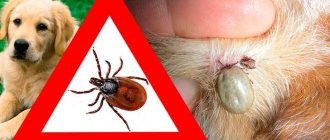
What does a sucking tick look like?
In a hungry state, the body of the arachnid is flat, oblong, dark in color - brown, brown, black.
The body size of an adult does not exceed 3 mm. Females are always larger than males. During the feeding process, the chitinous cover expands, and the parasite increases in size. The abdomen becomes oval and convex. The body color becomes red or becomes lighter - brown, beige, gray. The size of the inflated tick is 11*8*5 mm. Sometimes the size reaches 2 cm. From the front there is a small head, 8 pairs of tenacious legs. A swollen tick is inactive and, after saturation, simply falls off to the ground. In the soil, a well-fed female lays eggs, the nymph continues to develop - molts. A photo of a tick that has drunk blood is shown below. Nymphs differ from adults in body size and the number of legs - 6 instead of 8.
You can see what a tick that has drunk blood looks like on a dog or cat. Parasites lie in wait for the victim in tall grass, thickets, and thickets. Initially, the pest clings to the fur, explores the area, and looks for places favorable for eating. Then he drinks blood for several days.
Can a tick come out on its own after a bite?
When a tick lands on a person’s body, it looks for a convenient place to bite.
Most often, parasites choose:
- groin area;
- armpits;
- stomach;
- lower back;
- area behind the ears;
- scalp;
- breast;
- popliteal fossa;
- neck.
In these places the skin is thinnest with closely adjacent vessels. It takes from a few minutes to half an hour to find a place for an insect bite.
The greatest activity of parasites is observed from mid-spring to late autumn.
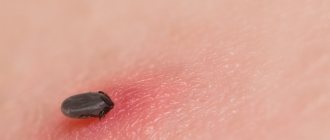
When bitten, the tick releases an anesthetic substance, which makes the insect invasion painless. The parasite completely immerses the head under the skin, leaving only the abdomen on the surface.
A hungry pest does not exceed 3 mm in size. As it fills with blood, it increases in diameter many times over. A well-fed individual can reach 1.5 cm. Once satiated, the tick itself crawls out of the skin.
If a tick falls off within the walls of a house, the chance of a repeated attack by the parasite is minimal. A well-fed insect leaves in search of a good place to breed; enclosed spaces are not suitable for this.
What to do if the tick head remains under the skin?
The tick's head may remain under the skin if it is removed carelessly or too quickly. It looks like a small splinter, so some are negligent about removing it, saying “the tick is dead, it no longer sucks blood, it will fall off on its own,” or they simply don’t notice
But this is not recommended. Remaining under the skin, the tick's proboscis will provoke inflammation and suppuration of the wound. Therefore, do not leave the head or proboscis of the tick under the skin, waiting for them to fall off on their own.
Take a sharp needle disinfected in alcohol and pick up the remaining proboscis and remove it. After a bite, a small wound will remain on the skin, which will heal quickly if the tick was not infectious. Treat the bite site with peroxide, then brilliant green or iodine. If the tick bite is very itchy, use Fenistil gel or a similar itching reliever. Try not to scratch the inflamed area to speed up the healing process.
To prevent the head of the tick from remaining under the skin, catch it as close as possible to the suction site
What happens to a tick when it drinks blood?
The tick sucks blood for several reasons - to continue development, replenish reserves, lay eggs. The larvae live in the soil where they developed into eggs. They wait for the victim to drink blood. Most often these are rodents, reptiles, and amphibians. At the end of the meal, it falls to the ground, molts, and turns into a nymph. To move to the next stage of development, blood is again needed.
Tick drunk on blood
A fertilized female will not be able to lay eggs until a sufficient amount of blood enters her body. During the feeding process, her body inflates, increasing to 1-2 cm. The female becomes clumsy and vulnerable. The main goal of a fed female is to get to the ground and lay eggs.
Does the tick die after it drinks blood - the male yes, the female not immediately - as soon as she completes her mission of laying eggs. The adult does not bite again.
Bite sites
As already mentioned, they most often stick to areas with thin skin. Most often this is the head, where there is hair, the back of the head, behind the ears, armpits, groin, knee bends, and stomach.
If we talk about the bite itself, namely the sensations that a person experiences, then this process goes unnoticed for a person. Therefore, it is impossible to detect it before it suctions strongly. This happens for the reason that the parasite’s body produces a special anesthetic enzyme, which it injects when biting, so the person does not experience any pain or discomfort.
The very first symptom is itching, which most often allows you to detect a tick on your body. Less commonly, other symptoms may be observed, for example, drowsiness, general malaise, aching joints, etc.
How to understand that a tick has bitten and how dangerous it is
In the forest or in the countryside, various insects can bite, one of them may be an infectious tick. How to understand that it was a tick that bit you? This can be determined by the appearance of the bite site. Quite often it starts to itch. In addition, the abdomen of the insect that absorbs blood increases in size. It can be detected by feeling the bite site.
It is important after each visit to an area potentially dangerous for insect attacks to inspect and feel your body from head to toe. Otherwise, how can you find out that a tick has bitten, because its bite is completely painless due to the release of a substance with analgesic properties by the insect at the time of the bite.
First of all, you need to identify the insect found on the body. How can you tell if it’s a tick or not? Perhaps its species has nothing to do with blood-sucking insects.
How do you know if you have a tick that can infect you with encephalitis? You need to be able to identify encephalitic or otherwise ixodid ticks. Their body does not exceed 4 mm in size. It looks like an oval pouch to which the proboscis and paws are attached. The insect's brain is located in the central part of the body. A hungry tick has a flat shape. The protective chitinous skeleton can be of different shades. There are light yellow mites and dark brown ones.
There are suckers on 4 pairs of legs. Their presence allows you to move not only along horizontal and inclined, but also along vertical surfaces. The paws contain tools for attaching to the victim's body. They are in the form of microscopic sized spines and denticles.
The chitinous dorsal shield in females covers a small part, only 1/3 of the back. Males have everything. This structure allows you to increase the elasticity of the female’s body and contributes to its increase in size by 15 times. A female that has drunk blood turns a dark gray color. Dangerous carriers of encephalitis are mainly the taiga and dog ticks, which are similar in size and shape. The taiga has a characteristic bright color of the abdomen. The ventral part of the dog is gray in different shades.
Knowing the appearance of the encephalitis tick allows you to promptly avoid contracting a serious illness. It is possible to know for sure whether someone is a carrier or not only after a laboratory test. Not only the ixodid mite, but also scabies, bed bugs, ear mites, spider mites and other types of parasites can cause harm to humans.
For those who have been bitten by a tick, the type of insect is not very important, what is important is whether or not it is a carrier of encephalitis. This can only be determined by testing the blood in a laboratory setting. However, sometimes the symptoms of the disease are manifested by the following signs:
- the appearance of blistering at the site of the bite, accompanied by redness;
- constant chills and an increase in the temperature of the bitten person up to 40 degrees;
- skin rash;
- the presence of general weakness, aching joints and headaches;
- photophobia;
- loss of consciousness for a short time;
- gastrointestinal upset accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- an increase in the size of the liver and (or) spleen;
- yellowing of the skin, etc.
If any of the listed symptoms are present, the person bitten should immediately contact a physician or infectious disease specialist!
The question of how to understand what kind of mite is under the skin is asked by many people on the Internet. Non-standard problem. If the insect ends up completely under the skin, this is considered the worst case scenario.
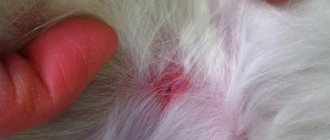
The insect under the skin looks like a new mole or a small ball different in color from the skin. If a tick has embedded itself, you feel discomfort in the area of contact.
How long does it take for a tick to stick?
It is worth saying that both females and males attack. But in this case, the bites are significantly different. The fact is that males need a minimum amount of food to be satisfied. They bite, quickly become saturated and fall off the body. Next, they look for females to mate with. It is precisely because of their rapid saturation that they are considered more dangerous. After all, their attacks go unnoticed in most cases and a person may not even realize that he has been bitten by a dangerous tick.
But females spend significantly more time on the body. The fact is that they need blood not only to satisfy their hunger, but also in order to form offspring. The offspring are formed inside the female during the period that she spends on the body. The female can latch on for three days and drink blood all this time.
But other situations are also possible when a female bites simply to satisfy her hunger. In order for her to be completely saturated, she needs about 20 ml of blood. The parasite can reach its normal level in several stages by sucking on a little blood and falling off, and then repeating the procedure several times.
How long does a tick drink human blood?
The parasite can fall off at any time after it has become attached to the skin. The duration of meals often varies from a few hours to several weeks. On average, the pest remains on the human body for 3-8 days, the maximum period is 14 days. A tick that has drunk blood falls off on its own. But this does not always happen within the specified time frame.
The duration of the meal is also determined by how hungry the parasite is. If it has not been fed for several months/years, it may well remain on the skin much longer. Sooner or later, the parasite filled with blood disappears. During this time, it will most likely be detected, since within a few weeks of parasitism this pest develops more severe symptoms.
Sometimes
– signs of more dangerous diseases (borreliosis, tick-borne encephalitis).
Duration of tick feeding
Can a tick fall off on its own?
After complete saturation, further stay of the parasite on the human body is impractical, so the insect carefully unclenches its jaws, removes its head and falls off on its own.
To ensure the vital activity of the parasite and the reproduction of offspring, ticks need soil where the female lays her eggs, so it is not typical for the parasite to remain for a long time in an unnatural environment, which is human housing. Therefore, as a rule, the insect does not bite again, even if it managed to escape unnoticed after consuming blood.
If the parasite has been infected with encephalitis or Lyme disease, symptoms of the disease will appear within two weeks after the bite.
What happens after saturation
As already mentioned about females, they drink blood for quite a long time. Most often at this time they become noticed and manipulations are carried out to remove them. But if the procedure went unnoticed, then the tick disappears after the bite. Females lay offspring, males look for females to mate with.
When the parasite was not noticed on the body, the person observed the consequences in the bite area. Most often, symptoms such as redness, inflammation, and itching appear, which disappear after a while. But allergic reactions that occur in severe forms may occur; in such situations, it is imperative to consult a doctor and use the correct treatment.
When the tick has sucked and fallen off, redness, slight swelling, and slight itching remain at the site of the bite. The skin is restored within a few days. In the presence of an allergic reaction, special treatment is required - the use of local, systemic antihistamines, antiallergic drugs. If the tick has been infected, symptoms of the disease appear after 14–60 days.
How to recognize that an infection has occurred?
Another danger of tick parasitism on the human body is that at the initial stage it is impossible to determine whether the parasite is infected with an infection. Signs appear after a few weeks (sometimes after 10 days), the speed of onset of symptoms depends on the sensitivity of the body, as well as the person’s immunity.
The parasite's saliva or external surfaces often contain harmful microorganisms. However, they are not present in all individuals, but only in those that have previously bitten infected animals and birds. If such a tick attacks a person, then we can assume the development of dangerous diseases, since the probability of this is quite high. For an infection to manifest itself, it takes time to develop and spread in the body.
Such a period
called incubation: infection has already occurred, but symptoms have not yet appeared.
Signs suggesting the development of infection:
- erythema, it can be quite large - up to 60 cm;
- temperature increase (and this happens sharply and to extreme values): 39...40°C;
- itching – the intensity of this manifestation can be high, itching is difficult to bear, resulting in scratching;
- swelling is a natural reaction of the human body to a developing inflammatory process.
Erythema on the skin after a tick bite
Danger to humans
These blood-sucking creatures pose a great threat to humans, as they can infect dangerous diseases. In this case, it does not matter at all whether it is found on the body, or whether it drank blood and fell off on its own; it is its bite that is dangerous. Therefore, it is very important to contact medical institutions when it is detected.
If you manage to save the insect, you can submit it for analysis, which will show whether this individual is infected. If you remove it from the body yourself, then you need to put it in a glass container along with a piece of damp cloth, which will not allow it to dry out. Analyzes are carried out with live insects, which allows you to obtain accurate results. If the parasite is dead, burst, or there is only a fragment of it, then research can be carried out, but the result will not be accurate.
In cases where you have not noticed the tick itself on your body, then symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately. These parasites can transmit diseases such as encephalitis and Lyme disease.
Lyme disease
This disease is manifested by such symptoms as fever, headache, body aches, weakness, and a cough and runny nose may also appear. These symptoms are similar to a cold or even the flu, so a person may not think about having a dangerous infectious disease. The main sign that you definitely need to pay attention to is the appearance of a large red spot on the body, which has a clear outline.
This disease affects the nervous and lymphatic systems. It is very important to start treatment at an early stage, since brain activity suffers, memory may deteriorate, and disturbances in thinking processes occur. The facial nerves are also affected as they are damaged.
If the correct treatment is applied, the disease can be completely cured. In situations where treatment is not applied, complications occur, which in severe forms are not always amenable to treatment.
Tick-borne encephalitis
This disease is very dangerous with complications. Encephalitis manifests itself with the same symptoms as the previous illness, only there is no reaction in the form of a circle on the skin.
If left untreated, the nervous system is affected; this process can occur as early as a week after infection. The person experiences severe headaches and epileptic attacks may occur. Next, internal organs are damaged, the liver, kidneys, etc. are destroyed.
Regarding children, the disease poses an even greater danger for them, since children cannot correctly describe their condition and talk about their feelings, which for parents does not allow them to create a complete picture and correctly respond to the situation. It is very important after each walk in nature to pay maximum attention to examinations and, at the slightest suspicion, consult a doctor.
In addition to the above diseases, ticks also carry other dangerous infections, which include typhoid, ehrlichiosis, fever, tularemia, etc. The diseases are treatable, the main thing is to seek medical help in time, then you can avoid serious consequences.
Hemorrhagic fever
By the name of this pathological condition, one can understand that its main symptom is a sharp increase in temperature to extreme values (39...40°C). In addition, signs characteristic of viral diseases appear. When a blood test is performed, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia are often diagnosed based on changes in its composition. One of the main signs of hemorrhagic fever is a violation of the integrity of the walls of blood vessels.
As a result,
their permeability increases, which contributes to redness of the outer integument.
Hemorrhagic fever after a tick bite
Viral infections
Tick-borne encephalitis is one of the dangerous viral infections that affects the peripheral and central nervous systems.
At the onset of the disease, chills and fever begin, then damage to the meninges, fever, vomiting, drop in blood pressure, and arterial hypertension occur. Possible death.
Infection with encephalitis occurs when the parasite sucks blood . The male tick sucks blood for a short time - several hours. But the female stays on the skin for many days. The incubation period of the virus lasts 1-2 weeks. During this period, the affected person may not experience any symptoms.
Next, a fever appears, which lasts acutely and is characterized by a very high temperature - up to 40 degrees . Severe headaches, dizziness, hallucinations, and muscle pain appear. Vomiting and nausea are possible. Confusion and deafness often occur. Complications of the disease include paralysis of muscles and nerves.
The disease is treated by administering ready-made antibodies, which are obtained from the blood masses of donors. In the first hours after the bite, it is especially important to administer immunoglobulin. Treatment with antiviral drugs, ribonuclease and interferon is also used.
Ixodid tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) is transmitted by ixodid ticks using saliva. The incubation period of the disease is 7-14 days.
Early symptoms of infections are fever, inflammation of joint tissues, erythema migrans, and elevated temperature. The disease affects the organs of vision, heart, blood vessels, and central nervous system. The course and outcome of the disease depends on timely access to doctors. Chronic borreliosis is especially difficult to treat.
Treatment includes:
- supportive and anti-inflammatory therapy;
- taking antibiotics;
- consumption of vitamins;
- prescription of immunomodulators.
Medicines are prescribed that relieve intoxication and regulate the functioning of internal organs.
Tick-borne typhus is another disease transmitted by insects. The disease is especially often caused by taiga ticks in Siberian regions.
The incubation period of the disease is 4-5 days. Further, the disease manifests itself as muscle pain, fever, and tissue necrosis. The disease has a favorable prognosis. In most cases, Tetracycline and antiviral drugs are prescribed for treatment.
Microbial infections
Ehrlichiosis is an infection transmitted through the saliva of a parasite. A focal infection is caused when an insect attaches itself to a person.
If you find a mark from a tick bite, you must go to the hospital. When bitten, Ehrlichia penetrates the bloodstream and causes the development of an inflammatory process.
Monocytic ehrlichiosis is characterized by:
- abdominal pain;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- hyperesthesia;
- chills;
- catarrhal symptoms;
- feverish condition.
In case of illness, it is important to periodically check the blood picture - complications such as leukopenia, anemia, lymphocytopenia are possible . Whole blood and serum are taken for research. Treatment of the disease is prescribed even before laboratory results are obtained. The main drug in therapy is Doxycycline.
Ixodid ticks also cause granulocytic anaplasmosis. The disease is caused by an intracellular parasite carried by ticks. Together with the insect's saliva, anaplasmas enter the bloodstream and infect neutrophils.
As a result, various inflammations develop in the internal organs. The acute course of the disease is characterized by severe kidney damage - proteinuria develops. Treatment comes down to eliminating the pathogen and symptoms of the disease.
Rickettsial infections
Mountain fever is an infection caused by an Ixodid tick bite. The causative agent is rickettsia bacteria. The disease is expressed in general intoxication and fever.
Special signs of the disease are:
- microinfarction;
- pathological changes in blood vessels;
- necrosis of cellular endothelium;
- blood clot formation;
- inflammatory process of arterioles.
As the infection progresses, an extensive measles rash appears. In the severe stage, the disease takes on a hemorrhagic form. The disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the kidneys and interstitial myocarditis.
Rocky Mountain fever is the most severe rickettsial infection.
At the onset of the disease, the following begins:
- nosebleeds;
- lymph nodes become inflamed;
- joints are affected.
There is headache and prostration of consciousness. A characteristic sign of the disease is damage to the central nervous system. Pneumonia and gangrene of the extremities may occur.
The treatment of mountain fever involves antibiotic therapy and drug relief of hemorrhagic changes and thrombosis.
Medications to normalize the temperature and antibiotics Doxycycline, Levomycetin, Tetracycline are prescribed. Heparin is administered intravenously using a dropper. Treatment is carried out in a hospital inpatient unit.
Coxiellosis (Q fever) is a rickettsial disease caused by tick bites. The causative agent of the disease can be found in dry tick feces. A person becomes infected with a fever from a tick bite. The incubation period lasts up to 17-19 days.
Then the symptoms begin:
- muscle pain;
- wheezing in the bronchi;
- bradycardia;
- heat;
- headache;
- eye pain.
Treatment boils down to eliminating the pathogen with antiviral therapy and eliminating symptoms. Recovery with proper treatment occurs after 2-4 weeks. However, in some cases, a relapse of the disease is possible.
Protozoal infection
The tick is a carrier of protozoa, bacteria, and viruses, so the appearance of a protozoal infection after a bite is not uncommon. The intestinal form of infection affects the entire gastrointestinal tract. Very often, with a mild course of the disease, a person does not pay attention to periodic attacks of loose stools and abdominal pain. No intoxication or increase in temperature is observed.
In severe cases, the stool may contain blood streaks and be jelly-like. Extraintestinal forms of the disease are manifested by damage to the liver, lungs, and brain.
Treatment of the pathology includes the use of Doxycycline, antibiotics, Etoftamide, Chloroquine. The prescription of medications depends on the form of the disease.
To prevent diseases, it is important to follow preventive measures when visiting the park area. There is a wide variety of parasite species in nature. It is important not to leave exposed areas of the body without clothing when walking in the forest, and also, if possible, apply insect repellents to the body.
What can you get infected from a tick bite?
If the tick itself came out and crawled away, this does not mean that it did not harm the human body. Ixodid ticks are carriers of various diseases. Those that are carriers of borreliosis and encephalitis are especially dangerous.
If a bite is detected, whether the tick is still there or has already fallen off and disappeared, you must immediately seek help from qualified specialists and monitor for symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis
Borreliosis manifests itself in the early stages in pain in the head, muscles, joints, fever up to 38 degrees, vomiting and deterioration in general well-being. Rare symptoms include sore throat, cough and runny nose. If intervention is not done in a timely manner, the lymphatic and nervous systems are affected. As the disease progresses, it can cause damage to the facial nerve and seriously affect the brain, for example, a person loses memory or the ability to think adequately.
If treatment is started on time, then in most cases it is possible to completely cure it with the correct selection of medications. When delayed, the complexity of therapy increases many times over; it does not help in all cases.
Tick-borne encephalitis
The Ixodid tick is also a carrier of encephalitis. If a person does not notice a tick bite in time, he risks becoming infected in approximately 60% of cases, these are official statistics. Tick-borne encephalitis is a dangerous disease; in the early stages it manifests itself with the same symptoms as borreliosis. Additional tachycardia and rapid heartbeat may be added, but there is no red round spot with a ring.
The extent of symptoms depends on the number of mites and the person's individual allergic reaction. It’s hardest for the elderly and young children.
It is especially dangerous if the infection occurs in young children. They cannot correctly assess the danger and symptoms that appear to them
It is extremely important for parents to examine their children after a walk in nature, especially carefully in places where ticks are most often found. If you have the slightest doubt, go to the hospital immediately
In addition, ticks carry a lot of other diseases dangerous to human health and life, such as tick-borne typhus, hemorrhagic fever, ehrlichiosis, tularemia and many others. Medicine has learned to cope with all of them to one degree or another if the patient seeks help in the early stages. Delaying it to the last minute can permanently deprive you of your health, and in some cases, your life.
The list of diseases that “bloodsuckers” can carry reaches 60, but we will consider the most common ones in more detail. The given symptoms will help a person who has been bitten by a tick on the head, leg or other parts of the body to monitor their health in order to notice its deterioration in time and consult a doctor for treatment.
Tick-borne encephalitis
This is a viral disease that affects the human nervous system. The incubation period is 4-14 days. The infection then causes the following unpleasant symptoms:
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- muscle weakness, numbness of the limbs and neck area;
- redness of the face, eyes and oral mucosa;
- severe headaches;
- loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting.
If the arachnid fell off at home
In a situation where the parasite bites a person and falls off after a few hours, it often goes unnoticed. A red spot, slight inflammation, and slight itching remain on the body. The tick falls off if it has fully satisfied its need for food and replenished its nutritional reserves.
Tick drunk on blood
If a thick tick falls off at home, there is no future for it. The nymph will not be able to continue development because there is no soil. The female will not be able to lay eggs for the same reasons. After some time, the parasite dies. The tick is dangerous if it has not drunk blood, then it can bite again. There is no need to worry too much about where the tick goes in the apartment. Even if he is not discovered, he will soon die.
How long does it take for the tick to fall off on its own?
The length of time the parasite stays on the body depends on its gender. The male can bite and, having had enough, detach himself after a few minutes. The time a male spends on a person increases if there is a female ready for reproduction.
Females require more blood to drink, so they can spend up to 10 days on a person, after which they detach and look for a place for successful reproduction.
Penetration of the insect's mouthparts under the skin and its removal may remain unnoticeable. A person discovers only a bite mark, which itches and swells after the pest leaves.
A tick cannot fall off a person on its own if he is hungry. But it can come unstuck and stick to another place. This is what individuals do if they did not find a convenient area for food the first time. In this case, several marks from one parasite remain on the body.
Danger from ixodid ticks
They are carriers of dangerous diseases. The most common are borreliosis and tick-borne encephalitis. Infection occurs during a bite. Borrelia are found in the saliva of the parasite, while the tick-borne encephalitis virus is found in the blood. The likelihood of infection increases with prolonged suction or improper removal.
It is impossible to say exactly how long it takes a tick to get drunk. If it remains on the human body for more than a day, the likelihood of contracting borreliosis increases. When bloated, his body becomes vulnerable. It bursts when pressed hard. When trying to remove it from the skin, the head may come off. Splashes of infectious blood enter a person's wound, causing infection with tick-borne encephalitis.
On a note!
If a tick has drunk blood, it increases in size and becomes noticeable. In areas dangerous for tick-borne encephalitis, it is not recommended to get the parasite yourself. You should immediately seek help at the emergency room or call the hotline. After removing the tick, it is sent to the laboratory for examination. If the result is positive, the victim is given immunoglobulin or an antibiotic. After 14 days you need to donate blood for analysis.
How to protect yourself from a tick bite?
It is known that a tick can catch on the clothing of any person, regardless of gender, race and age. Therefore, in order to protect yourself from the possible consequences of its bite, it is recommended to get a special vaccination. After all, vaccination is the most reliable way to protect yourself. After it, the body itself detects the threat and develops immunity.
It is also important to observe the following preventive measures:
- If you are in the forest, avoid dry dead wood. Ticks do not like moisture and sit only on dry branches. In addition, they do not like gloomy weather and do not bite at night.
- After visiting the forest and other natural places, you must carefully inspect your clothing.
- If you don't have special outdoor clothing, wear light-colored long sleeves. This way you can easily see the tick. Don't forget to tuck your pants into your socks or shoes, and wear a cap or bandana.
- If you find a tick crawling on you, catch it and then burn it or throw it in boiling water. After this, see if there is a red spot or blackhead on your skin. If there is, treat them with iodine. Next, it is recommended to go to a medical facility and get tested for infection.
Treatment at home
The danger of a tick bite is that self-medication in this case is unacceptable and can be fatal. Therefore, if you notice the appearance of early symptoms, you must immediately show the affected animal to a veterinarian.
Treatment of any infections, especially piroplasmosis (also known as babesiosis), should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since drugs to destroy pathogens are themselves toxic and should not be used without good reason. For the treatment of piroplasms, drugs such as Azidine, Berenil and Veriben are most often suitable.
Since piroplasmas destroy red blood cells and provoke excessive production of hemoglobin, which is fraught with damage to organs by decay products, plasmapheresis and hemodialysis are very effective in this case. The procedures are expensive, but they will certainly have a positive effect on the pet’s well-being.
In the future, after the cause of the disease has been destroyed, treatment consists of long-term cleansing of the body from intoxication. To do this, the dog is prescribed a course of vitamins, medications to support the heart, liver and kidneys, and saline solutions.
Actions of a tick after a bite
The parasite drinks blood from the dog to carry out the main tasks in its short life:
- The life cycle of a bloodsucker consists of several stages: egg, larva, nymph, adult. During the nymph stage, the parasite must undergo several metamorphoses. In order to move from one form of existence to another, you need good nutrition. So the larva strives to receive its portion of blood to transform into a nymph, and the nymph into an imago. After the parasite has drunk blood at various stages, it must leave its victim and reincarnate in a secluded place.
- Female arthropods need to eat well to carry out their main task - reproduction. After being bitten, she should lay a clutch of eggs in an inconspicuous place. If she succeeds, then the success of her mission is assured.
Ticks in dogs
If a tick on a dog drinks blood but is unable to leave the crime scene in time, its life is over. It can be damaged by a dog trying to scratch this place with its teeth or claws. Or the pet owner will find an attached or already dead tick among the fur. The total time the bloodsucker spends on the dog can be several days. And the shortest period of time in which he can accomplish his plans is about 6 hours.
What is the Ixodid tick?
There are 650 species of this insect.
Description and structure
The Ixodid tick is a parasite belonging to the order of ticks that can easily find hosts and transmit to them through saliva into the blood: encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), borreliosis or Lyme disease (can lead to disability or death, as it affects the joints, nervous system, eyes and heart).
The ixodid tick belongs to the order xodida. In a hungry state, the length of the female is about 4 mm. When saturated with blood, it reaches 10 mm and acquires a light gray tint. Males are more modest in size - up to 2.5 mm. All individuals have a hard shield on their back. Only the female stands out in that her shield is shorter than that of the male, namely, it covers a third of the body.
The color of the blood-sucking animal can be either yellow and brown, or black. Only those ticks that live in the tropical zone are brightly colored.
The entire surface of the insect's body is covered with a chitinous layer and looks like an oval sac with a trunk and paws with suction cups. The forelimbs are used to grip the prey. Ticks feed through their trunk, which is often mistaken for the head. The brain of the bloodsucker is located in the middle of the body in the center.
Life cycle
The parasitic insect has a time cycle of 1 to 4 years with prolonged feeding. They have complex ontogenesis, so not all of them reach adulthood.
Stages of development:
egg → larva → nymph → adult. To overcome the transformation barrier, the mite sheds its skin (molts).
Egg.
A female can lay more than 17,000 eggs in the ground. The duration of the process is from 30 to 40 days, depending on weather and temperature conditions. The embryo develops from 2 to 10 weeks at a humidity of no more than 65%.
Larva.
By autumn, the eggs hatch into larvae with 6 legs and hide under the leaves all winter. In spring they actively attack rodents and other small mammals. One meal every 5 days is enough for them. After this, they lie on the ground and wait to transform into a nymph. The tick remains in this stage from 1 week to a month. If there is no food, they can survive for about 24 months.
Nymph.
The nymph consumes its share of the blood, moults, and becomes an adult or imago. The duration of nutrition is approximately 8 days.
Imago.
Female adult ixodid ticks are distinguished by a single meal and live mainly on cattle. After drinking blood, they mate with males (who die immediately), lay eggs in the grass and die.
The main methods of protection against tick bites
You should not risk your health by going into nature, even if the risk of infection is not too high. It is recommended to consider a number of preventive measures and choose the most appropriate option for yourself.
Vaccine
This preventive measure is used at different times, but it is better to inject the inactivated virus before the parasite activity increases. Then the immunity will have time to form. Vaccination is carried out according to the scheme, with the minimum duration of the interval between injections being 30 days, the maximum being 7 months.
Introduction of the vaccine against tick-borne encephalitis
Workwear
Through dense material the parasite will not be able to bite. If a bite mark is found, it means that the tick had already attacked earlier, but was able to fall off on its own. In the future, it is recommended to wear special closed clothing when going on a picnic or fishing. It is equipped with traps; the surface of the material is smooth, which does not allow the parasite to move around the body of a potential victim. Additionally, the suit is treated with repellent substances, resulting in a double protective effect.
Protective suits against ticks for the whole family
Insurance
This is not exactly a preventive measure. The insurance policy provides the opportunity to conduct a quick, high-quality and most complete examination in case of a tick bite. In addition, regardless of whether the parasite fell off on its own or was forcibly removed, if the diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis or other diseases is confirmed (depending on what conditions are specified in the contract), treatment is carried out. Patient care is provided in certain medical institutions. Their list can be found in the annex to the agreement.
Seeking help from a medical center with insurance after a tick bite
Repellents
This is what repellents are called. They contain toxic substances. These can be insecticides, acaricides, or components of a combined action. Some areas are treated with repellents: the lower limbs in the area of the knee joints, hips, and chest. A ring barrier is created on each of these zones. The parasite has to change direction when it enters such areas.
However, the use of repellents does not guarantee complete protection. Against the backdrop of severe hunger, pests may try to overcome the obstacle. As a result, the parasite will still stick. For this reason, it is recommended to combine different preventive measures.
When applied to skin or clothing
the substance prevents the tick from moving.
Repellents that protect against tick attacks
Prevention of tick bites
Prevention of tick bites
To minimize the risk of being bitten by a tick, you should avoid direct contact with the parasite: walk on paved roads, avoid trees and bushes, and do not touch street animals that may carry parasites. If there is an urgent need to go into the forest, you need to remember the following rules to protect yourself from ticks:
- tuck each item of clothing into each other;
- cover your neck and head with a scarf or hood;
- tuck long hair under a headdress;
- wear light-colored clothing, on which the parasite will be better visible;
- avoid places with tall grass and dense thickets;
- use special anti-tick products: aerosols, creams.
After each trip to the forest or park, carefully examine yourself by undressing. Wash clothes immediately in hot water using powder. It is advisable to dry it in a special dryer or iron it with an iron at maximum setting.
Even if you follow these rules, you may not notice a tick bite on your body. If the parasite does not dig into the skin, but simply bites through the skin, the victim may be infected with a dangerous disease. To prevent this from happening, in regions with an increased level of infection with tick-borne encephalitis, vaccination of the population is carried out in medical institutions.
Vaccination takes place in 3 stages: 3 months pass after the first vaccination, then the second one is given, and exactly a year later the third. Then every three years you need to get only one vaccination. The vaccine stimulates the growth of antibodies in the human body and increases immunity to the virus. There is a type of emergency vaccination. It is indicated for people who will soon find themselves in an area where tick-borne encephalitis is endemic. Another option to protect yourself while in the area of tick-borne activity is to take the antiviral drug Yodantipirin throughout your stay.