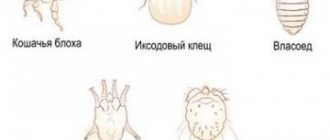
How are lice transmitted from person to person?
A louse is an insect that is not capable of flying or jumping over long distances. Therefore, there are only a few ways you can become infected with head lice.
Pediculosis is transmitted only as a result of close contact with a sick person or his personal belongings where parasites remain.
You can become infected with lice from another person in public places. Several types of parasites can be transmitted simultaneously. Depending on what part of the body insects live in, their type can be determined.
The routes of transmission of pediculosis directly depend on the type of insect:
- The head louse lives in the scalp. These parasites feel best on people with thick and long hair. The insects can be transmitted to a bald person or with very short hair, but the parasite will soon leave such a host. The infection is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through touching or using personal items - hats, combs, hairpins.
- Clothes lives in bedding, in the folds of clothes and on things in the closet. It is not capable of parasitizing on our body - the parasite crawls from underwear, bites a person and hides back in the underwear. This type of insect can be transmitted as a result of sleeping together on a shared bed, wearing someone else's clothes, or poor handling of linen and towels in hotels.
- Pubic, in addition to the pubis, lives in areas such as armpits, eyelashes, eyebrows, beard and mustache. Phthiriasis is most often transmitted through sexual contact with a patient. Venereal diseases are often transmitted simultaneously with pediculosis.
Close contact with infected people occurs frequently. Parasites are highly contagious and are transmitted in almost 100% of contacts with patients.
Ways of transmission of lice
As a rule, the source of infection with such parasites is a person and his clothes. The most common way is to touch heads. This route of transmission is most often found in kindergartens and schools. Only head lice can cross this way. As for clothes, they live on things, and not on the human body. Pubic parasites settle in intimate places.
Head lice get onto the hair through headscarves, panama hats, combs, hairpins and caps of the infected person. Clothes penetrate through clothing. Pubic lesions appear on the intimate area through towels, underwear or during sexual contact. A special feature of this group of parasites is that they live without food outside the human body for about 5 days. You can become infected with lice, for example, just by sleeping on the sheets on which the patient slept.
In addition, this disease spreads in water. It is known that lice swim in it for about 5 days until they find someone they can parasitize. Therefore, you should carefully choose places for swimming. You can get infected anywhere in an enclosed body of water or swimming pool. It is very important to wear a swimming cap, otherwise the insect will get into the swimmer's hair.
Not everyone knows, but 20 years ago girls were strictly forbidden to wear their hair down when appearing in a public place. Compliance with this rule helped protect Soviet children from lice.
Once lice enter the human body, they begin to multiply rapidly. One female can produce about three hundred eggs (nits) in a week. In approximately 40 days of its life, the ectoparasite is capable of causing enormous harm to the person whose blood it feeds on.
Head lice are carriers of dangerous diseases. Typhoid fever is considered one of the most terrible. Despite the fact that in our time it is quite difficult to meet it, more than 2% of people on the planet are infected with it. As for pubic lice, they can transmit some sexually transmitted diseases. There is an opinion that such ectoparasites are carriers of AIDS. Experts say that this is true.
Where and why can you get lice?
Lice infestation can occur in different ways:
- when traveling in crowded public transport;
- in the gym locker room;
- in swimming pools;
- in kindergartens or schools;
- when using the patient’s clothing or personal belongings;
- as a result of sexual intercourse with an infected person.
This disease mainly affects children, because in children's groups there is very close interaction. Children play and study together, and the cots in kindergartens are very close. When heads touch, the parasites are transmitted to a healthy child.
Children very often change clothes, elastic bands or hairpins. The personal belongings of a sick child in most cases contain nits or living individuals. This is how pediculosis is most often transmitted in girls.
Exoparasite eggs are perfectly preserved in a humid environment. For this reason, lice can be easily transmitted in places such as saunas, swimming pools, solariums, and gyms.
Using only your own hygiene items (combs, towels, clothes, hairpins) will avoid the transmission of parasites.
Incubation period for pediculosis
The incubation period of a disease is the length of time from infection to the onset of noticeable symptoms. In the case of pediculosis, this period is considered to be the time during which nits develop.
After landing on a person’s head, the parasite immediately begins to bite. But, as a rule, no one pays much attention to minor itching. Under favorable conditions, insects begin to actively reproduce.
Each female can lay up to 200 eggs per week, which develop into adults (egg - 3 nymph stages - adult) within 3 weeks.
Thus, the incubation period of head lice lasts 21 days. Body lice and pubic lice have a longer breeding season. The period of manifestation of symptoms can last for 50-60 days. An important role in preventing infection with the pubic and clothing variety is played by the level of personal hygiene and the frequency of changing clothes.
5Ways of infection
When infected with pediculosis, there must be close contact between a sick person and a healthy person. Lice are not transmitted if people are at a great distance from each other, since insects can neither fly nor jump far. It is important to note that the parasite can remain unharmed in water for 2 days, so infection with pediculosis through the aquatic environment (swimming pool) is very important.
First signs of infection
Once lice have been transmitted, they are very difficult to detect. The presence of several individuals is simply impossible to identify. Only after extensive reproduction and the appearance of a large number of nits can pediculosis be noticed.
Some of the main signs of head lice infestation include:
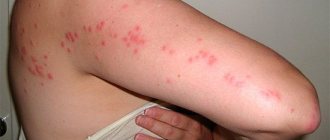
- skin itching (the most intense - on the back of the head and temples);
- there is a feeling of something moving on the skin;
- itching leads to scratching until it bleeds;
- possible appearance of pustular wounds at the sites of bites;
- if left untreated, the scalp becomes rough and takes on a gray tint;
- the appearance of sticky nits on the hair, which look like dandruff, but are very difficult to remove;
- when trying to crush a nit, a click is heard;
- upon careful examination of the scalp, you can notice the parasite.
Pediculosis pubis also manifests itself with itching and characteristic changes on the skin. Nits appear as dark spots at the base of the hair. With body lice, bites are localized on the body - stomach, chest, sides, shoulder blades.
How lice infection does not occur: myths and misconceptions
There are quite a lot of misconceptions about how lice can be transmitted:
- Lice only grow in dirty hair. This is not true. It has been scientifically proven that parasites, on the contrary, prefer clean and well-groomed hair and scalp.
- Pediculosis can only spread in children. In fact, age does not play any role. The parasite can be transmitted to both adults and children.
- Lice jump from head to head. It's not true, fleas jump. And lice are not able to fly or jump long distances. Only through close contact can a louse be transmitted.
- Lice are crawling around the house. It is a myth. The parasite cannot exist for a long time separately from the host. He needs constant nutrition. If the insect falls off its head, it will quickly die.
- Pets can serve as a source of infection. It is not true. Human louse cannot be transmitted from an animal, since cats and dogs have a different hair structure, and the parasite simply cannot hold on to it.
- Lice can come from nerves. This is a myth due to the fact that some people experience itching due to stress. Pediculosis has nothing to do with this.
- Parasites live under the skin. Another misconception. Mites – demodex or scabies – can live under the skin. Lice of any kind are ectoparasites, that is, they never penetrate into humans.
Ways of infection with pediculosis
So, first of all, you need to know about the ways in which bloodsuckers can get on a person, these include:
- Contact.
- Clothes.
- Personal items.
- Water.
- Surfaces.
If we talk about the most common method, then this is certainly direct contact. But the least probable are surfaces, but nevertheless possible. The fact is that these insects do not have the ability to jump and fly, but they run very fast.
The paws of these insects are not adapted to move on smooth surfaces; the parasite has 6 of them. The structure of the paws makes it possible to deftly move along the hair surface and hold firmly on it. It takes them half an hour to cover a distance of 50 cm.
Often, contact of a couple of seconds is not enough to move the insect, but if the host shakes his hair, it can easily get on the new owner; this also applies to personal belongings, when in contact with which it is easier for parasites to get on a person. You should be as attentive and careful in crowded places as possible.
Why is lice dangerous?
Pediculosis not only causes a lot of discomfort, but can also cause serious complications.
Lice infestation leads to unpleasant consequences:
- sleep disturbance;
- anxiety and irritability, neurosis;
- the appearance of purulent wounds due to infection;
- allergic reaction;
- roughening of the skin.
At the beginning of the last century, these insects were spreaders of dangerous infections.
Improved living conditions, personal hygiene, and medical developments have helped reduce the incidence of disease transmission through lice. However, it is worth knowing what diseases lice carry:
- Typhus is transmitted mainly through linen lice. The insect feeds on infected blood and becomes infected, although it itself does not get sick. Once on the body of a new host, the louse releases pathogenic bacteria in the feces. When scratching bite sites, these microorganisms penetrate the wound and then into the blood. A person develops fever, rash and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
- Relapsing fever can also be transmitted by body louse. Infection occurs in a similar way to typhus. Symptoms are fever, rash, yellowing of the skin, diarrhea with mucus, vomiting. The disease alternates between periods of exacerbation and improvement.
- Volyn fever is transmitted by both head lice and body lice through feces. The disease is not fatal, but it makes you feel worse for a long time. Symptoms include fever, joint and eye pain.
Prevention measures
No one is immune from lice infection. People are constantly in contact with others - in transport, schools, kindergartens, work groups. Prevention measures can help minimize the risk of insect transmission by reducing the likelihood of exposure to sick individuals and maintaining a healthy scalp.
Prevention of head lice consists of the following:
- do not wear other people's hats and clothing;
- do not use other people's accessories;
- have a personal comb and hygiene products;
- change underwear and bed linen regularly;
- iron the clothes after washing;
- avoid public places where there are a lot of people;
- take a shower at least once every two days, wash your hair at least once a week;
- periodically check your head for parasites;
- avoid casual sexual contacts;
- If you find lice, consult a doctor immediately.
Lice are a common problem, especially among children. These parasites feed on human blood and are transmitted only through close contact with a sick person or through the use of other people's hygiene items. Taking precautions helps keep you safe and minimizes the chance of lice transmission.
Lice
Three types of lice parasitize humans: head, body, and pubic. And since the incidence of not only head lice, but also body lice, is growing, Anna Popova is sounding the alarm: there is a threat of the spread of epidemic typhus, which these types of lice carry.
“Fortunately, cases of typhus have not been registered since 1998,” noted the head of Rospotrebnadzor. “But we have recorded cases of Brill’s disease, a recurrent form of epidemic typhus, in Moscow and in several regions - Tula, Kemerovo, Lipetsk, Samara, Nizhny Novgorod, Voronezh regions, as well as the Khabarovsk Territory.”
Moscow, the Moscow region, and St. Petersburg lead in the number of people infected with lice: in the capital, the incidence of head lice reached a “record” level of 1616.1 people per 100 thousand people, in St. Petersburg - 248.2 people per 100 thousand people. At the same time, an increase in incidence was recorded in another 22 regions, and, for example, in Karachay-Cherkessia it was simply explosive - five times over the year.
The fact that Moscow and the Moscow region are a high-risk zone can be explained simply: this is where streams of migrants flock. There are a huge number of homeless people here, many of whom carry several types of lice, including the most dangerous - body lice. To catch it, sometimes it is enough to come into contact with an infected person’s clothing in transport or in a crowd.
The Chief Sanitary Doctor’s concern is also shared by volunteer organizations helping the homeless. In many cities there is simply nowhere for homeless people to wash themselves or disinfect their clothes. In the whole of Moscow there are only two disinfection stations that receive tramps, and in St. Petersburg there is only one. “In many regions, such events are not funded at all,” notes Rospotrebnadzor.
Lice are most often found on people in sanitary inspection rooms or during hospitalization. Regular examinations of children in kindergartens and schools also produce results. True, the supervisory service warns that in many cities preventive measures are neglected, and if inspections are carried out, it is only formally, for show.
Popova demanded that regional authorities strengthen the fight against head lice and engage in prevention. The main thing is to work with the population. Everyone should understand: lice are not only unpleasant, but also really dangerous, and saving yourself from them is not at all difficult. You just need to know the basic precautions.
How to avoid infection: what you need to know about head lice
1.
Not only homeless people and tramps become infected with lice. The disease is equally likely to occur in everyone, both adults and children.
2.
Lice feed on the host's blood and attach eggs (nits) to the hair. The body louse lays eggs in the folds of clothing, sometimes sticking them to the hair on the human body. Briefly touching clothing or hair is sometimes enough to become infected. That is why it is better not to approach suspicious people and not sit next to them on public transport.
3.
Pubic lice live on the hair in the genital area, they are smaller than head lice, and it is quite difficult to detect them with the eyes. Infection occurs through sexual contact; you can also get these lice from dirty bedding.
4.
A recent study showed that the spread of lice among young people is facilitated by the fashion for selfies - in order to get into the frame of a phone camera, teenagers often stand closely, using the “head to head” principle. When sending a child to camp, you need to teach him other basic precautions: not to use someone else’s comb, hairpins or elastic bands, not to exchange clothes with friends, and not to sleep on someone else’s bed linen.
5.
For adults, swimming pools, baths, saunas, hairdressers and even natural bodies of water (fresh) pose a certain danger during the period of mass bathing.
6.
The first sign of infection is itching. It occurs due to the fact that when a louse bites, they secrete saliva that irritates the skin. Upon careful examination, you can detect both the lice themselves moving through the hair, and nits (head lice eggs), which are usually found at the roots of the hair.
7.
When parasites multiply rapidly, flaky plaques can form on the back of the head, temples, and behind the ears due to numerous bites. You can't comb them.
8.
Carry out periodic examinations of hair and clothing of children attending childcare facilities. And after a hike or trip to a camp, such an inspection is mandatory.
9.
Carefully inspect bedding on trains and hotels. To avoid risk, take a spare set of laundry from home.
10.
Usually you can cope with head lice on your own. “Folk” remedies such as kerosene or, for good measure, a solution of karbofos or other insecticides are unsafe. Pharmacies today offer simple and reliable anti-lice remedies, mainly in the form of shampoos. To speed up the treatment process, it is better to cut your hair short, regularly comb out nits with a fine comb, and treat with shampoo several times every few days. And don’t forget to thoroughly sanitize all clothing and bedding. If an allergic rash, pustular lesion, and especially fever appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How can you get infected from insects?
Encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis is transmitted by ixodid ticks. The central nervous system is affected, and there is a high risk of death (up to 2% of those infected) and disability. Every year, Roszdravnadzor publishes a list of tick-endemic areas. When going to the country, to the forest to pick mushrooms or for a walk, it is better to make sure that the region is not included in the risk zone for encephalitis. But precautions are always needed: protective clothing, hats, insect repellents. If you are bitten, you need to see a doctor: the tick will be sent for analysis, and the victim will be vaccinated, if necessary.
Lyme disease
In addition to encephalitis, a tick bite can cause you to become infected with Lyme disease. This bacterial disease can be suspected by the red spot that forms at the site of the bite. Later, headache, fever, pain and swelling of the joints appear. If the disease is not treated, relapses are possible for many years.
Congo-Crimean fever
Congo-Crimea hemorrhagic fever (Congo-Crimean) is a natural focal disease. For the first time, its causative agent was discovered by Russian doctors in Crimea, and later the same virus was found in African countries - Congo, Senegal, Nigeria, Kenya. Outbreaks occur in the warm season, in our area - from April - May to September. The virus is transmitted by a special tick that parasitizes animals. The infection can come to a person through contact with a harmless hedgehog or hare. The virus is also carried by rodents - wood mice.
Leishmaniasis
This parasitic disease is caused by the single-celled organism Leishmania. Pathogens are transmitted through the bite of an infected Phlebotomus mosquito. The disease occurs in several forms. Sometimes only the skin and mucous membranes are affected, but it happens that the infection spreads to internal organs (the most severe form is visceral lichenosis). If treatment is delayed, the patient faces severe disfigurement, disability and even death.
Chagas disease
Another name is American trypanosomiasis. Spread through contact with the feces of an infected triatomine bug, also known as the kissing bug. Bedbugs live in the walls of clay huts and come out at night to “hunt” as they feed on the blood of humans and animals. However, bedbugs are rare in American cities. But home-grown Russians have not been found to carry dangerous infections.