- Wild animals
- >>
- Arachnids
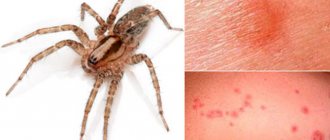
The white karakurt is one of the most dangerous creatures on earth. Despite the fact that outwardly it does not seem so threatening, the poison of this arthropod is deadly.
In this regard, a spider bite for animals such as a horse or shelter will definitely end in death. For a person, an insect bite can also be fatal if the required amount of qualified medical care is not provided in a timely manner. However, researchers and scientists argue that the poison of the white karakurt is somewhat less dangerous than that of the black representative of this species.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: White Karakurt
The white karakurt belongs to the arachnid arthropods, is a representative of the order of spiders, the family of web spiders, classified in the genus of the black widow, the species white karakurt.
Scientists do not have reliable information about the origin of these representatives of arthropods. The most ancient finds of the distant ancestors of the Karakurts date back to the Carboniferous Age, which is about four hundred million years ago. They are rightfully considered representatives of some of the most ancient living creatures preserved on earth.
Video: White karakurt
Some scientists suggest that the most ancient ancestors of modern poisonous spiders, including karakurts, lived in water. However, during the Paleozoic period, they moved into thickets of huge grass and impenetrable bushes. In thickets of dense vegetation they hunted various insects. Later, spiders appeared that could weave webs and entangle eggs with them for protection.
Interesting information. The strength of the poisonous substance of karakurt venom is 50 times greater than the strength of karakurt venom and 15 times the strength of rattlesnake venom.
About two hundred and fifty million years ago, arthropods appeared that learned to weave webs to create traps. With the onset of the Jurassic period, spiders learned to weave multiple webs and hang them in dense foliage. To make webs, arthropods used a long, thin tail.
Spiders spread widely across the earth during the formation of Pangnea. Later they began to be divided into species depending on the region of their habitat.
Description and life activity of karakurt
The poisonous karakurt spider belongs to the order of spiders of the family of web spiders from the genus of black widows. Translated from the Turkic language, the name is literally translated as a black worm. The Latin name Latrodectus tredecimguttatus reflects the external characteristics - 13 points on the back and the essence of the spider (biting robber). What does the karakurt spider, which is sometimes called the steppe spider, look like? In terms of size, the spider belongs to the medium arachnids. The size of the male is 4-7 mm, the female karakurt is 2-3 times larger and can reach 20 mm. The body of the eight-legged spider is black, with a pronounced abdomen. Both males and females have red spots or dots on the upper side of the abdomen. On the lower part of the abdomen a clear scarlet pattern is visible, similar to the outline of an hourglass. The spot on the abdomen often has a snow-white halo. Adults (males) can be completely black. Karakurt is a predator; it feeds on insects, which it uses a web to catch.
Despite its small size and non-threatening appearance, the karakurt's venom is 15 times stronger than that of a rattlesnake and 50 times stronger than that of a tarantula.
White karakurt, also related to web spiders, has a white or yellowish color. There is no hourglass pattern or spots on the body, but there are 4 indentations forming a rectangle. White spiders are much less poisonous, their bite is not dangerous to people, although the venom of the white karakurt is similar in its toxicological properties and effects on the human body and animals to the venom of the black widow. White karakurts can be found in Russia and neighboring countries, but the main habitat is located further south - in North Africa, the Middle East, and also in Central Asia. Let's focus on the black widow karakurt as the most dangerous representative of the swindlers, which you can meet at domestic resorts.
Appearance and features
Photo: White karakurt spider
The white karakurt really looks ominous. It inspires fear, and what’s worst is that, thanks to its color, it goes unnoticed. A distinctive feature of this particular type of arachnid is its body in the shape of a large ball, as well as long and thin limbs. There are four pairs of limbs. The first and last pair of legs are the longest. This spider is the only representative of its genus that has a white, grayish or yellowish tint.
Compared to black widows, white karakurts do not have an hourglass-shaped pattern. On the surface of the back you can see four small depressions in the shape of a rectangle.
The lower part of the body is always white or milky in color. The rest of the body may be gray or yellowish. These arthropods have pronounced sexual dimorphism - males are significantly smaller than females in size. The size of the female can reach 2.5 centimeters, while the size of the male does not exceed 0.5-0.8 centimeters.
The head is small, significantly smaller than the body, most often brown. On the head there are chelicerae, which are highly powerful and can easily bite through the chitinous shell of even large locusts. In the back of the abdomen there are several arachnoid warts, through which the web is released into the environment.
The white karakurt has a body structure typical of all other arachnids. It is divided into two parts - the cephalothorax and abdomen. Each of them contains vital organs. The cephalothorax contains: a gland that secretes a poisonous secretion, the esophagus, the sucking stomach, food outgrowths, and the anterior aorta.
The abdomen contains:
- Arachnoid gland;
- Liver;
- Intestines;
- Ostia;
- Ovaries in a female;
- Trachea;
- Posterior aorta.
Black fathead
Classification
Species: Karakurt – Latrodectus tredecimguttatus
Genus: Black widows
Family: Web spiders
Squad: Spiders
Class: Arachnids
Type: Arthropods
Subphylum: Invertebrates
Lifespan: up to 14 months (females), up to 10 months (males, unless eaten)
Surprisingly, it is not snakes, such as the viper and black mamba, that are considered the most poisonous, but spiders.
And the most poisonous of the order of arthropods is the karakurt spider (the photo and description may shock you).
Karakurt is also called the black widow. Black - because this is the color of the spider’s abdomen, legs, and head.
Widow - because the female, whose size is almost three times the size of the male, eats her spouse after the marriage ceremony.
But something else is more dangerous; this animal is very poisonous.
It is difficult to notice, because the karakurt even pulls its snares not vertically, like other spiders, but horizontally, and the thin threads are located chaotically, and not, as shown in cartoons, in a circle.
If you accidentally touch a spider, it will perceive this as aggression on your part, attack and bite.
It is difficult to notice the spider, because the karakurt even pulls its nets not vertically, like other spiders, but horizontally, and the thin threads are located chaotically, and not, as shown in cartoons, in a circle. If you accidentally touch a spider, it will perceive this as aggression on your part, attack and bite
Habitat
The karakurt spider lives (a photo taken in macro mode will show the animal on a pebble) mainly in the Crimea, southern Ukraine, Kazakhstan, southern regions of Russia, Afghanistan, Southern Europe, the Mediterranean, Central Asia and North Africa, Astrakhan steppes.
Recently they have migrated (probably due to global warming), and they can be found even in the Moscow region, Azerbaijan, Altai Territory and in some regions: Rostov, Volgograd, Novosibirsk.
One of the most common arthropods throughout the Earth is the black widow spider. Its variety has 31 subspecies. These spiders make their home in secluded places where there is little sun and enough small insects.
One of the most common arthropods throughout the Earth is the black widow spider.
The black widow troop gets its name from its notorious cannibalism. The female spider of this species eats the male after mating, and can feed on similar arthropods and even her own brood of spiderlings.
But some scientists refute these facts by the fact that such observations are carried out in laboratory conditions, where very often spiders have no choice but to eat their loved ones. And the male will not be able to avoid such a fate, because he has nowhere to run. But in the wild, in the natural environment, their behavior is significantly different.
Before mating, the male black widow courtes his lady for a long time and performs mating dances. Some scientists explain this flirting by the fact that sudden aggressive actions can provoke the spider to attack. In this case, the groom risks becoming dinner, and not the father of offspring.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Breed of cats with a short tail: varieties, care.
Due to such cannibalistic incidents, the lifespan of spiders is short. In addition, karakurt (black widow) is a favorite treat for many birds and mantises. Usually the bright color helps its owner, warning everyone about the poisonous properties of the body. But in this case, the female karakurt is not saved by her red spot on her abdomen.
The life cycle of spiders most often does not exceed a year, but there are also long-livers that reach three years. Among the latter, males cannot be found; in their natural habitat, their life is much shorter than that of females of this species. Only in artificial conditions can they live for a long time, without ever mating.
The most beautiful horses: description of breeds
KARAKURT black widow how to determine its habitat
In fact, the black widow spider is not aggressive. Karakurts bite people not out of a desire to kill or eat, but only for the sake of protection when a person poses a threat. Even an accidental intrusion into the territory of a karakurt provokes an attack by a spider.
A healthy adult may not be afraid of karakurt poison. Fatal consequences from a bite can only occur in sick people, children and the elderly. But be that as it may, an antidote is necessary for every victim. The black widow spider's venom, which enters the bloodstream, can lead to further problems with the psyche, nervous system and muscles.
The female black widow has stronger venom than the male.
The spider is much larger than its mate, has a red or orange hourglass mark on its abdomen and shiny dark organs.
The male is paler, with red or pink spots on the back. These karakurts have 4 pairs of legs approximately 12 mm long, and the body reaches 40 mm in females and approximately 20-25 mm in males.
The spider's web is stronger than silk, and to make it convenient to pull thin threads over prey, these spiders have curved bristles on the back pair of legs. Karakurt weaves thick fabrics, rather than delicate lace, to catch grasshoppers, various insects and other spiders.
Black mamba snake: description, lifestyle, interesting facts
Many people do not know what a black widow spider looks like and confuse the poisonous one with its relatives. There are a lot of dangerous spiders on Earth that look like black widows, each of them has its own habits and characteristics. In the vastness of Russia, Belarus and Ukraine, the false black widow is found.
For example, the white karakurt, which is most often found in steppe areas, is one of the subspecies of the black widow. This spider is not so poisonous; its bite will never lead to fatal consequences. But that doesn't mean it's safe to try his fangs.
Karakurt can live as a pet, and there is even a chance of growing a long-liver. But it is not suitable for beginners, because it has a peculiar character.
Most of the bites from poisonous spiders occur on such unfortunate hosts. Dealing with a poisonous pet requires a lot of experience and skill.
If large tarantulas more or less adapt to home life and can sit in the arms of their owner, then karakurts are not at all like that.
We suggest you read: White discharge in a cat after childbirth, causes, treatment
The black fathead is sometimes called the ladybug spider. It really resembles this bright insect: against the red or orange background of its abdomen, four black spots with a white border stand out.
Male black fatheads are small, but perhaps the brightest and most colorful of our spiders.
However, only the male looks so impressive. The female black fathead, although larger, is less brightly colored. It is usually velvety black, sometimes with yellow elements on the front.
24.05.2017
Every house or apartment is home to many different insects. Some people are not even aware of, while others are often noticed. One of the latter are spiders. Every person has been familiar with them since childhood.
Now I would like to talk about spiders that are not so familiar - black spiders. Sometimes they appear in private houses and apartments. Their appearance can often be terrifying, but are they really that scary?
Let's try to understand this issue, and also find out why black spiders appear in the house, why they are dangerous and how to deal with them.
There are many different spiders in nature, more than 40 thousand species. However, in the CIS countries their number is not as large as it might seem. Only a few of them, who have adapted to living with a person under the same roof, can get into the house.
Let's look at the main types:
- Haymaker. These are the familiar little light spiders with long legs. However, many do not know that adults can be quite large, and some become gray or almost black in color as they age. Many people don’t know, but this type of spider is poisonous. But you shouldn’t be afraid of it, because the harvester cannot bite through human skin, and therefore cannot cause harm.
- Black or gray spiders. They appear in residential areas less frequently, but still quite often. Their size is usually 0.5-1.5 cm. A special feature is the web in the shape of a pipe with complex patterns. They are also harmless to humans, although some of them can bite. The bite is similar to a mosquito bite, but it takes a little longer to go away. Such arthropods do not attack people themselves, but can do this when their lives or offspring are in danger.
- Tramp. Such spiders are even rarer and usually in rural areas. Their size is usually no more than three centimeters. Their color is usually dark brown, gray or black. A distinctive feature is great activity and the absence of cobwebs. This species is more dangerous and can bite humans. The bite is not fatal, although it is quite painful and can cause serious allergic reactions. They often end up in a house by accident and never stay in it for long.
- Horses. A distinctive feature is movement by jumping. They can be distinguished by the presence of eight large eyes. Like the haymaker, it cannot bite through human skin and is not capable of causing harm. Leads a daily lifestyle. The color of horses can vary depending on the species, ranging from bright yellow to black.
Other types of spiders do not get along with humans, so if you can meet them in the house, it is by accident. They can often be blown through a window or accidentally run in through a door.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Underwater submersible lamps for aquariums
Are there cockroaches, mice or other pests in your dacha or apartment? We need to fight them! They are carriers of serious diseases: salmonellosis, rabies.
Many summer residents are faced with pests that destroy crops and damage plants.
A person often encounters spiders - this can happen at home, in the forest, on the beach or on a hiking trip.
Therefore, it is advisable to know which of the representatives of the spider genus should be feared and preferably avoided, and which should not be paid attention to.
This article examines what poisonous spiders live in Russia, what is the degree of their danger, how their bite threatens a person, and how to provide first aid to the victim.
The territory of the Russian Federation is huge; more than a thousand species of spiders live in different parts of it. Many of them are poisonous and people should avoid them.
In a dark corner you can often find a cobweb, which indicates that its owner is lurking nearby. Most of the domestic spiders living in central Russia do not pose a danger to people; these small arthropods themselves try to avoid meeting them. But in regions where the climate is hotter, other spiders live - poisonous and dangerous.
Where does the white karakurt live?
Photo: Animal white karakurt
There is an opinion according to which the white karakurt lives only in uninhabited regions of the Naimb desert. However, this is not true. Changing climatic conditions have led to an expansion and change in the habitat of white karakurts.
Geographical regions of arachnid habitat:
- Southern regions of the Russian Federation;
- Northern part of the African continent;
- Southern part of Ukraine;
- Crimea;
- Iran;
- Mongolia;
- Türkiye;
- Kazakhstan;
- Azerbaijan.
White karakurts prefer areas where there is little precipitation and there is no severe frost. Favorite habitats are steppes, ditches, and ravines. They try to avoid flat, open areas in every possible way. Like the vast majority of arachnids, it chooses secluded, inaccessible places.
Likes to hide in burrows of small rodents, crevices, gaps between walls, and other remote, secluded corners. Karakurts do not tolerate severe frosts and harsh climates. They try to avoid excessive moisture, too light areas, and too hot climates.
It is quite possible to meet a white karakurt on the territory of plowed farm lands, abandoned or residential buildings, in attics, under the roofs of houses and barns.
White poisonous spiders. White karakurt
Not many people know that poisonous spiders are found not only in Australia or South America, they can live in your neighborhood. To understand this in more detail, we offer a rating of the most dangerous spiders that can live near us.
KARAKURT
One of the most insidious and dangerous spiders lives mainly in the south of our country (Crimea, Krasnodar region), but like other southern spiders, it can migrate to other regions during abnormal heat. Karakurt (from Turkic: “ka’ra” - black and “kurt” - worm) has a very dangerous poison that can lead to death if the bitten person is not helped in time. A karakurt bite causes unbearable pain spreading throughout the body. Only a serum developed against the venom of these spiders can save the bitten person. It is worth saying that only female karakurts are dangerous, which can be identified by a mark on their abdomen in the form of a red hourglass.
What does the white karakurt eat?
Photo: White Karakurt
The source of food for the white karakurt is insects that get caught in the web it weaves.
What is the power source:
- Arthropods are small in size;
- Cicadas;
- Locust;
- Grasshoppers;
- Flies;
- Horseflies;
- Beetles;
- Cicadas;
- Small rodents.
White karakurts have an extraintestinal structure of the digestive tract. When a victim enters the web, it pierces its body in several places and injects a poisonous secretion so that the victim's entrails are completely digested by the poison. After this, the spiders eat the liquid part of the body of their victim.
A horizontal web is most often used to catch insects. It is characteristic that the web does not have a typical trapezoidal pattern, but has a chaotic arrangement of threads that does not form any pattern. The white karakurt can create several such webs of traps. Most often they are placed among the foliage in such a way that it remains invisible to most insects or small rodents. Such traps are often left in burrows, small depressions in the ground.
The process of assimilation of food proceeds quite quickly, since almost everything has already been digested under the influence of the poisonous secretion. Among the variety of food sources, locusts and grasshoppers are singled out and given preference. White karakurts literally manage to live without food, or eat a very modest amount of food. White karakurts can live for about 10-12 months practically without food.
What does it eat?
In its natural habitat, arthropods hunt for small insects. To do this, the spider uses a trapping net stretched near the nest. The animal is characterized partially by external digestion. Poison is injected into the body of a victim entangled in a web, paralyzing the insect and gradually digesting the tissue inside the chitinous cover.
The spider bites the victim from all sides, leaving it unharmed for a while. It then sucks out the liquefied tissue, puncturing the protective coating. The empty chitinous shell remains hanging in the web for a long time.
Mosquitoes
Considering the small size of the spider, mosquitoes are quite suitable as objects for hunting. Insects fall into stretched nets, landing on the ground or grass, becoming victims of karakurts.
flies
The karakurt web can easily hold a fly. When the prey is securely entangled in the web, the spider begins to process the victim.
Cockroaches
Even such ancient species of insects are susceptible to successful attacks by karakurts. Like other victims, they are caught by spiders in a similar way - in the trapping web. The sharpness of the arthropod's jaws makes it easy to break through the chitinous coating to begin processing the victim.
How long does he live?
The maximum lifespan of the karakurt spider is up to five years. Considering the peculiarities of mating games of arthropods, females live significantly longer than males. But even female representatives are sometimes unable to survive the harsh winter. Therefore, these animals prefer warm climates.
But, given the high fertility and rapid development of offspring even in frosty winters, the population is successfully developing, increasing its numbers.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: White karakurt spider
White karakurts are active regardless of the time of day or weather conditions. They can be active and go out in search of food, as well as eat it, both in the light and in the dark. Males are less active. They use spider webs to make traps. Spiders weave it not in the form of certain shapes and figures, but by simply winding threads. It can get food like a hunter, that is, hiding behind bushes or in thickets of dense vegetation.
Burrows of small rodents, cracks in walls, ceilings, depressions in the soil, pits, etc. are chosen as places of residence. These representatives of arachnids have very acute hearing. This is why human bites have been reported. Spiders react sharply to unknown noise and, for the purpose of self-defense, try to attack first. Due to the fact that when people meet them they become a source of unnecessary noise, spiders attack them for the purpose of self-defense.
They do not tolerate frost and extreme heat well. In the spring-summer period, large migrations are observed in the habitat regions. They are due to the fact that spiders are trying to escape from extreme heat. After the white karakurt finds a safe shelter, the females entwine it with a web and begin to prepare for the appearance of offspring.
General information
How long the cross spider lives and what it looks like depends on its type:
- An ordinary cross. This is the most common of all spiders with a cross on its back. The size of females reaches 2.0-2.5 cm in length, and males - 1.1 cm. In addition, males have a narrower body. In both sexes, the body is covered with a waxy substance that retains water. The cephalothorax is protected by a reliable shell.
- Spider with a red cross. This species is characterized by small body size. Their color differs depending on the lighting. On the back there is a pattern resembling a red cross. Other body features do not differ from a regular cross.
- Barn spider. Females and males of this species of arthropod are approximately the same size. Females reach 1.3-2.2 cm in length, and males - 1.0-2.0 cm. This is a yellow spider, the center of its abdomen is represented by uneven brown notches. A dark stripe with two dazzling white spots runs along the lower part of the body.
- Meadow cross. Mainly lives where there is moisture and a lot of grass. The cross on it is dark or light in color. A blurry pattern resembling a leaf is visualized at the bottom. The body has a light green or brown tint. Light stripes are visible on the paws. The body length of a female is 1.7 cm, and that of a male is 0.8 cm. Females blend into their environment, changing their color, like chameleons.
- Marble cross. This species is characterized by pronounced sexual dimorphism. Females are significantly larger than males in size. Their length reaches 1.8 cm, males - up to 0.8 cm. These arthropods have a variety of shades and patterns. But most often they have an orange belly and a black pattern. This combination of colors served as the choice for the name of the species.
A pure black spider with a white cross on its back is just a work of human imagination. There are no representatives of this arthropod species with this color. The life cycle of different species of this arthropod varies within 1-2 years.
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Little white karakurt
The mating period for this representative of arthropods is seasonal and occurs in the middle - late summer. Males try to attract the attention of representatives of the opposite sex with the help of special pheromones. In selected shelters, females hang out poutine. This is necessary so that young individuals can gain a foothold on the web and fly away in search of their home. After the end of the mating season, the female individual lays eggs. Their number can reach 130-140 pieces.
When the autumn season arrives, the female dies. The laid eggs independently wait for spring in selected secluded burrows and other shelters. In the spring, with the arrival of wind, which helps get rid of the egg shell and give birth to young individuals. The hatched spiders do not scatter in different directions, but calmly remain in the hole to get stronger and acquire the necessary skills for independent survival. For this period, they have enough food that their mother prepared in reserve.
After the mother's reserves are depleted, the spiders begin to actively eat each other. As a result, only the strongest individuals survive. They leave the cocoon only the following spring, and by the summer of the same year they become sexually mature. The white karakurt is considered a very prolific representative of arachnids. The female can give birth to offspring up to two times a year.
Natural enemies of white karakurts
Photo: White karakurt spider
Despite the fact that these representatives of arthropods are practically the most dangerous in the world, they still have enemies in natural conditions, these are:
- Small livestock - sheep, goats. They are not exposed to the poisonous secretions of arthropods;
- Wasps are sphex. They tend to attack karakurts with lightning speed and inject their poisonous secretion into them;
- Insects are riders. They tend to lay eggs in the cocoons of this representative of the arthropod family;
- Jerzy. Not exposed to toxic secretions.
Most often, farmers who fear mass destruction of cattle due to the bites of white karakurts first allow sheep or goats to graze on a certain pasture. These animals are not sensitive to their bites, so they are often practically used to protect pasture for grazing cattle.
In some regions, there are large numbers of arthropods that can destroy an entire herd of cows.
Description
A characteristic feature of the white karakurt is its spherical abdomen and thin long legs. White karakurt is the only species of its genus whose body color is light, usually white or yellowish. There is no hourglass pattern like that of black widows. Instead, in the white karakurt, four pits-indentations are clearly visible on the smooth surface of the abdomen. They seem to form a rectangle. While the abdomen is almost always white, the cephalothorax and legs vary in color from tan to brown.
Males are significantly smaller than females.