What is the difference between a mouse and a rat?
Although these two animals belong to the same species, they have a lot of differences. But sometimes it can be very difficult to distinguish a rat from a mouse, so let’s start with the differences between these rodents:
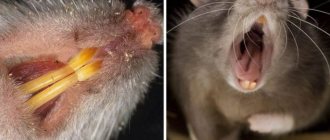
- The first and most important difference is the number of chromosomes. Mice have 20 of them, and rats have 22, which makes it impossible to cross these two species.
- Body length. The carcass of rats can reach 40 cm in length, while mice rarely grow more than 15 cm in length .
- Rodent weight. Rats can weigh up to 700 grams, and mice only reach 50 grams;
- Number of nipples. Rats have 12 of them, mice have 10.
- Activity. Mice sleep for short periods of time several times during the day. Rats sleep only once a day if no one disturbs them during sleep.
- Nutritional features. Both rats and mice are omnivorous rodents, but the diet of the former contains more protein foods. Mice prefer plant foods, and resort to eating beetles, frogs and worms much less often.
Now let's talk about what these two types of rodents have in common:
- long tails covered with horny scales and sparse hairs, a long elongated muzzle, rounded ears and eyes;
- both species can be domesticated;
- active at night;
- agile and dexterous;
- often live close to a human home . Far from humans, they most often live in countries with warm climates.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: Water rat
The water rat or water vole (Arvicola amphibius) is a small mammal that belongs to the order of rodents, the family of voles. The genus Water Voles includes only one species, Water Voles.
Rodents are very ancient and extremely common animals. Rodents inhabited our planet during the Cretaceous period. The oldest fossils of rodents date back to the Pleocene period, at which time the animals inhabited the territory of modern America. Over time, the appearance of animals has undergone changes, animals have successfully adapted to environmental changes, and at the moment there are 11 families of the rodent order in our country alone.
Video: Water rat
The vole family includes 15 genera. Most species of the vole family are small rodents with a small muzzle, small ears, short legs and a tail. The mouth has strong teeth with which they are able to gnaw through fairly hard wood. The fur of most rodents is short, while that of the water rat is long and thick. The Water Rat has a particularly long tail, which is slightly flattened on the sides, and there are no webbed toes on the hind feet. Water rats differ from other rats in having small, almost non-protruding ears, from gray voles in their large size, and from muskrats in the shape of their tail.
Palevaceae are one of the most numerous groups of rodents that can easily tolerate harsh environmental conditions and feed on low-nutrient foods such as greens, bark and roots of trees and shrubs, and grains. Water rats settle near bodies of water, but can also live in a field next to a body of water and in the forest. Animals of this species are active around the clock and live in burrows. They do not hibernate.
Where do rats live in nature?
Wild rats love to settle on the banks of rivers and reservoirs. In addition, they can be found in forests, fields and swampy areas.
Since these rodents are omnivores by nature and are distinguished by good intelligence, curiosity and adaptability, they are often prone to synatropy, that is, living near human habitats. Here rats settle in the basements of residential buildings, attics, barns, warehouses, vegetable gardens and fields sown with cereals, and even in landfills and sewers. In the wild, rats most often live in large groups, dominated by one male and two subordinate females .
Also, rat habitats can be divided into three groups according to weather conditions:
- Rats living in the North. Due to the cold weather, the animal tries to stay closer to human habitation all year round.
- Rats living in the middle zone. In summer, when it is warm, they settle in the wild: in forests, fields, meadows, swamps and along the banks of rivers, reservoirs and lakes. In winter, animals move to residential buildings where they can warm up. Only a few rats remain to spend the winter in the wild .
- Rats living in the South. These animals rarely settle close to people, since weather conditions allow them to live comfortably in the wild all year round, finding sufficient food and building comfortable housing for themselves.
Wherever the rodent settles, it will choose an area that is well protected from enemies. If it is a swampy area, then there should be dense vegetation. There should be a lot of bushes and voids in the soil near the water. The forest must have dense undergrowth in which the entrance to the burrow can be camouflaged.
Rat holes can be 3-5 meters long and 50-80 cm deep. Inside the rodent’s home, nests are built from grass, leaves, feathers and wool, rags and paper . The diameter of the nests can reach up to 30 cm. Sometimes animals settle in hollows or simply on tree branches, where they also build nests.
Rat lifestyle
Rats living in the wild are active in the dark, while animals that live near human habitation adapt to the rhythm of human life.
Rodents can lead a solitary lifestyle or gather in packs. In the wild, rats sometimes live in very large clans, occupying territories of up to 2,000 square meters. But this does not prevent them from developing new territories, expanding their possessions.
In colonies, the dominant position is occupied by the eldest and strongest male, who marks the boundaries of the group’s habitat, protecting himself from the invasion of strangers. The remaining males share places among themselves in the rigid hierarchical structure of the pack. Rodents living within the city and having stable access to food rarely leave their nest further than 20 meters and most often use familiar routes.
If necessary, rats are able to reach speeds of up to 10 km/h, jump from a place to a height of up to 1 meter, and overcome obstacles 80 cm high while moving. Rodents are very active, and can cover about 10-15 kilometers in a day in search of prey. Rats living near ponds and lakes are excellent swimmers and can spend up to 72 hours in water, while catching prey in it. Rats have poor eyesight, and hearing is good only at short distances.
What do rats eat?
Although rats are classified as omnivores, most of their diet consists of protein foods. They hunt small rodents, insects, frogs, lizards and often destroy bird nests. Rodents living on the shore can catch small fish and shellfish . Rats living near people feed on leftover human food and pet food.
Domestic rodents require a balanced diet, which includes special food and protein foods in the form of nuts, cheese and boiled meat. In addition, the rat should always have access to clean water, and rodents should be given a vitamin complex every six months.
IMPORTANT! You should not feed your rat leftover human food, as this can lead to digestive problems for your pet.
Benefits and harms
Rats are a vital link in every ecosystem. A striking example of this is the role of rodents in the “plant-mushroom” symbiosis. Rodents carry spores, ensuring their “meeting” with the necessary representatives of the flora.
Predatory animals and birds feed on rats. People use large rodents for scientific experiments. Decorative varieties of rats are bred for the purpose of domestication. They are often used in various educational projects and circus shows.
Rats are a necessary part of wildlife. An increase in population affects all elements of the ecosystem. The damage caused by rodents to people is enormous:
- damaged house walls and sewer pipes;
- damaged electrical wiring;
- poisoned crops;
- loss of part of the harvest harvested in storage;
- infection with infections (plague, salmonellosis, leptospirosis, pseudotuberculosis, etc.).
Wild rodents can cause significant damage to an orchard. They move freely through trees, damage the bark, and cause damage to shoots and fruits. Particularly dangerous are gray pasyuki, which have a rare appetite and aggressive character.
Types of rats
Gray rat
Most often it lives in swampy areas or near a body of water. The rodent's body length is 17-25 cm, the animal weighs about 140-390 g. The tail is always shorter than the body, and makes up 70% of its length. The skin is gray-brown in color, with a lighter shade on the belly. The muzzle is long and wide, the ears are small and round in shape. The lifespan of a rat is 2-3 years.
Black rat
A more aggressive species of rodent, which most often lives within the city. Black rats are smaller than gray ones. The body length of adult animals is 55-22 cm, and the weight is 132-300 g. The tail is densely covered with hair, and is usually 25-30% longer than the body, but does not exceed 30 cm. The skin is black-brown in color, with color on the abdomen most often white or yellow. The lifespan of a rodent is 2-2.5 years.
Turkestan rat
The Turkestan rat lives in the mountainous regions of Russia, Western Tien Shan, Pamir-Alai and northern India. The rodent's body length is 23 cm, the tail is hairy, and is equal to the length of the body, and sometimes shorter by several centimeters. The shape of the muzzle is relatively blunt and wide, the ears are small. The skin has a reddish-ochre-brown color. These rodents live on average two years.
Black-tailed rat
The habitat of this species is Australia and New Guinea, where the rodent prefers to occupy the coastal zone. The animal also has another name - fluffy-tailed rabbit rat , which it received thanks to its unusual tail, covered with long but sparse hairs closer to the end. The weight of the rodent is 200-230 g, body length is 15-23 cm, where the length of the tail is equal to the body. The color is most often brown-gray, with dark hairs on the back, while the belly and hind legs are white. Life expectancy 2.5-3 years.
Small rat
It is one of the three most common subspecies of rats found in the world. They live in Indonesia, New Zealand, Southeast Asia and Oceania. The small rat has the most modest body size among its relatives. An adult rat weighs 40-80 grams, its body length is 11.5-15 cm. The tail, as a rule, is equal to the length of the body, the color of the skin is brown. Life expectancy is 2-3 years.
Rat "Standard"
The most common type of house rat, which over time was able to be tamed by humans and made into their pet. The animals have a massive body, the length of which can reach 24 cm, weight ranges from 300 to 500 g, and largely depends on the sex and nutrition of the animals. The length of the tail can exceed the length of the body by 30-40%. Most often, the coat is dark brown or grayish in color. The lifespan of these rodents does not exceed 3 years.
Rat "Sphinx"
This is a type of decorative rat, completely devoid of hair. The size of their body does not exceed 25 cm, the length of the tail is 22-27 cm. The rat has large ears and almost no whiskers. These are friendly creatures with fragile health that need a lot of care and a warm place to live . The lifespan of rodents is 2.5-3 years.
Would you like to have a hairless rat?
Tailless rat
The rodent breed was bred in 1983. Rats are born completely tailless, due to which they have a rounded croup and a stocky body structure, the length of which is 22-28 cm and weight 250-400 grams. An animal may have a completely different skin color. Life expectancy is 3-3.5 years.
Curly rat
Another name for this breed is Rex. The animal has medium or long wavy fur. The size of an adult rodent is 8-20 cm, tail length 10-12 cm, weight from 350 to 600 g, depending on gender. The muzzle has a wide and blunt shape. The color of the skin can be any. Life expectancy – 3 years.
Rat "Dumbo"
The rodent got its name thanks to its large ears. This is a decorative breed of rat. Their body is quite short - 15-20 cm, and has a pear-shaped shape. The weight of an adult animal is 250-400 g. The color varies. These rodents live no more than 3 years.
Rat with eyes of different colors
This variety was brought to Europe from three countries: Japan, China and India. One of the rodent's eyes is usually pink, while the other is dark ruby or black. The body length is 20-30 cm, weight is about 300-500 g. The body of the rat is slightly rounded, the legs are short. The color of the skin is light gray, milky or white. Life expectancy 3 years.
Rats without tails
Recently, a new fashion has appeared that is gaining more and more fans - rats without a tail. They are called Manx . They look like hamsters with elongated bodies and muzzles, and in place of the tail there is just a small appendage.
Perhaps someone will like this type of hamster-like rats, but in reality these are ordinary disabled people. A rat's tail is everything. Thanks to him, she can live in peace, but as soon as she loses him, the rat loses all its abilities. Tailless rodents die quickly and are quite painful.
Therefore, if you really want to get yourself a pet rat, then get one with a tail. These rodents are quite clean and can wash their tails themselves. In addition, it is not as disgusting to the touch as many people think.
Rat breeding
Determining the sex of a rat is quite simple: males are larger and heavier than females, and by the age of 1.5-2 months, large testicles grow at the base of the animal’s tail.
The age of a rat can be determined by weighing the animal:
- At 2 months, males weigh 160-220 g, females 150-200 g;
- At 3 months, males weigh 250-310 g, females 210-250 g;
- At 4 months, males weigh 350-410 g, females 250-290 g;
- At 5 months, males weigh 450-490 g, females 290-340 g.
IMPORTANT! In adult individuals, the length of the tail is equal to the body, or slightly longer than it. Therefore, if a rat’s tail is smaller than its body, then the animal is not yet a year old.
When the rat is six months old, its weight remains unchanged. To understand that this is an old specimen, pay attention to the following signs:
- the animal's fur becomes sparse, dull, and sticks out in places;
- the skin on the tail becomes rough, rough, with many flaking keratinized particles;
- the incisors become significantly longer. Their back part is ground down, and the teeth take on the shape of a chisel.
Rodents living in their natural habitat breed mainly in the warm season, mainly in spring and autumn. Rats living close to human habitation, or decorative individuals, can reproduce regardless of the time of year.
The female's pregnancy lasts 22-24 days, after which 8-10 cubs are born. Rats are born naked, blind and helpless, so they need extra care. The problem is that babies cannot pass feces and urine on their own. The owner can help them along with the mother rat by massaging their bellies from time to time. This helps stimulate excretory processes.
The sex of the baby can be determined immediately after birth. Boys have a small hint of testicles at the base of their tail. A month after birth, young rats begin independent life, but they reach sexual maturity only at 3-4 months.