The marbled bug (Holyomorpha halys) belongs to the category of stink bugs and the order of Hemiptera. It is also called the brown marmorated bug. The bug's body resembles a pear fruit. It is called marbled because white and black spots are scattered throughout the body of this type of bug. The body shape is slightly flattened and resembles a shield. This is where the name came from.
Dimensions do not exceed 12-18 millimeters in length. The general color of the adult is brown or dark gray. Paws are brown. The antennae have white stripes. Seeing such stripes on the antennae of a bug, you can determine its identity. The peritoneum is light in color. The wings are membranous with dark markings. An adult bug can fly. The larva of the marbled bug is not adapted to flight.
Habitat
According to Timiryazev University, the bug first appeared in Russia sometime in 2014. Scientists of the Agrarian University. K. A. Timiryazeva, together with colleagues of the North Caucasus Horticultural Center, argue: early detection of the pest (marbled bug) allows you to save from 25 to 45% of the harvest. Therefore, preventive measures are very important. This approach is especially relevant for farms, large plantations of grapes, citrus fruits and other types of fruit-bearing crops. Preventive measures will help preserve the harvest and prevent loss of profit. It is worth adding that the shield bug or marbled bug is included in the Unified List of Quarantine Objects. Therefore, Rosselkhoznadzor can impose sanctions on products imported into the Russian Federation.
The homeland of the marbled bug is considered to be the countries of Southeast Asia, including China, Japan, as well as the countries of the Korean Peninsula, Taiwan and Vietnam.
What does it eat?
The marbled bug, like absolutely all bedbugs, has a piercing-sucking mouthparts. With its proboscis, the insect creates a puncture and sucks out juice from stems, leaves, inflorescences, buds, pods, fruits, berries and vegetables. His food, although strictly vegetarian, is still extremely varied. Marbled bugs happily feed on dozens of plant types, causing damage to a wide range of agricultural crops.
The menu of the marbled bug includes nuts, fruits, vegetables, grains and berries. The smelly pest's diet includes apples and pears, peach and apricots, citrus fruits and figs, beans and peas. This list also includes grapes, raspberries and blueberries, tomatoes and cucumbers, hazelnuts and pistachios, sweet peppers, dark nightshade and sunflower.
The marbled bug eats not only fruits, but also young shoots, buds, leaves, and stems. In the absence of cultivated plants, this insect makes do with wild and weed vegetation, so starvation certainly does not threaten this type of bug.
How to fight
The life of a pest is subject to biological rhythm. The time for active feeding and reproduction occurs in the summer; in the autumn, bedbugs hibernate. When answering the question of how to deal with the marbled bug, it is worth immediately emphasizing that the method of getting rid of the parasite is chosen in accordance with the biological rhythm of the pest.
Mechanical method
As daylight hours decrease and air temperatures drop, harmful organisms begin to look for a secluded place to hibernate. Representatives love warmth, frost destroys them. In the first half of autumn, insects look for dry, warm places.
Interesting fact! The increase in the number of pests becomes known just in the fall, when parasites tend to hide in people's homes. There are cases when insects cover the walls and ceilings of rooms and literally fall on their heads.
The wintering time of the bug is suitable for using mechanical methods of exterminating “uninvited guests.”
How to deal with the marbled bug mechanically?
It's simple - insects are collected by hand in local places and burned or drowned.
A vacuum cleaner will be a faithful assistant in this matter. To ensure that no smell remains in the device after fighting insects, you should use a disposable dust collector.
When it gets warmer outside, the bug becomes mobile - it is not easy to fight it mechanically. The insect does not lead a sedentary lifestyle and does not live indoors - the parasite prefers to fly around gardens and vegetable gardens in search of food. A chemical method of exterminating parasites comes to the farmer's rescue.
Chemical method
Answering the question of how you can get rid of the marbled bug, avoiding direct contact with it, it is worth recommending the use of special preparations.
Biologists suggest using the following means:
- Karate Zeon is one of the most effective products based on lambda-cyhalothrin. Before using the drug, it is necessary to dilute the composition (4 ml) in water (10 l). To forget about the problem forever, it is worth re-processing;
- Clipper. A chemical based on bifethrin. Apply the remedy for marbled bugs in an amount of 6 ml per 10 liters of water. Most effective against adults. A single treatment is sufficient;
- chemical insecticides (phosphorus, carbophosphorus, chlorophos).
Attention! Chemical pest control is carried out in early spring, when the insects are not yet strong after wintering.
When processing plants, safety precautions must be observed. This issue is especially relevant when it is necessary to persecute parasites in a residential area.
Biological method
How else can you kill the marbled bug?
Another alternative is biological control, which involves the use of natural enemies of the parasite - organisms that destroy eggs, larvae or adults. These include: birds, insects, painful viruses, fungi. The most radical insects in this regard are predators from the family of shield insects - Perillus, Podius. Not averse to feasting on the marbled bug and golden woodpecker, some ants and mantises.
Among the pathogenic fungi that are effective in controlling the pest, one can distinguish a strain of the entoparasitic fungus - Beauveria bassiana.
Traps
From mid-April - during the insect activation season - you can also use pheromone traps for the marbled bug. Aggregation pheromone is used for black pyramid and hanging or sticky traps. When the pest spreads massively, the pheromone of the bug Plautia stali is used. Based on this substance, a pyramid-shaped trap is made - a ground element more than a meter high, in the upper part of which there is a container with bait and a killing pesticide strip. The trap “works” because insects mistake it for a tree. The finished product can be purchased in America.
Insects are drawn to light; it is for this reason that light traps have begun to be used in pest control. The results of the research work led to the conclusion that lamps emitting black ultraviolet light attract early-season pests. The same method is successfully used for monitoring purposes, which helps to predict a problem and prepare in advance to solve it.
Is it possible to do without chemical insecticides and make a trap for parasites yourself? You can easily build a light trap at home. The easiest way is to fill a shallow baking tray with soapy water and turn on a light over it.
This “device” not only saves money, but is the safest.
Signs of appearance
This type of bug produces a very smelly secretion. Therefore, a person can immediately notice its appearance on his personal plot. The unpleasant aroma is intended to protect the bug from other representatives of the animal world. A special odor is produced by the endocrine glands and is similar to the odor emitted by a skunk or ferret. That’s why the common people also call it the “stink bug.” If you pick up such a bug in your hands, the unpleasant smell will remain on them for a long time.
The bug migrated from the countries of Southeast Asia. Gradually spread throughout America, Canada and England. In our country they live mainly in the territory of Abkhazia and the Krasnodar Territory. The climate prefers humid and warm.
Description and features
A small bug with a thyroid-shaped body can fly. Under the brown-gray pentagonal shell are membranous wings with dark spots. The length of an adult is 12-17 mm. It is not easy to distinguish the stink bug from its relatives.
But you can recognize the enemy by the white stripes located on the legs and antennae. Dark and light spots on the shell create marble graphics, which is how the bug got its name. The insect's peritoneum is light. If you look closely, you can see bluish spots on the head.
The scientific name of the insect is halyomorpha halys, the popular version is the Asian stink bug. The unflattering nickname was not given by chance. The bug emits an extremely unpleasant odor in two cases:
- to attract a couple of the opposite sex;
- in case of danger.
The marbled bug is easy to distinguish from harmless stink bugs by its black and white antennae
Special glands in the lower abdomen accumulate a special secretion until needed. The stink bug has been included in the list of quarantine objects since 2021, but this fact does not stop the insect from massively settling into houses, outbuildings, and storage facilities, where it has something to profit from.
The marbled bug is an insect of the order Hemiptera and is a plant pest. The oral apparatus of the shield bug is designed in such a way that it is capable of piercing the outer shell of plant fruits with a special proboscis, sucking out the juice, introducing saliva with enzymes.
After a bug's meal, the plant is susceptible to diseases and developmental disorders. The puncture site turns black, and plant tissue necrosis develops due to bacterial infection of the fetus.
The marbled bug is very harmful to plant productivity
Deformation and structural changes in the pulp affect the taste of fruits and vegetables. Unripe fruits fall off as their development stops; those remaining on trees and bushes rot.
Almost all plants are susceptible to stink bug attacks, but mostly fruit, grain, and vegetable crops. In Asia, the homeland of the marbled bug, scientists count over 300 plants that have been attacked by it, including flowers, shrubs, and vines.
Persimmons and tangerines fall off, hazelnuts hang empty, and spoiled grapes cannot be used to make juice or wine. The losses caused by the agricultural pest reach 40-70% of the total harvest. Huge financial losses befall gardeners and farmers due to the inability to export fruit crops.
In the United States, annual statistics record losses of tens of billions of dollars from bedbug infestations. The appearance of the pest in neighboring Abkhazia and in the southern regions of our country is causing concern among the population.
It is easy to notice the appearance of a bug in a garden plot by its characteristic smelly secretion, reminiscent of the secretions of a skunk or ferret. In nature, this ability serves as protection against enemies who avoid communicating with “fragrant” insects.
If you pick up a bug in your hands, the smell will linger on your palms for a long time. In people prone to allergic reactions, this phenomenon can cause, in addition to discomfort, painful manifestations.
Reproduction
The time for reproduction of the marbled bug is spring. Around mid-April. The female bedbug lays about 20-35 eggs. In this case, the total fertility of the female will be 200-350 eggs. Then he attaches the laid eggs to the back of the leaf. The size of the eggs varies from 1.3 to 1.7 millimeters.
Here are its breeding periods:
- May-June (mid-month);
- July-August (end of the month);
- August-October (mid-month).
Scientists call the process of reproduction itself “traumatic.” The male pounces on the female and pierces her abdomen with his genitals. In the resulting puncture, the male individual releases sperm. Males mate up to 200 times a day. As a result of such intercourse, the development of eggs begins in the abdominal cavity of the female.
Larvae
The larvae mature in five stages. In each period of ripening they look different. In the first stage, the larva or nymph is red or bright orange in color. The next stage is black color. In the last stage of ripening, a characteristic brown-white (marble) color is obtained. Ripening time is about 35-45 days. Like adults, larvae feed on the juices of fruits and plants. At air temperatures ranging from +20 to +30 degrees and above, stink bugs produce up to three offspring per year. At temperatures above 35 degrees the larvae die. Like the adult, the larva causes damage to plants.
ATTENTION! In places where eggs are laid, spots appear on the leaves, they fall off and dry out.
What does a parasite look like?
We are talking about a representative of shield insects, which means that the insect has a flattened body in the form of a shield. The length of the parasite is about 1.5 cm, width is 8-10 mm. This shield of the brown marmorated bug acts as the insect's weapon. As an additional protective measure, the pest uses an unpleasant odor that it emits at the time of threat. That is why the parasite is otherwise called “smelly”. A distinctive feature of the described species is the alternating black and white stripes on the last pair of insect antennae segments.
Harm or benefit of a bug
Let's consider the harm of a bedbug and whether there is any benefit from it.
Harm
The bug feeds on plants. The oral apparatus is adapted to the function of sucking juice from both fruit and berry and vegetable crops. Sucks juice from fruits and trees using its proboscis. The stinking pest does not disdain flowers, trees, and shrubs. Eats the fruits of tangerine trees and harms grapevines and other crops. It is no longer possible to make high-quality wine from grapes damaged by such a pest. The bug causes enormous damage to agricultural land. For example, in Abkhazia, such a bug eats up to 40% of the tangerine crop, approximately 50 to 70% of peaches, persimmons, pistachios and other crops. As a result, this type of bedbug can cause enormous financial damage. After all, most of these crops are exported to other countries.
The fruits of the bedbug's life:
- necrosis appears on the tree bark;
- the tree trunk under the bark becomes soft;
- the fruits do not have time to ripen and fall off;
- fruit and vegetable crops lose their taste and rot;
- the surface of vegetables and fruits becomes covered with bumps;
- leaves become withered and dry;
- spots appear on fruits and vegetables.
The bug we are considering feeds on more than 300 species of plants . He is very fond of the seeds of rosaceous plants. In the southern territories (Krasnodar Territory, Sochi, Abkhazia, Dagestan), it eats olives, figs, mulberries, and all types of nuts. Loves tomatoes, peppers, eggplant. As a result, the fruits do not ripen and their appearance deteriorates. You cannot eat such a fruit. In addition, when the temperature drops, insects move into human homes. A person who is hypersensitive may become allergic. After all, bedbugs smell terrible. In addition, the very sight of a bug “walking” around your home is very unpleasant.
Among other things, the marbled bug carries a disease called phytoplasmosis. People do not get this disease, but plants do. As a result, the leaves on trees and shrubs turn yellow, and unattractive spots appear on the fruits.
Benefit
There is no benefit from this type of bedbugs. Even animals and birds do not eat it, as it smells bad.
conclusions
In recent years, the invasion of the marbled bug has acquired the proportions of a natural disaster. Against the backdrop of climate change in the world, the pest’s habitat will expand significantly in the near future. Scientists claim that an increase in average winter temperatures of just one degree will lead to a 15% reduction in insect mortality. High fertility, ecological plasticity and migratory activity make the marbled bug an almost invincible pest. To date, measures taken by humans cannot regulate the number of the parasite; they are restraining in nature and only minimize the harm from its activities. All hope is for the discovery of a new pesticide that is harmful to bedbugs or the appearance of a natural enemy that will feed on insects while seriously reducing their numbers.
Does the marbled bug bite?
A bug can bite a person (they are especially “evil” during the mating period). Inflammation appears in the place where the bug bit. The bite site is itchy. Allergy sufferers can get anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema.
And yet, the bedbug’s mouthparts are not adapted to bite humans. Its proboscis is designed to suck juices from plants.
IMPORTANT! If a bug bites, you should wash the bite site with water or a weak alkaline solution. It is advisable to apply cold to the bite site. You can buy special ointments in pharmacies.
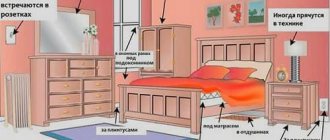
Pest in the house
The brown marmorated bug does not tolerate freezing temperatures. For wintering, he looks for heated buildings and climbs into houses. Why is the shield bug dangerous to humans? At the slightest contact with an insect, it emits a strong, unpleasant odor. In some people, it causes an allergic reaction in the form of a runny nose or conjunctivitis. The number of bedbugs in one house can reach thousands of individuals. The insect's mouthparts, in the form of a proboscis, are quite weak, so it does not bite human skin. A reaction in the form of dermatitis, itching or rashes can result from fluid from the shield bug's body getting on the skin.
Fighting methods
Let's consider ways to destroy the marbled bug.
Products and chemicals
In winter, bedbugs hibernate. Therefore, in winter we recommend collecting them manually. You can sweep them off the plants.
You can effectively “treat” plants using preparations based on phosphorus and nicotinamide. Preparations of the pyrethroid group are good.
The most effective drugs are considered:
- Aktara (VDG);
- Tanrek (VRK);
- Calypso (KS);
- Imidor (KS).
Natural enemies
The natural enemy of marbled bugs is the fungus Beauveria bassiama. Currently, drugs based on this fungus are being developed. Thyroid bugs can be eaten by wasps.
Traditional methods
If bedbugs come into your home, “bathe” them in a vinegar bath. To do this, you need to mix a tablespoon of vinegar with water (do not take a lot of water). Spray the areas where insects accumulate with the resulting solution. Vinegar water prevents the release of pungent odors.
Nicotinic acid (PP). Shake out the tobacco from 20 cigarettes. Soak in hot water. You need to take ≈ 4 liters. Spray the mixture onto the bedbugs. To prevent a skin reaction, wear gloves.
You can use a mixture of hot red pepper and water. A hot sauce (such as Tabasco) will also work. You can take any other one. This mixture will burn the chitinous cover of the pest bug. Wear gloves to prevent the skin on your hands from burning. If the mixture gets into your eyes, rinse immediately with water.
Protecting premises from bedbugs
The first cold weather forces shield bugs to seek shelter. They are able to penetrate small cracks, so home owners have to take protective measures. It is necessary to close the openings in window and door openings with seals. Garlic, essential oil, and garden plants (basil, mint, lavender) will help repel insects.
Mechanical way of fighting
In spring, bedbugs come out of hibernation. During this period, it is important to begin collecting and eliminating individuals, preventing them from reproducing. On the Black Sea coast and in the Krasnodar Territory, insects become active in early April. They leave shelters at temperatures ranging from 10-15°. Experts advise collecting them manually and destroying them.
Pheromone traps
The most effective method of controlling and eliminating pests is the use of pheromone traps. Several types of pheromones have been synthesized in the USA; this mixture attracts marbled bugs throughout the season. By design, traps can be ground or suspended. The first are a high pyramid (1.2 m), painted black. A 2-liter container is installed on the base, which contains odorous bait and insecticide. The hanging version has a smaller stand, but otherwise the device is the same. Adults and nymphs rush to the bait, but cannot get out of the flask.
After the pest invasion began, Russian scientists began synthesizing a new pheromone. Its testing was successful, but the adhesive version was not effective enough. Insects may come off the sticky base. In barrier-type structures, up to several hundred individuals can be collected. Attractant devices lure brown bugs to trees. Some of them fall into traps, the rest are destroyed manually, shaking them off the branches.
Light traps
A distinctive feature of insects is their desire for light; females and males actively fly towards the fire. Light traps are used to study the number and distribution of insects. But in apartments they help control pests. The device has a grid with electricity, upon touching which the insects die.
Do-it-yourself trap for marbled bugs
Homemade devices are no less effective than purchased designs. There are several options for traps:
- Lamp and soap solution. One of the simplest designs to prevent pests from entering the house. You will need a table lamp and a wide container with soap solution. It is enough to turn on the lighting in the evening and the insects will fly towards it and fall into the water.
Information. During testing, the trap was able to destroy 10 times more pests than the factory version.
- Plastic bottle and LED. Simple design from a 2 liter bottle. The container is cut into two parts, the top one being 1/3 of the total height. An LED flashlight is placed at the bottom of the bottle. The upper part is turned upside down and inserted into the base like a funnel. At night, marbled bugs will crawl inside towards the light, but will not be able to get out.
- White fabric. In the evening, wet a white sheet or towel until damp. Hang the fabric on a line in your yard. Bed bugs will crawl into the folds of the damp material; in the morning they are collected in a basin of soapy water.
- A large amount of fly tape is hung around the trees in the yard. Various insects, including bedbugs, will stick to them.
- Fake winter hut. In autumn, pests look for a dry and warm place to hibernate. One way to get rid of insects is to install several cardboard boxes filled with paper on your site. Shield insects climb into the false hut, which is then burned.
One of the pest’s vulnerabilities is a negative attitude towards strong odors. It can be scared away with an infusion of garlic or wormwood.