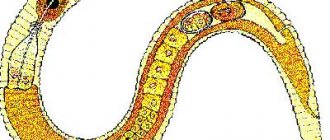
Concept
Nematodes - what are they? Round primordial worms, which are divided into free-living and parasitic. The former can live in the ground, seas and bodies of fresh water . Parasites exist at the expense of plants, animals and humans. Diseases caused by them in mammals are called nematodes.
Plant nematodes are divided into stem, root and leaf .
The root settles in the soil and harms the roots. Very often damages indoor plants. The leafy one lives and reproduces on leaves, moves quickly, is almost invisible, because its length does not exceed 1 mm. Stem nematodes grow twice as large and live inside stems.
Plant root affected by nematode - photo:
Prevention of pest occurrence
Since the fight against nematodes that have settled in the soil or on plants is an ineffective procedure, experienced farmers are advised to take all possible preventive measures to prevent the pest from appearing on the site. Among the most frequently recommended measures aimed at preventing invasion, experts call:
- Compliance with the rules of crop rotation when planting garden crops.
- Cultivate potato varieties that are resistant to worm damage.
- Provide autumn plowing of the garden plot.
- Avoid moving soil from infected areas.
- Buy seed material in specialized stores or from trusted suppliers.
- Avoid planting infected plants and using them as animal feed.
- The purchased soil must be calcined in the oven, since pathogenic forms of this species die when exposed to high temperatures.
- Ensure that newly acquired indoor flowers are kept in quarantine.
- Loosen the soil and remove weeds in a timely manner.
- Provide mineral and organic fertilizers, which will increase the efficiency of the plant’s defense system and minimize the risk of pest damage.
In addition to the listed measures, a systematic inspection of crops with an assessment of their condition, checking for the presence/absence of signs of damage is of great importance, which will allow the necessary measures to be taken in a timely manner to get rid of pests.
Structural features
All species have a highly developed muscular-cutaneous sac . It is formed by a plasmatic mass, which includes nuclei. The body is covered with a ringed or smooth cuticle. It is dense and elastic, secreted by the surface epithelium.
Four ridges protrude into the body cavity, which are located along the entire circumference of the body. The layer located under the skin (epithelium and hypodermis) consists of longitudinal muscles.
Nematodes have only reproductive, excretory, digestive and nervous systems. They do not have a respiratory or circulatory system.
The nervous system is primitive . It includes only a few nerves located longitudinally and the peripharyngeal ring. The secretions are carried out by the cervical gland and special cells.
Nematodes attach to the host using a sticky secretion synthesized by terminal glands located in the tail. Sexual dimorphism is quite clearly expressed, but there are some species - hermaphrodites .
Nematode worms - photo:
Eggs and larvae
The eggs are oval or egg-shaped and white in color. They are motionless and do not harm plants at all . A little face develops inside and goes through its first generation there. In total, it goes through from 2 to 5 juvenile stages of development, each of which ends with molting.
The presence of parasite larvae can only be detected using a microscope .
The larva is similar to adult males and has a white body. The back part is almost transparent, which is typical of herbivorous nematodes.
The most effective medications to combat nematodes
Name.
Main active substance.
Characteristics of the drug.
Gelmodol-VM
Relieves the wearer of helminths. It is allowed for younger and older age categories, because it has no side radios or contraindications for use.
Nemozol.
Albendazole in increased dosage.
A serious drug for getting rid of helminths. Its use allows you to block glucose processes in the intestines of the parasite, so a mandatory consultation with a parasitologist is required before taking the medicine. The medication is permitted, even for children, and is available in the form of syrup or tablets (for adults).
Mebendazole.
Removes helminths from the body and blocks the development of their larvae. The medication requires prior consultation with a parasitologist and has many adverse reactions.
Today, the most effective method of combating nematodes is oxygen therapy. When it is carried out, a certain amount of oxygen is introduced into the gastrointestinal tract of the host, then most of the parasites are killed. To promptly eliminate them from the body, laxatives containing magnesium sulfate, Glauber's salt, hay or rhubarb are used.
Nematodes in the soil
They are called root nematodes. The development period is 20 - 40 days , depending on the species. Their life cycle can take place in two directions:
- At the time of laying eggs, the female nematode was in the ground, and not in the plant - completely or partially, so the larvae emerge from the eggs into the ground. They begin to move until they get inside the roots. This development path is most often observed in the primary stages of infection.
- The female is located inside the root , the larvae come out there, travel a short distance along the roots and begin to feed on the contents. Such larvae cannot be eliminated by biological methods using predatory nematodes, bacteria and fungi.
Fighting methods
The pest is difficult to control: durable body coverings protect the worms from an aggressive environment and exposure to chemicals. In addition, they reproduce quickly. But difficult does not mean impossible in principle. Those who know the secrets of pest control can remove uninvited guests from the garden or greenhouse. True, you will have to put in a lot of effort. The number of pest colonies can be reduced mechanically, thermally, chemically or biologically. You should be prepared for the fact that methods do not always help one hundred percent. Much depends on the number of parasites.
Signs of defeat
General signs of a nematode are that plants stop developing , their growth is inhibited, new shoots appear much later than usual, flowering is very small and weak. Some of the shoots die at a young age, the rest lose their healthy appearance . Fruits are produced in very small quantities, sometimes there is no harvest at all .
Root nematodes (also called root-knot nematodes ) damage the root system. This manifests itself in many ways. The roots begin to branch strongly, while small lateral roots fall off and rot.
Due to this, the supply of sufficient nutrients is disrupted and the plant is weakened . The integrity of the roots is damaged, and numerous pathogenic viruses, fungi, and bacteria .
A weak plant is not able to fight their attack and begins to hurt. In the habitats of nematodes, convex formations - galls and ulcers, as well as necrotic areas. They change color from the original yellow to dark chestnut.
When almost all the roots die, the lower leaves of the diseased plant wither and hang lifelessly even after watering .
Externally, the damaged root system looks poorly developed and has no root hairs . Large roots are excessively thick and deformed. They are watery and break when touched. The color is always brownish, the surface is strewn with small longitudinal cracks .
Stem nematodes develop in stems and live off them. As a result, the shoots become deformed, thicken , and acquire a spindle-shaped shape. The leaf blades develop incorrectly and are too small. The stems become covered with cracks and fill with water.
Adult plants begin to simultaneously produce a large number of stepchildren , which grow rapidly. Flowering and fruiting are very sparse, flowers and fruits are small and ugly.
Leaf nematodes damage the leaves and form characteristic necrosis in the form of a mosaic . They are separated by leaf veins. The petioles break easily, the leaves become swollen, watery, and small. If there is pubescence, it acquires an unnaturally large size .
Types of nematodes with description
There are three types of plant nematodes:
They affect not only garden and garden plants, but also indoor plants. Their principle of life is the same - they feed on plant juices. However, they differ somewhat in body shape, size, and habitat.
Leaf (strawberry) nematode
The leaf nematode has a thread-like body shape. Nematode worms reach 1 mm in length. They have a beige color. They are located on the foliage, where they penetrate through damage to the leaf blade or through pores on their lower parts.
Signs of plant damage by parasites are:
- the appearance of brown spots of irregular shape on the leaves;
- leaves curl, weaken, lose color;
- petioles swell;
- plant growth slows down;
- buds are affected by brown spots;
- the leaf plate becomes thinner;
- The yield is significantly reduced:
- Glossy spots form on the lower part of the leaves, which over time acquire a dark red tint.
Over time, plants affected by pests dry out and rot. Nematodes survive winter well in dry foliage. Pests spread to plants through contaminated soil, weeds, and nearby affected crops.
Important! Leaf nematodes die when exposed to bare soil. However, if they are on fallen leaves, they continue to parasitize, breed and crawl to other plants
Therefore, for prevention and control, it is necessary to regularly remove fallen leaves from the area. The plants most susceptible to parasites are:
- strawberries;
- chrysanthemum;
- nephrolepis;
- carnation;
- aster;
- dahlia;
- orchid;
- Crassula.
Stem nematode
Stem nematodes have a thread-like body and reach 1 mm in length. They parasitize the stems, buds, and flowers of plants. They penetrate the victim through plant rhizomes. Damage to a crop by stem worms is manifested by the following symptoms:
- shoots stop growing;
- the stems thicken and lose color;
- the buds turn pale and dry out;
- Over time, the plant dries out and dies.
Despite the fact that pests love moisture, stem worms can maintain vital activity, even staying for a long time on dry leaves and plant scales. They spread through infected runners, bulbs, tubers, cuttings, and much less frequently through seeds or contaminated soil.
Plants such as parsley, onions, garlic, tomatoes, radishes, and cucumbers are most susceptible to these parasites.
Did you know? The lifespan of worms can reach up to 2 years.
Root (knot) nematode
The root nematode is the largest and reaches 2 mm in length. It also differs from previous species in that it affects the nervous system of plants.
It parasitizes the rhizomes of plants, forming seals on them - galls.
Plants affected by soil nematodes gradually wither, weaken, and stop growing. The leaves are curling. The roots located below the galls stop developing and die. At the same time, the root beard (thin thread-like roots) begins to grow abundantly. Such roots do not contribute to the growth of the crop, but only take away nutrients from them.
Important! It is important to distinguish nematode galls from natural thickenings on the roots of some plants that retain moisture. The latter are white in color, while the galls are yellow or brown.
Root-knot nematodes spread through contaminated soil, remains of roots, seeds, bulbs, equipment, and from nearby plants. Chrysanthemums, ficuses, dracaenas, begonias, lilies, and aloe are most susceptible to these pests.
How to prevent the development of infection?
impossible , to destroy existing nematodes .
Therefore, many plant growers use preventive measures that help prevent plant infection and not acquire diseased seedlings.
Outdoors
- If in some area last season there was an invasion of nematodes, from which the plant suffered, then it must be treated with insecticides . Do not plant plants that may be affected by this species.
- Weeds should be removed immediately after they appear throughout the season, the soil should be cleared of them in the fall, and plant debris should be immediately destroyed by burning or feeding to herbivores. Do the same with the tops of cultivated plants after harvesting.
- Conduct regular inspections of plants and pick off suspicious leaves and twigs and dispose of them immediately.
- If a nematode attack is suspected, watering from above is immediately stopped . Otherwise, the parasites will begin to emerge en masse and crawl away in search of new victims. When watering such plants, only the root system should be moistened.
At home, greenhouses and conservatories
- Plants are placed at a sufficient distance from each other so that conditions of excessive moisture and crown contact that are favorable for the development of nematodes do not arise.
- Affected specimens are placed in a quarantine zone , where there is no chance of infection of healthy plants.
- Leaves and shoots that are clearly affected by parasites are immediately torn off and destroyed .
- Soil for planting is not taken from open areas , especially after strawberries, raspberries, vegetables and strawberries. Or at least steam it before using it.
- Containers left over from plants must be sterilized before new ones are planted in them. It is best to boil them and the trays.
- You cannot use a common tray for several plants. Each one should have an individual one that is deep enough.
- cow manure as fertilizer .
- Growing watercress in greenhouses dramatically reduces nematode populations.
When selecting planting material
- The mother plant for cuttings must be absolutely healthy in appearance , just like seedlings purchased in a store or at the market.
- Young plants brought home must undergo heat treatment before planting.
- Before planting, it is necessary to add a mixture of lime in the amount of 100 g per square meter and sulfur in the amount of 50 g per square meter before planting.
How to get rid of potato nematode
Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to completely remove the nematode from your garden. But every vegetable grower is quite capable of greatly reducing the number of pests on the site and ultimately achieving a satisfactory harvest of tubers. The main thing is to properly build a system to combat this parasite.
If the amount of the pest is no more than 5 cysts per 100 cm3 of soil, then it has almost no effect on the yield level. Potato growers observe a noticeable decrease in yield when this indicator reaches 15 cysts per 100 cm3 or more. Next we will describe how to slow down the development of the nematode.
Use of purchased chemicals
Conventional insecticides are not suitable for controlling the parasite population. More effective, special preparations from the group of nematicides are used against nematodes.
The following drugs are used most often:
- Means of contact action:
- Lindan;
- Karbofos;
- Phosphamide.
- Products used as fumigants. They have a negative effect on worms, penetrating through the respiratory system. This includes:
- Nemagon;
- Chloropicrin;
- Carbation.
- Biological nematicides. These agents have a narrowly targeted effect and show good effectiveness against nematodes. Here is a short list of them:
- Basamil;
- Metarizin.
Traditional recipes for combating potato nematode
It is worth mentioning right away that there are no effective folk remedies against nematodes. Scalding the soil with boiling water gives little noticeable results in the fight against stem nematode larvae. However, a similar procedure can be carried out in small areas, but in medium-sized gardens and especially large ones, this is a very labor-intensive operation.
Some summer residents claim that by sowing marigolds next to potatoes, they can improve the situation. The smell of these flowers is really unpleasant to the nematode. But is it enough to give up food?
Agrotechnical measures
This list of actions is aimed rather at prevention against nematodes, in order to prevent the pest from entering an area that has not yet been infected. Here's their essence:
- placing onion peels in the planting holes when planting potatoes, which are unpleasant to the nematode;
- give the area where potatoes are grown rest for the season;
- sow green manure after harvesting early potatoes, and plow them in in the fall;
- compliance with crop rotation - to grow potatoes in one place for several years in a row;
- use for planting healthy tubers;
- disinfection of tubers before planting with hot water;
- removal of plant residues from ridges;
- carry out all work to care for the crop in a timely manner - watering, weeding, hilling.