. The body length of the female reaches 4.7 mm, the male – 3.7 mm.
The oral apparatus of lice consists of piercing needles enclosed in a soft tube (proboscis) that turns out of the mouth, the edges of which fit tightly to the pierced skin. The process of blood sucking occurs through muscle contractions of the pharyngeal pump and pharynx. The parasite's saliva contains an enzyme that prevents blood from clotting.
The short esophagus carries blood into the stomach, which can become very distended. An adult can drink from 0.001 to 0.003 ml. blood. Lice are sexually dimorphic, so females are often larger and heavier, so they drink more blood. Before being saturated with blood, the louse has a light gray tint. After the blood has entered the body of the parasite, the body acquires a dark red color.
Females live 40-45 days, during this period they manage to lay from 100 to 150 eggs . The female lays about 4 nits per day. A new nit turns into a louse in 6-8 days. During the first 8 days of life, the young parasite experiences 3 molts and can reproduce. This type of insect is dangerous to humans, as it is a carrier of typhus.
Pubic louse
This parasite is also called the flathead (lat. Phthirus pubis). They live on the human body in those areas where there is hair with a triangular cross-section, namely in the pubic area, on the genitals and around the anus. Sometimes pubic lice can be found in the armpits, on the chest and even on the stomach. The louse can never be found on the scalp, since these hairs have a round cut shape, and the limbs of the pubic louse are not adapted to attach to them.
The parasite feeds exclusively on human blood. Without new portions of blood, the insect dies within 24 hours . Having pierced the wall of a blood vessel, the insect expands the esophagus, drawing blood into itself like a pump. At the same time, she injects an enzyme into the wound that prevents blood clotting. The ploshchitsa feeds every 4-5 hours.
The insect's body usually has a light brown tint, making the parasite hardly noticeable on pubic hair. Body length is 1.5-2 mm, in larvae from 0.7 to 1 mm. With strong and large paws spread out, the louse may appear very wide. The color of the pubic louse is slightly brown.
The egg laid by the female develops in 5-7 days, the larva develops in about 13-17 days, and three moults occur during this period. After this, the adult begins to reproduce. The disease caused by the appearance of these parasites is called pediculosis pubis or phthiriasis.
Classification of parasites
If lice and nits are found on the body, you need to determine their type:
- head;
- linen or clothes;
- pubic.
Types and classification of lice.
Parasites of these species do not have wings. Lice that live on the head can only exist on the scalp. This is due to the structure of the paws, the presence of protrusions that help move along the hairs. These parasites are not found on other parts of the body.
Lice are not visible on long brown hair. They are detected when unpleasant symptoms appear: pediculosis is accompanied by itching. As the number of parasites increases, the discomfort increases. There is a feeling of some movement on the surface of the head.
Body lice live on woven material: clothing, underwear and bed linen. Their life activity differs little from the principle of existence of their head brothers: they feed on blood, reproduce, leaving nits on the fibers of the fabric. This type of parasite is common among people of low social status: homeless people, beggars, etc.
Body lice and nits appear only on clothing; they cannot survive on the scalp. Parasites bite people and feed on blood, but at the same time they are not able to move throughout the human body due to the lack of long, hard hairs on it. The lice are held securely on the woven material. This allows them to stay close to a food source at all times.
From the name you can tell that pubic lice live on the pubic area. They do not move throughout the body and scalp. This is explained by the structure of the parasites' legs: they can capture triangular-shaped hair, the kind that grows in the intimate area. It is easier to fight insects of this type, because the area of infestation of the pubis is much smaller than the localization area of human lice.
Photo under a microscope
If you look at a head louse under a microscope, you can see in detail the grayish translucent chitin that makes up its shell. The oblong body has an ellipsoidal shape, and the edges are covered with rounded convexities. You can also look at the three pairs of legs that attach the louse to the hair.
The flathead has lighter chitin, a short body without the characteristic rounded bulges at the edges. This type of parasite also has 3 pairs of legs.
The pubic louse is very different from previous species . Its body consists of translucent brown chitin. The shape of the body resembles a diamond, as it has a significant expansion closer to the head. Three pairs of legs have an impressive size, due to which the insect looks even wider.
Do lice jump?
Another important detail - do lice jump or crawl, or maybe fly? Lice do not jump or fly. Their paws are tenacious enough to grab a hair, but they are not adapted to jumping. Lice have wings, but they are reduced, and the parasites do not use them in any way.
Therefore, answering the question whether lice jump or not, we can say with confidence that lice only crawl. Thanks to this, they cannot be transmitted from person to another over long distances; therefore, if a certain distance is maintained, it is quite possible to communicate with an infected person.
Lice on animals
Cats, dogs, and other pets with fur can get lice. More often they are called lice eaters. These parasites feed on hair and dead skin flakes. They cannot bite through skin or drink blood.
Compared to human parasites, lice eaters are smaller in size. They have a rounded body and a triangular head, the front of which has a small notch for capturing hairs. The jaws of lice eaters are very strong, which allows them to easily bite off pieces of skin. It is this process that causes severe itching in the pet.
Even pets who are never outdoors can become infected with these parasites. This can happen like this:
- In contact with street animals;
- When grooming or cutting, if the tools have been infested with insects;
- When the owner comes into contact with stray animals infected with lice eaters.
IMPORTANT! All types of lice are specific to their hosts. Therefore, a person cannot become infected with lice eaters, and a pet cannot become infected with human parasites.
Pubic lice
Pubic lice are the smallest parasites that can live on the human body. Their dimensions barely reach 2 mm, their legs have a powerful structure, and their color makes them stand out even more from other insects - transparent brown. In their place of residence they are almost invisible, they merge with the overall structure of the hair, resembling a small compaction. Interestingly, their eyes are reduced. They see very poorly; the only factor by which parasites navigate is smell.
They are not equipped with wings and powerful pushing legs; the most they can do is crawl on the surface. They often settle in the groin area, much less often they colonize the armpits, eyebrows and eyelashes. A lice bite of this kind can only be felt by a hypersensitive person. The parasite is too small to cause noticeable discomfort during this process.
What size are lice?
The smallest parasite:
- Hoplopleura is tenacious. This is a louse that lives on house mice, field mice and hamsters. The insect has a body length of 0.8-1 mm in males and 1-1.4 mm in females;
- The pubic louse also has small body sizes - from 1.5 to 2 mm.
Medium-sized parasites are:
- Sheep linognath. Lives on different parts of the body of domestic sheep. Reach from 2.1 mm. up to 2.8 mm. in length;
- Linognath is bristly. Lives on domestic dogs and cats. Sometimes found in some species of foxes. Body length from 1.8 mm. up to 2.4 mm;
- Equine hematopinus live on domestic donkeys and horses. Body length from 3 mm. up to 3.5 mm;
The largest parasites:
- Porcine hematopin. The length of the female is 5 mm, the male is 4 mm;
- Head louse. Body length is 2-4 mm;
- Cootie. Body length from 3.7 mm. 4.7 mm.
Structure of a louse
Let's return to the main question of what a lice looks like.
Insects that parasitize humans are divided into three groups:
- pubic;
- clothes;
- head lice.
A little later we will look at each of them in more detail. All species have their own physiological characteristics, but in general the structure of parasites is as follows:
- Head . The head of a louse is very small. The eyes on it are either atrophied and look like pigment spots, or are completely absent. In fact, visual perception is far from the most important thing for lice. Bloodsuckers rely more on their sense of smell.
- The oral apparatus is presented in the form of two piercing needles and a proboscis, with the help of which the insect draws in blood like a pump.
- Limbs . Like most parasites, lice have three pairs of legs. Each has claws with which they cling to the hairs of the victim.
- The louse's abdomen is large and translucent. The internal organs are visible through it.
The body length of pests ranges from 1 to 4 mm (depending on the species). Color: from almost white to dark gray or brown.
Now let's look at each type of human lice individually.
Types of lice depending on color
Parasites of the following colors are found:
- Brown;
- Red;
- Grey;
- Black.
Brown
Most lice are different shades of brown. Sometimes there are even insects of yellowish tints, such as sheep linognath. Most parasites that live on animals have this exact color.
Red
Only one type of lice has this color - porcine hematopin . Most of the parasite's body is colored from red to dark pink. There are dark spots on the sides of the body.
Also, the body of a parasite feeding on blood can acquire a red tint immediately after it has bitten its victim.
Grey
Head lice and body lice have this color . The first variety has a darker shade.
Black
Sometimes among the head parasites there are black individuals. This color of chitin is due to the temperature at which insect eggs developed. If a person caught lice during a very cold or, conversely, very warm period of time, then each new generation will have a darker color. Temperature changes cause the insect's body to secrete more pigment. Although. In fact, the louse remains gray, but the increased amount of pigment causes our eyes to see a black insect in front of us.
Where do they come from?
Considering that such parasites do not have wings, they can move from one host to another only through direct contact between healthy and infected people.
Causes of lice.
This is the main reason, but there are also indirect ones:
- using other people's hair accessories, hats (if lice remain on them);
- violation of hygiene rules: hair, body, wardrobe items are not cleaned for a long time, which allows parasites to actively reproduce;
- the use of other people's towels and clothes also contributes to infection if there are insect eggs on them;
- on a train, where hygiene rules are not always followed, nits remain on fallen hairs and bedding;
- when swimming in bodies of water: lice remain viable for a certain period; while in water, they do not die and can find a new host, but the likelihood of this is low.
The methods of infection are determined by the type of lice. For example, parasites that live on hair are carried on elastic bands, caps, and panama hats. You can become infected with pubic lice by using towels or other people's underwear. Another way is sexual contact.
Types of lice - depending on appearance
The body of parasites has a flattened shape. The legs are relatively short, but very tenacious, allowing the insects to hold tightly to a person or animal. Usually they have three pairs.
The body of lice, like other insects, consists of three parts: head, chest and abdomen. The head has an angular-oval shape, narrowed at the front, on which there is a pair of short antennae and a pair of simple eyes. The mouth opening is located on the front of the head.
The parasites' chest has a trapezoidal shape and consists of 3 closely connected segments, each of which has a pair of legs attached. At the end of each paw there is a well-developed movable claw, forming something like a claw.
In general, all types of lice have the same structure. Therefore, they can be divided only by the shape of the chest and abdomen:
- Oval (or ovoid) shape . Like head or body parasites;
- Diamond Shape. For example, pubic lice have this form.
Lice have completely absent wings . These parasites once had wings, but during the course of evolution and the acquisition of a parasitic lifestyle, they lost them as unnecessary. If you encounter an insect with wings, know that it is definitely not a louse.
Characteristics of lice
The diet of all parasites without exception is the same - human blood. The entire life cycle from a nit (parasite egg) to an adult takes place exclusively on or near the human body, since when they enter the wild, the viability of lice decreases, and it is impossible to meet them in such an environment.
A distinctive feature of lice from other parasites is the frequency of food intake - they bite the host several times a day. This is what brings significant discomfort to a person, especially when it comes to a child’s skin or allergic reactions.
What color are lice?
- red;
- brown;
- gray;
- black.
This video talks about the types of lice and pediculosis:
All these features are common to all pests. But each individual species has its own specifics.
The variety of lice in humans is represented by the following types:
- head;
- pubic;
- wardrobe
What do nits (larvae) of all types look like?
The appearance of the larvae resembles small capsules. The shell of such a capsule consists of an adhesive substance with which the nit is attached to the hair. At the top of the capsule there is a small hole covered with a lid. When hatching, the louse pushes out the lid and the shell is removed.
REFERENCE. All parts of the nit capsule can only be seen under a microscope. Without such magnification, empty capsules and those with a developing parasite inside look the same to our eyes.
Nits grow within 7-8 days at a temperature of 30 degrees Celsius. The size of the larvae depends on the species to which they belong. In any case, the size of the nit will be in the range of 0.5 mm. (pubic and mouse parasites) up to 0.8 mm. in the largest species (pork, clothes and head varieties).
Head type of insects
The head louse is the most common type of such insect. They are larger in size and have a dark body color. They are ideally suited for life in the scalp; it is extremely rare to see parasites in the beard in people with thick chin hair.
A comfortable temperature regime for the life of head lice is considered to be the normal body temperature of people ; when it increases or decreases, their vital functions are disrupted, however, in order to destroy lice, more serious heat treatment is necessary.
The presence of head lice in a person can be determined by a thorough examination of the scalp.
Checking for infection with this type of head lice is carried out by examining the hairline and identifying parasite eggs, which they lay just above the base of the hair. Head parasites begin to energetically annoy their host in the dark. They are often nocturnal and at this time begin to actively feed.
The myth about subcutaneous lice is quite common. It gained popularity only because of the difficulty of detecting parasites. Due to its size (and the head louse is a rather large insect), the pest cannot get under the skin, and if it does end up there, it will try to get out quickly or die, since such a habitat is unfavorable for it.
If nits are not found in the hair, but there are blisters and itching on the skin, then there is a high probability of infection with other pests - scabies mites. This type of parasite actually lives under the skin, and infection with them leads to more serious diseases. If you notice the first symptoms indicating scabies, you should immediately go to a specialist.
The life cycle of head lice lasts two to three weeks, of which 5-6 days are the development of an adult from a nit. During this time, head lice live exclusively in the hair, since if they enter another environment, they die within a few days.
Nits are small, oval, light-colored eggs that are easily visible with a regular lamp, but you need to look for them using a magnifying glass.
How you can get infected and the main symptoms
Any person or animal can become infected with lice. Some people believe that pediculosis is a dirty disease. But this is not true at all. Parasites don't care where they settle. You can catch lice only through contact with an infected person or his personal belongings (if it is body or pubic parasites).
Symptoms of infection
- Constant skin itching;
- Rash directly at the bite sites;
- Scratching (appears after a long period of lice infestation);
- The appearance of nits on the hair.
Signs of any type of lice
Knowing the signs of lice and how to combat them, you can take the necessary measures in a timely manner.
- Itching of the skin, resulting in severe scratching. Such damage may contribute to the development of secondary infection.
- Appearance of a rash. A few days after the lice bites, red spots appear, which subsequently have a bluish tint.
- At the site of damage, ulcers and boils develop, as well as pigmentation and induration.
- The presence of dead nits, live ones, as well as the lice themselves.
The identification of such symptoms of pediculosis signals the need to take urgent measures to remove the parasites.
Signs of lice
How to treat pediculosis and get rid of parasites
Before choosing a particular medicine, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe the most effective course of treatment.
Medicines and drugs
- Para-Plus. The drug is sprayed from the roots to the ends of the hair and wait 10-15 minutes. After this, thoroughly wash off the remaining product with shampoo suitable for your hair type. Para-Plus is highly toxic and therefore prohibited for children under 2.5 years of age;
- Parasidosis. Before starting the procedure, the hair is slightly moistened, then the product is applied along the entire length of the hair and left for 10 minutes. After this, the hair is again moistened with water and the preparation is rubbed into the skin. After 5 minutes, the head should be thoroughly rinsed with shampoo;
- Medifox. The drug is applied to the affected areas of the skin and rubbed in with gentle movements. You need to wash off the medicine after 20 minutes using shampoo. To completely eliminate lice, the procedure must be repeated many times.
IMPORTANT! Medifox should only be used locally to avoid side effects such as vomiting, diarrhea and severe intoxication.
Mechanical method
This method should be supplemented with medications or folk remedies. After you use the main medicine, you need to literally comb out lice and nits from your hair. A metal comb is used for this. The procedure must be repeated as many times as you use the main drug.
Shampoos
- VEDA-2. Shampoo made in Russia. The product is applied to damp hair and stays on for about 50-60 minutes. after which it is washed off. 1 application is enough. But to be sure that all parasites have died, you can repeat the procedure after 12 days;
- Hygia. Lather your hair from roots to ends with shampoo and leave for 30 minutes. After this, rinse your hair thoroughly and comb out the parasites with a comb. Shampoo manufacturer – Bulgaria.
Folk remedies
The most popular and effective means are:
- A mixture of kerosene and water in a ratio of 1:3;
- Tar soap;
- Essential oils: lavender, tea tree.
All of the above products are applied to damp hair and left for 30-40 minutes, after which the hair is combed to remove lice and nits with a metal comb.
Have you learned more useful information about lice?
Not really
Infection with head lice can be quite unpleasant and dangerous. Therefore, you should not delay and wait for the insects to breed. Choose any of the above remedies and remove the parasites as soon as possible.
- about the author
- VK profile
Methods for killing lice and nits
To get rid of parasites and their offspring, it is necessary to carry out treatment in different ways. First of all, prepare the tool. To remove nits from the body, you need a special comb - this is a special tool in the form of a comb with frequently spaced teeth. Without such a tool, any therapy method will not provide the required result.
This is due to the fact that nits have a dense shell, and chemicals (most of them) almost do not penetrate through it. It is possible to kill parasite larvae at this stage of development mechanically. It is advisable to use a comb to remove lice from hair. However, this remedy does not help remove parasites from clothes.
Special comb for lice.
To combat lice on the scalp, chemicals are used. They are used as an auxiliary measure. The mechanism of action is based on damage to the central nervous system of parasites.
There are also preparations for treating hair and body that allow you to remove lice due to the ability of the active substance to clog their respiratory tract.
To quickly remove parasites, you can use improvised means at the same time. They are used to treat infected parts of the body, hair. Some of the substances repel parasites, others help get rid of adult lice.
Such substances have no effect on nits. They are not aggressive enough, so they do not destroy the shell of the louse offspring. As a result, nits remain on the hair. The process of lice reproduction is not interrupted even after the end of the course of treatment.
This is explained by the fact that when using the listed methods, the main rule is not followed: parasites must be removed from the head with a special device. This product can be used in the fight against lice even as a main measure, without using chemicals. The comb removes nits and lice from the skin.
However, live parasites are too mobile, so we first poison them with drugs and then remove them with a special tool. You can treat lice on your own without the help of a doctor.
There is another method that does not require investment. With its help, you can quickly cure lice at home. It is necessary to cut off the hair on which parasites live at the root. The desired result is achieved in 20 minutes; getting rid of lice in this case eliminates re-infection, since no nits remain. This is an accessible method, but it is not suitable for everyone, as it greatly changes the appearance.
In the fight against clothing parasites, it is recommended to use the temperature method. So, clothes can be boiled. At the same time, the properties of the fabric are taken into account so as not to spoil things on which parasites are found. Washing in an automatic machine at high temperatures is considered effective.
Parasites are afraid of boiling water and die quickly if the ambient temperature exceeds +45°C. Things infested with lice are taken out into the cold or left in the freezer, first wrapped in plastic. Ironing can also destroy nits.
Drug therapy
Lice medications.
Drugs that act against parasites have restrictions on their use. For children, a lice remedy is chosen based on age. Pay attention to the composition.
It is better to use the anti-parasite product after preliminary testing. To do this, apply a small amount of the substance to the skin; if no side effects appear after 20-30 minutes, you can use the drug.
Effective means to destroy lice and nits on the body:
- Nittifor. You can purchase the drug in the form of a cream or lotion. When applied, lice are killed by permethrin. This is an insecticide of the pyrethroid group. It affects the nervous system of parasites. Nits are also susceptible to the influence of this product. To kill lice, you need to apply the substance to the affected areas of the body and scalp. It is also used in the fight against parasites in children from 5 years of age. Contraindications: lactation period, pregnancy, tendency to allergies. If the skin is severely damaged, even if it is severely infected, the product should not be used.
- Parasite parasite can be purchased in lotion form. The product is used to treat the body against parasites; for each case, different forms of release are used: lotion, shampoo, spray. It contains dimethicone and mineral oil. The product is used for head lice in children over 3 years of age. It is used to treat body and hair against lice. Paranit effectively destroys nits and adult parasites. During processing, dehydration of lice occurs.
- A couple plus. The product is available in aerosol form. It is distinguished by its high efficiency in the fight against parasites, since it contains several active substances: malathion, permethrin, piperonyl butoxide. The last of the substances enhances the effect of insecticides. This allows you to speed up the process of destroying parasites. The composition of the product includes an organophosphate insecticide (malathion) and a substance from the pyrethroid group. Thanks to this combination, insects die faster because they are exposed to agents that act differently.
- Pedilin. This parasite repellent contains the insecticide tetramethrin. Piperonyl butoxide enhances its effect. The product is used to combat parasites. Pedilin is not used to eliminate pubic parasites and body lice. The active substance accumulates in the body of the insect, which leads to its self-poisoning.
- Nyuda. You can purchase the product in spray form. The active ingredient in the composition is dimethicone. The mechanism of action is based on the destruction of blood-sucking insects by blocking the respiratory tract. It is enough to apply the product once to the infected areas of the skin. There is no need to do this again, since the insects die immediately after the initial treatment. If you use the product correctly, you can get rid of insects on your body forever in 1 day. Nuda is used to treat children from 3 years of age. The advantage is the destruction of nits.
- Parasidosis +. The product destroys insects caused by pediculosis. However, it can also be used to treat parasitic diseases caused by body and pubic insects. Available in a bottle. The active substances are phenothrin, acetic acid, and camphor. The product can be used to remove blood-sucking insects from the body and head, taking into account contraindications: pregnancy, lactation, epilepsy, skin diseases accompanied by skin damage. Parasidosis is approved for use in the treatment of children over 2 years of age.
- Hygia. This product is produced in the form of a liquid for treating affected areas: body, head. Contains only permethrin. Additionally, the product contains acetic acid. The manufacturer claims that Hygia can also destroy nits. The product paralyzes insects, as a result they lose their ability to reproduce. At the same time, the nits peel off from the hair, which is due to the presence of acetic acid in the composition. The drug can be used in children from 5 years of age.
Mechanical methods
If you do not plan to have a short haircut, it is better to consider using a special lice treatment - a comb with frequently spaced teeth. It should be used simultaneously with medications, but when you are allergic to chemicals, it is acceptable to consider this method as the main one. This product is not suitable for killing insects on the body. It is used when you need to remove parasites from hairy areas. Instructions:
- It is recommended to spread a white sheet or plastic wrap on the floor. It is important that nits and adult lice removed from hair are visible. You can use this product to remove parasites from your body over a sink or bathtub.
- The treatment is carried out when the hair is washed with shampoo. It is recommended to additionally rinse them in a weak vinegar solution.
- To carry out the procedure for destroying lice and nits, prepare a container with vinegar and napkins.
- The comb is drawn through the hair starting from the temporal bone. First you need to separate the strands. You should move towards the second temporal bone.
- As the process progresses, the comb is cleaned of lice and nits using a napkin and moistened with vinegar.
ethnoscience
Recipes:
- Dust soap is often used to treat the scalp. This remedy is also used for the body. However, in this case, the goal is to repel lice, since nits are not detected on the body. It is necessary to soak the product for up to 40 minutes. Then you need to wash off the soap suds. Treat hair with vinegar.
- Kerosene, turpentine. To destroy nits and adult lice, use any of these means. The substance is mixed with vegetable oil in a ratio of 1:10. The product causes a burn, so you cannot keep it on your body for a long time. The duration of kerosene treatment is 8-10 hours. Turpentine is applied to the skin for a short time - after 40 minutes the product must be washed off. To enhance the effect, the treated area is covered with polyethylene.
Types of lice
There are three types of lice - head, pubic and bed lice, the signs of which differ little from each other, except that head lice live in the scalp, pubic lice, respectively, on the pubis and legs (provided there is vegetation there). Linen (bed, clothes) lice are a very rare phenomenon, unlike the other two types, but sometimes they still occur.
When a body louse parasite appears, the symptoms are as follows:
- this is the largest of all types of lice (measuring from 2.2 to 4.6 cm in length);
- unlike its relatives, it sucks blood on open areas of the skin;
- Body lice have relatively long antennae and a smooth, large abdomen without pronounced segments.
The linen louse lives mainly in the folds of underwear. It is dangerous because it is a carrier of diseases such as typhus and relapsing fever. To get rid of linen lice, it is enough to treat clothes with an insecticide and wash them well (or boil them). It is also important to air the laundry in the sun for a week after treatment.
Self-detection of head lice
Larvae of the 2nd and 3rd stages are larger. They are also called nymphs. Already 1.5 hours after hatching from the egg, the young larva begins to feed on the blood of its owner, sucking blood up to 8 times a day. The optimal development temperature is 30-32°C. Under these conditions, each larval stage develops from 3 to 5 days.
Adult lice are also quite sensitive to temperature fluctuations. The most favorable conditions for body lice are a temperature of 30-32°C with a relative air humidity of 75-85%, for head lice - a temperature of 28 to 29°C with a relative air humidity of 25-50%. Under such conditions and normal nutrition, female body louse live up to 46 days, males - up to 32 days. Male and female head louse live a week less than body louse.
Normal diet for adult lice on humans: female body louse 5-8 times a day, female head louse 6-12 times. Males are half as large. Fasting period for adult lice: at 40°C up to 12 hours, at 37°C - up to 2 days, at 25-30°C - up to 5 days, at 10-20°C - up to 10 days. Humid air has a beneficial effect on their viability.
It is possible for lice to feed on rabbits. Thus, a laboratory “rabbit” race of lice has been created, on which they conduct observations and obtain the necessary amount of material for healthcare.
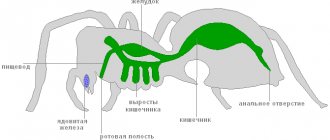
Pthirus pubis has a short body, wide in the thoracic part. The body length of the female is 1.5 mm, the male is about 1 mm. The head is relatively large. The eyes lie directly behind the base of the antennae. On the sides of the abdomen there are warty outgrowths with long hairs. The most strongly developed third pair of legs with large claws curved in a helical manner. This provides the flathead with a tight attachment to the host’s hairs.
Fig.3. Pthiruspubis - pubic louse
The lice live on the hairs of the body, and with severe lice infestation they can be found on the mustache, beard, eyebrows, but can also be on the arms, right up to the outside of the hands. The entire life cycle of the plant is completed in 22-27 days. The lifespan of a female is 17 days, a male is 22 days.
In human pathology, lice are important as permanent specific ectoparasites, causative agents of pediculosis and phthiriasis, and Pediculus humanus is also a carrier of pathogens of particularly dangerous infectious diseases - typhus, relapsing fever and Volyn fever.
Being on the human body, lice cause him a feeling of disgust, and also cause him anxiety when crawling and biting. The individual sensitivity of people to lice bites varies: some are very sensitive to the bites of even one louse, others are little sensitive to bites, and others gradually become insensitive after being in a lice-infested environment for a long time. When lice saliva gets on human skin, it irritates nerve endings and causes itching. With severe and prolonged infestation, pigment spots appear on the skin, resulting from the destruction of hemoglobin in places of tissue hemorrhages (melasma). The skin becomes thick and rough. A “vagrant disease” arises. Constant itching and scratching lead to secondary, rather severe symptoms. Secondary gates open for pyogenic bacteria, fungi and other pathogenic organisms.
The most severe form of this combined action of pyogenic bacteria and lice is tangle - damage to the skin of the scalp, as a result of which the hair is glued together with serous-purulent secretions into one continuous lump, under which there is a weeping purulent surface. It is very difficult to treat mats.
However, the main and most important significance of lice is the transmission of pathogens of typhus and relapsing fever.
The causative agent of typhus, Provachek's rickettsia, enters the louse's stomach along with the blood of a typhus patient, penetrates the epithelium of the stomach and multiplies there. Cells swollen from multiplying rickettsiae are destroyed, and rickettsiae enter the intestinal lumen, from where they are excreted along with feces. Human infection occurs as a result of skin contamination with louse feces containing the pathogen and rubbing of rickettsiae into scratches and wounds on the body. There are no rickettsiae in the saliva of lice.
This method of transmitting the causative agent of the disease is called contamination, in contrast to inoculation, when the causative agent of the disease is actively introduced into the bloodstream by the carrier, through a bite. The development of rickettsia in the body of a louse lasts 4-7 days, after which the pathogen begins to be excreted in feces. From this moment on, the louse becomes dangerous to humans. Rickettsia live in lice until the end of their life, which is much shorter for infected lice. By the 10-17th day, all infected lice die.
The main carrier of typhus rickettsia is the body louse. A.V. Pshenichnoe and A.V. Grembovskaya experimentally proved that the head louse is also a carrier of Provachek's rickettsia, but the development of the pathogen in it is delayed for 3-5 days, and it persists in the louse for up to 20-35 days. Rickettsiae are not transmitted transovarially.
The mechanism of transmission by lice of the causative agent of epidemic or relapsing fever - Obermeyer's spirochetes (Borrellia recurrentis) is generally similar. Spirochetes also enter the lice's intestines along with the patient's blood. But after 15 minutes they pass through the intestinal wall into the body cavity and begin to multiply there.
In the first days after infection, there are few spirochetes in the hemolymph of lice and it is difficult to detect them, but on the 8-10th day their number increases and lasts until 19-21 days, then drops sharply and remains at a low level until the end of life.
The louse becomes dangerous on the 5-6th day after infection and practically remains so until the end of its life. But it poses the greatest danger to humans during the period of mass reproduction of spirochetes, i.e. from the 8th to the 21st day. The presence of spirochetes in the body of a louse does not affect its lifespan. Infection of a person with relapsing fever occurs when a louse is crushed and the skin damaged by scratching is contaminated with the hemolymph of crushed insects containing pathogens.
Lice are carriers of the causative agents of Volyn or trench fever - Rickettsia quintana. The mechanism of transmission of this pathogen is the same as Provacek's rickettsia. Rickettsia develops in the epithelial cells of the louse's stomach and appears in insect feces on days 5-12. From this time on, the louse becomes infectious to humans and retains this ability until the end of its life. The pathogen is not transmitted transovarially and by a louse bite.
The pubic louse does not have epidemic significance, since its infection with any pathogen of a vector-borne disease has not been established. However, human infection with phthisis (phthiriosis) is a very painful phenomenon that requires careful and persistent treatment.
Can uninfected lice kill a living person? It all depends on their quantity. The critical mass of them that a person cannot withstand is 65-75 thousand pieces. There is a description of this kind of phenomena in the literature.
The fight against lice has important anti-epidemic significance. It is divided into preventive and exterminatory measures. Preventive measures include personal hygiene and hygienic maintenance of the home - regular washing of the body while simultaneously changing underwear and bed linen, cleaning clothes and household items; strict sanitary supervision of places where people gather - marinas, train stations, sanatoriums, hotels, etc., compliance with the established sanitary regime in them; sanitary treatment of people transported in an organized manner - migrants, recruited workers, military units, etc.; sanitary checkpoints should be organized for them at large stations and ports; sanitary educational work among the population, increasing the general cultural level and sanitary literacy of the population.
Exterminatory control measures include physical and chemical methods of lice control. Exposure to high temperatures on linen and clothing, treatment with hot air in dry air chambers. Low temperatures are only effective below 14°C, as they kill nits in a relatively short time.
When using mechanical methods, lice are combed out with a fine-toothed comb, hair cut short, and all hairy areas of the body must be shaved. Removing lice from linen or clothing is done using a brush or vacuum cleaner. Parasites removed from clothing must be burned.
The arsenal of chemical control agents is currently extensive, and there are many effective drugs. Their choice depends on the object of processing, conditions, time and location. Like other insects, lice develop resistance to chemicals, for example, DDT, HCH. In such cases, they usually switch to other substances.
, an order of insects, blood-sucking external parasites of mammals. Includes approx. 300 species, incl.