The American cockroach is very adaptable and can often resist pesticides. It has more than 50 taste buds, it is capable of regenerating tissue, and its sense of smell is three times superior to that of other insects. This is an insidious enemy in your home.
The American cockroach is now common in tropical climates. They are the largest species of cockroaches and pests found in homes. The American cockroach is considered one of the fastest running insects in the world, traveling at speeds of up to 50 body lengths per second. And, unlike most cockroaches, it is also capable of flying short distances using its wings. In large infestations, there is a strong odor from the secretions produced by these insects.
Origin of the species and description
Like other cockroach species found in the United States, the insect originated in tropical Africa.
Slave ships were the main means of transport for these insects. European ships sailing to the New World via Africa arrived with an unexpected colonizer: the American cockroach.
Acting from the late sixteenth century to the early nineteenth century, American cockroaches actively conquered America and Europe.
The ecology of the slave ship created meeting places for various species of animals, both living and dead, including cats, rats, pigs, goats, poultry and monkeys, as well as American cockroaches.
Female American cockroaches that invaded ships in West Africa were laying eggs that would hatch in 24 to 38 days. Ships were often left in African ports while they slowly filled with captured slaves from villages near and far, giving the cockroaches plenty of time to breed.
Ships made repeated transatlantic voyages between Europe, Africa and America, and cockroaches multiplied, since methods of controlling them in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries were not very effective: they were smoked out or doused with boiling water.
Cockroaches and other pests devoured food products intended to support human life. Cockroaches even spoiled insect specimens collected by Henry Smithman, an English entomologist who sailed on these ships to study the termites and ants of Sierra Leone in the late eighteenth century.
Periplanet Americana
Although the Americans “brazenly appropriated” the insect for themselves, this cockroach comes from Central Africa. An inhabitant of tropical forests, although it does well in arid areas if there is a source of water. Today it is a synanthropic species that has spread with the help of humans to the Middle East, Southern Europe and reached North America.
Interesting!
The African cockroach entered America on the ships of slave traders who caught their goods in Africa.
Periplaneta Americana is one of the representatives of the genus Periplanet, which has 7 species. In the United States, the American cockroach has several other names;
- ship - memory of the slave trade;
- Bombay canary - it is not clear where it came from;
- kakerlak – borrowing from Norwegian.
The names “water beetle” and “palm beetle” are also often found. Both are incorrect. A real water beetle is a swimming beetle. Sometimes this is also called the water bug. The name "palm beetle" actually belongs to the California cockroach. But an Americana nymph in its final stage of development is often confused with an adult California cockroach. They look really very similar. But the periplanet is not averse to settling in human habitation, while the Florida palm cockroach prefers the wild.
Appearance and features
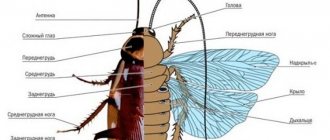
The American cockroach, Periplaneta americana, is one of the most common cockroach species and can grow to approximately three to five centimeters in length. Both males and females are approximately the same size. In males, the wings extend slightly beyond the abdomen, while females may appear wider in the abdomen. Both sexes have additional articulated appendages at the tip of the abdomen. The insect's body appears flat, which makes it easy to penetrate through cracks and other openings into the house.
Adult American cockroaches are reddish-brown or red in color. The area behind their heads is outlined in yellow. You can study the photo of our hero in detail.
Features of the view
American cockroaches choose to live in damp and warm places where food waste dumps or food storage areas are accessible.
Adults, larvae and nymphs lead a hidden lifestyle during the daytime, and at night they become active and move or fly in small jumps across contaminated areas in search of food.
Insects are mainly found in underground communications and basements, in residential buildings, in greenhouses, in food stores, and storage facilities.
In their natural environment, American cockroaches live in rotting wood and organic debris. They easily enter rooms through window or door cracks, which is facilitated by the flattened shape of their body.
Currently reading: Why cockroaches are called stasiks - versions and facts
American cockroaches feed on food scraps, garbage from garbage containers, and even excrement. In the absence of food, they can eat anything that contains organic matter of animal or plant origin. American cockroaches can eat leather, soap, fabrics, paper, and indoor flowers.
Insects are afraid of lack of moisture. The American cockroach cannot live even a week without water. Given this feature of the insect, the cold blockade technique is often used in the fight against them, isolating them from the water source.
This type of insect differs in its life expectancy. Males live up to 1.5 years, and females up to 3 years. They are long-lived in the insect world.
Pests have a significant impact on the epidemiological situation in cities, since they are carriers of helminth eggs and pathogens.
It is important to pay attention to the inspection wells of sewer systems, from where cockroaches easily penetrate into living quarters.
Where does the American cockroach live?
American cockroaches usually live outdoors. They prefer warm, moist places such as flower beds and under mulch. They live in trees. American cockroaches are very common in the sewer systems of many American cities.
American cockroaches enter homes to find water or food. They can easily pass under doors if the weather conditions are uncomfortable for them. Basement windows and garages are also common passageways. When American cockroaches enter homes, they often go to bathrooms, kitchens, laundry rooms and basements.
How to get rid
In cold climates, they move indoors to search for a warm environment and food. I penetrate into apartments and houses through sewer connections, under doors, through air ducts, and other openings. The insect population is removed using insecticides.
It is necessary to close cracks and crevices through which parasites penetrate. Another way to prevent the appearance of cockroaches is to carefully check new furniture, boxes, suitcases, and grocery bags.
What does the American cockroach eat?
The American cockroach is an omnivore. It consumes any decaying organic matter, is a scavenger and will eat almost anything. It prefers sweets, but has also been observed to consume paper, boots, hair, bread, fruit, book bindings, fish, peanuts, old rice, putrid sake, the soft interior of animal hides, cloth, and dead insects.
Outdoors, American cockroaches feed on leaves, tiny particles of wood, fungi and algae. They also eat small insects. Indoors, American cockroaches forage under appliances, in drains, in kitchen cabinets and on the floor. They eat crumbs, leftover food and spilled food they find. They will also eat pet food left out overnight.
Does a cockroach bite?
This question cannot be answered unequivocally. There is an opinion that, due to their large size and the presence of a powerful mouthparts, American cockroaches are capable of attacking a sleeping person and trying to gnaw off the epidermis on open areas of the body.
However, in the conditions of a modern apartment, it is difficult to imagine such a large cockroach colony, whose representatives would risk attacking such large prey as a person from hunger.
The danger for a person, especially a person with bronchial asthma or allergic diseases, lies in the very presence of Periplaneta Americana in a residential area.
Insect extract has pronounced allergic properties. Young children suffering from atopic dermatitis and asthma are especially sensitive to the allergen. In apartments heavily populated by pests, insects often touch food, children's toys and any household items, carrying allergens and pathogenic bacteria on their paws. Therefore, all the attention of the owners should be focused precisely on the intensive fight against these harmful insects.
Features of character and lifestyle
The American cockroach is most likely to be found in and around restaurants, grocery stores, bakeries, home kitchens, and other food preparation areas. Cockroaches generally prefer warm, damp areas. Like most indoor pests, they seek out sources of food and water, as well as a safe place to rest and breed.
Females produce many egg capsules, 14-16 eggs each hatching in 50-55 days into grayish-brown "nymphs". American cockroaches prefer to lay their eggs in protected, moist areas. Nymphs will molt 9 to 13 times before reaching maturity.
Effect of temperature
A comfortable temperature for American cockroaches is about 30 degrees Celsius.
When the temperature outside drops, you may find that American cockroaches have appeared indoors. They get into air ducts, around utility pipes, small cracks and crevices, sewer connections and under doors. They can be found near bathtubs, clothing baskets and bathroom fixtures.
Flying cockroaches
They will fly in high temperatures. They can move from building to building.
Habitats
Adults and nymphs can be found in a variety of places. In the north they can usually be found in warm tunnels or in large public buildings. They are often found near sewer access, near garbage and pumps.
Nymphs can be found in dark basements and floor drains. In basements, they can be found in corners high on walls or in floor drains.
American cockroaches also prefer damp areas and access to water. Indoors they will choose dark, damp places.
Outdoors, they can be found in moist, shady areas such as yards, hollow trees, woodpiles and mulch. Sometimes they can be found under roof tiles or attics.
Lifestyle
The American cockroach is a modest insect. It is nocturnal, hiding in a dark, damp place during the day. In warm climates it prefers to live outdoors, but in “cold” states it lives in apartments and human houses. Along with the black cockroach, the American crawls into apartments through sewer drains and cracks in the foundation. Its body is adapted to penetrate very small crevices. Periplanet Americana is even better adapted to such “sabotage” activities than the black eastern cockroach.
If you have a food warehouse, you can be sure that the American cockroach will settle there.
Reproduction of American cockroaches
Like other cockroach species, the American cockroach lays its eggs in an egg capsule called an "ootheca".
The oothecae are about 8 millimeters in size, dark brown in color and symmetrical in shape, each capsule containing about 16 eggs. The female cockroach lays an egg capsule within a day of formation and produces a new egg every nine to ten days.
During her one-year life, a female American cockroach produces an average of 10 egg capsules, but can reach a maximum of 30. The ovary contains enough water to grow the eggs until they hatch. Young American cockroaches hatch in 24 to 60 days. The rate of development from egg to adult depends on the ambient temperature.
What do pests eat?
Since this species lives directly next to humans, its diet is quite varied. What American cockroaches eat includes:
- pieces of meat;
- bread crumbs;
- fruits vegetables;
- sugar, sweets;
- leftover dairy products;
- sunflower oil;
- remnants of synthetic semi-finished products.
This species, just like the Prussians and black long-horned beetles, likes to live in places with large accumulations of garbage and rotten food. Therefore, throw garbage out of your home more often and check your kitchen for food debris. A photo of these insects is attached below.
Fighting methods
Residents of America have also made progress in inventing means to remove their unpleasant neighbors. We will tell you what they are poisoned with overseas:
- Aerosol Mosquitall.
- American gel against cockroaches Maxforce.
- Electric trap against crawling insects.
A highly effective American cockroach repellent that can fight most household pests. It is convenient to use even when fighting furniture moths, the larvae of which live in the upholstery of armchairs and sofas. The insecticide that Mosquitall uses in its aerosols is the most powerful poison for use at home by non-professionals. But, despite the fact that the poison has a strong effect on insects, it is absolutely safe for humans in small quantities. However, be careful: if you inhale the insecticide in large quantities, it may cause an allergic reaction. In addition, this poison does not have an unpleasant odor, which will save you from the need to ventilate the room after using the aerosol.
If you don't know how to get rid of this scourge, use Maxforce gel. This type of insecticide is convenient to use if you cannot find a colony of longhorned beetles. One package of such gel will be enough to treat an average two-room apartment against crawling insects. Typically, baseboards and corners are treated with this gel - places where crawling pests are quite common.
An electric trap is a fairly popular way to quickly get rid of insects in the world.
This device consists of a housing with wires running along the bottom surface. Such a device is installed in an unsightly, dark and damp place - this is where pests are most often found. The trap will come with a special bait. It will need to be placed in the center of the trap body. After installation, the device is connected to the network, and electric current begins to flow through the wires. The insect will smell the bait and immediately try to get to it. But as soon as it ends up on the wires of the trap, it will instantly die from the effects of electric current. Gradually, the body of the trap will be filled with insect corpses, so you will have to clean it periodically. To do this, a special brush is included with the trap, which will help clean the trap from insects. After this, the trap is ready for use again. This method of getting rid of pests is suitable if you are rarely at home or are afraid to use toxic chemicals in your apartment, which are contained in aerosols and gels.
Traditional methods
Over the entire life of a person with his unpleasant neighbors, many folk remedies have been invented to get rid of American cockroaches in an apartment.
1. The most popular folk remedy for removing barbels is boric acid. This powder is also suitable for getting rid of many other types of insects.
You will need:
- a teaspoon of boric acid;
- a teaspoon of sugar or honey;
- a glass of warm water.
To make such a product, follow these steps:
- Mix boric acid, sugar, water.
- Use the resulting solution to treat all surfaces in the house where cockroaches can pass, including baseboards and corners of the apartment.
Boric acid, together with the sweetness, which is a bait, enters the victim’s esophagus, is digested and turns into a deadly poison, from which the insect instantly dies.
2. Another effective method for getting rid of pests in an apartment is ammonia. Surprisingly, everything that helps humans is a deadly poison for insects. Pests are very afraid of ammonia and will flee from places that have this pungent odor.
You will need:
- 50 drops of ammonia;
- liter of water.
You will need to do the following:
- Add 50 drops of ammonia to the water. If you don't mind the smell of this alcohol, you can add more.
- Treat the baseboards and corners of the apartment with the resulting solution, as well as all surfaces in the kitchen and bathroom.
Where to buy special means of control
Now let’s look at which stores in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Nizhny Tagil, Krasnodar, Minsk and Kyiv you can buy all of the above insecticidal products to combat American and other types of cockroaches. Below is a table with store names, addresses and prices for the chemical insecticides we listed above:
| Name of shop | Address | Product name | Price, rub |
| Southern Yard | Moscow, st. Shcherbakovskaya, 58 | Aerosol Mosquitall | 160 |
| Range | St. Petersburg, Prospekt Prosveshcheniya, 69 | Gel Maxforce | 100 |
| Cinderella | Nizhny Tagil, st. Parkhomenko, 124 | Electric insect trap | 550 |
| ABC of cleanliness | Krasnodar, st. Kubanskaya Embankment, 64 | Aerosol Mosquitall | 180 |
| Cosmohit | Belarus, Minsk, st. Krasnaya, 18 | Electric insect trap | 745.89 BYN rub. |
| Domestic | Ukraine, Kyiv, st. Molodogvardeyskaya, 20 | Gel Maxforce | 45 UAH |
Is this type of cockroach dangerous for humans?
Like any synanthropic insects, the American species is quite dangerous for humans. These pests love to live in landfills and sewers, and we all know how many unpleasant microorganisms live in these places:
- Insects, coming into a human home with garbage, bring on their legs a large number of fungal infections, pathogenic bacteria and worm eggs.
- Moreover, these barbels are capable of biting if there is no source of water or food nearby. Their strong chitinous jaws are capable, unlike other longhorned beetles, of chewing through human skin more significantly.
- Traces from the bites of these insects can bleed and also cause severe allergic reactions.
Return to description
Egg capsules
Female American cockroaches make protective cases for their eggs. They are in the form of capsules. After forming a capsule, the cockroach deposits it in a warm, humid room.
American oothecae are about 38 mm long. They are dark in color - reddish or black-brown. Homeowners often find these pods in basements, laundry rooms, or kitchens. They can be under cabinets or behind appliances. American cockroaches also store their egg capsules behind objects in garages and sheds.
When the eggs hatch, tiny nymphs emerge from the capsule. As they grow, small cockroaches shed their skin. Given plenty of food, American cockroaches can develop from egg to adult in as little as 5.5 months.
Life cycle of a cockroach
The American cockroach has three life stages: egg, several larval instars, and adult. The life cycle from egg to adult averages about 600 days, and the adult life span can be an additional 400 days.
Nymphs emerge from the egg in about six to eight weeks and mature in about six to twelve months.
Adults can live up to one year, and an adult female will give birth to an average of 150 children in her lifetime. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity affect the development time of the American cockroach. Outdoors, the female prefers moist, hidden places.
Eggs: Female American cockroaches lay their eggs about a week after mating. At the peak of her reproductive period, she may lay down two capsules per week. Females produce on average one ootheca per month for ten months. The female deposits a capsule near a food source, sometimes sticking it to the surface using a special secretion from her mouth. The deposited ootheca contains water sufficient for the development of eggs. When stored, the shell of the egg turns brown or black after a day or two. It is about 8 mm long and 5 mm high.
Nymph: The nymph stage begins when the egg hatches and ends with the emergence of the adult cockroach. The number of molts of the American cockroach varies from six to 14. The first instar American cockroach turns white immediately after hatching, then turns grayish-brown. After molting, subsequent cockroach nymphs are white and then reddish-brown, with the posterior edges of the thoracic and abdominal segments being darker in color. The wings are absent during the nymphal stages, and the wing flaps become visible in the third or fourth instar. Complete development from egg to adult takes about 600 days. Nymphs, like adults, actively obtain food and water.
Adult: The adult American cockroach is reddish-brown in color with a pale brown or yellow stripe along the edge of the pronotum. Males are longer than females because their wings extend 4–8 mm beyond the tip of the abdomen. Males and females have a pair of slender, articulated paired appendages at the tip of their abdomen. Male cockroaches have cerci with 18 to 19 segments, while females have 13 to 14 segments. Male American cockroaches have a pair of palps between the cerci, but females do not.
White cockroaches
Photo source: https://albin0s.ru/page/albino-cockroach
You won’t find an albino cockroach in nature, but black and red varieties can change the color of their chitinous coating for various reasons.
Immediately after molting, cockroaches are white, and this is not uncommon. But during the shedding of the cover, the insect tries to hide, which makes it difficult to see the white cockroach.
There is another reason for their danger. After baiting with poisons and insecticides, surviving individuals can become white and even transparent. These are quite tenacious creatures, and therefore can turn white after being caught in a fire. White color is not a sign of purity in the insect world.
Social structure and reproduction
Female cockroaches do not need a male to lay eggs, but they do enjoy company. A new study shows that virgin female cockroaches living socially produce offspring faster than virgin females living alone.
It's not particularly pleasant to imagine happening under the refrigerator, but female American cockroaches can produce eggs through parthenogenesis, a type of asexual reproduction. Like many other arthropods that can reproduce in this way, cockroaches tend to only do so if males are not available. Offspring born through parthenogenesis develop only from the mother's egg, so they have less genetic diversity than offspring created by sexual reproduction.
In American cockroaches, eggs produced by parthenogenesis have lower survival rates than eggs produced by copulation, but the offspring of single mothers are able to survive and mate.
The researchers found that a lack of males could not be the sole cause of parthenogenesis. Females should be able to discriminate not only the general absence of males, but also the proportion of males associated with them and the probability of finding a mate at a particular population density.
To test the influence of the social environment, the researchers placed female cockroaches in different situations. In the control group, the male and female were kept together and were allowed to mate. In other cases, females were kept with one, two, three or four other females. The third group of females were kept with castrated males. The researchers also tested the effects of adding pheromones, chemicals that insects use to communicate, to groups of all-female cockroaches.
The researchers then calculated the number of eggs laid in each condition and how long it took the females to lay the eggs. They found that virgin cockroaches alone lay eggs through parthenogenesis in an average of 13 days, give or take about four days. Virgin cockroaches kept in groups were significantly more likely to re-lay eggs. For example, female cockroaches kept in formation began laying eggs after an average of 10 days, give or take a couple of days.
Cockroaches have a sense of solidarity. Virgin cockroaches kept in all-female groups lay their second clutch of eggs much earlier than virgin cockroaches left alone (an average of 18 days versus 25 to 30 days for isolated cockroaches).
Adding pheromones did not shorten the cockroaches' time to parthenogenesis, although being with castrated males delayed the process more than with females, the researchers found.
By synchronizing parthenogenesis, females in a group can benefit by ensuring the survival of more of their offspring, the researchers wrote. Cockroach nymphs hatched together will be safe, which may counter the disadvantage that they hatch at lower rates than offspring produced through sexual reproduction.
The researchers added that this may be a very primitive example of female cooperation. While male cockroaches housed together tend to fight until they bite off each other's antennae. Females, on the contrary, huddle together and, apparently, even coordinate their reproductive schedules. This is due to the general ecology of the population, as males tend to leave colonies to avoid inbreeding, while conspecific females stick together.
Biology [edit]
Characteristics[edit]
Of all the common cockroach species, the American cockroach has the largest body size; before metamorphosis, molts 6–14 times (mostly 13 times); and has the longest life cycle, up to approximately 700 days. [7]
Its average length is about 4 cm (1.6 in) and its height is about 7 mm (0.28 in). [8] They are reddish-brown with a yellowish edge to the pronotum, in the area of the body behind the head. Immature cockroaches are similar to adults, except that they are wingless.
The cockroach is divided into three parts; the body is flattened, broadly oval, the head is covered with a corymbose pronotum. The pronotum is a plate-like structure that covers all or part of the dorsal surface of the thorax of some insects. They also have chewing mouthparts, long segmented antennae, and leathery forewings with delicate hindwings. The third section of the cockroach is the abdomen. [9]
The insect can move quickly, often slips out of sight when threatened, and can fit into small cracks and under doors despite its fairly large size. It is considered one of the fastest running insects. [10]
In the experiment P. americana
recorded a record speed of 5.4 km/h (3.4 mph), about 50 body lengths per second, which would be comparable to a human running at 330 km/h (210 mph). [11] [12]
It has a pair of large compound eyes, each with over 2,000 individual lenses (ommatidia, hexagonal apertures that provide a type known as mosaic vision, with greater sensitivity but less resolution, often seen at night, hence called night vision) . - a very active nocturnal insect that avoids light. [ citation needed
]
American cockroach nymphs are capable of limb regeneration. [7]
Morphology [edit]
The American cockroach exhibits a characteristic insect morphology: its body has subdivisions such as a head, trunk and abdomen. The body, or thorax, is divided into prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax. Each thoracic segment gives rise to a pair of walking appendages (known as running legs). The organism has two pairs of wings. The forewings, known as tegmina, arise from the mesothorax and are dark and opaque. The hind wings arise from the metathorax and are used in flight, although cockroaches rarely resort to flight. The abdomen is divided into 10 segments, each surrounded by chitinous exoskeleton plates called sclerites, including dorsal tergites, ventral sternites, and lateral pleurites.
Life cycle[edit]
American cockroaches have three developmental stages: egg, nymph and adult. [13] Females produce a case of egg (ootheca) that protrudes from the tip of the abdomen. On average, females produce 9–10 oothecae, although sometimes they can produce up to 90. After about two days, the egg cases are placed on the surface in a safe place. The egg cases are about 0.9 cm (0.35 in) long, brown, and purse-shaped. Immature cockroaches emerge from their eggs in 6–8 weeks and take 6–12 months to mature. After hatching, the larvae feed and undergo a series of 13 moults (or ecdysis). Adult cockroaches can live for another year, during which the females produce an average of 150 young. The reproductive cycle of the American cockroach can last up to 600 days; [7] It is capable of reproducing through facultative parthenogenesis. [7]
Genetics [edit]
The American cockroach genome is the second largest insect genome after Locusta migratoria
.
About 60% of its genome consists of repeating elements. About 90% of the genome can be found in other members of Blattodea. Genetically, the American cockroach is closer to two species of termites, Zootermopsis nevadensis
and
Macrotermes natalensis
, than to the German cockroach. The genome encodes a large number of chemoreceptor families, including 522 taste receptors and 154 olfactory receptors. The 522 taste receptors represent the largest number among insects whose genomes have been sequenced. About 329 taste buds are involved in the perception of bitter taste. [7] These traits, along with expanded groups of genes related to detoxification, the immune system, growth and reproduction, are believed to be one of the reasons for the cockroach's ability to adapt to human living spaces. [14]
Diet[edit]
American cockroaches are omnivores and opportunistic feeders that eat materials such as cheese, beer, tea, leather, baked goods, starch in book bindings, manuscripts, glue, hair, dried leather flakes, dead animals, plant materials, dirty clothes and glossy clothes. clothes. paper with starch sizing. [2] [13] They especially love to ferment foods. [15] They have also been observed feeding on dead or injured cockroaches of their own or other species.
Natural enemies of American cockroaches
It may seem that cockroaches are winning the war against humanity. They outnumber us, they will likely outlive our species, and it is a never-ending battle just to keep them out of our basements, kitchens, and attics. But people have allies in the fight against cockroaches. Without these natural predators, cockroaches would be ankle-deep in some places. So thank centipedes, ants, frogs, lizards, snakes and even scorpions for this. These predators love to catch and eat cockroaches. Mice treat cockroaches like a chocolate bunny; they bite off the head, eat the entrails, and discard the tough legs and wings.
Cats are also ferocious enemies of cockroaches. Running cockroaches are great entertainment for cats. However, you should discourage your cat from eating cockroaches. They have thick, cartilaginous exoskeletons, fragments of which can become lodged in a cat's throat. They can also be rough on your cat's digestive system, leading to vomiting. Although cockroaches are not poisonous, they may have been poisoned by pesticides.
If you are really bothered by cockroaches and want a pet to eliminate them, you can try getting a gecko. These ferocious lizards have suction cup legs and kill cockroaches where they live, under sinks, around baseboards and in other narrow cracks. However, you may have trouble sleeping to the sound of scurrying geckos squelching crunchy cockroaches in the dark.
Habitat
American cockroaches are widespread, primarily in the countries of South and North America. This species also spread throughout Africa, displacing its ancestor. Scientists have noticed that at the moment, insects are actively spreading throughout Europe. However, the species did not take root in Russia for two reasons. Firstly, large sizes. In conditions of fairly strong winter cold, large insects die. Secondly, there are numerous offspring, for which there is not enough food in the conditions of Central and Northern Russia. For the same reason, cockroaches rarely appear in apartments where it is difficult to feed their offspring. But if it appears in a house where there is enough food in the public domain, it will multiply at an incredible rate.
In urban environments, the American cockroach can be found in industrial buildings with heating, in sewers, in ventilation shafts, and in food processing plants. Every year this species gets closer to humans and learns to live in an urban environment, feeding on food waste.
These insects can often be found on ships and airplanes. They travel mainly with food products packed in cardboard.
Population and species status
The American cockroach has spread throughout the world thanks to commerce. This cockroach is often found in commercial and large buildings such as restaurants, grocery stores, bakeries and anywhere food is prepared and stored. The American cockroach is rarely found in homes, but infestations can occur after heavy rain. They can grow in huge numbers, with more than 5,000 sometimes found in individual sewer pits.
Outdoors, American cockroaches are found under shingles and in attics. Cockroaches live outside but will roam indoors in search of food and water or to avoid extreme weather conditions. In Florida, areas such as trees, wood piles, garbage structures, and organic waste piles around homes provide ample food, water, and hiding places for cockroaches.
Mass migrations of American cockroaches are a common occurrence. They migrate into houses and apartments from sewers through water pipes, as well as from trees and shrubs located next to buildings or with branches hanging over roofs. During the day, the American cockroach, which reacts negatively to light, rests in shelters near water pipes, sinks, bathtubs and toilets, where the microclimate is suitable for survival.
Breeding
American cockroaches are often bred by insect lovers. This is quite an interesting pet to watch. Interestingly, females tend to their offspring for some time after the larvae hatch from the egg, although this is rather uncharacteristic behavior for cockroaches. The ritual of courtship between a male and a female also looks beautiful. And the very spectacular appearance of the American advocates his elevation to the category of pets.
Cockroaches of this species are often raised to feed amphibians and lizards. Fast-growing and prolific insects are able to fully provide the inhabitants of terrariums with high-quality protein food.
And yet, despite all its positive qualities, one feature makes a native of America not very suitable for the role of a pet - the ability to emit pheromones. In nature, insects use them to scare off enemies or attract sexual partners. In urban conditions, for people susceptible to allergies, this trait can cause a serious exacerbation of the disease.
Otherwise, these are quite cute insects, ordinary inhabitants of the cages of avid cockroach lovers. If you consider yourself one of those, you will probably be interested in reading about other types of cockroaches. The reaction of ordinary people to uninvited strangers varies. For example, like this girl in the video: