Varieties
If you are seriously thinking about how to deal with spider mites on indoor plants, then you should first find out what type they are and can be encountered.
So far, scientists have identified the six most common:
- Standard. First of all, it colonizes the lower leaves, and only then, when the family grows, it begins to infect all living things further, killing almost everything in its path. Usually, fighting it without chemicals is useless.
- Red is a large variety of pest. These individuals reproduce well at high temperatures, which leads to the death of almost everything animate where it settles.
- False is an extremely dangerous type. It is extremely small in size, it does not weave a web and does not leave any traces of its presence, so its arrival will be known only when the fetus inevitably dies.
- Atlantic. It usually infects exotic palms and bushes, but can spread to any other. This species is rare. It multiplies when there is high humidity in the room.
- The cyclamen reptile loves high air moisture. Visually similar to a large layer of dust, so it is often confused with it.
- Wide is one of the easiest parasites to resist. Although eggs are laid every few days, the females do not dive or hide, so it is extremely easy to fight it. Its appearance is immediately noticeable by a large layer of dust. Reviews from people confirm that it is quite easy to remove.
Arachnoid
Small parasites affect cultivated, wild, and indoor plants. They live in numerous colonies and feed on juices. When there is a massive infestation of spider mites, a flower or tree stops developing, blooming, bearing fruit, and gets sick. If proper measures are not taken by the person, he dies.
On a note!
The main sign of the presence of a pest is the presence of cobwebs. As well as twisted leaves and fallen inflorescences. White mites can be gourmets - they attack one type of plant, or omnivores - they infect everything in their path. They hide on the underside of leaves or in the soil. Body size does not exceed 4 mm. To combat the pest, acaricidal, insecticidal preparations, and folk remedies are used.
The most active representatives of entomophages
Ladybug (coccinellidae)
The most effective enemy of any variety of aphids.
Moreover, the greatest damage is caused not by the adult beetle, but by its larva. If an adult destroys up to 50 aphids per day, then a larva destroys over 500. Great fertility is another advantage of this bright, cute bug. One female lays up to 300 eggs per season. In addition to aphids, it preys on whiteflies, mealybugs and Colorado potato beetle larvae.
Fast, predatory beetles, actively feed in the evening and at night. They are distinguished by an elongated body of dark colors with a metallic sheen. It is one of the most useful predators in the fight against plant pests.
One adult beetle can eat up to 350 caterpillars over the summer. Having found the victim, it releases a toxic liquid on it, which quickly dissolves the organs and tissues of the insect. The beetle eats the resulting liquidy homogeneous mass. The larva is even more voracious and destroys many more pests.
A spectacularly colored flying predator, often pretending to be something else, such as a wasp. Disguise is needed to escape from enemies. The adult fly feeds on flower nectar, while the larva benefits.
It eats spider mites, aphids and the eggs of many insects. While the larval stage lasts, the individual eats up to 2000 pests. Flies can be attracted by planting hogweed, carrots, dill and some other umbelliferae.
Lacewing
An insect with a long bright green body. Quite prolific, some species can produce up to 1500 eggs per season. The larvae are very voracious and happily destroy eggs of pests, aphids and herbivorous small mites. They are often used to kill insects not only in garden plots, but also in greenhouses.
After emerging from the eggs, the riders begin to feed on the internal organs of the victim, leading to their death.
Birds
To destroy pests, tits, swifts, flycatchers, pikas, starlings, wagtails, nuthatches, and redstarts should be attracted to the areas. All of them feed on numerous caterpillars, beetle larvae and adults, bringing very tangible benefits in the fight against harmful insects.
Birds are well attracted to hedges made of branching shrubs such as acacia, rose hips, and gooseberries. You can arrange feeders and bird houses (birdhouses and titmouses).
Appear in March and disappear at the end of October. Peak activity occurs in May-June, September-October. Favorable living conditions are temperatures within 20 degrees Celsius, high humidity, tall grass, thickets, and shrubs. The greatest represent that they endure,. They are found in the wild, city parks, public gardens, and near houses. One of the most pressing questions is who eats ticks in nature.
It's tick season. Why is it better to wear white clothes in the forest?
Every tenth person is dangerous
“Almost every tenth tick can transmit infections when bitten, including those that cause serious diseases,” says Dr. Oleg Zaikin. – Previously, the danger threatened mainly the inhabitants of the taiga regions - from the Urals to the Pacific Ocean. Now infected ticks are not a novelty in the central regions of the country.”
— But in the spring I want to be in nature more often...
“This year, dangerous bloodsuckers woke up earlier than usual. Last year, 3,242 people in our region sought medical help for tick bites. Already at the beginning of April this year, the number of victims exceeded one hundred.
Where do you live, tick?
— Oleg Nikolaevich, have ticks really become a real disaster?
— You can “pick up” a tick not only in the forest, but also in a park, in a city square, in the grass along the roadsides or in the country. After all, these “biters” do not live in trees, as many believe, but in tall grass, on the ground and on bushes. 20 percent of bites are recorded in cities. In particular, uncollected garbage near residential buildings and playgrounds can become an ideal place for ticks to “ambush”. Sometimes people can suffer from ticks that are brought into the house on clothes or along with flowers and branches.
Fear the sick enemy
— Why is a tick dangerous? What serious diseases did you mention?
— The tick bite itself is not terrible. It causes redness, itching and slight swelling in the wound area. Infections that can enter a person’s bloodstream through saliva when bitten by a tick are dangerous. The bite of an infected, as we say, ixodid tick becomes the cause of diseases such as tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis, and ehrlichiosis.
In tick-borne encephalitis, the central nervous system is affected. The consequences of the disease can be irreversible - persistent paralysis of the muscles of the arms and neck, the development of periodic convulsive seizures, possible disability and death.
Ticks can be the cause of Lyme borreliosis. This is a disease when the musculoskeletal system, nervous and cardiovascular systems are affected, which leads to long-term disability and disability.
The first signs of tick-borne infections are largely similar and manifest themselves in the form of general malaise, fever up to 37.5–38 degrees, headache, nausea, and irritability. If similar symptoms are observed after a tick bite, the algorithm is as follows: the earlier the diagnosis is made and effective treatment is prescribed, the greater the likelihood of a complete recovery.
There was no registration
- But, as you know, the disease is easier to prevent... Does the rule apply to infection carriers such as ticks?
— It’s good to say that tick-borne encephalitis has not been registered in our region. Therefore, getting vaccinated against ticks is, fortunately, not relevant for us... Unless a person is planning to go to the taiga. As for tick-borne borreliosis, research at the Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Belgorod Region confirmed the facts of tick infection with this pathogen. For residents of our region, the most reliable way to prevent tick-borne infections is personal protection against tick bites.
No to sandals, yes to a hood
- What does this protection consist of?
— Ticks choose a secluded place on the body to attach themselves. Therefore, the “dress code” is very important. When going out into nature, it is advisable to dress in light and plain clothes - this way the “pest” can be immediately noticed. You should leave as few openings as possible for the tick: you need closed shoes (shoes, boots), not sandals; a long-sleeved shirt must be tucked into trousers, trousers must be tucked into boots, knee socks or socks with a thick elastic band. And you definitely need to protect your head with a hood or scarf tucked under the collar.
A very reliable method of protection is external inspection. The tick does not bite immediately: it takes up to two hours for it to attach itself. This means that it is necessary to conduct self- and mutual examinations at least every 1.5–2 hours to detect clinging ticks. Particular attention should be paid to places where the skin is thin and delicate - behind the ears, on the neck, under the armpits. You should also carefully look for them in the hair on your head. It is important to use modern protective equipment for processing outerwear and equipment. Various types of creams and sprays are sold in stores in a large assortment.
The road leads to the emergency room
- What should I do if bitten by a tick?
— Initial consultation can be obtained by calling an ambulance. To remove a tick, it is better to go to the emergency room. Even if a tick bites someone, this does not mean that the person will get encephalitis or borreliosis. A person only gets sick from ticks that are themselves infected. But in any case, the tick must be pulled out. The longer the tick sits, the more difficult it is to do this - another argument in favor of regular inspections. Removing an embedded parasite is a must.
- And how do you know if everything worked out?
— Once you have the tick removed, keep it for testing for the presence of the pathogen. Ideally, you need to submit the tick for microbiological analysis. To do this, the insect needs to be placed in a medicine bottle (or test tube), put a damp cotton swab in it, close it tightly - and off you go. The tick must be delivered to the laboratory no later than two days from the moment of the bite and always alive.
A towel in your hands
— Ticks often attack in the garden. How to independently check whether they have chosen the dacha area?
— A white waffle towel is perfect for the experiment - ticks easily “stick” to it. Walk around the area, running the cloth over the surface of the grass and bushes. Examine the matter. Found ticks? It will not be superfluous to treat the grass and bushes with insecticides.
But fighting alone is unsafe and useless. It’s better to come to an agreement with your neighbors and the board of the dacha cooperative and call a paid disinfection service. Specialists will treat the area with special substances that are harmless to people and pets, but kill ticks.
The tick that bit you must be delivered alive to the laboratory of the Regional Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology at the address: Belgorod, Zheleznyakova Street, 2. Opening hours: Monday - Friday from 8:00 to 15:30. Phone 34–09–65.
The addresses and telephone numbers of disinfection services (there are 18 of them in the region) can be found via the Internet or at the office of Rospotrebnadzor for the Belgorod region, telephone: 34–03–16.
Security measures
Of course, it is difficult to refuse a trip to nature, but this is not necessary, just take the problem seriously and do not neglect safety measures. The first thing to do is choose the right clothes. Choose a jacket or cardigan with cuffs and a collar that fits tightly to your neck, thereby protecting it. Be sure to wear hats. Choose pants that can be tucked into socks. Also, be sure to tuck your jacket into your pants. This will block access to your body. Inspect each other's clothing for ticks.
Parasites wake up with the first warmth and become active at a temperature of +5°. Optimal conditions are when the temperature does not exceed +20°. On hot days they are not active and hide in thickets and wet areas.
Not many people can resist picking a beautiful flower and smelling it. This is not worth doing. There are cases where, while sniffing a fragrant flower, the black-legged parasite entered the respiratory tract. It is very difficult to remove it from this area.
How to find a place for a picnic without ticks and why does a tick need to be detected within an hour?
News about the pandemic has overshadowed information about another danger - tick-borne infections. However, tick season is in full swing. According to long-term observations, its peak occurs in June. Roskachestvo shares expert advice about ticks.
facts about ticks
- Ticks can survive underwater for 3 weeks. Therefore, do not flush the tick in the toilet. He will most likely survive this. And who knows, maybe he will crawl out to take revenge.
- Ticks do not like heat, but need warmth and high humidity - they prefer places where air humidity is above 85%. Therefore, they are especially active after rain.
- The tick can survive in the house for several days. Arachnids can be removed from clothing using adhesive tape.
- Vaccination does not protect against ticks! A vaccinated person remains defenseless against all infections except tick-borne encephalitis.
Why do you need a white sheet at a picnic?
Epidemiologist, head of the Rospotrebnadzor Office for the Kaliningrad Region Elena Babura:
Elena Babura
When you go on a picnic, take a white sheet with you. Our specialists check green areas for the presence of ticks with a white flag - they simply run a white cloth over the grass and look at the “harvest”. We don’t find any species! If you have chosen a place to rest, run a white sheet over the grass and see if it is worth staying there or if it is better to look for another clearing. You need to look for another place even if only one tick is attached to the sheet.
— Ticks do not fall from trees, as many people believe. They crawl slowly from bottom to top. They sit on the grass or on a bush and feel the approach of a “victim” – a person or an animal – one and a half meters away,” explains Elena Babura. — Ticks cling to clothing and begin to climb towards thin skin. Slowly but surely they find the right place on the body.
They won’t dig into the heel; the ticks’ favorite places are the groin, armpits, neck, delicate skin behind the ears, and on the head.
From the moment the small arthropod makes its way, an average of an hour and a half passes. This is exactly the time during which it can be detected. The tick bites in painlessly - the saliva contains an analgesic and “cement”, and on the oral cavity there are hooks located against the movement, which makes it difficult to pull it out of the skin. In the first second of the bite, the virus from the tick’s saliva infects the blood.
WHAT DO TICKS INFECT?
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist Ekaterina Morozova:
— The list of infections that ticks can transmit to us is long, with tick-borne viral encephalitis in first place. This is an infection that affects the brain matter. Mortality ranges from two percent (Central European subtype of the virus) to 20 percent (Far Eastern subtype of the virus). All people are susceptible to infection with tick-borne encephalitis, regardless of age and gender. The risk of developing inflammation of the meninges and brain matter is higher in weakened patients - children, the elderly and people with chronic diseases are at risk. Fortunately, vaccines have been developed against tick-borne encephalitis.
How to remove a tick?
It is better to do this with a doctor at a trauma center in a polyclinic at your place of residence or any trauma center, Rospotrebnadzor specialists advise.
You need to remove ticks yourself very carefully so that the proboscis with which it has dug into the skin does not remain in it. This can be done with tweezers or special pliers.
You need to grab the tick closer to the mouthparts, holding the tweezers strictly perpendicular to the surface of the skin. After capturing, rotate the bloodsucker’s body around its axis and remove it. Disinfect the bite site with any means suitable for this purpose (70% alcohol, 5% iodine, cologne). Then wash your hands well with soap. If a black spot remains at the site of the tick bite - the mouthparts, treat this area with 5% iodine.
If you notice a bite, but the tick is not found, then after three weeks you need to be tested for antibodies to Borrelia.
How to protect yourself?
Epidemiologists claim that many of those bitten were not injured in the forest, but in local areas and summer cottages. Ticks can come directly into your home on animals - dogs and cats; they can be brought by guests on clothes or with wildflowers and branches.
— Anti-tick sprays or lotions are a good way to protect yourself. The main thing is to read the instructions, advises Ekaterina Morozova. - In addition to age restrictions, it indicates the time during which the product is effective, and the range is large - from 30 minutes to several hours. Even when using these products, check your clothes and skin every hour and a half. First of all, look carefully at the folds of the skin: ticks love warm and moist places.
Remember that it is easier to see the insect on light-colored clothing.
where to go for Tula residents?
You can test ticks for infection in laboratories (for a fee):
- FBUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Tula Region" (Tula, Oboronnaya St., 114, tel. 37−39−56);
- LLC "Tula Diagnostic Laboratory" (Tula, Moskovskaya str., 17, tel. 21−23−69).
If a red spot forms at the site of attachment, body temperature rises, muscle pain, rash, or general malaise appear, you must immediately consult a doctor, informing him about the fact of tick attachment.
Preventive measures for purchased seedlings and adult plants
You can protect plants using different methods:
- maintain air humidity and temperature at the required level (see above);
- parts of plants that have begun to deteriorate must be removed immediately;
- In the heat of summer, violets should be washed regularly in the shower;
- indoor plants should be placed at some distance from each other;
- Before the start of the pest activity season, violets are treated with chemicals with acaricidal properties.
Considering that the development cycle of a mite from egg to adult is 1-3 weeks, it is necessary to maintain quarantine when purchasing new plants: they are placed separately from other flowers, having previously been treated with an acaricidal preparation.
Removing affected leaves will help temporarily get rid of pests.
Neighborhood Danger
Neighborhood with ticks is dangerous for humans, even with those insects that do not feed on blood. Bed and dust mites defecate up to 20 times a day. And it is insect excrement that contains enzymes that contribute to the development of contact allergies. Also, the chitinous shell from dead ticks, when crushed into microscopic particles, enters the air and causes irritation of the mucous membranes of the nose and mouth.
Dust and bed mites cause:
- dermatitis;
- asthma;
- tearfulness;
- rhinitis;
- sneezing;
- cough;
- itching;
- rashes.
Ixodid mites are no less dangerous to humans, although they do not appear in their homes very often, unlike bed and dust mites. These insects are carriers of diseases, and when they bite, pathogens enter the open wound, which leads to serious complications.
Ixodid ticks cause the development of:
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- borrelosis (Lyme disease);
- fevers, etc.
To avoid unpleasant consequences from various types of mites, you need to know what you can use to treat the room. This will get rid of this unpleasant neighborhood and protect all the inhabitants of the house.
Bites on the skin
How dangerous are ticks for humans?
Almost all arachnids that can harm humans belong to the group of ixodid ticks, which are cosmopolitan in the field of nutrition and, in the process of development from larvae to adults, drink the blood of various animals, including humans.
Feeding on animals in nature, ticks absorb pathogens with blood. In the next phase of development, if the tick feeds on a person, infection occurs through the saliva of the arachnid. Since the main blood-sucking parasites are ixodids, these arthropods are rightly called the most dangerous ticks in the world. Any species of Ixodid can transmit borreliosis, encephalitis and ehrlichiosis.
Ixodid species and habitats
It is not difficult to distinguish a non-dangerous tick from a dangerous ixodid tick. When we hear the word “tick,” we all imagine an ixodus, thinking little about the other body shapes of these arthropods. In a hungry state, all ixodids have an egg-shaped body with a sharp tip at the anterior end. The most dangerous representatives of this family are taiga (forest) and dog ticks. Even a person who had never left the city encountered the latter type. The canine has long been a synanthropic species, breeding in the dark and damp corners of human buildings. They are the ones that hang in clusters on stray dogs in the summer. But ticks hanging on animals can no longer be dangerous to people if this is the last stage of development, and the arthropods feed before laying eggs. A larva or nymph that falls off an animal becomes dangerous at the next stage of development.
Ixodid ticks
The color of ixodids can be different:
- Canine: the male is covered with a dark brown shiny shield, the female has a gray belly peeking out from under the shield. Lives everywhere.
- Taiga: a red belly peeks out from under a brown shield. Forest habitat with undergrowth.
- Lugovoi: All species in this group have a white pattern on the back. Prefers herbaceous biotopes.
- Amblyoma: white spot in the middle of the brown back, white stripes on the paws. Lives in tropical areas.
- The dermacentor is similar to that of a dog, but the chest is whitish in color. Lives throughout Eurasia.
- Hyalomma is brown in color with striped, brownish-yellow legs. Prefers deserts and semi-deserts of Central and Central Asia, North Africa, and the Middle East. Found in Europe.
Argaceae
12 species from the Argasaceae family attack humans. Representatives of the family have an oval body shape with legs partially hidden under the shell. The Persian tick is often confused with the bedbug due to the similarity in appearance. But the bug has a chitinous cover, while argasids have a soft, leathery shell.
Argasid saliva is toxic. Bites cause itching and rashes on the human body. What kind of poisonous ticks the species Ornithodorus coriaceus is can be understood by the fact that the Mexican population is afraid of the bites of this bloodsucker as much as they are afraid of rattlesnakes. But this species lives on the North American continent and can only be encountered on a tourist trip.
Argasid mites
Other representatives of Argasaceae successfully exist in Russia:
- Caucasian. It parasitizes mainly birds; it attacks humans when the poultry house is heavily infested. Lives in Transcaucasia, in the south of Ukraine.
- Persian. Yellowish-brown when hungry. It parasitizes birds and prefers mild climates.
- Shell-type. The main host is pigeons. If it is very hungry, it also bites humans. But in the latter case it dies much faster.
- Poselkovy. One of the most dangerous species for humans. Carries relapsing fever and borreliosis. Can lay eggs already infected with spirochetes.
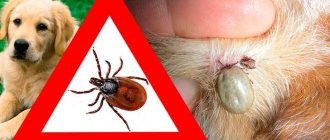
Are ticks on dogs dangerous for humans?
We found out whether ticks are dangerous for dogs a little higher, now we will tell you about the danger dog ticks pose to humans and how to protect yourself from this danger. First, we need to clarify that dog scabies mites are not able to live on human skin, so it is impossible to get scabies from a dog. Secondly, demodicosis is a non-contagious disease; it is also not transmitted from dogs to humans.
Only ixodid ticks pose a real danger. A dog can bring them into the house on its fur, and they can attach themselves to a person. If it is an encephalitis tick, a person can become infected with a dangerous disease when removing the tick from a dog with bare hands. In addition to encephalitis, a person can become infected with the following diseases from dog ticks: borreliosis, tularemia, Marseilles fever.
To protect yourself, you need to carefully examine not only the dog, but also yourself after a walk in the fresh air, remove attached parasites from the dog’s body using rubber gloves, and use ultrasonic repellers and repellents.
White ticks in dogs are not as rare as they might seem. What ticks are white in color and what to do if you find a parasite on your pet, we’ll look into it below.
How to protect a person from the taiga tick and the consequences of its bite
Measures aimed at protecting people from parasites:
- destruction of plants, dead wood, bushes, grass by burning;
- the use of toxic substances for treating clothing;
- upon returning from a walk, it is necessary to inspect clothing and outer coverings for the presence of brown-black ticks;
- vaccination;
- the use of special suits that completely cover the human body;
- treating the surrounding area with liquid substances of a toxic nature, which reduces the population of parasites; this measure is used during pest activity (May-June).
Specialized anti-mite suits
Designed specifically to protect against blood-sucking arthropods. Features of such products:
- loose cut, which allows you to wear the suit over clothes without restricting movement;
- Smooth material is used for sewing, thanks to this the tick cannot get caught, and when it tries to climb onto the host’s body, it falls;
- the presence of catch valves in different areas (pants, sleeves, back, chest), which allows you to catch the tick, as a result, the parasite will not get on open skin;
- At the bottom of the trousers there are muffs that provide protection for the body (tucked into shoes, socks).
It is recommended to additionally treat such clothing with toxic substances.
The most popular suits of the “anti-mite” family
Acaricides and repellents
Both groups include chemical substances; they differ in structure and properties. Thus, acaricides are products developed specifically for removing ticks. These include:
- organophosphorus compounds, for example based on malathion;
- pyrethroids;
- sulfur-based products;
- Bromopropylate;
- Clofentesine;
- Phenazakhin;
- Pyridabene.
Acaricides and repellent preparations for taiga ticks
This makes it difficult for ticks to detect warm-blooded creatures. If the parasites do get onto a person, they will receive a dose of poison, since repellents contain toxic substances, but will not die. This group includes:
- Reftamide Maximum;
- Medilis for mosquitoes;
- Off! Extreme.
Vaccination is almost 100% guaranteed
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is carried out, since this is the most dangerous disease, the carrier of which is a tick. Perform 2 vaccinations. Moreover, you should take a break (30 days) between them.
An important condition is to complete the last vaccination procedure 2 weeks before you plan to travel to an area where there is an increased risk of an encephalitis tick bite.
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is the most reliable way of protection
Insurance
Recently, an alternative option has become popular - purchasing a full package of insurance services, which includes:
- providing first aid for a bite when a parasite is found on the body;
- treatment for infection with a pathogen of any of the diseases listed in the insurance policy;
- restoration of the body after relief of disease symptoms.
It is important to understand the difference between preventive measures and the provision of outpatient, inpatient care. So, if a person is insured, he can receive a full range of services
Insurance will only provide you with payment for treatment, but will not protect you
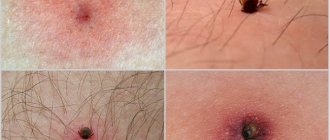
What does a tick look like?
Sometimes a family vacation in nature is overshadowed by an unpleasant event - the discovery of a tick on yourself, your children, or your animals. To know how to act, you need to understand what a tick is and how to recognize it. Ticks are not insects (do not confuse them), but arthropods of the arachnid class. You can meet them in almost every corner of the world. There are more than 850 known species of ticks. But the main thing is to determine that it is a tick, and not a harmless bug.
Appearance
All ticks go through several stages of development before becoming adults. Moreover, they pose a danger at all life stages, even in the body of the larva. An adult tick is the size of an apple seed. They have no wings, they are flat and oval in shape until densely saturated with mammalian blood. Adult ticks have eight legs, while larvae have only six.
The color of ticks can be greyish-white, brownish, black, reddish-brown or yellowish. It all depends on the specific species.
The color of ticks can be greyish-white, brownish, black, reddish-brown or yellowish.
Habitat
Ticks can be found in wooded and bushy areas, as well as tall weeds and tall grass. If you find a strange bite after walking in such places, it was probably a tick. Tiny predators climb onto grass or bushes and wait for a person (or animal) to get too close.
Ticks quickly crawl up you to reach soft places suitable for biting. Carefully inspect the clothing. If you see small dark spots, these are most likely mites. Doctors recommend taking a warm shower with soap after every picnic or forest walk. Clothing should also be washed in hot water to kill all possible ticks. Or store it in a closed bag or other container.
Where to look for ticks on the body?
Ticks are most likely to crawl to the darkest, softest, warmest places:
- head;
- armpits;
- groin area;
- area behind the ears.
What ticks can be white?
Both micro and macro mites can have a white color. Among the first: flour mites, dust mites, spider mites - such mites do not bite people and animals, and received their names due to their habitat. The maximum harm from these invisible mites is allergic reactions, plant diseases (spider webs), in general, it is not difficult to prevent their appearance, you just have to keep an eye on the cleanliness of your home. But the white ear mite, or so-called. The skin beetle may well be dangerous for a pet.
You may find a small, poppy seed-sized white mite on your dog or cat's ear. These ear mites can cause otodectosis - that is, animals experience severe itching in the ear, an allergic reaction to the waste products of these microscopic parasites. There is nothing terrible in this, but cats and dogs try to scratch their ears, and the resulting scratches and wounds, as is known, can cause further irritation, suppuration, etc.
If your pet has ear mites, contact your veterinarian; most likely, he will prescribe ear drops that need to be instilled into the previously cleaned ear.
White ticks are more common in cats than in dogs, and, of course, in those animals that are outdoors and in contact with others.
Scabies
The parasitic mite causes an unpleasant disease - scabies. The disease is accompanied by severe itching and damage to the skin. The first symptoms appear on the hands - between the fingers; as the pest multiplies, it spreads to the stomach, legs, hips, back, genitals, chest, neck.
It builds numerous passages under the skin at night, so it is at this time that unpleasant symptoms intensify. With mass infection, body temperature rises, insomnia, weakness, irritability, and decreased ability to work are observed. Mating of scabies mites occurs at night on the surface of the skin; some of the parasites remain on things and in the patient’s bedding.
Infection of people occurs through contact from the patient and his belongings. For therapy, antiparasitic drugs are used - benzyl benzoate emulsion, ointments, sprays. At the same time, wash items at high temperatures and clean using chlorine.
Armored mites - red-brown in color
Representatives of this group affect the properties of the soil, namely, the decomposition of organic matter. The tick affects creatures living in the soil. These are small parasites, they are characterized by increased activity. Thus, there are several hundred thousand individuals per 1 m2.
Pests go through stages of development: larval stage, nymph (3 stages), imago. Depending on the species, there are dark brown and black ticks. Body length less than 1 mm. The eggs of such arthropods are also brown in color, but have a reddish tint.
Photo of oribatid mite
Given that parasites spend most of their time underground, it is not always possible to quickly classify them. It is recommended to further study the features of the appearance of such individuals.
Oribati mite in a flower pot
Through their activity, oribatid mites contribute to soil formation
Types of subcutaneous mites
There are usually only two types of mites in the human body, which can be found in different areas of the body depending on their characteristics:
- Demodex brevis lives inside the sebaceous glands, which are connected to the hair follicles. The size of the parasite is quite small; it usually grows to 0.15-0.48 mm in length.
- Demodex folliculorum lives directly in the follicles themselves, which are located over the entire surface of the head, including on the front part. The body size is usually 0.2-0.4 mm.
The brown tick is a blood-fed parasite
These pests have some differences. First of all, it is noted that representatives of these species belong to the Amblyomminae family. Brown ticks often carry dangerous diseases. They can be found in areas with different landscapes: forest belts, steppes. They attack people and animals. There are the following types of brown parasites:
- dermacentor reticulatus – the size of an adult is 4.3 mm (and the female is smaller than the male, which is not typical for representatives of the order Ixodidae), the limbs are brown, there is a light pattern on the abdomen;
- dermacentor marginatus - lives in the steppes, promotes infection with typhus, encephalitis, Omsk fever, a characteristic feature is its significant body size (up to 5 mm), affects large domestic animals, as well as hares, hedgehogs and other small inhabitants of the forest-steppe zone.
Photo: Brown mite / Dermacentor reticulatus
It is possible to better study the body structure of such parasites. To do this, it is recommended to look at their photographs.
Photo: Dermacentor reticulatus
These ticks carry serious diseases.
Photo: Grass mite / Dermacentor marginatus
There are some differences between representatives of different species of the order Ixodidae. For this reason, it is recommended to additionally look at the photo.
Photo: Dermacentor marginatus
Photo: Dermacentor marginatus